f8943b6492a73c87b9bbf93eba386d10.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 130
 LANGUAGE AND CULTURE
LANGUAGE AND CULTURE
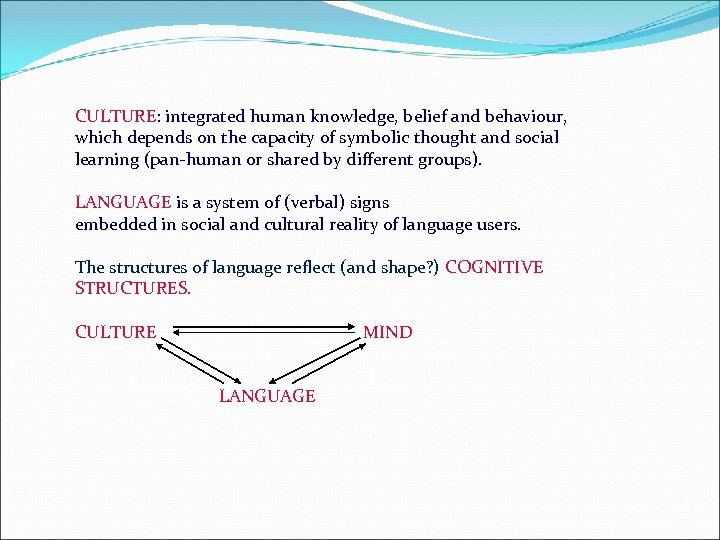 CULTURE: integrated human knowledge, belief and behaviour, which depends on the capacity of symbolic thought and social learning (pan-human or shared by different groups). LANGUAGE is a system of (verbal) signs embedded in social and cultural reality of language users. The structures of language reflect (and shape? ) COGNITIVE STRUCTURES. CULTURE MIND LANGUAGE
CULTURE: integrated human knowledge, belief and behaviour, which depends on the capacity of symbolic thought and social learning (pan-human or shared by different groups). LANGUAGE is a system of (verbal) signs embedded in social and cultural reality of language users. The structures of language reflect (and shape? ) COGNITIVE STRUCTURES. CULTURE MIND LANGUAGE
 LANGUAGE DIVERSITY 6. 000 -7. 000 languages in the world Languages by the number of speakers: Mandarine Chinese 847, 000 Hindi 366, 000 English 341, 000 Spanish 330. 000, 000 Bengali Arabic Portuguese Russian Japanese German …. 2000 languages – less than 1000 speakers
LANGUAGE DIVERSITY 6. 000 -7. 000 languages in the world Languages by the number of speakers: Mandarine Chinese 847, 000 Hindi 366, 000 English 341, 000 Spanish 330. 000, 000 Bengali Arabic Portuguese Russian Japanese German …. 2000 languages – less than 1000 speakers
 Distribution/concentration of languages: English – official language in 52 countries 900 languages on Papua New Guinea (5 -10 million people) high density also in Caucasus, (Native) California… ½ of languages no longer used by children 1/3 of languages less than 1000 speakers English: 615. 000 non-technical words (over 2, 000, if slang and techical words added) (imported from more than 240 languages) average use in daily speech 800 -1000 words college graduates 10. 000 -20. 000
Distribution/concentration of languages: English – official language in 52 countries 900 languages on Papua New Guinea (5 -10 million people) high density also in Caucasus, (Native) California… ½ of languages no longer used by children 1/3 of languages less than 1000 speakers English: 615. 000 non-technical words (over 2, 000, if slang and techical words added) (imported from more than 240 languages) average use in daily speech 800 -1000 words college graduates 10. 000 -20. 000
 Where does all this diversity come from? Franz Boas (1858 -1942), anthropologist “Since the total range of personal experience which language serves to express is infinitely varied, and its whole scope must be expressed by a limited number of phonetic groups, it is obvious that an extended classification of experience must underline all articulate speech. ”
Where does all this diversity come from? Franz Boas (1858 -1942), anthropologist “Since the total range of personal experience which language serves to express is infinitely varied, and its whole scope must be expressed by a limited number of phonetic groups, it is obvious that an extended classification of experience must underline all articulate speech. ”
 Where does all this diversity come from? Different languages – different implicit classification of experience: Inuit: aput qana piqsirpoq qimuqsuq ‘snow on the ground’ ‘falling snow’ ‘drifting snow’ ‘snow drift’ Linguistic classifications reflect, not dictate thought.
Where does all this diversity come from? Different languages – different implicit classification of experience: Inuit: aput qana piqsirpoq qimuqsuq ‘snow on the ground’ ‘falling snow’ ‘drifting snow’ ‘snow drift’ Linguistic classifications reflect, not dictate thought.
 Edward Sapir (1884 -1939), anthropologist-linguist formal completeness of each language as a symbolic system:
Edward Sapir (1884 -1939), anthropologist-linguist formal completeness of each language as a symbolic system:
![“The outstanding fact about any language is its formal completeness [. . . ] “The outstanding fact about any language is its formal completeness [. . . ]](https://present5.com/presentation/f8943b6492a73c87b9bbf93eba386d10/image-8.jpg) “The outstanding fact about any language is its formal completeness [. . . ] [W]e may say that a language is so constructed that no matter what any speaker of it may desire to communicate [. . . ] the language is prepared to do his work. ” “The Hopi language is capable of accounting for and describing correctly. . . all observable phenomena of the universe. . . Just as it is possible to have any number of geometries other than the Euclidean”. Linguistic classifications channel thought: “ Language is guide to social reality [. . . ] Human beings do not live in the objective world alone [. . . ] but are very much at the mercy of the particular language which has become the medium of expression for their society [. . . ] No two languages are ever sufficiently similar to be considered as representing the same social reality. . . «
“The outstanding fact about any language is its formal completeness [. . . ] [W]e may say that a language is so constructed that no matter what any speaker of it may desire to communicate [. . . ] the language is prepared to do his work. ” “The Hopi language is capable of accounting for and describing correctly. . . all observable phenomena of the universe. . . Just as it is possible to have any number of geometries other than the Euclidean”. Linguistic classifications channel thought: “ Language is guide to social reality [. . . ] Human beings do not live in the objective world alone [. . . ] but are very much at the mercy of the particular language which has become the medium of expression for their society [. . . ] No two languages are ever sufficiently similar to be considered as representing the same social reality. . . «
 Benjamin Lee Whorf (1897 -1941) known for his descriptions of Nahuatl, Hopi, Mayan and other native American languages the need for calibration – objective non-linguistic evaluation (physical sciences? ) “The very natural tendency to use terms derived from traditional grammar, like verb, noun, adjective, passive voice, in describing languages outside of Indo-European is fraught with grave possibilities of misunderstanding”
Benjamin Lee Whorf (1897 -1941) known for his descriptions of Nahuatl, Hopi, Mayan and other native American languages the need for calibration – objective non-linguistic evaluation (physical sciences? ) “The very natural tendency to use terms derived from traditional grammar, like verb, noun, adjective, passive voice, in describing languages outside of Indo-European is fraught with grave possibilities of misunderstanding”
 “We cut nature up, organize it into concepts, and ascribe significances as we do, largely because we are parties to an agreement to organize it in this way – an agreement that holds throughout our speech community and is codified in the patterns of our language. The agreement is, of course, and implicit and unstated one, but its terms are absolutely obligatory…” Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis = the structure of a language affects the way in which its speakers conceptualize the World.
“We cut nature up, organize it into concepts, and ascribe significances as we do, largely because we are parties to an agreement to organize it in this way – an agreement that holds throughout our speech community and is codified in the patterns of our language. The agreement is, of course, and implicit and unstated one, but its terms are absolutely obligatory…” Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis = the structure of a language affects the way in which its speakers conceptualize the World.
 Categorization of the World comparison of things (phenomena) that are not alike but similar in (at least) one important way conceptual metaphor source domain (more concrete > target domain (more abstract) metaphor mapping: = a systematic set of correspondences that exist between constituent elements of the source and the target domain […] To know a conceptual metaphor is to know the set of mappings that applies to a given sourcetarget pairing. Time is a path. I fear the days ahead. Time is money. Don’t waste my time.
Categorization of the World comparison of things (phenomena) that are not alike but similar in (at least) one important way conceptual metaphor source domain (more concrete > target domain (more abstract) metaphor mapping: = a systematic set of correspondences that exist between constituent elements of the source and the target domain […] To know a conceptual metaphor is to know the set of mappings that applies to a given sourcetarget pairing. Time is a path. I fear the days ahead. Time is money. Don’t waste my time.
 Lakoff, George & Mark Johnson (1980) Metaphors We Live By. Chicago: University of Chicago Press How does one’s conceptualization (categorization) of the world become culture? (integrated human knowledge, belief and behaviour, which depends on the capacity of symbolic thought and social learning (pan-human or shared by different groups). memetic theory: culture and language united by memes: meme > Greek mīmēma ‘something imitated’ Richard Dawkings, The Selfish Gene (1976) “Culture is an aggregate of many different meme sets or memeplexes shared by the majority of population. Language – created by memes and for memes is [also] the principal medium used for spreading memes. ”
Lakoff, George & Mark Johnson (1980) Metaphors We Live By. Chicago: University of Chicago Press How does one’s conceptualization (categorization) of the world become culture? (integrated human knowledge, belief and behaviour, which depends on the capacity of symbolic thought and social learning (pan-human or shared by different groups). memetic theory: culture and language united by memes: meme > Greek mīmēma ‘something imitated’ Richard Dawkings, The Selfish Gene (1976) “Culture is an aggregate of many different meme sets or memeplexes shared by the majority of population. Language – created by memes and for memes is [also] the principal medium used for spreading memes. ”
 Cultural schemas/frames a) Did you hear that the guy who the police were looking for’s red Cortina got stolen? b) Will they deny that a nun who your shopkeeper was chatting up’s large settee got replicated? c) No head injury is too trivial to ignore.
Cultural schemas/frames a) Did you hear that the guy who the police were looking for’s red Cortina got stolen? b) Will they deny that a nun who your shopkeeper was chatting up’s large settee got replicated? c) No head injury is too trivial to ignore.
 “Grammar is thick with cultural meaning. Encoded in the semantics of grammar we find cultural values and ideas, we find clues about the social structures. ” N. J. Enfield: Ethnosyntax. Explorations in Grammar and Culture. OUP 2002
“Grammar is thick with cultural meaning. Encoded in the semantics of grammar we find cultural values and ideas, we find clues about the social structures. ” N. J. Enfield: Ethnosyntax. Explorations in Grammar and Culture. OUP 2002
 LANGUAGE FAMILIES AND LANGUAGE TYPOLOGY
LANGUAGE FAMILIES AND LANGUAGE TYPOLOGY
 EUROPE
EUROPE
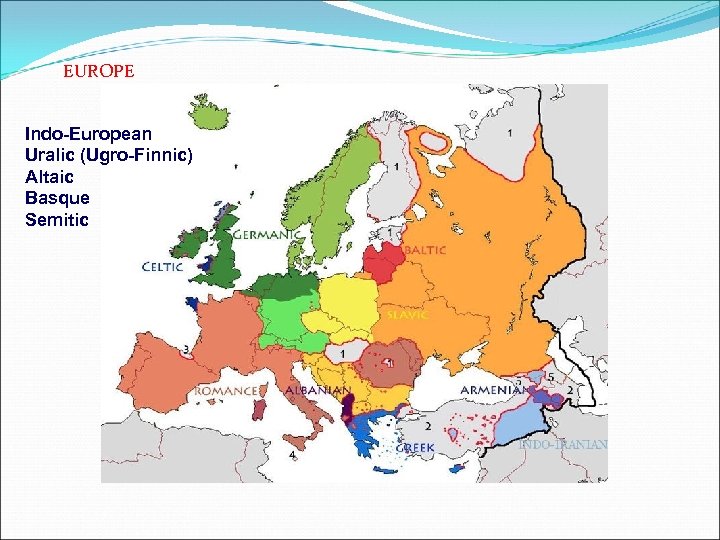 EUROPE Indo-European Uralic (Ugro-Finnic) Altaic Basque Semitic
EUROPE Indo-European Uralic (Ugro-Finnic) Altaic Basque Semitic
 INDO-EUROPEAN LANGUAGES from the Indo-Eropean Parent language, spoken about 5000 -3000 AD in south-eastern Russia patriarchal society > kinship terms, masculine pantheon social stratification: slave < ‘warrior’, ‘man’ wulf, birch, beech, bear cow, dog, plough, seed
INDO-EUROPEAN LANGUAGES from the Indo-Eropean Parent language, spoken about 5000 -3000 AD in south-eastern Russia patriarchal society > kinship terms, masculine pantheon social stratification: slave < ‘warrior’, ‘man’ wulf, birch, beech, bear cow, dog, plough, seed
 inflectional language(s) nouns: 3 numbers + collective (? ) – drevje : drevesa 3 genders 8 or 9 cases: nominative, vocative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, locative, directive (? ) instrumental verbs: tense/aspect: present, imperfect, aorist, perfect, pluperfect, future mood: indicative, imperative, subjunctive, optative voice: active, middle persons: 3
inflectional language(s) nouns: 3 numbers + collective (? ) – drevje : drevesa 3 genders 8 or 9 cases: nominative, vocative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, locative, directive (? ) instrumental verbs: tense/aspect: present, imperfect, aorist, perfect, pluperfect, future mood: indicative, imperative, subjunctive, optative voice: active, middle persons: 3
 Indo-Iranian languages: Indic: Vedic, Sanskrit, Hindi, Bengali, Urdu, Romany… chakra, ashram, guru, karma, caste Iranian: Avestan, Iranian, Pashto, Kurdic, Ossetic, Tadjik… Balkan (‘upper house’), Bagdad (‘given by God’), balcony, caravan, candy, dervish, mag(ic), paradise
Indo-Iranian languages: Indic: Vedic, Sanskrit, Hindi, Bengali, Urdu, Romany… chakra, ashram, guru, karma, caste Iranian: Avestan, Iranian, Pashto, Kurdic, Ossetic, Tadjik… Balkan (‘upper house’), Bagdad (‘given by God’), balcony, caravan, candy, dervish, mag(ic), paradise
 Armenian attested from 5 th c. AD Bible translation by St Mesrob Grabar – classical Armenian Apostolic Church Christianity as national religion (301) language: strong Iranian influence, convergeance with Caucasic languages glottalized consonants (ejectives)
Armenian attested from 5 th c. AD Bible translation by St Mesrob Grabar – classical Armenian Apostolic Church Christianity as national religion (301) language: strong Iranian influence, convergeance with Caucasic languages glottalized consonants (ejectives)
 Albanian descended from Illyrian? Thracian? Ptolomy (150 AD) – Illyrian tribe Albani Middle Ages – Arbër, Arbëresh 16 th c. - Shqipëria ‘land of eagles’(? ) shqip ‘understand each other’ Arnaut – Turkish name
Albanian descended from Illyrian? Thracian? Ptolomy (150 AD) – Illyrian tribe Albani Middle Ages – Arbër, Arbëresh 16 th c. - Shqipëria ‘land of eagles’(? ) shqip ‘understand each other’ Arnaut – Turkish name
 1190 – independent state Gheg – since 16 th c. (north) Tosk – official Albanian (south)
1190 – independent state Gheg – since 16 th c. (north) Tosk – official Albanian (south)
 Baltic languages: Latvian, Lithuanian, Old Prussian (extinct)
Baltic languages: Latvian, Lithuanian, Old Prussian (extinct)
 Anyone wishing to hear how Indo-Europeans spoke should come and listen to a Lithuanian peasant. (Antoine Meillet) pitch accent, free accent two grammatical genders (masculine and feminine)
Anyone wishing to hear how Indo-Europeans spoke should come and listen to a Lithuanian peasant. (Antoine Meillet) pitch accent, free accent two grammatical genders (masculine and feminine)
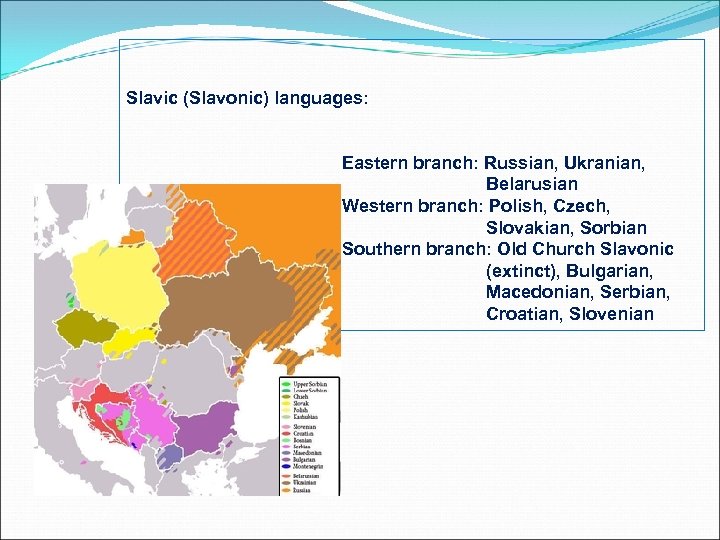 Slavic (Slavonic) languages: Eastern branch: Russian, Ukranian, Belarusian Western branch: Polish, Czech, Slovakian, Sorbian Southern branch: Old Church Slavonic (extinct), Bulgarian, Macedonian, Serbian, Croatian, Slovenian
Slavic (Slavonic) languages: Eastern branch: Russian, Ukranian, Belarusian Western branch: Polish, Czech, Slovakian, Sorbian Southern branch: Old Church Slavonic (extinct), Bulgarian, Macedonian, Serbian, Croatian, Slovenian
 GREEK LANGUAGE(S) Minoan civilization on Crete (settled 128. 000 BC, signs of agriculture 5000 BC) named by Arthur Evans Linear A Minoan eruption (Thera, Santorinin) - 2 nd millenium BC, tsunami
GREEK LANGUAGE(S) Minoan civilization on Crete (settled 128. 000 BC, signs of agriculture 5000 BC) named by Arthur Evans Linear A Minoan eruption (Thera, Santorinin) - 2 nd millenium BC, tsunami

 Minoan eruption – Thera (Santorini) ashes, tsunami, deforestation Mycenaean conquest
Minoan eruption – Thera (Santorini) ashes, tsunami, deforestation Mycenaean conquest
 Mycenean Greek – Linear B Ancient Greek: Aeolic Ionic (Asia Minor, Attic) Doric Greek alphabet < Phoenician syllabary Katharevousa Hellenistic Koinē > modern Greek Demotic (official in Greece, Cyprus)
Mycenean Greek – Linear B Ancient Greek: Aeolic Ionic (Asia Minor, Attic) Doric Greek alphabet < Phoenician syllabary Katharevousa Hellenistic Koinē > modern Greek Demotic (official in Greece, Cyprus)
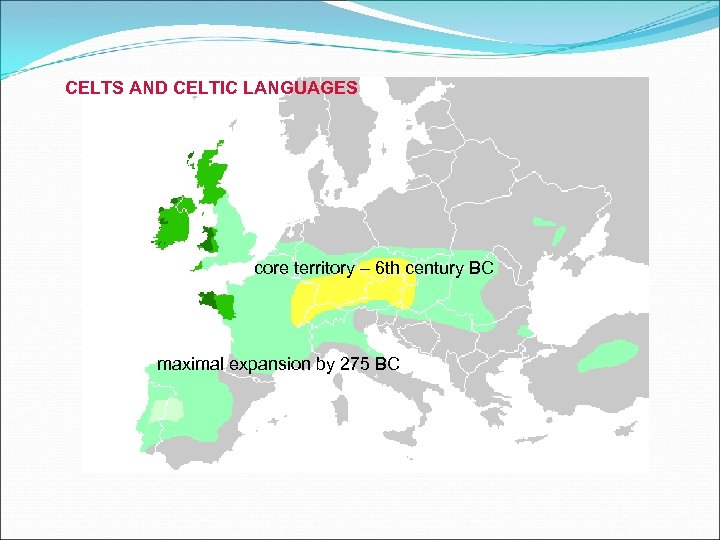 CELTS AND CELTIC LANGUAGES core territory – 6 th century BC maximal expansion by 275 BC
CELTS AND CELTIC LANGUAGES core territory – 6 th century BC maximal expansion by 275 BC
 CELTIC LANGUAGES (insular Celtic) Brythonic: -Welsh (Cymric) -Cornish -Breton Gaelic: -Irish Gaelic -Scottish Gaelic -Manx
CELTIC LANGUAGES (insular Celtic) Brythonic: -Welsh (Cymric) -Cornish -Breton Gaelic: -Irish Gaelic -Scottish Gaelic -Manx
 Brehon Law – the early Celtic law women’s rights to property, the king’s position and duties, status grading of clerics, lay men and poets, payment for injury, sick maintenance….
Brehon Law – the early Celtic law women’s rights to property, the king’s position and duties, status grading of clerics, lay men and poets, payment for injury, sick maintenance….
 linguistic typology of Celtic languages: -V-S-O order -consonant mutation -vigesimal numeric system 20 as the base number: French (quatre-vingts) Resian dialect of Slovene (trikart dwesti nu deset) English (score)
linguistic typology of Celtic languages: -V-S-O order -consonant mutation -vigesimal numeric system 20 as the base number: French (quatre-vingts) Resian dialect of Slovene (trikart dwesti nu deset) English (score)
 counting base: no base (Melanisia: thumb, wrist, elbow, shoulder…) quarternary: (Maori, Papua New Guinea, other Austronesian languages) quinary: sub-base of vigesimal systems octal: American languages vigesimal: Mayan, Nahualt, Celtic…. decimal, duodecimal…
counting base: no base (Melanisia: thumb, wrist, elbow, shoulder…) quarternary: (Maori, Papua New Guinea, other Austronesian languages) quinary: sub-base of vigesimal systems octal: American languages vigesimal: Mayan, Nahualt, Celtic…. decimal, duodecimal…
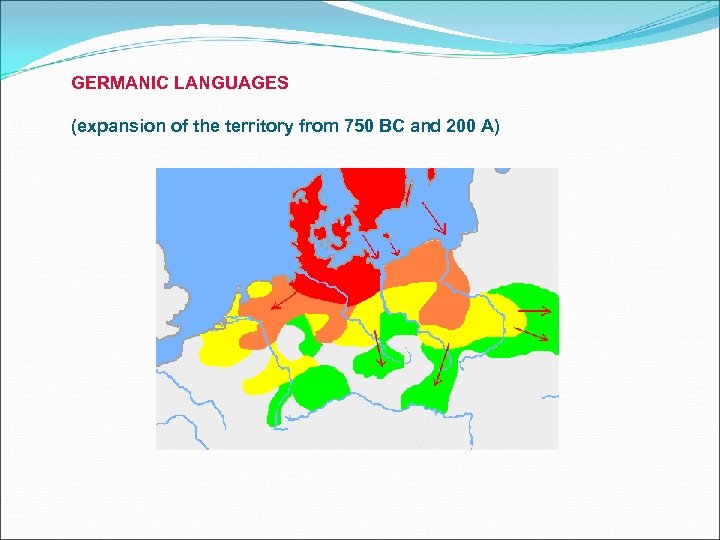 GERMANIC LANGUAGES (expansion of the territory from 750 BC and 200 A)
GERMANIC LANGUAGES (expansion of the territory from 750 BC and 200 A)
 Western: Northern: German Yiddish Plattdeutsch (Low German) Swiss German (Alemannic) Dutch Afrikaans Flemish Frisian English Scots Danish Faroese Islandic Norwegian (Nynorsk, Bokmal) Swedish Eastern: Gothic Vandalic ….
Western: Northern: German Yiddish Plattdeutsch (Low German) Swiss German (Alemannic) Dutch Afrikaans Flemish Frisian English Scots Danish Faroese Islandic Norwegian (Nynorsk, Bokmal) Swedish Eastern: Gothic Vandalic ….
 GOTHS migration from the Baltic to the Black Sea Wulfila (4 th c. AD) Crimean Gothic
GOTHS migration from the Baltic to the Black Sea Wulfila (4 th c. AD) Crimean Gothic
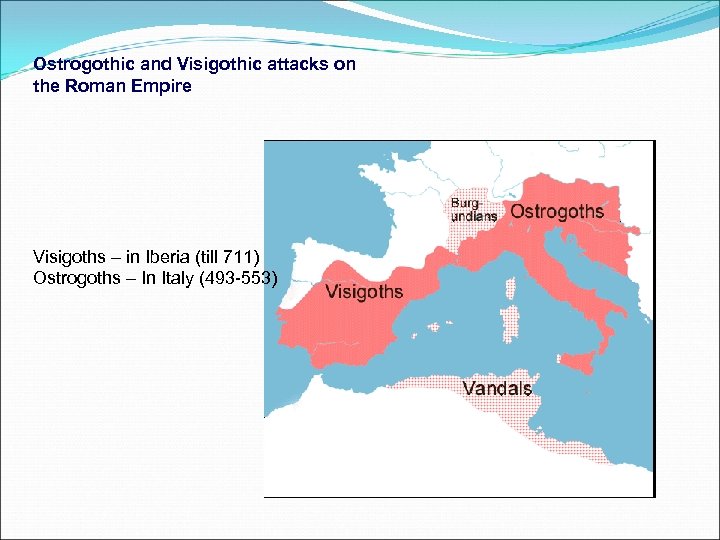 Ostrogothic and Visigothic attacks on the Roman Empire Visigoths – in Iberia (till 711) Ostrogoths – In Italy (493 -553)
Ostrogothic and Visigothic attacks on the Roman Empire Visigoths – in Iberia (till 711) Ostrogoths – In Italy (493 -553)
 Gothic art
Gothic art
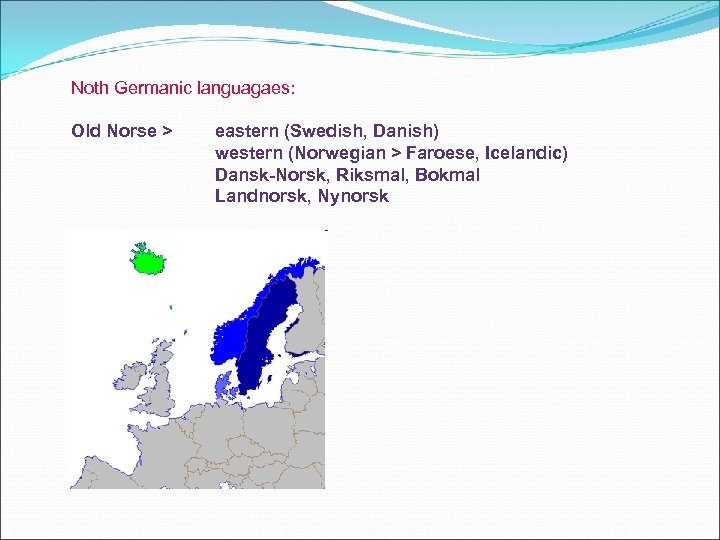 Noth Germanic languagaes: Old Norse > eastern (Swedish, Danish) western (Norwegian > Faroese, Icelandic) Dansk-Norsk, Riksmal, Bokmal Landnorsk, Nynorsk
Noth Germanic languagaes: Old Norse > eastern (Swedish, Danish) western (Norwegian > Faroese, Icelandic) Dansk-Norsk, Riksmal, Bokmal Landnorsk, Nynorsk
 West Germanic languages Bavarian Alemanic High German High Franconian Frankish Low Franconian North Sea (Ingvaeonic) Dutch Frisian English Saxon (Low German, Plattdeutsch)
West Germanic languages Bavarian Alemanic High German High Franconian Frankish Low Franconian North Sea (Ingvaeonic) Dutch Frisian English Saxon (Low German, Plattdeutsch)
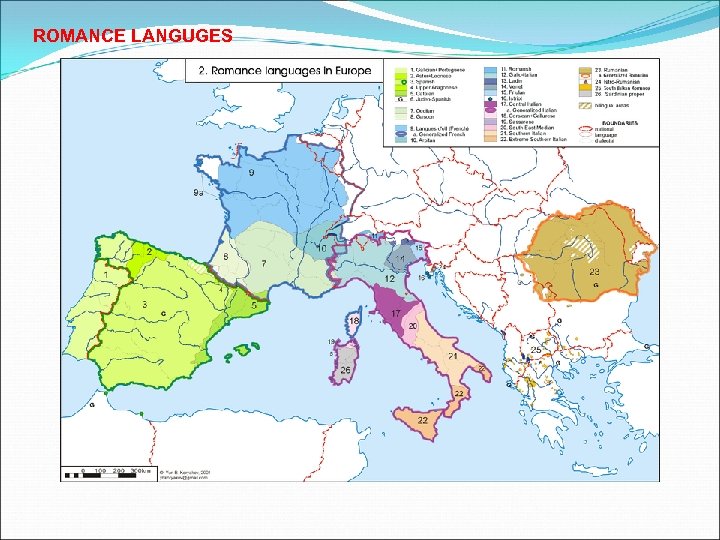 ROMANCE LANGUGES
ROMANCE LANGUGES
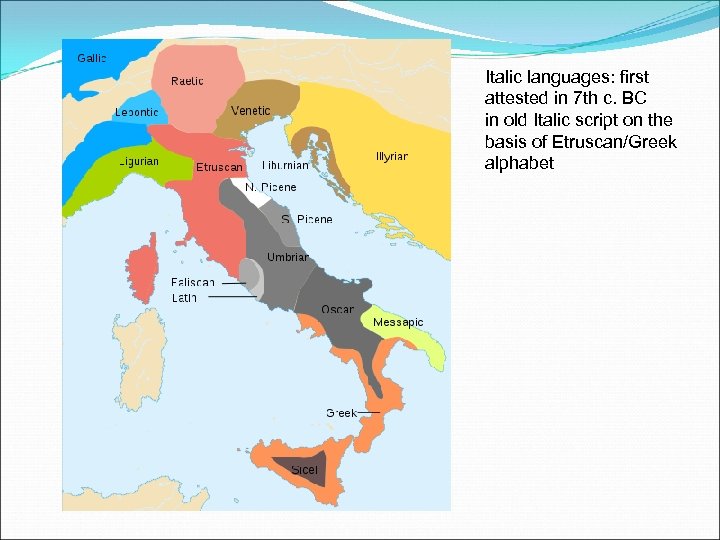 Italic languages: first attested in 7 th c. BC in old Italic script on the basis of Etruscan/Greek alphabet
Italic languages: first attested in 7 th c. BC in old Italic script on the basis of Etruscan/Greek alphabet
 Oscan , Umbrian, Latin ØArchaic Latin (7 th-2 nd c. BC): scattered inscriptions, Plautus, Terence, Cato the Elder… ØClassical Latin (Golden and Silver Age): Cicero, Caesar, Horace, Vergil, Ovid, Seneca… Ø Vulgar Latin (spoken Latin, from 3 rd c. ) > Romance languages: Gallo-Romance languages: French (attested since 9 th c. ): langue d’oïl, langue d’oc Central French, Norman French (Anglo-Norman), Walloon Occitan > Provençal Corsican?
Oscan , Umbrian, Latin ØArchaic Latin (7 th-2 nd c. BC): scattered inscriptions, Plautus, Terence, Cato the Elder… ØClassical Latin (Golden and Silver Age): Cicero, Caesar, Horace, Vergil, Ovid, Seneca… Ø Vulgar Latin (spoken Latin, from 3 rd c. ) > Romance languages: Gallo-Romance languages: French (attested since 9 th c. ): langue d’oïl, langue d’oc Central French, Norman French (Anglo-Norman), Walloon Occitan > Provençal Corsican?
 Ibero-Romance languages: Spanish Castilian (standard Spanish), attested since 11 th c. Catalan (official language in Andorra, co-official in Catalonia, Balearic Islands and Valencia, spoken also in Alghero on Sardinia) Portuguese Ladino (Judaeo-Spanish) Italian (since 10 th c. – dialects of Tuscany) Sardinian? Rhaeto-Romance languages: Ladin Friulian Romansch Istriot? Romanian
Ibero-Romance languages: Spanish Castilian (standard Spanish), attested since 11 th c. Catalan (official language in Andorra, co-official in Catalonia, Balearic Islands and Valencia, spoken also in Alghero on Sardinia) Portuguese Ladino (Judaeo-Spanish) Italian (since 10 th c. – dialects of Tuscany) Sardinian? Rhaeto-Romance languages: Ladin Friulian Romansch Istriot? Romanian
 ETRUSCAN Tusci, Etrusci (Latin) Tyrrennioi (Greek) Rassena, Rasna (Etruscan) since 8 th c. BC – 3 rd c. BC
ETRUSCAN Tusci, Etrusci (Latin) Tyrrennioi (Greek) Rassena, Rasna (Etruscan) since 8 th c. BC – 3 rd c. BC
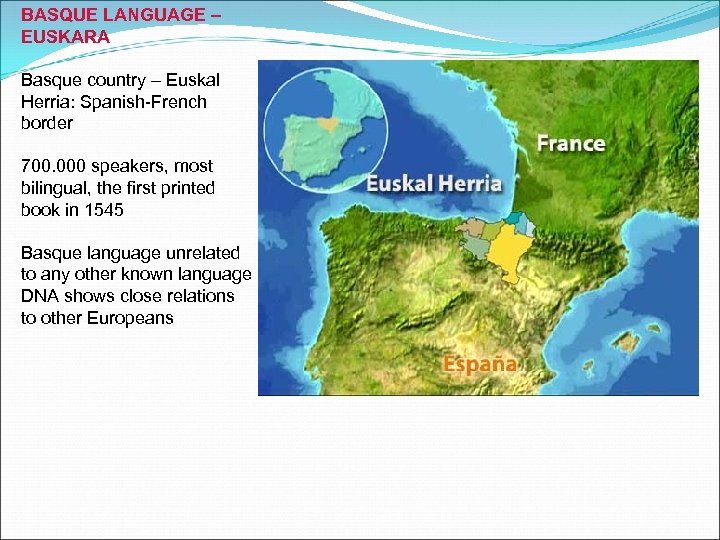 BASQUE LANGUAGE – EUSKARA Basque country – Euskal Herria: Spanish-French border 700. 000 speakers, most bilingual, the first printed book in 1545 Basque language unrelated to any other known language DNA shows close relations to other Europeans
BASQUE LANGUAGE – EUSKARA Basque country – Euskal Herria: Spanish-French border 700. 000 speakers, most bilingual, the first printed book in 1545 Basque language unrelated to any other known language DNA shows close relations to other Europeans
 ergative-absolutive language complex agreement system: the auxiliary agrees with the subject, direct and indirect object very complex nominal paradigm, (9 cases, 2 numbers, postpositioned article)
ergative-absolutive language complex agreement system: the auxiliary agrees with the subject, direct and indirect object very complex nominal paradigm, (9 cases, 2 numbers, postpositioned article)
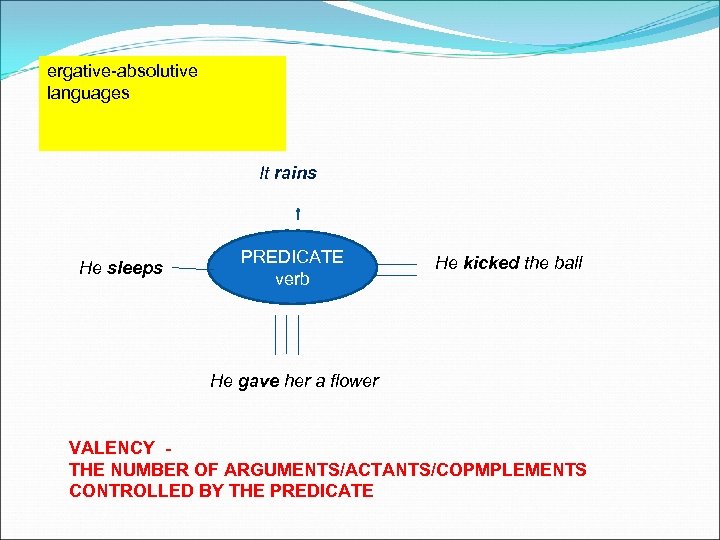 ergative-absolutive languages It rains He sleeps PREDICATE verb He kicked the ball He gave her a flower VALENCY - THE NUMBER OF ARGUMENTS/ACTANTS/COPMPLEMENTS CONTROLLED BY THE PREDICATE
ergative-absolutive languages It rains He sleeps PREDICATE verb He kicked the ball He gave her a flower VALENCY - THE NUMBER OF ARGUMENTS/ACTANTS/COPMPLEMENTS CONTROLLED BY THE PREDICATE
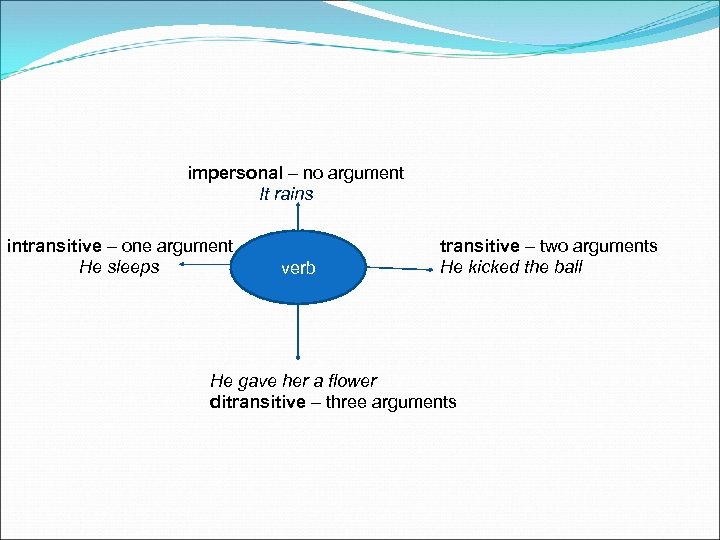 impersonal – no argument It rains intransitive – one argument He sleeps verb transitive – two arguments He kicked the ball He gave her a flower ditransitive – three arguments
impersonal – no argument It rains intransitive – one argument He sleeps verb transitive – two arguments He kicked the ball He gave her a flower ditransitive – three arguments
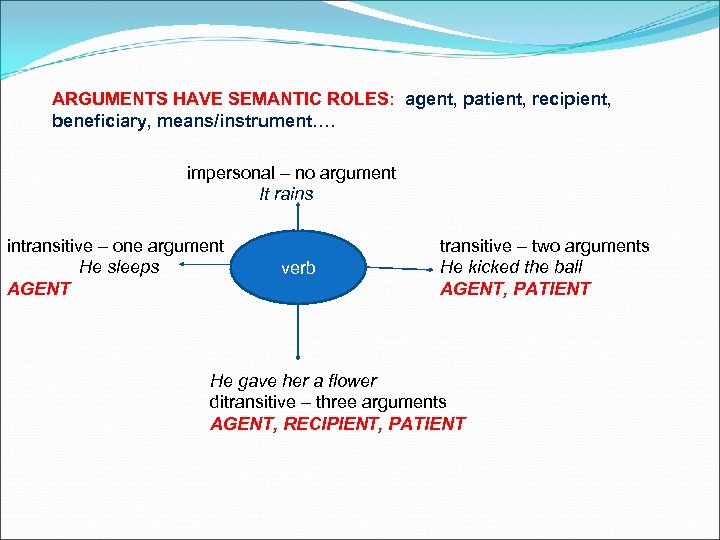 ARGUMENTS HAVE SEMANTIC ROLES: agent, patient, recipient, beneficiary, means/instrument…. impersonal – no argument It rains intransitive – one argument He sleeps AGENT verb transitive – two arguments He kicked the ball AGENT, PATIENT He gave her a flower ditransitive – three arguments AGENT, RECIPIENT, PATIENT
ARGUMENTS HAVE SEMANTIC ROLES: agent, patient, recipient, beneficiary, means/instrument…. impersonal – no argument It rains intransitive – one argument He sleeps AGENT verb transitive – two arguments He kicked the ball AGENT, PATIENT He gave her a flower ditransitive – three arguments AGENT, RECIPIENT, PATIENT
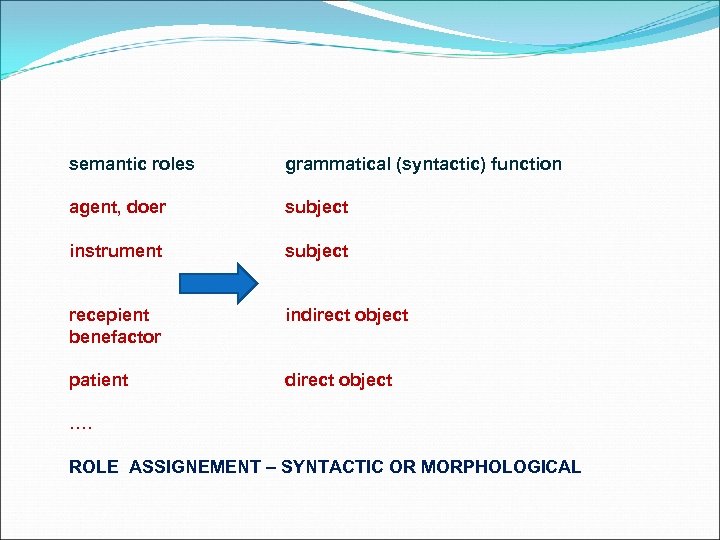 semantic roles grammatical (syntactic) function agent, doer subject instrument subject recepient benefactor indirect object patient direct object …. ROLE ASSIGNEMENT – SYNTACTIC OR MORPHOLOGICAL
semantic roles grammatical (syntactic) function agent, doer subject instrument subject recepient benefactor indirect object patient direct object …. ROLE ASSIGNEMENT – SYNTACTIC OR MORPHOLOGICAL
 ROLE ALIGNMENT ergative - absolutive : nominative – accusative intransitive agent/subject transitive patient/object ABSOLUTIVE CASE intransitive agent/subject NOMINATIVE CASE transitive agent/subject ERGATIVE CASE transitive patient/object ACCUSATIVE CASE Basque: Gizona etorri da. man-ABS arrived-AUX Japanese Otoko ga tsuita. man-NOM arrived Gizonak mutila ikusi du. man-ERG boy-ABS saw-AUX Otoko ga kodomo o mita man-NOM child-ACC saw
ROLE ALIGNMENT ergative - absolutive : nominative – accusative intransitive agent/subject transitive patient/object ABSOLUTIVE CASE intransitive agent/subject NOMINATIVE CASE transitive agent/subject ERGATIVE CASE transitive patient/object ACCUSATIVE CASE Basque: Gizona etorri da. man-ABS arrived-AUX Japanese Otoko ga tsuita. man-NOM arrived Gizonak mutila ikusi du. man-ERG boy-ABS saw-AUX Otoko ga kodomo o mita man-NOM child-ACC saw
 ergative languages: Basque Caucasian (Kartvelian=Georgian) Tibetan Native American (Chinook, Eskimo-Aleut, Mayan) Australian
ergative languages: Basque Caucasian (Kartvelian=Georgian) Tibetan Native American (Chinook, Eskimo-Aleut, Mayan) Australian
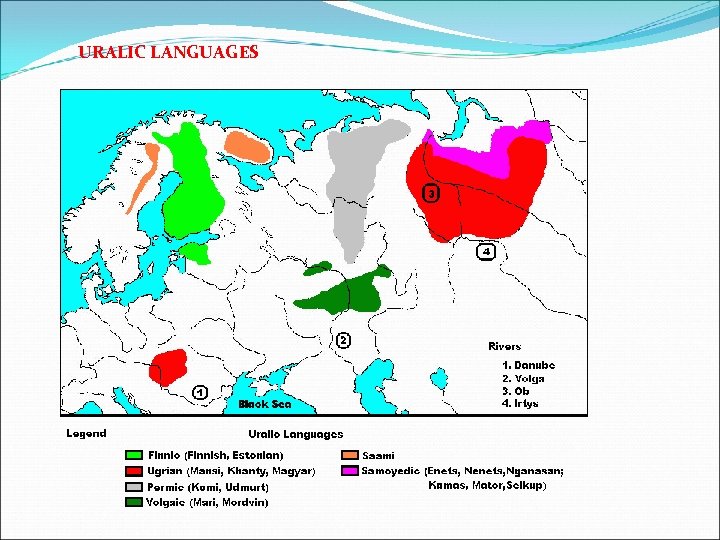 URALIC LANGUAGES
URALIC LANGUAGES
 URALIC LANGUAGES proto-Uralic (the Ural Mountains) § UGRO-FINNIC Finnic: Finnish, Estonian, Sami (Lappish) Ugric: Hungarian § SAMOYEDIC
URALIC LANGUAGES proto-Uralic (the Ural Mountains) § UGRO-FINNIC Finnic: Finnish, Estonian, Sami (Lappish) Ugric: Hungarian § SAMOYEDIC
 FINNISH (SUOMI) official language in Finland settled at least 8500 BC Swedish rule from 12 th century – 1249 Swedish – the dominant language of higher classes 17 th century – Sweden and Russia fought over Finland 1809 – Finland becomes an autonomous Great Duchy of Russia Finnish language gains recognition Kalevala – 1835 (Elias Lönnrot) independence delared on December 6, 1917
FINNISH (SUOMI) official language in Finland settled at least 8500 BC Swedish rule from 12 th century – 1249 Swedish – the dominant language of higher classes 17 th century – Sweden and Russia fought over Finland 1809 – Finland becomes an autonomous Great Duchy of Russia Finnish language gains recognition Kalevala – 1835 (Elias Lönnrot) independence delared on December 6, 1917
 FINNISH (SUOMI) official language in Finland settled at least 8500 BC Swedish rule from 12 th century – 1249 Swedish – the dominant language of higher classes 17 th century – Sweden and Russia fought over Finland 1809 – Finland becomes an autonomous Great Duchy of Russia Finnish language gains recognition Kalevala – 1835 (Elias Lönnrot) independence delared on December 6, 1917
FINNISH (SUOMI) official language in Finland settled at least 8500 BC Swedish rule from 12 th century – 1249 Swedish – the dominant language of higher classes 17 th century – Sweden and Russia fought over Finland 1809 – Finland becomes an autonomous Great Duchy of Russia Finnish language gains recognition Kalevala – 1835 (Elias Lönnrot) independence delared on December 6, 1917
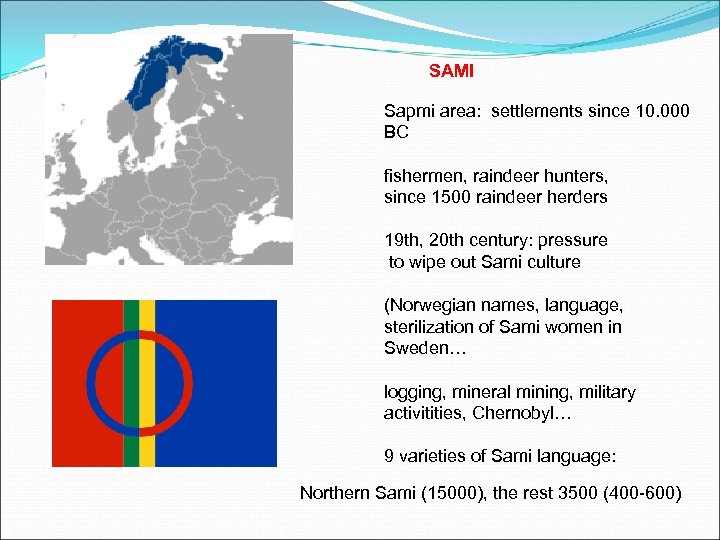 SAMI Sapmi area: settlements since 10. 000 BC fishermen, raindeer hunters, since 1500 raindeer herders 19 th, 20 th century: pressure to wipe out Sami culture (Norwegian names, language, sterilization of Sami women in Sweden… logging, mineral mining, military activitities, Chernobyl… 9 varieties of Sami language: Northern Sami (15000), the rest 3500 (400 -600)
SAMI Sapmi area: settlements since 10. 000 BC fishermen, raindeer hunters, since 1500 raindeer herders 19 th, 20 th century: pressure to wipe out Sami culture (Norwegian names, language, sterilization of Sami women in Sweden… logging, mineral mining, military activitities, Chernobyl… 9 varieties of Sami language: Northern Sami (15000), the rest 3500 (400 -600)
 HUNGARIAN – Ugric language Pannonia (9 th BC – end of 4 th AD) – Roman province Huns, Ostrogoths, Lombards, Gepids, Avars and Slaves Magyars led by Arpad – since 895 federation of tribes Saint Stephan I – Hungary integrated into feudal Christian Europe -Latin official language until 19 th c. 1200 – funeral oration 1430 s – Bible translation 1533 – first printed book (letters of St. Paul) agglutinative language, up to 18 cases 2 conjugations: definite for transitive, indefinite for intransitive verbs four levels of politeness kinship terms depend on the relative age (younger/older) separate prefixes for up to eleventh ancestors and tenth descendants surname generally comes first
HUNGARIAN – Ugric language Pannonia (9 th BC – end of 4 th AD) – Roman province Huns, Ostrogoths, Lombards, Gepids, Avars and Slaves Magyars led by Arpad – since 895 federation of tribes Saint Stephan I – Hungary integrated into feudal Christian Europe -Latin official language until 19 th c. 1200 – funeral oration 1430 s – Bible translation 1533 – first printed book (letters of St. Paul) agglutinative language, up to 18 cases 2 conjugations: definite for transitive, indefinite for intransitive verbs four levels of politeness kinship terms depend on the relative age (younger/older) separate prefixes for up to eleventh ancestors and tenth descendants surname generally comes first
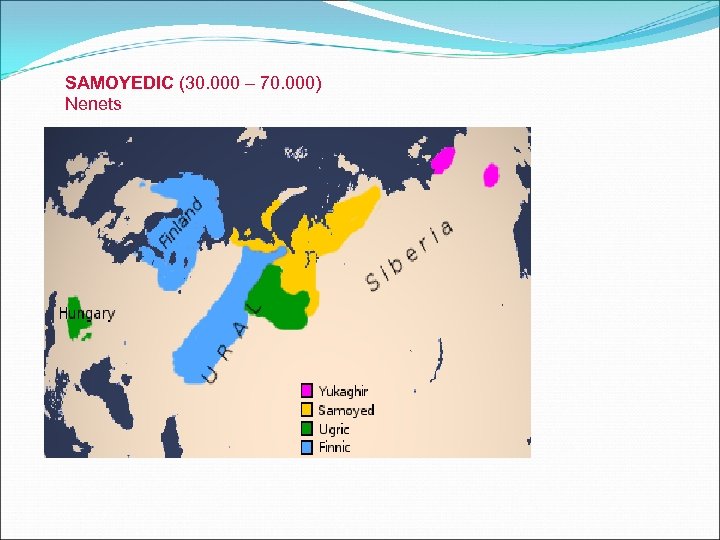 SAMOYEDIC (30. 000 – 70. 000) Nenets
SAMOYEDIC (30. 000 – 70. 000) Nenets
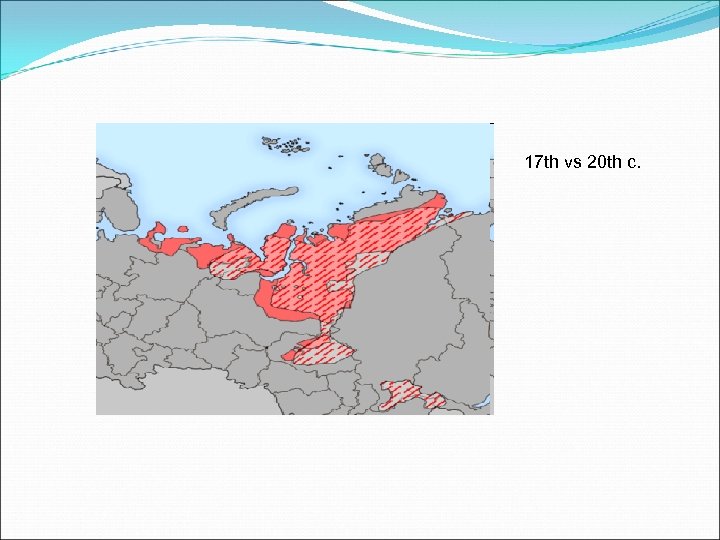 17 th vs 20 th c.
17 th vs 20 th c.
 TYPOLOGY OF URALIC LANGUAGES nominative-accusative alignment elaborate case systems agglutination no grammatical gender dual in Samoyedic and Sami languages vowel harmony
TYPOLOGY OF URALIC LANGUAGES nominative-accusative alignment elaborate case systems agglutination no grammatical gender dual in Samoyedic and Sami languages vowel harmony
 FINNISH NOUN CASES • nominative talo • genitive talon • accusative talo • partitive taloa • translative taloksi • instructive taloin • abessive talotta • essive talona • comitative taloineen LOCATIVE internal: • inessive talossa • elative talostani • illative taloonsa LOCATIVE external • adessive talolla • ablative talolta • allative talolle house of the house (object, complete) (object, part, incomplete) into (change) a house with, using the house without a house as a house together with the house in the house from inside of the house into the house at the house from the house to the house
FINNISH NOUN CASES • nominative talo • genitive talon • accusative talo • partitive taloa • translative taloksi • instructive taloin • abessive talotta • essive talona • comitative taloineen LOCATIVE internal: • inessive talossa • elative talostani • illative taloonsa LOCATIVE external • adessive talolla • ablative talolta • allative talolle house of the house (object, complete) (object, part, incomplete) into (change) a house with, using the house without a house as a house together with the house in the house from inside of the house into the house at the house from the house to the house
 ALTAIC LANGUAGES
ALTAIC LANGUAGES
 ALTAIC LANGUAGES: • TURKIC Turkish (83 millions), Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Uzbek, Azerbaijani, Turkmen, Uigur, Chuvash (Bulgarian), Yakut (360. 000) • MONGOLIAN Mongolian (Khalka), Kalmyk, Buryat • TUNGISIC Evenki, Manchu
ALTAIC LANGUAGES: • TURKIC Turkish (83 millions), Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Uzbek, Azerbaijani, Turkmen, Uigur, Chuvash (Bulgarian), Yakut (360. 000) • MONGOLIAN Mongolian (Khalka), Kalmyk, Buryat • TUNGISIC Evenki, Manchu
 TYPOLOGY - vowel harmony -agglutination -SOV word order Vowel harmony: result of distant assimilation of vowels in neighbouring syllables – adjustment of the vowels in the bound morpheme to the vowel in the stem Turkish ev ‘house’ - ev-ler ‘houses’ kadin ‘woman’ - kadin-lar ‘women’ Agglutination: ev – N. Sg. ev-ler N. pl. ev-i D. sg. ev-ler-i D. pl.
TYPOLOGY - vowel harmony -agglutination -SOV word order Vowel harmony: result of distant assimilation of vowels in neighbouring syllables – adjustment of the vowels in the bound morpheme to the vowel in the stem Turkish ev ‘house’ - ev-ler ‘houses’ kadin ‘woman’ - kadin-lar ‘women’ Agglutination: ev – N. Sg. ev-ler N. pl. ev-i D. sg. ev-ler-i D. pl.
 SINO-TIBETAN LANGUAGES CHINESE LANGUAGES TIBETO-BURMAN LANGUAGES
SINO-TIBETAN LANGUAGES CHINESE LANGUAGES TIBETO-BURMAN LANGUAGES
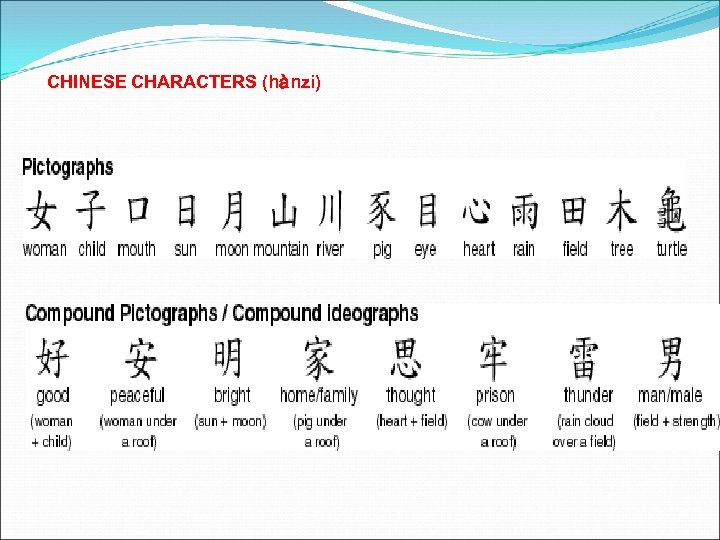 CHINESE CHARACTERS (hànzi)
CHINESE CHARACTERS (hànzi)
 PHONO-SEMANTIC COMPOUNDS radical + phonetic clue mother = woman + “sounds like horse”
PHONO-SEMANTIC COMPOUNDS radical + phonetic clue mother = woman + “sounds like horse”
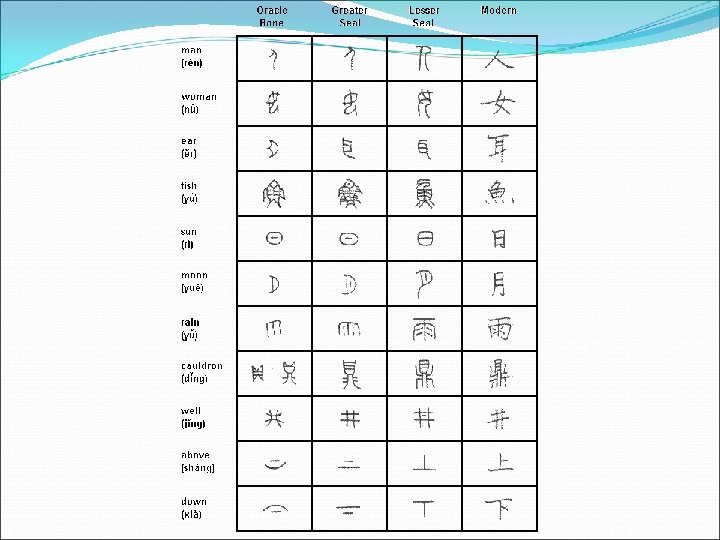
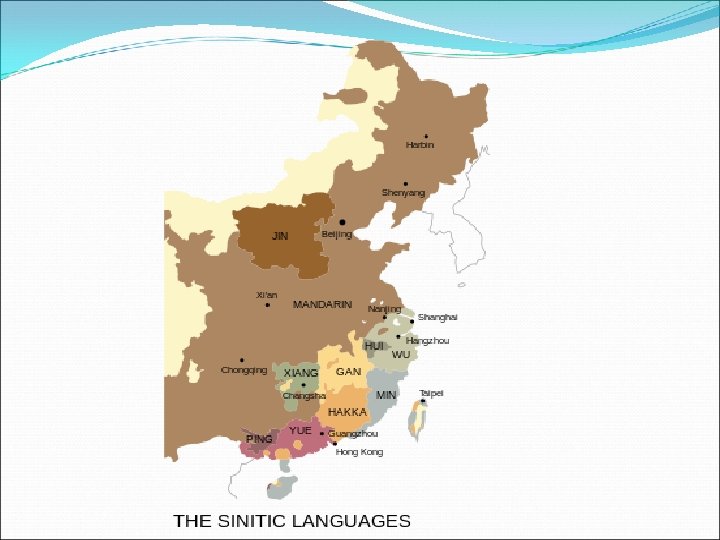
 CHINESE LANGUAGES Han languages - Hànyŭ Wén-yán – 1500 BC – logographic writing system Báihuà – 1917 reformed languages (written) Simplified Chinese – since 1956 (2. 238 characters simplified) Simplified Chinese Pŭtōnguà ‘common language’ -1949 – spoken standardized language based on Mandarin (official in China and Taiwan, Singapore and UN) Mandarin (850) Cantonese (Yue) (70) – Guangong, Hong Kong, Macau, overseas Wu (90) - Shanghai Min (50) – Taiwan (Taiwanese), Southeast Asia Hakka - southern China, Xiang – Hunan (central China)….
CHINESE LANGUAGES Han languages - Hànyŭ Wén-yán – 1500 BC – logographic writing system Báihuà – 1917 reformed languages (written) Simplified Chinese – since 1956 (2. 238 characters simplified) Simplified Chinese Pŭtōnguà ‘common language’ -1949 – spoken standardized language based on Mandarin (official in China and Taiwan, Singapore and UN) Mandarin (850) Cantonese (Yue) (70) – Guangong, Hong Kong, Macau, overseas Wu (90) - Shanghai Min (50) – Taiwan (Taiwanese), Southeast Asia Hakka - southern China, Xiang – Hunan (central China)….
 Typology of Chinese languages isolating languages SVO tonal languages classifiers In isolating languages free morphemes prevail. Words are mostly monomorphemic. khi tôi dên nhà ban tôi, chúng tôi bát dâu làm bài. when I come house friend I plural I begin do lesson article
Typology of Chinese languages isolating languages SVO tonal languages classifiers In isolating languages free morphemes prevail. Words are mostly monomorphemic. khi tôi dên nhà ban tôi, chúng tôi bát dâu làm bài. when I come house friend I plural I begin do lesson article
 Tonal languages have tonemes, i. e. phonemes which differe only in the register (pitch) and/or its contour (shift). Tonal languages: Chinese, Thai, Vietnamese, sub-Saharan African languages, Native American languages ไหมใหมไหมมย IPA: /mǎi mài mâi mái/ "Does new silk burn? “ (Thai tong-twister) 妈妈骂马的麻吗? /媽媽罵馬的麻嗎? Pinyin: māma mà mǎ de má ma? "Is mom scolding the horse's hemp? “ (Mandarin)
Tonal languages have tonemes, i. e. phonemes which differe only in the register (pitch) and/or its contour (shift). Tonal languages: Chinese, Thai, Vietnamese, sub-Saharan African languages, Native American languages ไหมใหมไหมมย IPA: /mǎi mài mâi mái/ "Does new silk burn? “ (Thai tong-twister) 妈妈骂马的麻吗? /媽媽罵馬的麻嗎? Pinyin: māma mà mǎ de má ma? "Is mom scolding the horse's hemp? “ (Mandarin)
 Classifers are morphemes which refer to some innate semantic feature of the content word they are used with. They can be used with different word classes. Classifier languages: Chinese, Thai, Australian languages, Mayan… Murrinhpatha (Australian): Nanti kamarl : C: generic + eye = eye Kura kamarl : C: water + eye = pond Mi kamarl: C: non-meat food + eye = seed Nominal: (Yidini) bama waguja: C: human + man Numerical: (Thai) luuk saam khon: child + three-C: human Verbal: (Waris) sa ka-m put-ra-ho-o coconut + me + C: kokos + meni + C: round + give ….
Classifers are morphemes which refer to some innate semantic feature of the content word they are used with. They can be used with different word classes. Classifier languages: Chinese, Thai, Australian languages, Mayan… Murrinhpatha (Australian): Nanti kamarl : C: generic + eye = eye Kura kamarl : C: water + eye = pond Mi kamarl: C: non-meat food + eye = seed Nominal: (Yidini) bama waguja: C: human + man Numerical: (Thai) luuk saam khon: child + three-C: human Verbal: (Waris) sa ka-m put-ra-ho-o coconut + me + C: kokos + meni + C: round + give ….
 Chinese classifers (measure words) between numerals/demonstratives and nouns 五wǔ five 头 tóu CL 牛niú cattle general classifer, books, flat objects, animals, large buildings and mountains, domestic animals, long and flexible animals, horses…
Chinese classifers (measure words) between numerals/demonstratives and nouns 五wǔ five 头 tóu CL 牛niú cattle general classifer, books, flat objects, animals, large buildings and mountains, domestic animals, long and flexible animals, horses…
 JAPANESE many typological characteristic of Altaic languages (agglutination, SOV word order) Chinese influence – lexicon, writing system Chinese characters – kanji (< hanzi) (several thousands) 2 syllabaries: kana scripts: katakana, hiragana (46 basic characters each) Latin script: romaji
JAPANESE many typological characteristic of Altaic languages (agglutination, SOV word order) Chinese influence – lexicon, writing system Chinese characters – kanji (< hanzi) (several thousands) 2 syllabaries: kana scripts: katakana, hiragana (46 basic characters each) Latin script: romaji
 JAPANESE many typological characteristic of Altaic languages (agglutination, SOV word order) Chinese influence – lexicon, writing system Chinese characters – kanji 2 syllabaries: kana script: katakana, hiragana Latin script: romaji: Watashi-wa kissaten-de koohi-o nam-da. コーヒー 飲 んだ 喫茶店
JAPANESE many typological characteristic of Altaic languages (agglutination, SOV word order) Chinese influence – lexicon, writing system Chinese characters – kanji 2 syllabaries: kana script: katakana, hiragana Latin script: romaji: Watashi-wa kissaten-de koohi-o nam-da. コーヒー 飲 んだ 喫茶店
 JAPANESE many typological characteristic of Altaic languages (agglutination, SOV word order) Chinese influence – lexicon, writing system Chinese characters – kanji 2 syllabaries: kana script: katakana, hiragana Latin script: romaji WATASHI wa KISSATEN de koohi o NAM da
JAPANESE many typological characteristic of Altaic languages (agglutination, SOV word order) Chinese influence – lexicon, writing system Chinese characters – kanji 2 syllabaries: kana script: katakana, hiragana Latin script: romaji WATASHI wa KISSATEN de koohi o NAM da
 HONORIFICS grammatical or morphosyntactic encoding of the relative social status of a) the addressee b) the referent c) the bystander d) the circumstances Examples: • T-V distinction in many Indo-European languages • 3 different linguistic “styles” in Japanese, 4 in Javanese and Nahuatl, 6 in Korean… • “avoidance speech”: Australian, Austranesian, American, Cushitic and Bantu languages (e. g. different words used in the presence of opposite sex parents-in-law, children-in-law, cross-cousins in Dyrbal)
HONORIFICS grammatical or morphosyntactic encoding of the relative social status of a) the addressee b) the referent c) the bystander d) the circumstances Examples: • T-V distinction in many Indo-European languages • 3 different linguistic “styles” in Japanese, 4 in Javanese and Nahuatl, 6 in Korean… • “avoidance speech”: Australian, Austranesian, American, Cushitic and Bantu languages (e. g. different words used in the presence of opposite sex parents-in-law, children-in-law, cross-cousins in Dyrbal)
 Honorifics in English: Mr, , Mrs. , Ms, . Miss, Doctor, Captain, Coach, Officer, Reverend, Father, Professor… Sir, Madam, Your Honour, Your Majesty, Your Highness (below royalty) Your Excellency (heads of state, ambassadors, governors, bishops) Your Eminence (cardinals)
Honorifics in English: Mr, , Mrs. , Ms, . Miss, Doctor, Captain, Coach, Officer, Reverend, Father, Professor… Sir, Madam, Your Honour, Your Majesty, Your Highness (below royalty) Your Excellency (heads of state, ambassadors, governors, bishops) Your Eminence (cardinals)
 HONORIFIC SPEECH - KEIGO polite language: TEI NEIGO desu at the end of the sentence, masu at the end of the verb, prefixes o- or go- for nouns used by television presenters, the “safest” form to be learned by non-native speakers respectful language: SON KEIGO special forms or words used, lengthy polite expressions, e. g taberu ‘eat’, nomu ‘drink’ > meshiagaru hito ‘person’ > kata: 人 > 方 -when talking about/to superiors and customers; - not used when referring to oneself. -in business, professional capacity humble language: KEN YOOGO similar to respectful language but used when referring to oneself
HONORIFIC SPEECH - KEIGO polite language: TEI NEIGO desu at the end of the sentence, masu at the end of the verb, prefixes o- or go- for nouns used by television presenters, the “safest” form to be learned by non-native speakers respectful language: SON KEIGO special forms or words used, lengthy polite expressions, e. g taberu ‘eat’, nomu ‘drink’ > meshiagaru hito ‘person’ > kata: 人 > 方 -when talking about/to superiors and customers; - not used when referring to oneself. -in business, professional capacity humble language: KEN YOOGO similar to respectful language but used when referring to oneself
 HONORIFIC WORDS/particles, added to nouns or names chan – children, pets, close friends little girls kun – people of lower social status, boys san – the most common marker of respect (Mr. Mrs, also for family members) sama – ‘esteemed’ sensei – ‘master, teacher’
HONORIFIC WORDS/particles, added to nouns or names chan – children, pets, close friends little girls kun – people of lower social status, boys san – the most common marker of respect (Mr. Mrs, also for family members) sama – ‘esteemed’ sensei – ‘master, teacher’
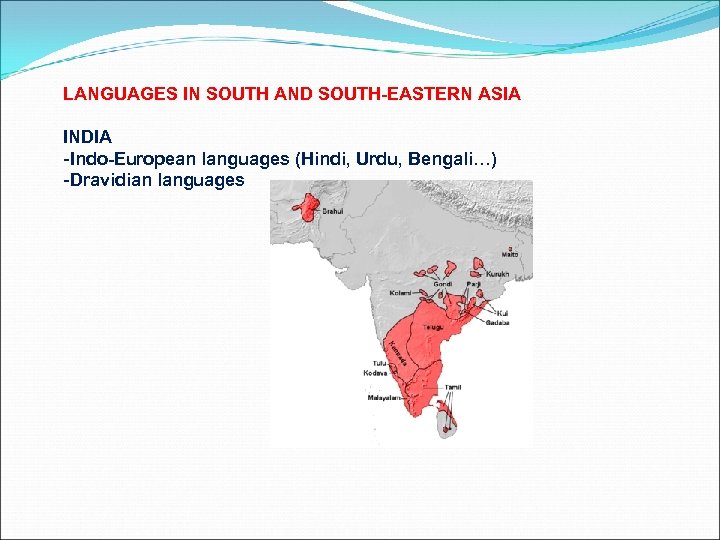 LANGUAGES IN SOUTH AND SOUTH-EASTERN ASIA INDIA -Indo-European languages (Hindi, Urdu, Bengali…) -Dravidian languages
LANGUAGES IN SOUTH AND SOUTH-EASTERN ASIA INDIA -Indo-European languages (Hindi, Urdu, Bengali…) -Dravidian languages
 LANGUAGES IN SOUTH AND SOUTH-EASTERN ASIA INDIA -Indo-European languages (Hindi, Urdu, Bengali…) -Dravidian languages INDOCHINA -Sino-Tibetan languages (> Tibeto-Burmese > Burmese) -Tai languages (Thai, Lao/Laotian) -Austro-Asiatic languages (Khmer, Mon, Vietnamese? )
LANGUAGES IN SOUTH AND SOUTH-EASTERN ASIA INDIA -Indo-European languages (Hindi, Urdu, Bengali…) -Dravidian languages INDOCHINA -Sino-Tibetan languages (> Tibeto-Burmese > Burmese) -Tai languages (Thai, Lao/Laotian) -Austro-Asiatic languages (Khmer, Mon, Vietnamese? )
 LANGUAGES IN AUSTRALIA AND OCEANIA AUSTRALIA • Indo-European languages (English) • Australian Aboriginal languages; Tasmanian languages
LANGUAGES IN AUSTRALIA AND OCEANIA AUSTRALIA • Indo-European languages (English) • Australian Aboriginal languages; Tasmanian languages
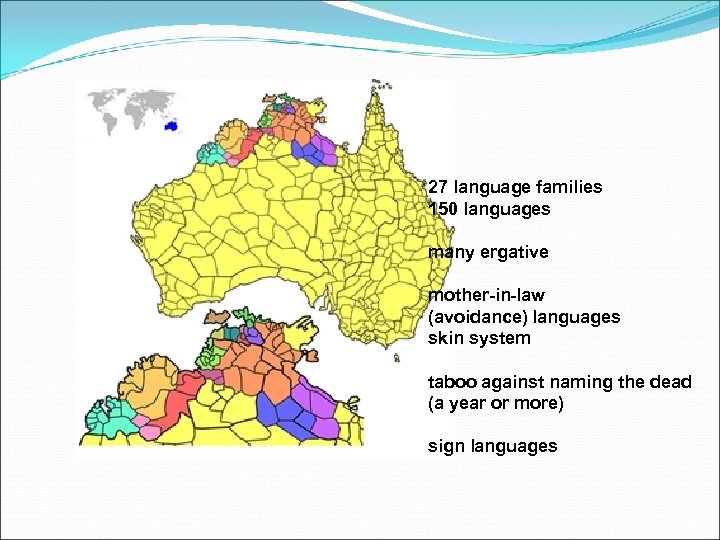 27 language families 150 languages many ergative mother-in-law (avoidance) languages skin system taboo against naming the dead (a year or more) sign languages
27 language families 150 languages many ergative mother-in-law (avoidance) languages skin system taboo against naming the dead (a year or more) sign languages
 LANGUAGES IN AUSTRALIA AND OCEANIA INDIAN OCEAN, INDONESIA, MALESIA, PACIFIC OCEAN Austronesian languages: Formosan, Malagasy, Indonesian, Malay, Javanese, Filipino (Tagalog), Maori, Samoan, Tahitian, Hawaiian, Tongic…. Papuan languages 800 languages, 60 families, only a few more than 100. 000 speakers polysynthetic some are tonal PIDGIN AND CREOLE LANGUAGES
LANGUAGES IN AUSTRALIA AND OCEANIA INDIAN OCEAN, INDONESIA, MALESIA, PACIFIC OCEAN Austronesian languages: Formosan, Malagasy, Indonesian, Malay, Javanese, Filipino (Tagalog), Maori, Samoan, Tahitian, Hawaiian, Tongic…. Papuan languages 800 languages, 60 families, only a few more than 100. 000 speakers polysynthetic some are tonal PIDGIN AND CREOLE LANGUAGES
 PIDGIN AND CREOLE LANGUAGES SOCIO-LINGUISTIC DEFINITION: pidgin: auxiliary language, emerging where more than two languages in contact, no native speakers, the use restricted to certain fields of life (e. g. trade) creole: first language of communication GEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION: Pacific and Indian Ocean, Australia, West Africa, Caribean islands, South America…
PIDGIN AND CREOLE LANGUAGES SOCIO-LINGUISTIC DEFINITION: pidgin: auxiliary language, emerging where more than two languages in contact, no native speakers, the use restricted to certain fields of life (e. g. trade) creole: first language of communication GEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION: Pacific and Indian Ocean, Australia, West Africa, Caribean islands, South America…
 LINGUISTIC CHARACTERISTICS: lexifier language, common grammatical features pidgin: the number of grammatical categories reduced, the encodement transparent, poor morphology creole: reassertion of grammatical categories, grammaticalization of lexemes, basic morphology Tok Pisin: balus ‘bird’ kaikai ‘eat’ bubu ‘great parent/child’ lotu ‘church’ rokrok ‘frog’ tambu ‘in-laws’ (< taboo) pikinini ‘child’ kantiri ‘sister’s child, uncle’
LINGUISTIC CHARACTERISTICS: lexifier language, common grammatical features pidgin: the number of grammatical categories reduced, the encodement transparent, poor morphology creole: reassertion of grammatical categories, grammaticalization of lexemes, basic morphology Tok Pisin: balus ‘bird’ kaikai ‘eat’ bubu ‘great parent/child’ lotu ‘church’ rokrok ‘frog’ tambu ‘in-laws’ (< taboo) pikinini ‘child’ kantiri ‘sister’s child, uncle’
 belo kaikai belhat manki gras bilong fes gras no gut maus gras sit haus, liklik haus moni manmeri solwara gat bel hevi
belo kaikai belhat manki gras bilong fes gras no gut maus gras sit haus, liklik haus moni manmeri solwara gat bel hevi
 Papa bilong mipela, Yu stap long heven. Nem bilong yu i mas i stap holi. Kingdom bilong yu i mas i kam. Strongim mipela long bihainim laik bilong yu long graun, olsem ol i bihainim long heven. Givim mipela kaikai inap long tude. Pogivim rong bilong mipela, olsem mipela i pogivim ol arapela i mekim rong long mipela. Sambai long mipela long taim bilong traim. Na rausim olgeta samting nogut long mipela. Kingdom na strong na glori, em i bilong yu tasol oltaim. Tru.
Papa bilong mipela, Yu stap long heven. Nem bilong yu i mas i stap holi. Kingdom bilong yu i mas i kam. Strongim mipela long bihainim laik bilong yu long graun, olsem ol i bihainim long heven. Givim mipela kaikai inap long tude. Pogivim rong bilong mipela, olsem mipela i pogivim ol arapela i mekim rong long mipela. Sambai long mipela long taim bilong traim. Na rausim olgeta samting nogut long mipela. Kingdom na strong na glori, em i bilong yu tasol oltaim. Tru.
 decreolisation: basilect mezolect acrolect
decreolisation: basilect mezolect acrolect
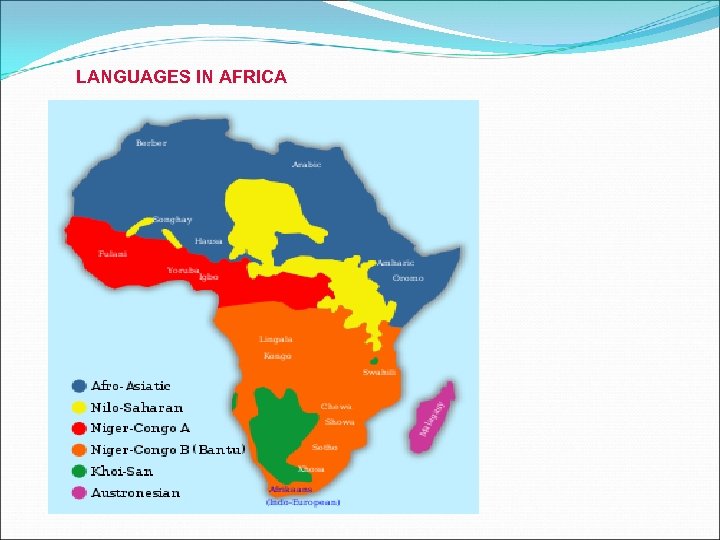 LANGUAGES IN AFRICA
LANGUAGES IN AFRICA
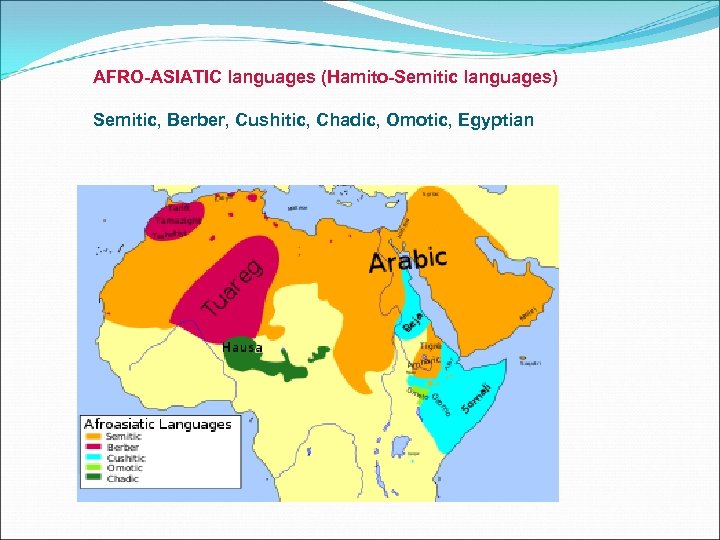 AFRO-ASIATIC languages (Hamito-Semitic languages) Semitic, Berber, Cushitic, Chadic, Omotic, Egyptian
AFRO-ASIATIC languages (Hamito-Semitic languages) Semitic, Berber, Cushitic, Chadic, Omotic, Egyptian
 8 th BC – Aramaic becomes the common language of communication in the Middle East > after 3 rd BC, also the spoken language of Jews Hebrew remains the literary and liturgical language of Jews 19 th c. – Eliezer ben Yehuda – 4000 new words, 1959 dictionary of modern Hebrew – Ivrit Arabic – until 7 th c. on the Arabian penninsula – with expansion of Islam 8 th c. > northern Africa, Spain, India… 610 – Muhammad recieved revelations by Gabriel (Jibril) Koran (Quran) – classical Arabic > modern literary Arabic algebra, alcohol, alchemy, zenith, nadir, zero, cipher…
8 th BC – Aramaic becomes the common language of communication in the Middle East > after 3 rd BC, also the spoken language of Jews Hebrew remains the literary and liturgical language of Jews 19 th c. – Eliezer ben Yehuda – 4000 new words, 1959 dictionary of modern Hebrew – Ivrit Arabic – until 7 th c. on the Arabian penninsula – with expansion of Islam 8 th c. > northern Africa, Spain, India… 610 – Muhammad recieved revelations by Gabriel (Jibril) Koran (Quran) – classical Arabic > modern literary Arabic algebra, alcohol, alchemy, zenith, nadir, zero, cipher…
 Amharic – Ethiopia, (from Ge’ez)
Amharic – Ethiopia, (from Ge’ez)
 Typology of Semitic languages introflection (nonconcatanative/discontinuous morphology) kitāb "book" kutub "books" kātib "writer" kuttāb "writers" kataba "he wrote" yaktubu "he writes" VSO word order some dialects only 3 vowels most dialects 3 numbers 2 genders – masculine and feminine
Typology of Semitic languages introflection (nonconcatanative/discontinuous morphology) kitāb "book" kutub "books" kātib "writer" kuttāb "writers" kataba "he wrote" yaktubu "he writes" VSO word order some dialects only 3 vowels most dialects 3 numbers 2 genders – masculine and feminine
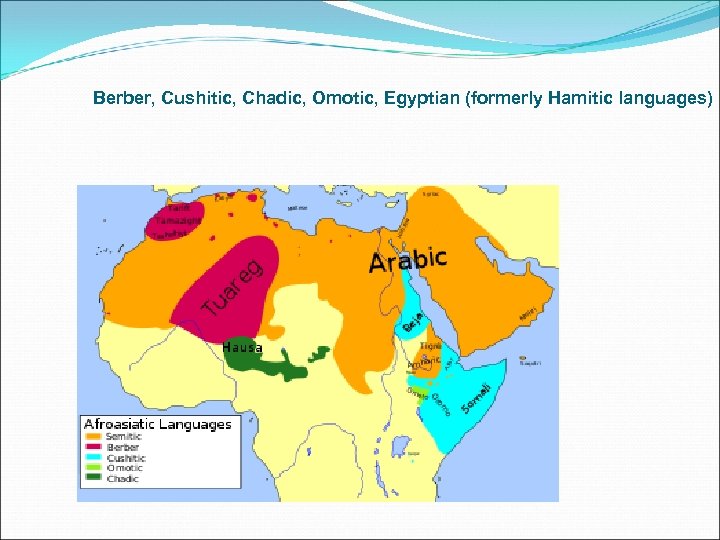 Berber, Cushitic, Chadic, Omotic, Egyptian (formerly Hamitic languages)
Berber, Cushitic, Chadic, Omotic, Egyptian (formerly Hamitic languages)
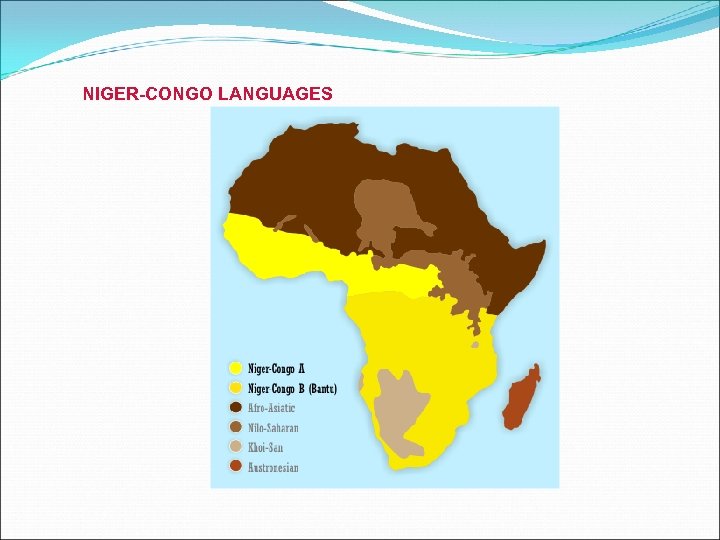 NIGER-CONGO LANGUAGES
NIGER-CONGO LANGUAGES
 Niger-Congo (1350) Yoruba, Fula, Akan BANTU languages (535, 250 mutually intelligible) Cameroon (proto-Bantu language) 2000 -3000 years ago eastward and southward Swahili Xhosa Zulu Rwanda Swazi Kongo Shona Ndebele…
Niger-Congo (1350) Yoruba, Fula, Akan BANTU languages (535, 250 mutually intelligible) Cameroon (proto-Bantu language) 2000 -3000 years ago eastward and southward Swahili Xhosa Zulu Rwanda Swazi Kongo Shona Ndebele…
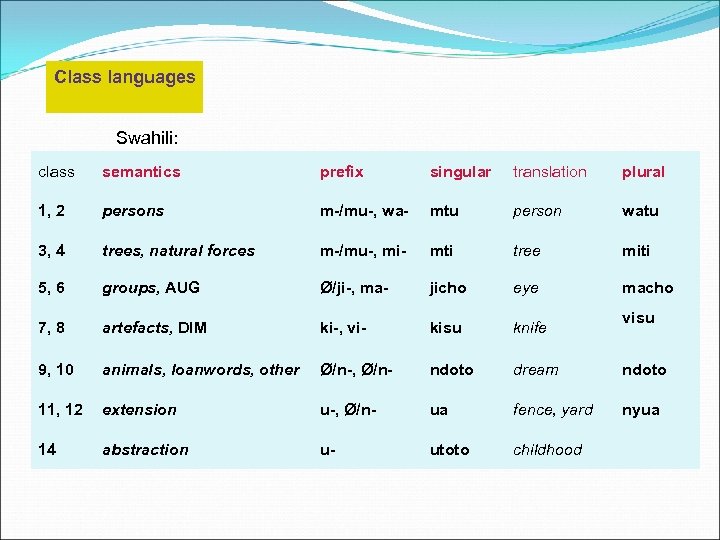 Class languages Swahili: class semantics prefix singular translation plural 1, 2 persons m-/mu-, wa- mtu person watu 3, 4 trees, natural forces m-/mu-, mi- mti tree miti 5, 6 groups, AUG Ø/ji-, ma- jicho eye macho 7, 8 artefacts, DIM ki-, vi- kisu knife 9, 10 animals, loanwords, other Ø/n-, Ø/n- ndoto dream ndoto 11, 12 extension u-, Ø/n- ua fence, yard nyua 14 abstraction u- utoto childhood visu
Class languages Swahili: class semantics prefix singular translation plural 1, 2 persons m-/mu-, wa- mtu person watu 3, 4 trees, natural forces m-/mu-, mi- mti tree miti 5, 6 groups, AUG Ø/ji-, ma- jicho eye macho 7, 8 artefacts, DIM ki-, vi- kisu knife 9, 10 animals, loanwords, other Ø/n-, Ø/n- ndoto dream ndoto 11, 12 extension u-, Ø/n- ua fence, yard nyua 14 abstraction u- utoto childhood visu
 AGREEMENT, CONCORD AGGLUTINATION Mtoto mdogo amekisoma. ‘a small child has read it’ Watoto wadogo wamekisoma ‘small children have read it’ amekisoma: a = class marker of the subject me = perfect tense ki = class marker of the object (< kitabu ‘book’) soma = root morpheme ‘read’
AGREEMENT, CONCORD AGGLUTINATION Mtoto mdogo amekisoma. ‘a small child has read it’ Watoto wadogo wamekisoma ‘small children have read it’ amekisoma: a = class marker of the subject me = perfect tense ki = class marker of the object (< kitabu ‘book’) soma = root morpheme ‘read’
 KHOISAN LANGUAGES
KHOISAN LANGUAGES
 Khoi-Khoi ‘first people’ Khoi-Khoi > many speak Bantu languages Nama (Namibia), a. k. a. Hottentot San ‘outsiders’, Bushmen Kalahari, about 75. 000 still hunters gatherers land conflict with Botswana Clicks reduplication for plural 3 tones 3 genders, feminine and masculine nouns 3 numbers, neuter nouns 2 numbers SOV
Khoi-Khoi ‘first people’ Khoi-Khoi > many speak Bantu languages Nama (Namibia), a. k. a. Hottentot San ‘outsiders’, Bushmen Kalahari, about 75. 000 still hunters gatherers land conflict with Botswana Clicks reduplication for plural 3 tones 3 genders, feminine and masculine nouns 3 numbers, neuter nouns 2 numbers SOV
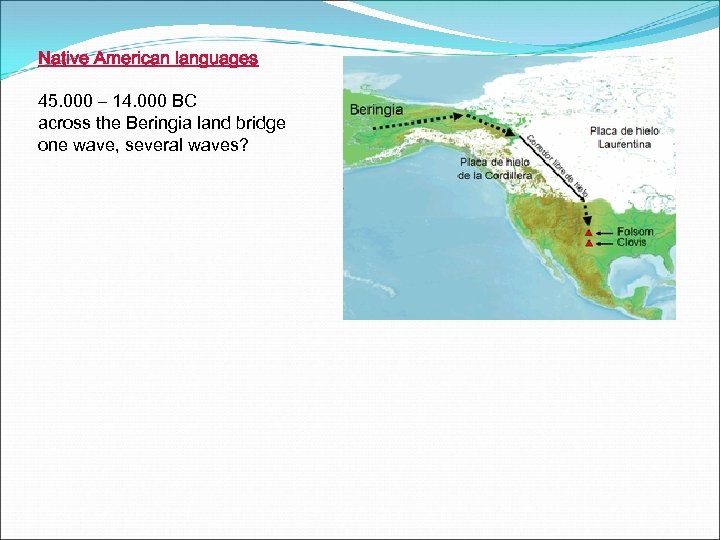 Native American languages 45. 000 – 14. 000 BC across the Beringia land bridge one wave, several waves?
Native American languages 45. 000 – 14. 000 BC across the Beringia land bridge one wave, several waves?
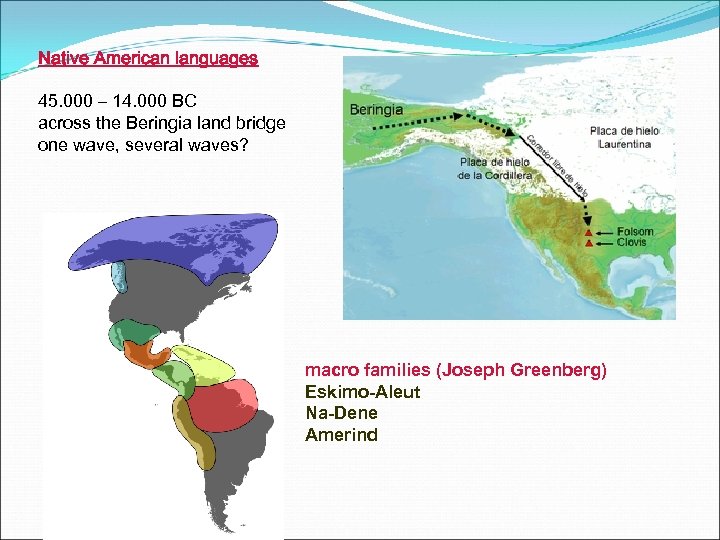 Native American languages 45. 000 – 14. 000 BC across the Beringia land bridge one wave, several waves? macro families (Joseph Greenberg) Eskimo-Aleut Na-Dene Amerind
Native American languages 45. 000 – 14. 000 BC across the Beringia land bridge one wave, several waves? macro families (Joseph Greenberg) Eskimo-Aleut Na-Dene Amerind
 pre. Columbian America: over 1500 languages, 10 million in North America, 30 million Central America 50 million South America today: North America: 200. 000 speakers Central America: 6 million speakers South America: 12 million speakers Most populous: Navajo, Inuit, Nahuatl, Mayan, Quechua Aymara, Guarani… Mayan – 6 million Nahuatl – 1, 5 million Guarani – 5 million Quechua – 6 -7 million Navajo – 170. 000 speakers
pre. Columbian America: over 1500 languages, 10 million in North America, 30 million Central America 50 million South America today: North America: 200. 000 speakers Central America: 6 million speakers South America: 12 million speakers Most populous: Navajo, Inuit, Nahuatl, Mayan, Quechua Aymara, Guarani… Mayan – 6 million Nahuatl – 1, 5 million Guarani – 5 million Quechua – 6 -7 million Navajo – 170. 000 speakers
 History of Native American – European relations Columbus: “They traded with us and gave us everything they had, with good will. . they took great delight in pleasing us. . They are very gentle and without knowledge of what is evil; nor do they murder or steal. . Your highness may believe that in all the world there can be no better people. . They love their neighbours as themselves, and they have the sweetest talk in the world, and are gentle and always laughing”…
History of Native American – European relations Columbus: “They traded with us and gave us everything they had, with good will. . they took great delight in pleasing us. . They are very gentle and without knowledge of what is evil; nor do they murder or steal. . Your highness may believe that in all the world there can be no better people. . They love their neighbours as themselves, and they have the sweetest talk in the world, and are gentle and always laughing”…
 Leyes de Burgos 1512 Leyes nuevas 1542: forbade maltreatment, endorsed conversion to Catholicism, pregnant women protected hammock provided, meat on Sundays, sacred dances allowed, no physical abuse allowed… typhus, influenza, smallpox, measles…
Leyes de Burgos 1512 Leyes nuevas 1542: forbade maltreatment, endorsed conversion to Catholicism, pregnant women protected hammock provided, meat on Sundays, sacred dances allowed, no physical abuse allowed… typhus, influenza, smallpox, measles…
 Indian Removal Act – 1830 (Andrew Jackson) Trail of Tears http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Nfo_Lnu. DJ 1 c&feature=related
Indian Removal Act – 1830 (Andrew Jackson) Trail of Tears http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Nfo_Lnu. DJ 1 c&feature=related
 Pine Ridge Reservation, Wounded Knee incident in 1973
Pine Ridge Reservation, Wounded Knee incident in 1973
 Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act of 1975
Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act of 1975
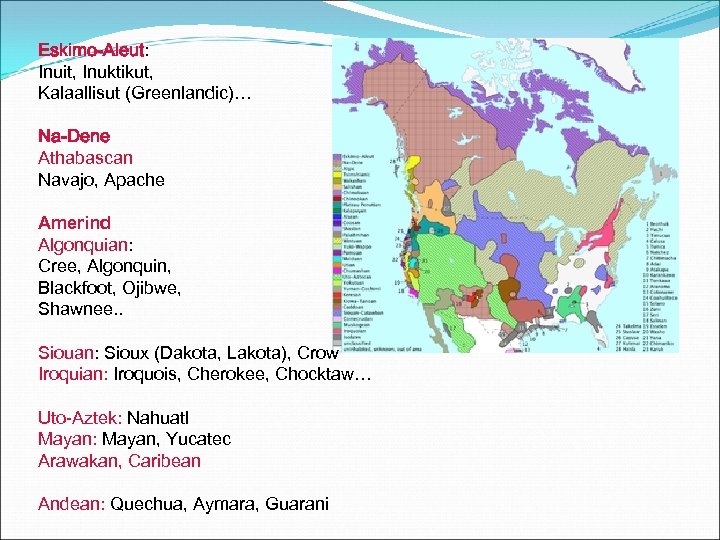 Eskimo-Aleut: Inuit, Inuktikut, Kalaallisut (Greenlandic)… Na-Dene Athabascan Navajo, Apache Amerind Algonquian: Cree, Algonquin, Blackfoot, Ojibwe, Shawnee. . Siouan: Sioux (Dakota, Lakota), Crow Iroquian: Iroquois, Cherokee, Chocktaw… Uto-Aztek: Nahuatl Mayan: Mayan, Yucatec Arawakan, Caribean Andean: Quechua, Aymara, Guarani
Eskimo-Aleut: Inuit, Inuktikut, Kalaallisut (Greenlandic)… Na-Dene Athabascan Navajo, Apache Amerind Algonquian: Cree, Algonquin, Blackfoot, Ojibwe, Shawnee. . Siouan: Sioux (Dakota, Lakota), Crow Iroquian: Iroquois, Cherokee, Chocktaw… Uto-Aztek: Nahuatl Mayan: Mayan, Yucatec Arawakan, Caribean Andean: Quechua, Aymara, Guarani
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 implosive, ejective phonemes
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 implosive, ejective phonemes
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 implosive, ejective phonemes polysynthetic
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 implosive, ejective phonemes polysynthetic
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 implosive, ejective phonemes polysynthetic ergative
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 implosive, ejective phonemes polysynthetic ergative
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 implosive, ejective phonemes polysynthetic ergative classifiers
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 implosive, ejective phonemes polysynthetic ergative classifiers
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 implosive, ejective phonemes tonemes polysynthetic ergative classifiers alienable/inalienable possession animacy marking many mood, tense and aspect distinctions
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 implosive, ejective phonemes tonemes polysynthetic ergative classifiers alienable/inalienable possession animacy marking many mood, tense and aspect distinctions
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 from Nahuatl: Nimitztētlamaquiltīz ni-mits-teː-tla-maki-ltiː-s' I-you-someone-something-give-CAUSATIVE-FUTURE "I shall make somebody give something to you"[6]
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=XFay. FUiyv 20 from Nahuatl: Nimitztētlamaquiltīz ni-mits-teː-tla-maki-ltiː-s' I-you-someone-something-give-CAUSATIVE-FUTURE "I shall make somebody give something to you"[6]
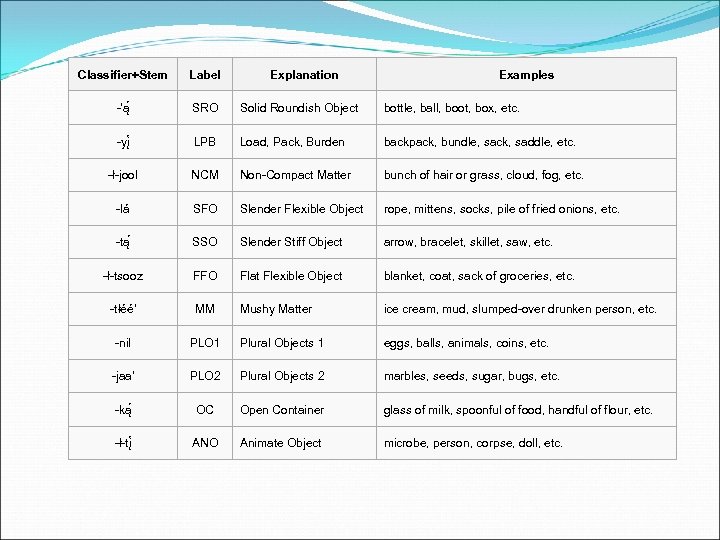 Classifier+Stem Label Explanation Examples -'ą SRO Solid Roundish Object bottle, ball, boot, box, etc. -yį LPB Load, Pack, Burden backpack, bundle, sack, saddle, etc. -ł-jool NCM Non-Compact Matter bunch of hair or grass, cloud, fog, etc. -lá SFO Slender Flexible Object rope, mittens, socks, pile of fried onions, etc. -tą SSO Slender Stiff Object arrow, bracelet, skillet, saw, etc. -ł-tsooz FFO Flat Flexible Object blanket, coat, sack of groceries, etc. -tłéé' MM Mushy Matter ice cream, mud, slumped-over drunken person, etc. -nil PLO 1 Plural Objects 1 eggs, balls, animals, coins, etc. -jaa' PLO 2 Plural Objects 2 marbles, seeds, sugar, bugs, etc. -ką OC Open Container glass of milk, spoonful of food, handful of flour, etc. -ł-tį ANO Animate Object microbe, person, corpse, doll, etc.
Classifier+Stem Label Explanation Examples -'ą SRO Solid Roundish Object bottle, ball, boot, box, etc. -yį LPB Load, Pack, Burden backpack, bundle, sack, saddle, etc. -ł-jool NCM Non-Compact Matter bunch of hair or grass, cloud, fog, etc. -lá SFO Slender Flexible Object rope, mittens, socks, pile of fried onions, etc. -tą SSO Slender Stiff Object arrow, bracelet, skillet, saw, etc. -ł-tsooz FFO Flat Flexible Object blanket, coat, sack of groceries, etc. -tłéé' MM Mushy Matter ice cream, mud, slumped-over drunken person, etc. -nil PLO 1 Plural Objects 1 eggs, balls, animals, coins, etc. -jaa' PLO 2 Plural Objects 2 marbles, seeds, sugar, bugs, etc. -ką OC Open Container glass of milk, spoonful of food, handful of flour, etc. -ł-tį ANO Animate Object microbe, person, corpse, doll, etc.
 Mayan numeral classifiers: untek wop – jahuacte tree - unts’it wop – a stick from that tree tek = plant ts’it = elongated object
Mayan numeral classifiers: untek wop – jahuacte tree - unts’it wop – a stick from that tree tek = plant ts’it = elongated object
 Mayan numeral classifiers: untek wop – jahuacte tree - unts’it wop – a stick from that tree tek = plant ts’it = elongated object Animacy scale in Navajo: humans/lightning → infants/big animals → mid-size animals → small animals → insects → natural forces → inanimate objects/plants → abstractions
Mayan numeral classifiers: untek wop – jahuacte tree - unts’it wop – a stick from that tree tek = plant ts’it = elongated object Animacy scale in Navajo: humans/lightning → infants/big animals → mid-size animals → small animals → insects → natural forces → inanimate objects/plants → abstractions
 Mayan numeral classifiers: untek wop – jahuacte tree - unts’it wop – a stick from that tree tek = plant ts’it = elongated object contrast between alienable and inalienable possession Animacy scale in Navajo: humans/lightning → infants/big animals → mid-size animals → small animals → insects → natural forces → inanimate objects/plants → abstractions
Mayan numeral classifiers: untek wop – jahuacte tree - unts’it wop – a stick from that tree tek = plant ts’it = elongated object contrast between alienable and inalienable possession Animacy scale in Navajo: humans/lightning → infants/big animals → mid-size animals → small animals → insects → natural forces → inanimate objects/plants → abstractions
 “wigwam words” hickory, pecan, chipmunk, papoose, moose, squaw, igloo, kayak , pow-wow, moccasin, racoon, tomahawk, totem… chocolate, tomato, condor, coke, chili, hammock…
“wigwam words” hickory, pecan, chipmunk, papoose, moose, squaw, igloo, kayak , pow-wow, moccasin, racoon, tomahawk, totem… chocolate, tomato, condor, coke, chili, hammock…
 Native American toponyms: Arkansas (Arkans - tribe), Oklahoma (red people), Arizona (little springs), Michigan (great water), Chicago (place of onions), Mississippi (big river), Missouri (person who has a canoe), Utah (mountain top dwellers), Wyoming (place of the big plain), Dakota (another name for Sioux), Idaho (tribe),
Native American toponyms: Arkansas (Arkans - tribe), Oklahoma (red people), Arizona (little springs), Michigan (great water), Chicago (place of onions), Mississippi (big river), Missouri (person who has a canoe), Utah (mountain top dwellers), Wyoming (place of the big plain), Dakota (another name for Sioux), Idaho (tribe),
 Nebraska (flat river), Texas (via Spanish tejas = friends), Iowa (tribe), Kansas (tribe), Minnesota (cloudy river), Illinois (tribe), Ohio (fine river), Tennessee (after a Cherokee village Tanase), Kentucky (meadowland), Alabama (tribe Alibamon), Wisconsin (gathering of waters), Connecticut (beside the long tidal river), Canada (village, community), Manitoba (great spirit), Ontario (beautiful lake), Manhattan (island of many hills) etc.
Nebraska (flat river), Texas (via Spanish tejas = friends), Iowa (tribe), Kansas (tribe), Minnesota (cloudy river), Illinois (tribe), Ohio (fine river), Tennessee (after a Cherokee village Tanase), Kentucky (meadowland), Alabama (tribe Alibamon), Wisconsin (gathering of waters), Connecticut (beside the long tidal river), Canada (village, community), Manitoba (great spirit), Ontario (beautiful lake), Manhattan (island of many hills) etc.


