USA_Education.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 52
 LANGUAGE AND AREA Education system in the USA Julia Veklich
LANGUAGE AND AREA Education system in the USA Julia Veklich
 PLAN Part I 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Preschool Elementary and secondary education Junior and senior high school Basic curricular structure Electives Advanced courses Grading scale Standardized testing Education of students with special needs Public and Private schools
PLAN Part I 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Preschool Elementary and secondary education Junior and senior high school Basic curricular structure Electives Advanced courses Grading scale Standardized testing Education of students with special needs Public and Private schools
 PLAN Part II 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. College and university Undergraduate educational Available undergraduate streams Credit system Grade Pint average (GPA) Cost The status ladder Curriculum issues Funding for K-12 schools Charter Schools Control and Competittiveness
PLAN Part II 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. College and university Undergraduate educational Available undergraduate streams Credit system Grade Pint average (GPA) Cost The status ladder Curriculum issues Funding for K-12 schools Charter Schools Control and Competittiveness
 The American system of school education differs from the systems in other countries. There are state public schools, private elementary schools and private secondary schools. Public schools are free and private schools are fee-paying.
The American system of school education differs from the systems in other countries. There are state public schools, private elementary schools and private secondary schools. Public schools are free and private schools are fee-paying.
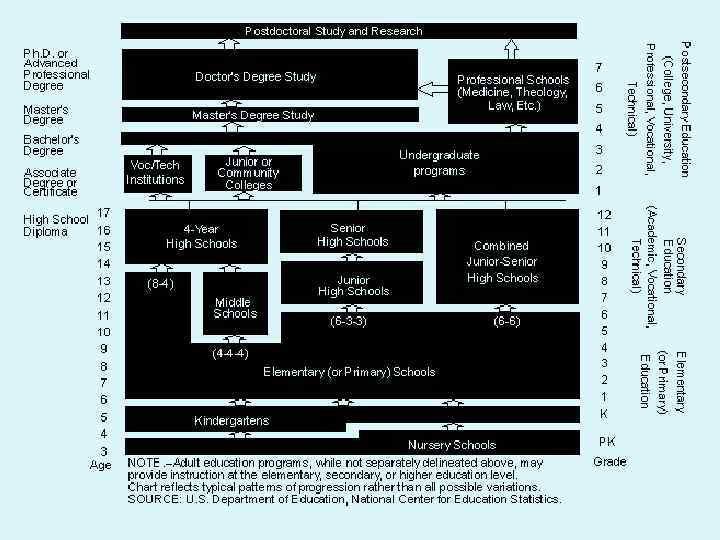
 The general pattern of education in the USA is an eight-year elementary school, followed by a four-year high school. This has been called 8 -4 plan organization. It is proceeded, in many localities, by nursery schools and kindergartens. It is followed by a four-year college and professional schools. This traditional pattern, however, has been varied in many different ways. The 6 -3 -3 plan consists of a six-year elementary school, a three-year junior high school, and a threeyear senior high school. Another variation is a 6 -6 plan organization, with a six-year elementary school followed by a six-year secondary school.
The general pattern of education in the USA is an eight-year elementary school, followed by a four-year high school. This has been called 8 -4 plan organization. It is proceeded, in many localities, by nursery schools and kindergartens. It is followed by a four-year college and professional schools. This traditional pattern, however, has been varied in many different ways. The 6 -3 -3 plan consists of a six-year elementary school, a three-year junior high school, and a threeyear senior high school. Another variation is a 6 -6 plan organization, with a six-year elementary school followed by a six-year secondary school.
 STUDY TIME The length of the school year varies among the states. Wide variation exists also in the length of the school day. A common practice is to have school in session from 9: 00 to 12: 00 in the morning and from 1: 00 to 3: 30 in the afternoon, Monday through Friday. The school day for the lower grades is often from 30 minutes to an hour shorter. Most schools require some homework to be done by elementary pupils.
STUDY TIME The length of the school year varies among the states. Wide variation exists also in the length of the school day. A common practice is to have school in session from 9: 00 to 12: 00 in the morning and from 1: 00 to 3: 30 in the afternoon, Monday through Friday. The school day for the lower grades is often from 30 minutes to an hour shorter. Most schools require some homework to be done by elementary pupils.
 Education in the United States is mainly provided by the public sector, with control and funding coming from three levels: federal, state, and local. Child education is compulsory. Public education is universally available. School curricula, funding, teaching, and other policies are set through locally elected school boards with jurisdiction over school districts with many directives from state legislatures. School districts are usually separate from other local jurisdictions, with independent officials and budgets. Educational standards and standardized testing decisions are usually made by state governments.
Education in the United States is mainly provided by the public sector, with control and funding coming from three levels: federal, state, and local. Child education is compulsory. Public education is universally available. School curricula, funding, teaching, and other policies are set through locally elected school boards with jurisdiction over school districts with many directives from state legislatures. School districts are usually separate from other local jurisdictions, with independent officials and budgets. Educational standards and standardized testing decisions are usually made by state governments.
 The ages for compulsory education vary by state. It begins from ages five to eight and ends from ages fourteen to eighteen. A growing number of states are now requiring compulsory education until the age of 18.
The ages for compulsory education vary by state. It begins from ages five to eight and ends from ages fourteen to eighteen. A growing number of states are now requiring compulsory education until the age of 18.
 Compulsory education requirements can generally be satisfied by educating children in public schools, statecertified private schools, an approved home school program. In most public and private schools, education is divided into three levels: elementary school, middle school, and high school.
Compulsory education requirements can generally be satisfied by educating children in public schools, statecertified private schools, an approved home school program. In most public and private schools, education is divided into three levels: elementary school, middle school, and high school.
 In almost all schools at these levels, children are divided by age groups into GRADES, ranging from kindergarten (followed by first grade) for the youngest children in elementary school, up to twelfth grade, the final year of high school. The exact age range of students in these grade levels varies slightly from area to area. Post-secondary education, better known as “college” in the United States, is generally governed separately from the elementary and high school system.
In almost all schools at these levels, children are divided by age groups into GRADES, ranging from kindergarten (followed by first grade) for the youngest children in elementary school, up to twelfth grade, the final year of high school. The exact age range of students in these grade levels varies slightly from area to area. Post-secondary education, better known as “college” in the United States, is generally governed separately from the elementary and high school system.
 v Most children enter the public education system around ages five or six; v The American school year traditionally begins in August or September; v Children are assigned into year groups known as grades, beginning with preschool, following by kindergarten and culminating in twelfth grade; v developmentally disabled children may be held back a grade and gifted children may skip ahead early to the next grade; v the American educational system comprises of 12 grades of study over 12 calendar years of primary and secondary education before graduating and becoming eligible for college admission.
v Most children enter the public education system around ages five or six; v The American school year traditionally begins in August or September; v Children are assigned into year groups known as grades, beginning with preschool, following by kindergarten and culminating in twelfth grade; v developmentally disabled children may be held back a grade and gifted children may skip ahead early to the next grade; v the American educational system comprises of 12 grades of study over 12 calendar years of primary and secondary education before graduating and becoming eligible for college admission.
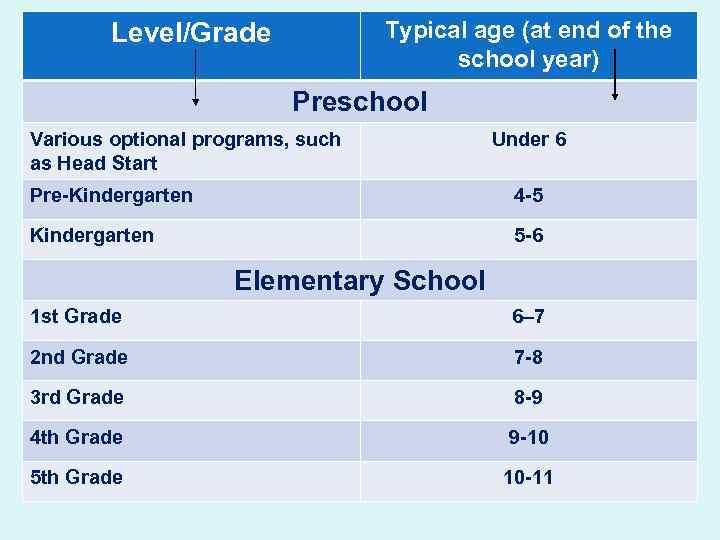 Typical age (at end of the school year) Level/Grade Preschool Various optional programs, such as Head Start Under 6 Pre-Kindergarten 4 -5 Kindergarten 5 -6 Elementary School 1 st Grade 6– 7 2 nd Grade 7 -8 3 rd Grade 8 -9 4 th Grade 9 -10 5 th Grade 10 -11
Typical age (at end of the school year) Level/Grade Preschool Various optional programs, such as Head Start Under 6 Pre-Kindergarten 4 -5 Kindergarten 5 -6 Elementary School 1 st Grade 6– 7 2 nd Grade 7 -8 3 rd Grade 8 -9 4 th Grade 9 -10 5 th Grade 10 -11
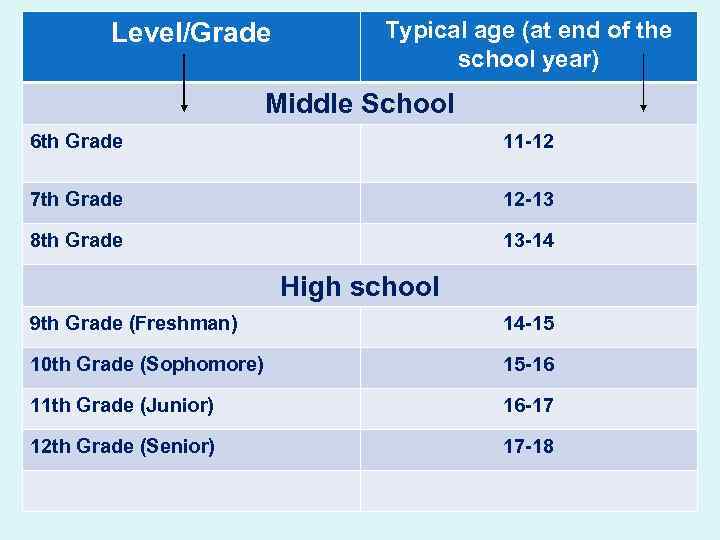 Level/Grade Typical age (at end of the school year) Middle School 6 th Grade 11 -12 7 th Grade 12 -13 8 th Grade 13 -14 High school 9 th Grade (Freshman) 14 -15 10 th Grade (Sophomore) 15 -16 11 th Grade (Junior) 16 -17 12 th Grade (Senior) 17 -18
Level/Grade Typical age (at end of the school year) Middle School 6 th Grade 11 -12 7 th Grade 12 -13 8 th Grade 13 -14 High school 9 th Grade (Freshman) 14 -15 10 th Grade (Sophomore) 15 -16 11 th Grade (Junior) 16 -17 12 th Grade (Senior) 17 -18
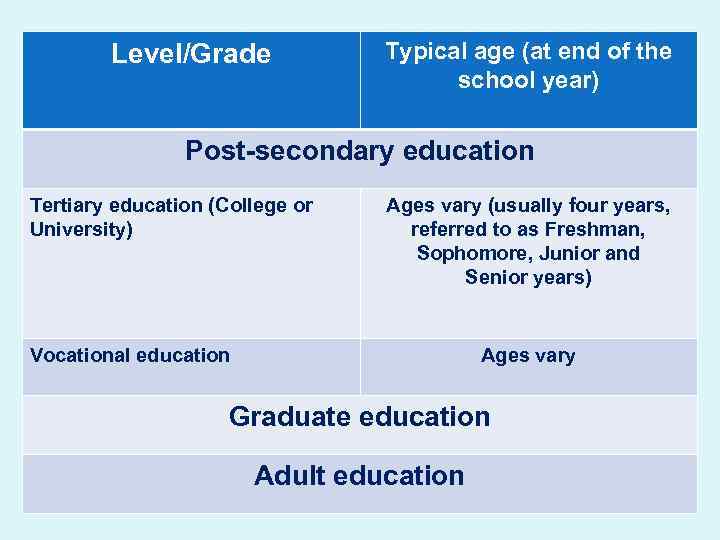 Level/Grade Typical age (at end of the school year) Post-secondary education Tertiary education (College or University) Ages vary (usually four years, referred to as Freshman, Sophomore, Junior and Senior years) Vocational education Ages vary Graduate education Adult education
Level/Grade Typical age (at end of the school year) Post-secondary education Tertiary education (College or University) Ages vary (usually four years, referred to as Freshman, Sophomore, Junior and Senior years) Vocational education Ages vary Graduate education Adult education
 Preschool education is the provision of education for children before the commencement of statutory education, usually between the ages of three and five, dependent on the jurisdiction. Preschool is also known as nursery school, or kindergarten.
Preschool education is the provision of education for children before the commencement of statutory education, usually between the ages of three and five, dependent on the jurisdiction. Preschool is also known as nursery school, or kindergarten.
 Preschool work is organized within a framework that professional educators create. The framework includes: § structural component (administration, class size, teacherchild ratio, etc. ); § process (quality of classroom environments, teacher-child interactions, etc); § alignment component(standards, curriculum, assessments). They are associated with each individual unique child that has both social and academic outcomes.
Preschool work is organized within a framework that professional educators create. The framework includes: § structural component (administration, class size, teacherchild ratio, etc. ); § process (quality of classroom environments, teacher-child interactions, etc); § alignment component(standards, curriculum, assessments). They are associated with each individual unique child that has both social and academic outcomes.

 § Schooling is compulsory for all children in the United States. § Most children begin elementary education with kindergarten and finish secondary education with twelfth grade. § Most parents send their children to either a public(they are free) or private institution. § Most students attend school for around six hours per day. § Most schools have a summer break period for about two and half months from June through August. § Parents may also choose to educate their own children at home.
§ Schooling is compulsory for all children in the United States. § Most children begin elementary education with kindergarten and finish secondary education with twelfth grade. § Most parents send their children to either a public(they are free) or private institution. § Most students attend school for around six hours per day. § Most schools have a summer break period for about two and half months from June through August. § Parents may also choose to educate their own children at home.
 Elementary school is a school of kindergarten through fifth grade where basic subjects are taught. Elementary school provides and often remain in one or two classrooms throughout the school day. Dawnville Elementary school
Elementary school is a school of kindergarten through fifth grade where basic subjects are taught. Elementary school provides and often remain in one or two classrooms throughout the school day. Dawnville Elementary school
 The curriculum within public elementary education is determined by individual school districts. The school district selects curriculum guides and textbooks that are reflective of a state's learning standards and benchmarks for a given grade level. School systems vary widely not only in the way curricular decisions are made but also in how teaching and learning take place.
The curriculum within public elementary education is determined by individual school districts. The school district selects curriculum guides and textbooks that are reflective of a state's learning standards and benchmarks for a given grade level. School systems vary widely not only in the way curricular decisions are made but also in how teaching and learning take place.
 Secondary school most commonly consists of a total of seven years, referred to as sixth through twelfth grades. The ninth through twelfth grades are most commonly referred to as high school. Upon completion of twelfth grade, American students are awarded a certificate called the high school diploma.
Secondary school most commonly consists of a total of seven years, referred to as sixth through twelfth grades. The ninth through twelfth grades are most commonly referred to as high school. Upon completion of twelfth grade, American students are awarded a certificate called the high school diploma.
 Middle school and Junior high school are any school intermediate between elementary school and senior high school. It usually includes sixth, seventh and eighth grade; for "Junior high", ninth grade. Students are given more independence in choosing their own classes.
Middle school and Junior high school are any school intermediate between elementary school and senior high school. It usually includes sixth, seventh and eighth grade; for "Junior high", ninth grade. Students are given more independence in choosing their own classes.
 Junior high school any school intermediate between elementary and senior high school. It usually includes grades seven and eight, and sometimes six or nine. In some locations, junior high school includes grade nine only, allowing students to adjust to a high school environment.
Junior high school any school intermediate between elementary and senior high school. It usually includes grades seven and eight, and sometimes six or nine. In some locations, junior high school includes grade nine only, allowing students to adjust to a high school environment.
 Senior high school is a school attended after junior high school. High school usually runs either from grades 9 -12 or from grades 10 -12. The students in these grades are commonly referred to as freshmen (grade 9), sophomores (grade 10), juniors (grade 11) and seniors (grade 12). Canyon High School Little Rock Central High School
Senior high school is a school attended after junior high school. High school usually runs either from grades 9 -12 or from grades 10 -12. The students in these grades are commonly referred to as freshmen (grade 9), sophomores (grade 10), juniors (grade 11) and seniors (grade 12). Canyon High School Little Rock Central High School
 At the high school level, students take a broad variety of classes. The following minimum courses of study are required in nearly all U. S. high schools: § Science (usually two years minimum, normally biology, chemistry and physics) § Mathematics (usually two years minimum, normally including algebra, geometry, algebra II) § English (usually four years minimum, including literature, humanities, etc. ) § Social sciences (usually three years minimum, including various history, government/economics courses) § Physical education (at least one year) Many states require a "health" course in which students learn about anatomy, nutrition, first aid, sexuality, and birth control. Anti-drug use programs are also usually part of health courses.
At the high school level, students take a broad variety of classes. The following minimum courses of study are required in nearly all U. S. high schools: § Science (usually two years minimum, normally biology, chemistry and physics) § Mathematics (usually two years minimum, normally including algebra, geometry, algebra II) § English (usually four years minimum, including literature, humanities, etc. ) § Social sciences (usually three years minimum, including various history, government/economics courses) § Physical education (at least one year) Many states require a "health" course in which students learn about anatomy, nutrition, first aid, sexuality, and birth control. Anti-drug use programs are also usually part of health courses.
 Many high schools offer a wide variety of elective courses. Types of electives include: § Visual arts (drawing, sculpture, painting, photography, film) §Performing arts (drama, band, chorus, orchestra, dance) §Technology education §Computers (word processing, programming, graphic design) §Athletics §Publishing (journalism/student newspaper) §Foreign languages (Spanish, French are common; Chinese, Latin, Greek, German, Italian)
Many high schools offer a wide variety of elective courses. Types of electives include: § Visual arts (drawing, sculpture, painting, photography, film) §Performing arts (drama, band, chorus, orchestra, dance) §Technology education §Computers (word processing, programming, graphic design) §Athletics §Publishing (journalism/student newspaper) §Foreign languages (Spanish, French are common; Chinese, Latin, Greek, German, Italian)
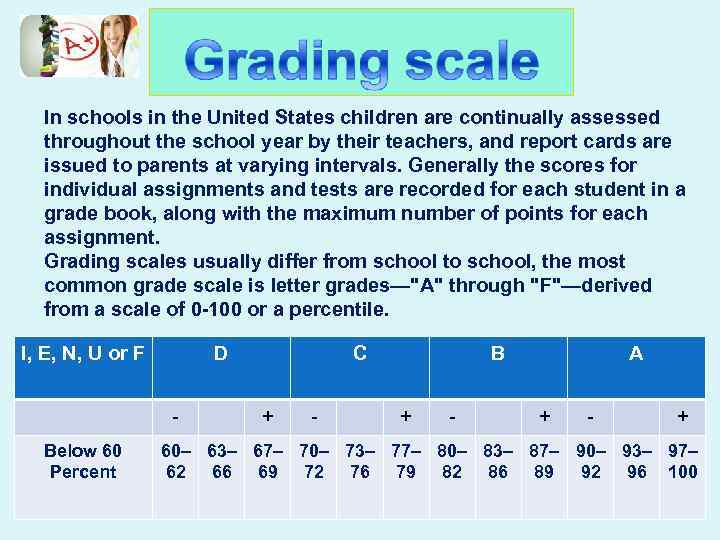 In schools in the United States children are continually assessed throughout the school year by their teachers, and report cards are issued to parents at varying intervals. Generally the scores for individual assignments and tests are recorded for each student in a grade book, along with the maximum number of points for each assignment. Grading scales usually differ from school to school, the most common grade scale is letter grades—"A" through "F"—derived from a scale of 0 -100 or a percentile. I, E, N, U or F D - Below 60 Percent C + - B + - A + - + 60– 63– 67– 70– 73– 77– 80– 83– 87– 90– 93– 97– 62 66 69 72 76 79 82 86 89 92 96 100
In schools in the United States children are continually assessed throughout the school year by their teachers, and report cards are issued to parents at varying intervals. Generally the scores for individual assignments and tests are recorded for each student in a grade book, along with the maximum number of points for each assignment. Grading scales usually differ from school to school, the most common grade scale is letter grades—"A" through "F"—derived from a scale of 0 -100 or a percentile. I, E, N, U or F D - Below 60 Percent C + - B + - A + - + 60– 63– 67– 70– 73– 77– 80– 83– 87– 90– 93– 97– 62 66 69 72 76 79 82 86 89 92 96 100
 All American states must test students in public schools statewide to ensure that they are achieving the desired level of minimum education, such as on the Regents Examinations in New York, or the Florida Comprehensive Assessment Test (FCAT). During high school, students may take one or more standardized tests depending on their postsecondary education preferences and their local graduation requirements. The SAT and ACT are the most common standardized tests that students take when applying to college.
All American states must test students in public schools statewide to ensure that they are achieving the desired level of minimum education, such as on the Regents Examinations in New York, or the Florida Comprehensive Assessment Test (FCAT). During high school, students may take one or more standardized tests depending on their postsecondary education preferences and their local graduation requirements. The SAT and ACT are the most common standardized tests that students take when applying to college.
 Public schools § public schools are free tax-funded § class size varies from one district to another § curriculum decisions are made at the local and state levels Private schools § includes parochial schools , non-profit independent schools, and for-profit private schools § private schools have various missions: most of them take sports very seriously and recruit athletes heavily, others are for gifted students, students with learning disabilities or other special needs, or students with specific religious affiliations § private schools have no legal obligation to accept any interested student § private schools offer the advantages of smaller classes
Public schools § public schools are free tax-funded § class size varies from one district to another § curriculum decisions are made at the local and state levels Private schools § includes parochial schools , non-profit independent schools, and for-profit private schools § private schools have various missions: most of them take sports very seriously and recruit athletes heavily, others are for gifted students, students with learning disabilities or other special needs, or students with specific religious affiliations § private schools have no legal obligation to accept any interested student § private schools offer the advantages of smaller classes
 chool ublic S P lstadt Car Deerfie ld Acad emy
chool ublic S P lstadt Car Deerfie ld Acad emy
 Post-secondary education in the United States is known as college or university and commonly consists of four years of study at an institution of higher learning. The four undergraduate grades are commonly called freshman, sophomore, junior, and senior years. Once admitted, students engage in undergraduate study, which consists of satisfying university and class requirements to achieve a Bachelor's degree in a field of concentration known as a major. The most common method consists of four years of study leading to a Bachelor of Arts, a Bachelor of Science , or sometimes another bachelor's degree such as Bachelor of Fine Arts, Bachelor of Social Work , Bachelor of Engineering or Bachelor of Philosophy. Five Year Professional Architecture programs of Architecture Degree.
Post-secondary education in the United States is known as college or university and commonly consists of four years of study at an institution of higher learning. The four undergraduate grades are commonly called freshman, sophomore, junior, and senior years. Once admitted, students engage in undergraduate study, which consists of satisfying university and class requirements to achieve a Bachelor's degree in a field of concentration known as a major. The most common method consists of four years of study leading to a Bachelor of Arts, a Bachelor of Science , or sometimes another bachelor's degree such as Bachelor of Fine Arts, Bachelor of Social Work , Bachelor of Engineering or Bachelor of Philosophy. Five Year Professional Architecture programs of Architecture Degree.
 Graduate study, conducted after obtaining an initial degree and sometimes after several years of professional work, leads to a more advanced degree such as a Master's degree, which could be a Master of Arts, Master of Science, Master of Business Administration, Master of Education or other less common Master's degrees. Some students pursue a graduate degree that is in between a master's degree and a doctoral degree called a Specialist in Education. After additional years of study students may earn a Doctor of Philosophy or other doctoral degree, such as Doctor of Arts, Doctor of Education, Doctor of Medicine, Doctor of Physical Therapy.
Graduate study, conducted after obtaining an initial degree and sometimes after several years of professional work, leads to a more advanced degree such as a Master's degree, which could be a Master of Arts, Master of Science, Master of Business Administration, Master of Education or other less common Master's degrees. Some students pursue a graduate degree that is in between a master's degree and a doctoral degree called a Specialist in Education. After additional years of study students may earn a Doctor of Philosophy or other doctoral degree, such as Doctor of Arts, Doctor of Education, Doctor of Medicine, Doctor of Physical Therapy.
 Dartmouth College is a private, Ivy League university in Hanover, New Hampshire, United States. It comprises a liberal arts college, Dartmouth Medical School, Thayer School of Engineering, and Tuck School of Business, as well as 19 graduate programs in the arts and sciences. Incorporated as "Trustees of Dartmouth College, " it is one of the nine Colonial Colleges founded before the American Revolution. With an undergraduate enrollment of 4, 196 and a total student enrollment of 5, 987, Dartmouth is the smallest school in the Ivy League. Vox clamantis in deserto The voice of one crying in the wilderness December 13, 1769
Dartmouth College is a private, Ivy League university in Hanover, New Hampshire, United States. It comprises a liberal arts college, Dartmouth Medical School, Thayer School of Engineering, and Tuck School of Business, as well as 19 graduate programs in the arts and sciences. Incorporated as "Trustees of Dartmouth College, " it is one of the nine Colonial Colleges founded before the American Revolution. With an undergraduate enrollment of 4, 196 and a total student enrollment of 5, 987, Dartmouth is the smallest school in the Ivy League. Vox clamantis in deserto The voice of one crying in the wilderness December 13, 1769
 Brown University is a private, Ivy League university located in Providence, Rhode Island, United States. Founded in 1764 prior to American independence from the British Empire as the College in the English Colony of Rhode Island Providence Plantations early in the reign of King George III (1760– 1820), Brown is the third oldest institution of higher education in New England seventh oldest in the United States. Brown consists of The College, Graduate School, Alpert Medical School, and the School of Engineering. In Deo Speramus In God We Hope Established 1764
Brown University is a private, Ivy League university located in Providence, Rhode Island, United States. Founded in 1764 prior to American independence from the British Empire as the College in the English Colony of Rhode Island Providence Plantations early in the reign of King George III (1760– 1820), Brown is the third oldest institution of higher education in New England seventh oldest in the United States. Brown consists of The College, Graduate School, Alpert Medical School, and the School of Engineering. In Deo Speramus In God We Hope Established 1764
 Harvard University is a private Ivy League university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, established in 1636 by the Massachusetts legislature. Harvard is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and the first corporation (officially The President and Fellows of Harvard College) chartered in the country. Harvard's history, influence, and wealth have made it one of the most prestigious universities in the world Veritas/ Truth September 8, 1636 (OS) September 18, 1636 (NS)
Harvard University is a private Ivy League university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, established in 1636 by the Massachusetts legislature. Harvard is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and the first corporation (officially The President and Fellows of Harvard College) chartered in the country. Harvard's history, influence, and wealth have made it one of the most prestigious universities in the world Veritas/ Truth September 8, 1636 (OS) September 18, 1636 (NS)
 Yale University is a private Ivy League university located in New Haven, Connecticut. Founded in 1701 in the Colony of Connecticut, the university is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States. Incorporated as the Collegiate School, the institution traces its roots to 17 thcentury clergymen who sought to establish a college to train clergy and political leaders for the colony. In 1718, the College was renamed Yale College to honor a gift from Elihu Yale, a governor of the British East India Company. In 1861, the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences became the first U. S. school to award the Ph. D Lux et veritas Light and truth 1701
Yale University is a private Ivy League university located in New Haven, Connecticut. Founded in 1701 in the Colony of Connecticut, the university is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States. Incorporated as the Collegiate School, the institution traces its roots to 17 thcentury clergymen who sought to establish a college to train clergy and political leaders for the colony. In 1718, the College was renamed Yale College to honor a gift from Elihu Yale, a governor of the British East India Company. In 1861, the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences became the first U. S. school to award the Ph. D Lux et veritas Light and truth 1701
 Columbia University is a private research university in Manhattan, New York City and one of the eight members of the Ivy League. Columbia is the oldest institution of higher learning in the state of New York, the fifth oldest in the United States, and one of the country's nine Colonial Colleges founded before the American Revolution. It was founded in 1754 as King's College by royal charter of George II of Great Britain, and is one of only three United States universities to have been established under such authority. In lumine Tuo videbimus lumen In Thy light shall we see the light 1754
Columbia University is a private research university in Manhattan, New York City and one of the eight members of the Ivy League. Columbia is the oldest institution of higher learning in the state of New York, the fifth oldest in the United States, and one of the country's nine Colonial Colleges founded before the American Revolution. It was founded in 1754 as King's College by royal charter of George II of Great Britain, and is one of only three United States universities to have been established under such authority. In lumine Tuo videbimus lumen In Thy light shall we see the light 1754
 Cornell University is an Ivy League university located in Ithaca, New York, United States. It is a private land-grant university, receiving annual funding from the State of New York for certain educational missions. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, the university was intended to teach and make contributions in all fields of knowledge—from the classics to the sciences and from theoretical to the applied. "I would found an institution where any person can find instruction in any study. " - Ezra Cornell, 1865
Cornell University is an Ivy League university located in Ithaca, New York, United States. It is a private land-grant university, receiving annual funding from the State of New York for certain educational missions. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, the university was intended to teach and make contributions in all fields of knowledge—from the classics to the sciences and from theoretical to the applied. "I would found an institution where any person can find instruction in any study. " - Ezra Cornell, 1865
 Princeton University is a private research university located in Princeton, New Jersey, United States. The school is one of the eight universities of the Ivy League, and is one of the nine Colonial Colleges founded before the American Revolution. Princeton provides undergraduate and graduate instruction in the humanities, social sciences, natural sciences, and engineering. Princeton does not offer professional schooling generally, but it does offer professional master's degrees (mostly through the Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs) and doctoral programs. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth, New Jersey, as the College of New Jersey, the university moved to Newark in 1747, then to Princeton in 1756 and was renamed Princeton University in 1896. Dei sub numine viget Under God's power she flourishes 1746
Princeton University is a private research university located in Princeton, New Jersey, United States. The school is one of the eight universities of the Ivy League, and is one of the nine Colonial Colleges founded before the American Revolution. Princeton provides undergraduate and graduate instruction in the humanities, social sciences, natural sciences, and engineering. Princeton does not offer professional schooling generally, but it does offer professional master's degrees (mostly through the Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs) and doctoral programs. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth, New Jersey, as the College of New Jersey, the university moved to Newark in 1747, then to Princeton in 1756 and was renamed Princeton University in 1896. Dei sub numine viget Under God's power she flourishes 1746
 Undergraduate educational There a large number of programs available for Undergraduate within the US. In all major universities. Undergraduate programs have high standards of admission. In the US most undergraduate takes place at four year colleges or universities. In the United States students in their first, second, third and fourth years of study are called respectively, Freshmen, sophomores, juniors and seniors. Some institutions offer primarily or exclusively undergraduate while most universities offer graduate study as well. Successful completion of undergraduate work generally requires the completion of many courses of varying subject and difficult and concentration or major that focuses on a particular academic discipline. Most students have to pay a huge amount of tuition fee which varies for different categories of students. Once students take the standardized test (SAT or ACT) they choose their kinds of programs depending on the type of degree they want to pursue.
Undergraduate educational There a large number of programs available for Undergraduate within the US. In all major universities. Undergraduate programs have high standards of admission. In the US most undergraduate takes place at four year colleges or universities. In the United States students in their first, second, third and fourth years of study are called respectively, Freshmen, sophomores, juniors and seniors. Some institutions offer primarily or exclusively undergraduate while most universities offer graduate study as well. Successful completion of undergraduate work generally requires the completion of many courses of varying subject and difficult and concentration or major that focuses on a particular academic discipline. Most students have to pay a huge amount of tuition fee which varies for different categories of students. Once students take the standardized test (SAT or ACT) they choose their kinds of programs depending on the type of degree they want to pursue.
 Available Undergraduate streams Arts and Humanities. These would cover the following film studies, theatre, visual arts, performing arts, writing, African – American studies, Advertising and Public Relations, Creative Photography, dance, Education, English, Economics, French and Romance Languages Studies… Sciences: These would include the following Accounting, Actuarial Science, Agriculture, Anatomy, Animal Sciences, Astronomy, Botany, Chemistry, Computer Sciences, Virology, Zoology… Engineering and Technology: These would include – Engineering, Biomedical Engineering, Bioinformatics, Earth and Environmental Engineering, Industrial. Business Management: Engineering and Technology, Transportation, Sports, Security, Resource, PROJECT, Marketing, Finances…. Services: US Freedom Corps, Police Academy, Army, Airforce, Navy, AFS.
Available Undergraduate streams Arts and Humanities. These would cover the following film studies, theatre, visual arts, performing arts, writing, African – American studies, Advertising and Public Relations, Creative Photography, dance, Education, English, Economics, French and Romance Languages Studies… Sciences: These would include the following Accounting, Actuarial Science, Agriculture, Anatomy, Animal Sciences, Astronomy, Botany, Chemistry, Computer Sciences, Virology, Zoology… Engineering and Technology: These would include – Engineering, Biomedical Engineering, Bioinformatics, Earth and Environmental Engineering, Industrial. Business Management: Engineering and Technology, Transportation, Sports, Security, Resource, PROJECT, Marketing, Finances…. Services: US Freedom Corps, Police Academy, Army, Airforce, Navy, AFS.
 Credit system In the US system of education the term course is different from what we know. Academics in higher education is divided into modules called “courses”. Credit hours At the undergraduate level you are required 4 years of study and minimum number of credit hours which usually varies from 120 – 130. Most colleges and universities follow either a quarter – based calendar system. In a quarter systems, the academic year is divided into three sessions called quarters. Each quarter lasts about 12 weeks. In the semester system, academic year is divided into two semesters – the fall and the spring.
Credit system In the US system of education the term course is different from what we know. Academics in higher education is divided into modules called “courses”. Credit hours At the undergraduate level you are required 4 years of study and minimum number of credit hours which usually varies from 120 – 130. Most colleges and universities follow either a quarter – based calendar system. In a quarter systems, the academic year is divided into three sessions called quarters. Each quarter lasts about 12 weeks. In the semester system, academic year is divided into two semesters – the fall and the spring.
 Grade Point average (GPA) GPA is the grading system used in the colleges and universities of the US. The grades are A, B, C and D. A is the highest grade with 4 points, B with 3, C with 2 and D with 1, F is assigned to a student, if he fails in a particular subject.
Grade Point average (GPA) GPA is the grading system used in the colleges and universities of the US. The grades are A, B, C and D. A is the highest grade with 4 points, B with 3, C with 2 and D with 1, F is assigned to a student, if he fails in a particular subject.
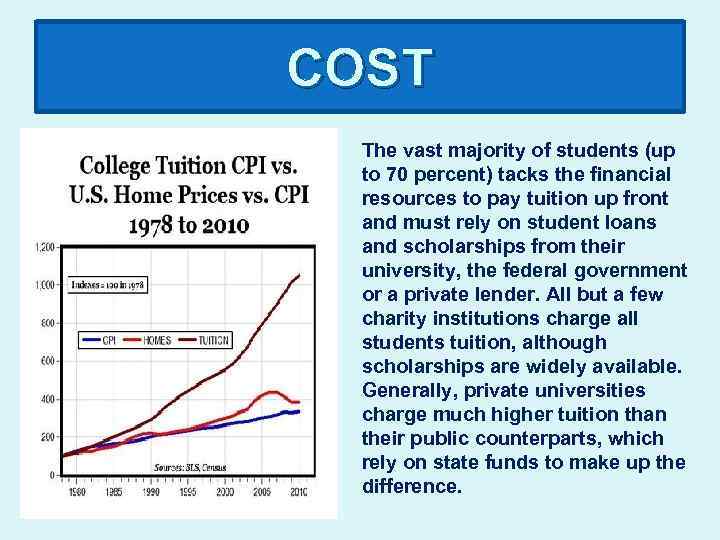 COST The vast majority of students (up to 70 percent) tacks the financial resources to pay tuition up front and must rely on student loans and scholarships from their university, the federal government or a private lender. All but a few charity institutions charge all students tuition, although scholarships are widely available. Generally, private universities charge much higher tuition than their public counterparts, which rely on state funds to make up the difference.
COST The vast majority of students (up to 70 percent) tacks the financial resources to pay tuition up front and must rely on student loans and scholarships from their university, the federal government or a private lender. All but a few charity institutions charge all students tuition, although scholarships are widely available. Generally, private universities charge much higher tuition than their public counterparts, which rely on state funds to make up the difference.
 COST
COST
 THE STATUS LADDER American college and university faculty, staff, and applicants monitor rankings produced by magazines such as US. News and World Report, Academic Ranking of World Universities test preparation services such as The Princeton Review or another university itself such as the Top American Research Universities by the University of Florida’s The Center. In the popular mind, approximately 25 institutions compose the ‘top tier’ of American higher learning. However, this ‘ladder’ is not absolute. Most would cite the 8 universities that compose the Ivy League and a small number of elite, private research universities.
THE STATUS LADDER American college and university faculty, staff, and applicants monitor rankings produced by magazines such as US. News and World Report, Academic Ranking of World Universities test preparation services such as The Princeton Review or another university itself such as the Top American Research Universities by the University of Florida’s The Center. In the popular mind, approximately 25 institutions compose the ‘top tier’ of American higher learning. However, this ‘ladder’ is not absolute. Most would cite the 8 universities that compose the Ivy League and a small number of elite, private research universities.
 Curriculum issues Curriculum in the US varies widely from district. Not only do schools offer an incredible range of topics and quality, but private schools may include religious classes as mandatory for attendance. A large issue facing the curriculum today is the use of the English language in teaching. English is spoken by over 95% of the nation and there is a strong national tradition of upholding English as the de facto official language.
Curriculum issues Curriculum in the US varies widely from district. Not only do schools offer an incredible range of topics and quality, but private schools may include religious classes as mandatory for attendance. A large issue facing the curriculum today is the use of the English language in teaching. English is spoken by over 95% of the nation and there is a strong national tradition of upholding English as the de facto official language.
 Funding for K-12 schools Funding for schools in the US is complex. One current controversy stems much from the No Child Left Behind Act. The Act gives the Department of Education the right to with hold funding if it believes a school, district or even a state is not complying and is making no effort to comply. According to a 2011 article in the Washington Post, the Washington D. C. public school district spends $ 12979 per student per year. This is the third highest level of funding per student out of the 100 biggest school districts in the US.
Funding for K-12 schools Funding for schools in the US is complex. One current controversy stems much from the No Child Left Behind Act. The Act gives the Department of Education the right to with hold funding if it believes a school, district or even a state is not complying and is making no effort to comply. According to a 2011 article in the Washington Post, the Washington D. C. public school district spends $ 12979 per student per year. This is the third highest level of funding per student out of the 100 biggest school districts in the US.
 Funding for college At the college and university level, funding becomes an issue due to the sheer of gaining it. Some of the reason for the confusion at the college university level in the US is that student loan funding is not split in haft, haft is managed by the Department of Education directly, called the Federal Direct Student Loan Program.
Funding for college At the college and university level, funding becomes an issue due to the sheer of gaining it. Some of the reason for the confusion at the college university level in the US is that student loan funding is not split in haft, haft is managed by the Department of Education directly, called the Federal Direct Student Loan Program.
 Charter Schools Herbst (2006) explains the charter-school movement was born in 1990. Charter schools have spread rapidly in the US, based on the promise to create less bureaucratic schools that vest ‘management authority in a group of community members, parents, teachers, and students’ to allow for the ‘expression of diverse teaching philosophies and culture and social life styles’. Herbst ultimately maintains that charter schools have produced mixed results.
Charter Schools Herbst (2006) explains the charter-school movement was born in 1990. Charter schools have spread rapidly in the US, based on the promise to create less bureaucratic schools that vest ‘management authority in a group of community members, parents, teachers, and students’ to allow for the ‘expression of diverse teaching philosophies and culture and social life styles’. Herbst ultimately maintains that charter schools have produced mixed results.
 Control and Competitiveness There is some debate about where control for education actually lies. Education is not mentioned in the constitution of the US. The US federal government exercise its control through the US Department of Educational accreditation decisions are made by voluntary regional associations. The national results in international comparisons have often below the average of developed countries.
Control and Competitiveness There is some debate about where control for education actually lies. Education is not mentioned in the constitution of the US. The US federal government exercise its control through the US Department of Educational accreditation decisions are made by voluntary regional associations. The national results in international comparisons have often below the average of developed countries.


