f2f9bb10a0463dbe483ad3386a8d1444.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
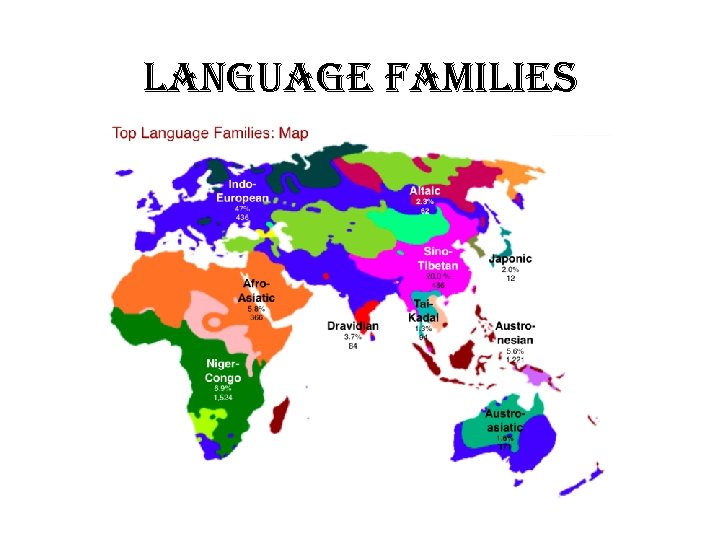 language Families
language Families
 Evolution of Language • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=i. WDKs Hm 6 g. TA
Evolution of Language • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=i. WDKs Hm 6 g. TA
 The Language Tree Organization: • 19 main language families, many others • Each family has its own branches • Each branch has its own groups • Each group has its own language • Each language has its own dialects
The Language Tree Organization: • 19 main language families, many others • Each family has its own branches • Each branch has its own groups • Each group has its own language • Each language has its own dialects
 What is a language family? • A group of languages organized by a common heritage.
What is a language family? • A group of languages organized by a common heritage.
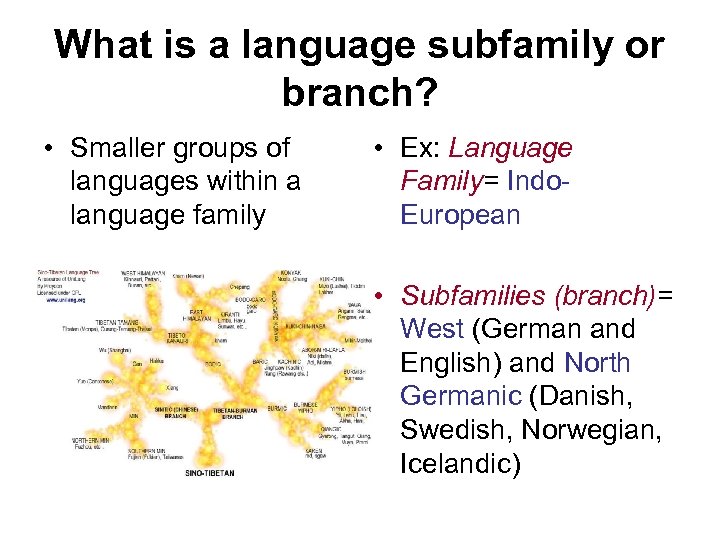 What is a language subfamily or branch? • Smaller groups of languages within a language family • Ex: Language Family= Indo. European • Subfamilies (branch)= West (German and English) and North Germanic (Danish, Swedish, Norwegian, Icelandic)
What is a language subfamily or branch? • Smaller groups of languages within a language family • Ex: Language Family= Indo. European • Subfamilies (branch)= West (German and English) and North Germanic (Danish, Swedish, Norwegian, Icelandic)
 What is a Language Group? • People whose languages are descended from a common tongue. • Ex: Spanish and French belong to the same language group because both French and Spanish are Romance Languages • Or English and German belong to same group.
What is a Language Group? • People whose languages are descended from a common tongue. • Ex: Spanish and French belong to the same language group because both French and Spanish are Romance Languages • Or English and German belong to same group.
 All the different Language Families you need to know! 1. Indo-European 2. Sino-Tibetan 3. Afro-Asiatic 4. Niger-Congo 5. Altaic- Uralic
All the different Language Families you need to know! 1. Indo-European 2. Sino-Tibetan 3. Afro-Asiatic 4. Niger-Congo 5. Altaic- Uralic
 Indo-European • Largest Language Family in the World! 50% of people on the earth speak a language from this family • Is Divided into 8 Branches – – – – 1. Indo-Iranian (South Asia) 2. Romance (Southwestern Europe) 3. Germanic (Northwestern Europe & North America) 4. Balto-Slavic (Eastern Europe) 5. Albanian 6. Armenian 7. Greek 8. Celtic
Indo-European • Largest Language Family in the World! 50% of people on the earth speak a language from this family • Is Divided into 8 Branches – – – – 1. Indo-Iranian (South Asia) 2. Romance (Southwestern Europe) 3. Germanic (Northwestern Europe & North America) 4. Balto-Slavic (Eastern Europe) 5. Albanian 6. Armenian 7. Greek 8. Celtic
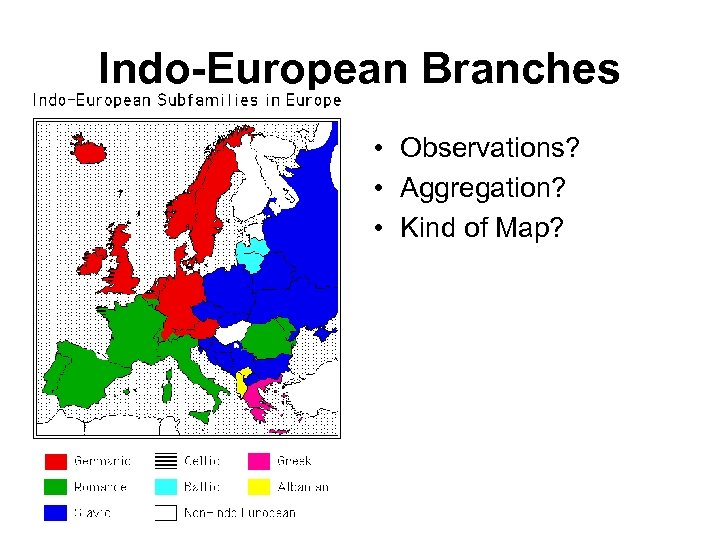 Indo-European Branches • Observations? • Aggregation? • Kind of Map?
Indo-European Branches • Observations? • Aggregation? • Kind of Map?
 Germanic Branch of Indo. European • West Germanic Group • High Germanic subgroup: German, • Low Germanic subgroup: English, Dutch, Flemish, Afrikaans, Frisian • Northern Germanic Group – – Swedish Danish Norwegian Icelandic
Germanic Branch of Indo. European • West Germanic Group • High Germanic subgroup: German, • Low Germanic subgroup: English, Dutch, Flemish, Afrikaans, Frisian • Northern Germanic Group – – Swedish Danish Norwegian Icelandic
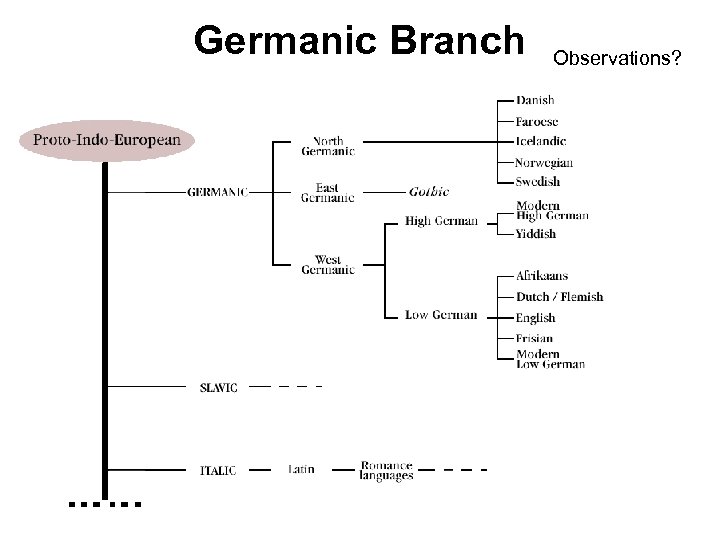 Germanic Branch Observations?
Germanic Branch Observations?
 Indo-Iranian Branch of Indo. European • Eastern (Indic) – – – Hindi (India) Urdu (Pakistan) Bengali (Bangladesh) Gujarati (India) Panjabi (India) • Western (Iranian) – Persian or Farsi (Iran) – Pashto (Afghanistan and Pakistan) – Kurdish (Iran, Iraq, Turkey)
Indo-Iranian Branch of Indo. European • Eastern (Indic) – – – Hindi (India) Urdu (Pakistan) Bengali (Bangladesh) Gujarati (India) Panjabi (India) • Western (Iranian) – Persian or Farsi (Iran) – Pashto (Afghanistan and Pakistan) – Kurdish (Iran, Iraq, Turkey)
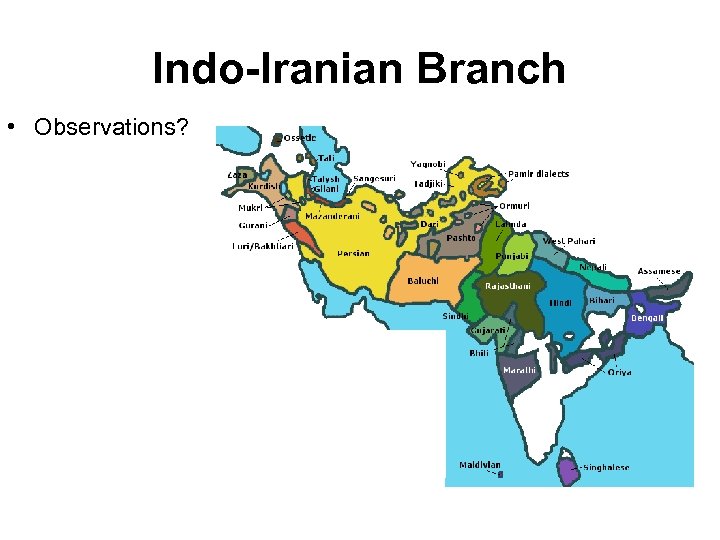 Indo-Iranian Branch • Observations?
Indo-Iranian Branch • Observations?
 Balto-Slavic Branch of Indo. European • East Slavic and Baltic – Russian (Russia) – Ukrainian (Ukraine) – Belarusian (Belarus) • West and South Slavic – – Polish (Poland) Czech (Czech Republic) Slovak (Slovakia) Bosnian (Bosnia) • Use Cyrillic alphabet – Croatian (Croatia) • Use Cyrillic alphabet – Serbian (Serbia) • Use Cyrillic alphabet
Balto-Slavic Branch of Indo. European • East Slavic and Baltic – Russian (Russia) – Ukrainian (Ukraine) – Belarusian (Belarus) • West and South Slavic – – Polish (Poland) Czech (Czech Republic) Slovak (Slovakia) Bosnian (Bosnia) • Use Cyrillic alphabet – Croatian (Croatia) • Use Cyrillic alphabet – Serbian (Serbia) • Use Cyrillic alphabet
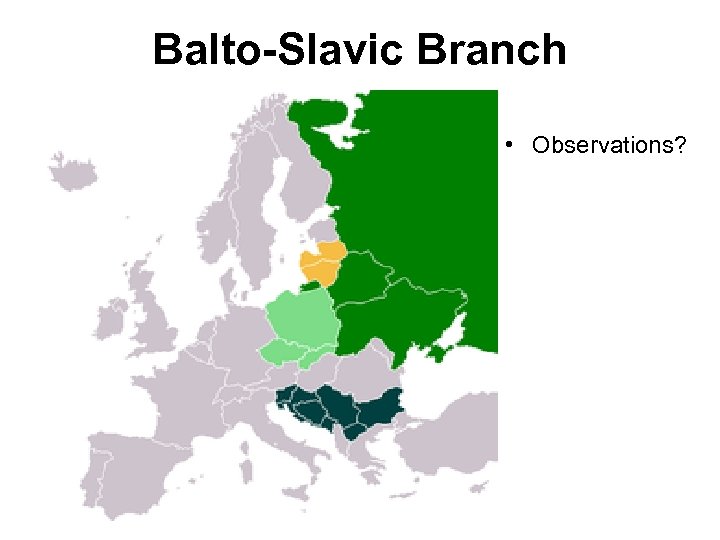 Balto-Slavic Branch • Observations?
Balto-Slavic Branch • Observations?
 Romance Branch of Indo. European • Evolved from the Latin language spoken by the Romans 2, 000 years ago • The four most widely used are Spanish, Portuguese, French, and Italian • The fifth in importance is Romanian
Romance Branch of Indo. European • Evolved from the Latin language spoken by the Romans 2, 000 years ago • The four most widely used are Spanish, Portuguese, French, and Italian • The fifth in importance is Romanian
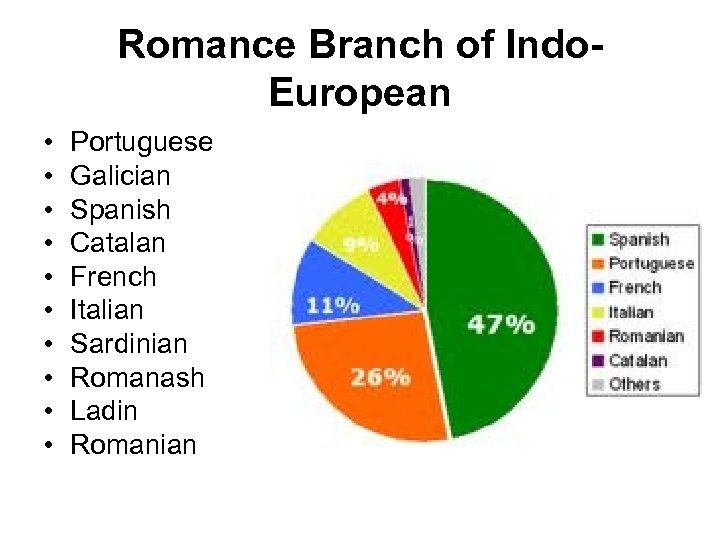 Romance Branch of Indo. European • • • Portuguese Galician Spanish Catalan French Italian Sardinian Romanash Ladin Romanian
Romance Branch of Indo. European • • • Portuguese Galician Spanish Catalan French Italian Sardinian Romanash Ladin Romanian
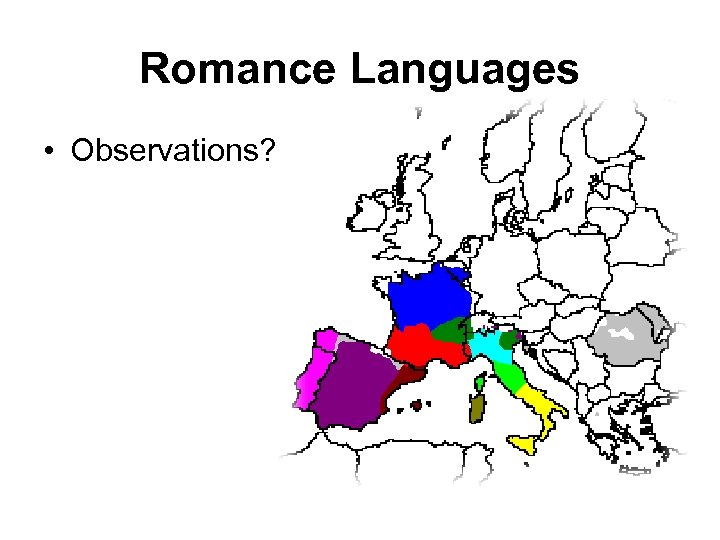 Romance Languages • Observations?
Romance Languages • Observations?
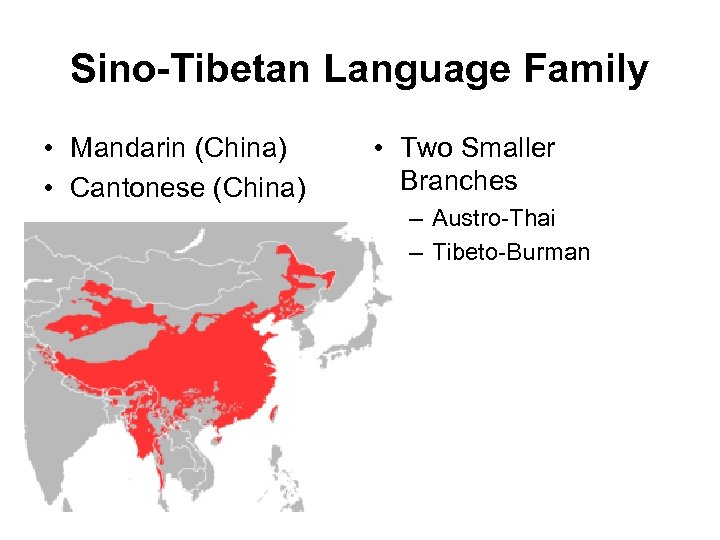 Sino-Tibetan Language Family • Mandarin (China) • Cantonese (China) • Two Smaller Branches – Austro-Thai – Tibeto-Burman
Sino-Tibetan Language Family • Mandarin (China) • Cantonese (China) • Two Smaller Branches – Austro-Thai – Tibeto-Burman
 Japanese and Korean each have their own language families • Japanese • Korean • Japan being an • Written in a system isolated island country known as hankul and has developed a onumen language very • (This system has different than Chinese each letter represent languages. a sound. )
Japanese and Korean each have their own language families • Japanese • Korean • Japan being an • Written in a system isolated island country known as hankul and has developed a onumen language very • (This system has different than Chinese each letter represent languages. a sound. )
 Afro-Asiatic Language Family • Language spoken primarily in northern Africa and southwestern Asia. • World’s 4 th largest language family • Internationally significant because its languages were used to write the holiest books of the world’s three major world religions: Bible and the Quran.
Afro-Asiatic Language Family • Language spoken primarily in northern Africa and southwestern Asia. • World’s 4 th largest language family • Internationally significant because its languages were used to write the holiest books of the world’s three major world religions: Bible and the Quran.
 Afro-Asiatic Language Family Arabic Hebrew • Official language in • Bible two dozen countries • Spoken by some • The United Nations people of Jewish faith added Arabic as its 6 th official language in 1973.
Afro-Asiatic Language Family Arabic Hebrew • Official language in • Bible two dozen countries • Spoken by some • The United Nations people of Jewish faith added Arabic as its 6 th official language in 1973.
 Altaic and Uralic Language Families Altaic • Thought to have originated in the steppes bordering the Qilian Shan and Altai mountains between Tibet and China. Uralic • Thought to have originated from people living in the Ural mountains of present day Russia
Altaic and Uralic Language Families Altaic • Thought to have originated in the steppes bordering the Qilian Shan and Altai mountains between Tibet and China. Uralic • Thought to have originated from people living in the Ural mountains of present day Russia
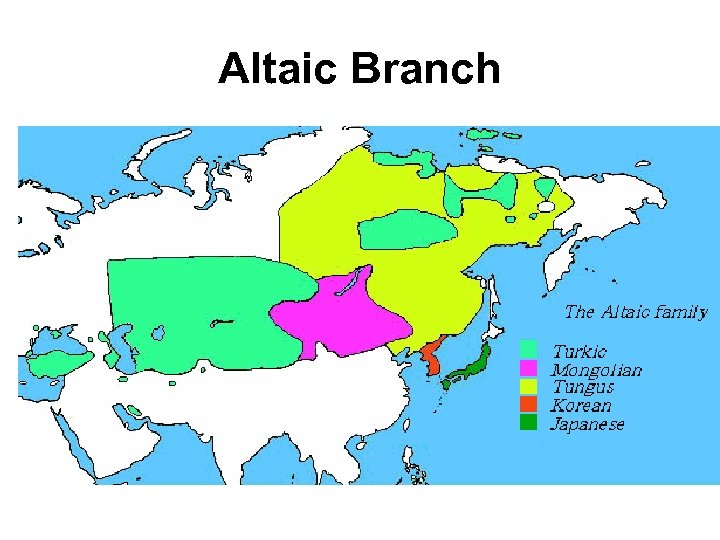 Altaic Branch
Altaic Branch
 Altaic Language Family • • • Turkish Azerbaijani Uzbek Kazakh Uyghur Turken • These countries were once part of the former Soviet Union. They were forced to speak Russian during that time, but with the fall of the Soviet Union they know each have their own language. • What are some problems you foresee with this?
Altaic Language Family • • • Turkish Azerbaijani Uzbek Kazakh Uyghur Turken • These countries were once part of the former Soviet Union. They were forced to speak Russian during that time, but with the fall of the Soviet Union they know each have their own language. • What are some problems you foresee with this?
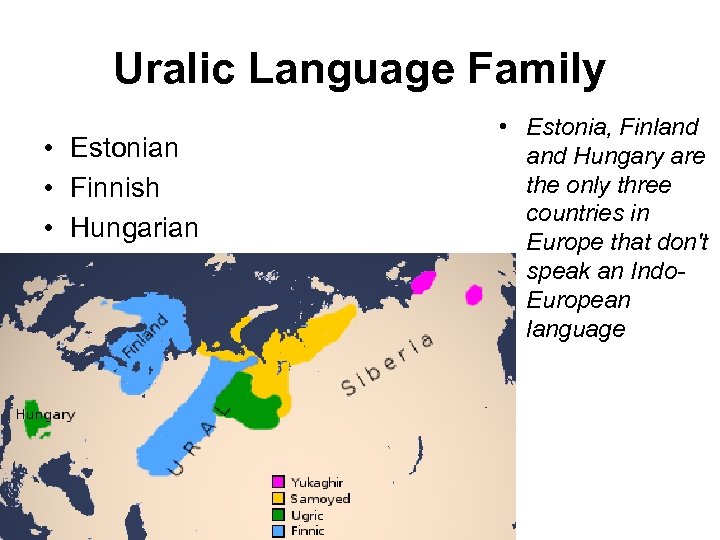 Uralic Language Family • Estonian • Finnish • Hungarian • Estonia, Finland Hungary are the only three countries in Europe that don't speak an Indo. European language
Uralic Language Family • Estonian • Finnish • Hungarian • Estonia, Finland Hungary are the only three countries in Europe that don't speak an Indo. European language
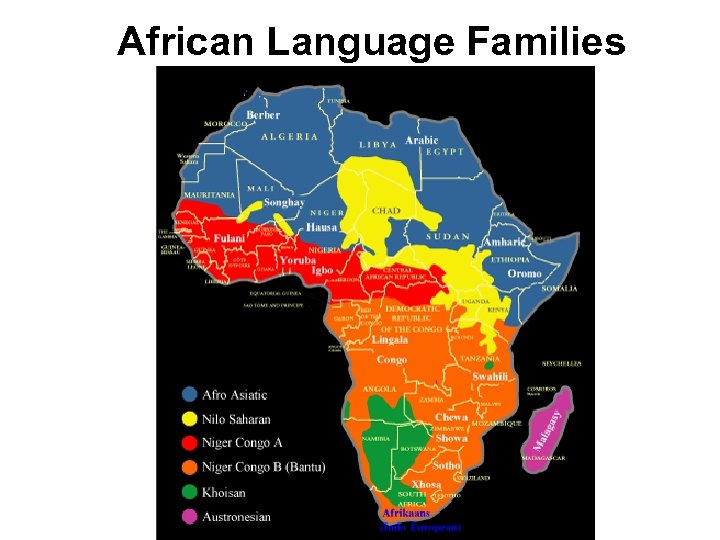
 African Language Families • Niger-Congo Family – 95% of sub-Saharan African speaks Niger-Congo languages – Includes Swahili • Nilo-Saharan Family – Languages spoken in north central Africa • Khoisan Family – Languages spoken in southwest Africa – Distinct use of clicking sounds/ Hottentot • Austronesian Family – Mostly spoken by people in Indonesia, but Africa’s island of Madagascar speaks a language from this family.
African Language Families • Niger-Congo Family – 95% of sub-Saharan African speaks Niger-Congo languages – Includes Swahili • Nilo-Saharan Family – Languages spoken in north central Africa • Khoisan Family – Languages spoken in southwest Africa – Distinct use of clicking sounds/ Hottentot • Austronesian Family – Mostly spoken by people in Indonesia, but Africa’s island of Madagascar speaks a language from this family.
 African Language Families
African Language Families
 How to Speak Khoisan • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=31 zz. M b 3 U 0 i. Y
How to Speak Khoisan • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=31 zz. M b 3 U 0 i. Y
 2007 FRQ 2015 FRQ
2007 FRQ 2015 FRQ
 Two words to make sure you know! • Lingua Franca – A language mutually understood and commonly used in trade by people have different native languages. • Globalization – Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.
Two words to make sure you know! • Lingua Franca – A language mutually understood and commonly used in trade by people have different native languages. • Globalization – Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.
 Guiding Question: • Why are some lesser used minority languages currently undergoing a revival in an era of increased globalization?
Guiding Question: • Why are some lesser used minority languages currently undergoing a revival in an era of increased globalization?
 What are examples of minority languages? • • Welsh Basque Inuktitut Celtic Gaelic Hebrew Breton
What are examples of minority languages? • • Welsh Basque Inuktitut Celtic Gaelic Hebrew Breton
 Why are minority languages being revived? • Groups want to maintain their culture. Preserve their folk culture by resisting English. – Example: Elders teaching young people – Example: In Cornwall, England: Cornish is taught in grade schools , some church services, and adult evening classes in an effort to maintain their distinct culture.
Why are minority languages being revived? • Groups want to maintain their culture. Preserve their folk culture by resisting English. – Example: Elders teaching young people – Example: In Cornwall, England: Cornish is taught in grade schools , some church services, and adult evening classes in an effort to maintain their distinct culture.
 Some Cornish for you… • • • NEBAS LAVAROW / Some phrases. Greetings: Durdatha whye! Good day to you! Deeth daa. Good day. Metten daa. Good Morning. Ha soce! Hello mate. Darzona! God bless (on meeting). Gothewhar daa. Good evening. Lowena tha whye! or Betho whye lowenack! Happiness to you!
Some Cornish for you… • • • NEBAS LAVAROW / Some phrases. Greetings: Durdatha whye! Good day to you! Deeth daa. Good day. Metten daa. Good Morning. Ha soce! Hello mate. Darzona! God bless (on meeting). Gothewhar daa. Good evening. Lowena tha whye! or Betho whye lowenack! Happiness to you!
 Why are minority languages being revived? • Devolution - transfer of power from a higher to a lower level of government OR Separatist (regional autonomy) • Example: Central government allows a minority language in a region that wishes to have a separate identity to be used – Welsh in Wales (United Kingdom)- The 1988 Education Act make Welsh language training mandatory in schools in Wales.
Why are minority languages being revived? • Devolution - transfer of power from a higher to a lower level of government OR Separatist (regional autonomy) • Example: Central government allows a minority language in a region that wishes to have a separate identity to be used – Welsh in Wales (United Kingdom)- The 1988 Education Act make Welsh language training mandatory in schools in Wales.
 Separatist • Example: The Basque’s in Spain promote their language as a way to resist the central Spanish government and dominate Spanish culture.
Separatist • Example: The Basque’s in Spain promote their language as a way to resist the central Spanish government and dominate Spanish culture.
 Why are minority languages being revived? • Unity in a Multicultural state – The central government may adopt two or more official languages to reduce threat of secession – Ex: Canada • What languages has Canada made official? Who are they worried about leaving?
Why are minority languages being revived? • Unity in a Multicultural state – The central government may adopt two or more official languages to reduce threat of secession – Ex: Canada • What languages has Canada made official? Who are they worried about leaving?
 Why are minority languages being revived? • Nationalism- government policies to increase nationalism in a country. – Ex: Some newly independent states reestablish the indigenous language as a statement of political and cultural independence. – Ex: Hebrew in Israel – Ex: Azerbaijani in Azerbaijan (formerly of Soviet Union)
Why are minority languages being revived? • Nationalism- government policies to increase nationalism in a country. – Ex: Some newly independent states reestablish the indigenous language as a statement of political and cultural independence. – Ex: Hebrew in Israel – Ex: Azerbaijani in Azerbaijan (formerly of Soviet Union)
 Why are minority languages being revived? • Modern Electric Communications – Internet, telephone, cable TV, radio, specialized newspapers – Enable small groups of people to stay in touch and reinforce the use of a minority language.
Why are minority languages being revived? • Modern Electric Communications – Internet, telephone, cable TV, radio, specialized newspapers – Enable small groups of people to stay in touch and reinforce the use of a minority language.
 Why are minority languages being revived? • Tourism – Some languages have become part of the tourist landscape because tourists want to see something authentic – Ex: Welsh and Irish
Why are minority languages being revived? • Tourism – Some languages have become part of the tourist landscape because tourists want to see something authentic – Ex: Welsh and Irish
 Why are minority languages being revived? • Government policy to support minority language for nonpolitical reasons. • Ex: European Union’s Bureau for Little Used Languages or the end of forced assimilation of Native Americans in the United States.
Why are minority languages being revived? • Government policy to support minority language for nonpolitical reasons. • Ex: European Union’s Bureau for Little Used Languages or the end of forced assimilation of Native Americans in the United States.


