eda7df09bd74e03de2a9c882bad6cddb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49

Laboratory Medicine Program Pathology 2020 Vision Sylvia L. Asa, MD, Ph. D

What Is Pathology? • Pathology, from the greek πάθος, pathos, “feeling, suffering” and λογία, logia “study of” • the study and diagnosis of disease through examination of organs, tissues, bodily fluids, and whole bodies Laboratory Medicine Program

The Origins of Pathology • The Autopsy • Dates back to ancient Egypt and Greece • The tool of the Physician-Scientist – To identify the cause of death – To explain signs and symptoms of disease Laboratory Medicine Program

The First Clinical Applications • Surgical Pathology by surgeons • Laboratory hematology by hematologists • Biochemistry in nephrology and endocrinology • Microbiology in infectious diseases Laboratory Medicine Program

Pathology 2010 • Laboratory-based clinical testing – Focus on QA/QC/GLP • Microscope-based anatomical pathology • Custodianship of patient samples on behalf of patient • Representative of patient in Quality of Care events (M&M rounds) • Minimal or no patient contact Laboratory Medicine Program

The Pathology Diagnosis • The pathological diagnosis is the gold standard that indicates the presence or absence of disease, the type of disease, and its classification • Therapeutic decisions are based on the pathology diagnosis – a misdiagnosis can result in unnecessary, harmful and aggressive therapy or inadequate treatment Laboratory Medicine Program

Pathology is an Interpretive Discipline BREAST • Atypia on breast core needle biopsies: reproducibility and significance. • The impact of inter-observer variation in pathological assessment of node-negative breast cancer on clinical risk assessment and patient selection for adjuvant systemic treatment. • Inter-observer reproducibility of HER 2 immunohistochemical assessment and concordance with fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH): pathologist assessment compared to quantitative image analysis Laboratory Medicine Program

Pathology is an Interpretive Discipline GENITOURINARY • Interobserver variability between expert urologic pathologists for extraprostatic extension and surgical margin status in radical prostatectomy specimens • Intraobserver and interobserver variability of fuhrman and modified fuhrman grading systems for conventional renal cell carcinoma • Intra- and interobserver reproducibility of interpretation of immunohistochemical stains of prostate cancer Laboratory Medicine Program

What Does This Mean for Patients? • • • Is the diagnosis right? Is the treatment right? Is the prognosis right? Was the trial right? Are the data reliable? Laboratory Medicine Program

Pathology 2000 -2010 Laboratory Medicine Program

Challenges for 2020 • Volume – aging population – higher sensitivity for early disease • Demand – Sophisticated knowledgeable population – Culture of “instant gratification” • New technologies – – genomics proteomics informatics robotics ‘tissue soup’ instead of tissue Laboratory Medicine Program 11

The Challenge for 2020 • Faster • Better – Higher quality – Personalized • Cheaper • Innovative Laboratory Medicine Program
The New Paradigm: Faster • Pathology must be faster – “Same Day” diagnosis – Automation – 24/7 labs Laboratory Medicine Program

The New Paradigm: Faster • Speech-recognition integrated with LIS means instant reporting without the need for dictatyping R E P H C A E Laboratory Medicine Program 14

The New Paradigm: Better • Synoptic Reporting – Complete • Standardized formats (CAP checklists) – Adaptable and flexible • No more verbose reports that no one reads! – Database technology • • Statistics collection Administrative tracking QA monitoring Academic data mining Laboratory Medicine Program
The New Paradigm: Better What is “Correct”? • Objective classification by – m. RNA expression – DNA sequencing – Response to therapy Laboratory Medicine Program
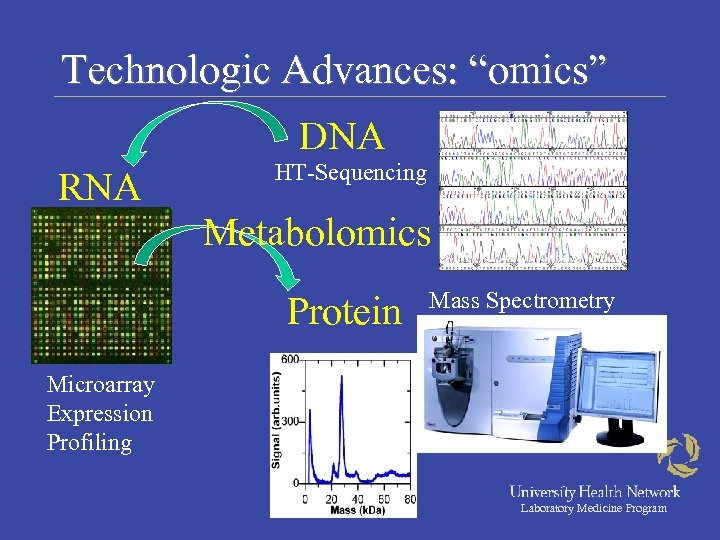
Technologic Advances: “omics” DNA RNA HT-Sequencing Metabolomics Protein Mass Spectrometry Microarray Expression Profiling Laboratory Medicine Program

The New Paradigm: Better Subspecialty Pathology – All cases reported by a pathologist with expertise in the specific subspecialty required – Benefits: • Better quality and faster patient care • Fiscal responsibility: 1 pathologist per case • Pathologist satisfaction – enhanced academic excellence – Challenges: • Requirement for appropriate staffing in all areas and redundancy Laboratory Medicine Program 18

Digital Pathology • Whole slide imaging • A disruptive enabling technology Laboratory Medicine Program 19

Digital Pathology Enables • Remote access R E T T • Multiple viewers E B • Immediate access to the right pathologist at the right time Laboratory Medicine Program 20

Requirements for Full Adoption • Workflow integration R E P – From the lab to the pathologist • LIS integration A E – Barcodes – Slide tracking and retrieval H C Laboratory Medicine Program
Informatics: The LIS • LIS as part of the e-chart • LIS e-orders and processes • Specimen tracking and management • Integration of lab data from all disciplines into a consolidated report Laboratory Medicine Program 22

Computer-Assisted Diagnostics • Automated analysis of: – Measurement – Mitoses – Ki 67 LI – Other IHC • intensity • distribution – Her 2 FISH – Hematology • QA of technical quality – Section thickness – Stain quality ? Need for Westgard rules in AP? • Cellavision – More? Laboratory Medicine Program

Digital Pathology Enables • Novel approaches to address issues of inter - and intra-observer variability GENIE© (GENetic Imagery Exploration) is a GP software system that builds automatic feature extraction algorithms for image analysis, utilizing spectral and spatial signatures of the images “GENIE© can recognize benign and malignant areas in H&E stained slides and it does not have intra- or interobserver variation in the analysis” Laboratory Medicine Program 24

The New Paradigm: Personalized • Patient-Centred Care • Individualized diagnostics • Targeted therapies All based on “omics” Will “omics” replace pathology? Laboratory Medicine Program 25
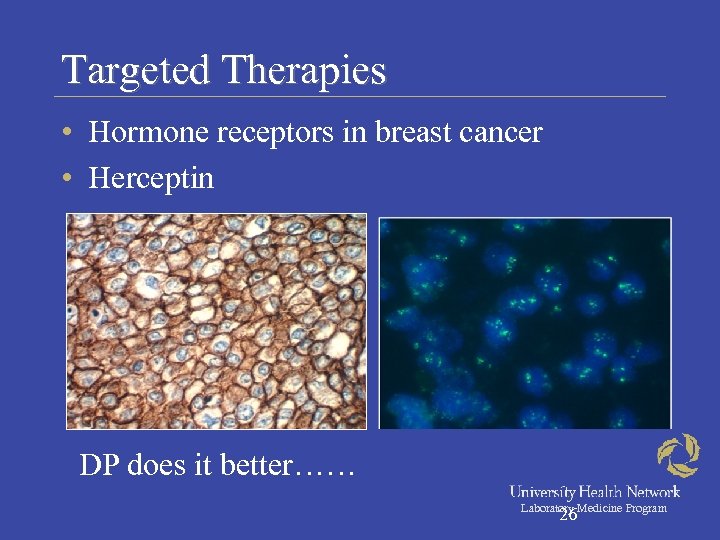
Targeted Therapies • Hormone receptors in breast cancer • Herceptin DP does it better…… Laboratory Medicine Program 26
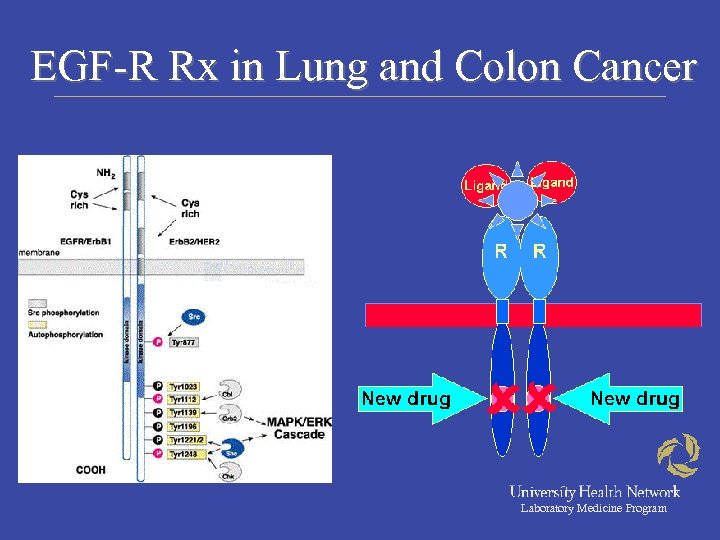
EGF-R Rx in Lung and Colon Cancer Laboratory Medicine Program
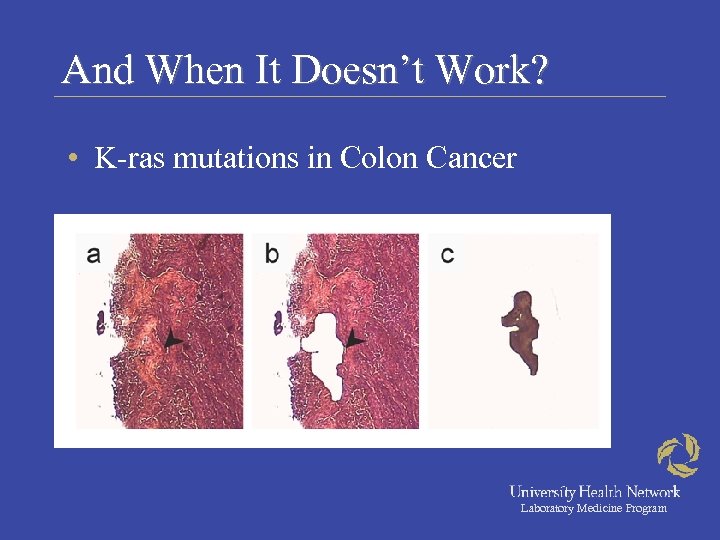
And When It Doesn’t Work? • K-ras mutations in Colon Cancer Laboratory Medicine Program
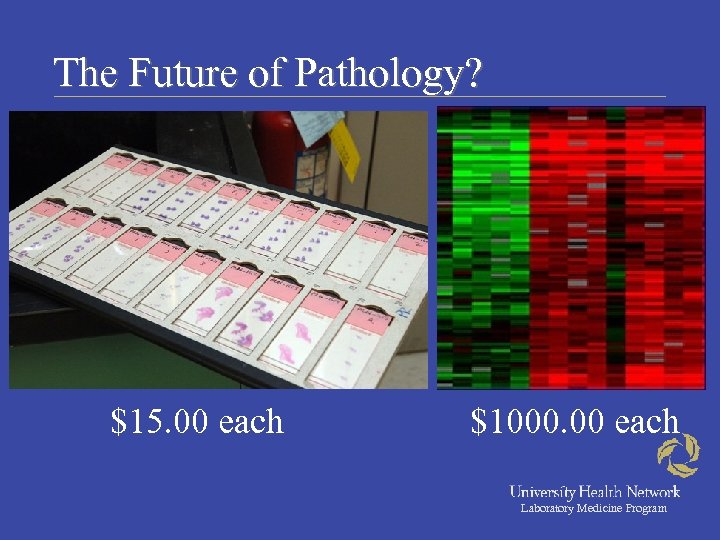
The Future of Pathology? $15. 00 each $1000. 00 each Laboratory Medicine Program
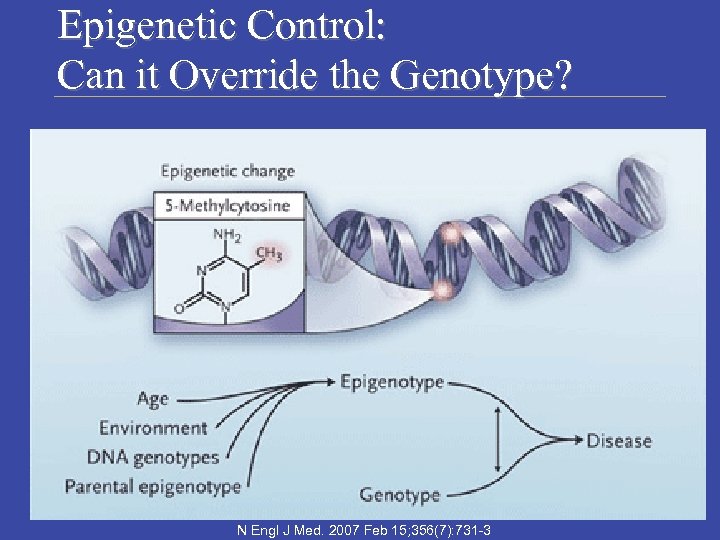
Epigenetic Control: Can it Override the Genotype? Laboratory Medicine Program N Engl J Med. 2007 Feb 15; 356(7): 731 -3
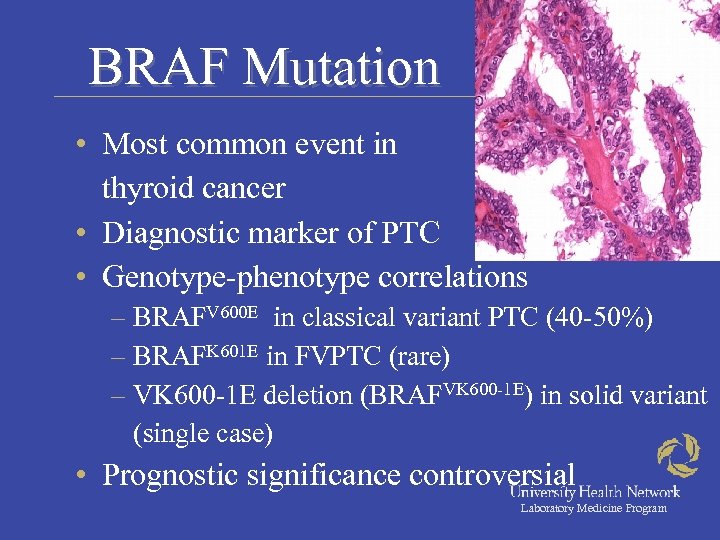
BRAF Mutation • Most common event in thyroid cancer • Diagnostic marker of PTC • Genotype-phenotype correlations – BRAFV 600 E in classical variant PTC (40 -50%) – BRAFK 601 E in FVPTC (rare) – VK 600 -1 E deletion (BRAFVK 600 -1 E) in solid variant (single case) • Prognostic significance controversial Laboratory Medicine Program
BRAF Mutation & Outcome • BRAF mutant carriers show increased risk of tissue invasion compared to WT cases • However, when classified morphologically, classic papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) showed much higher risk estimates for invasive outcomes compared with follicular variant PTCs, independent of BRAF mutational status • The combined risk of BRAFV 600 E mutant allele and morphology showed higher risk values for the classic wild type cases, indicating that morphologic classification as classic PTC is a stronger predictor of aggressive behavior than BRAF mutation Cheng et al, 2010 submitted Laboratory Medicine Program
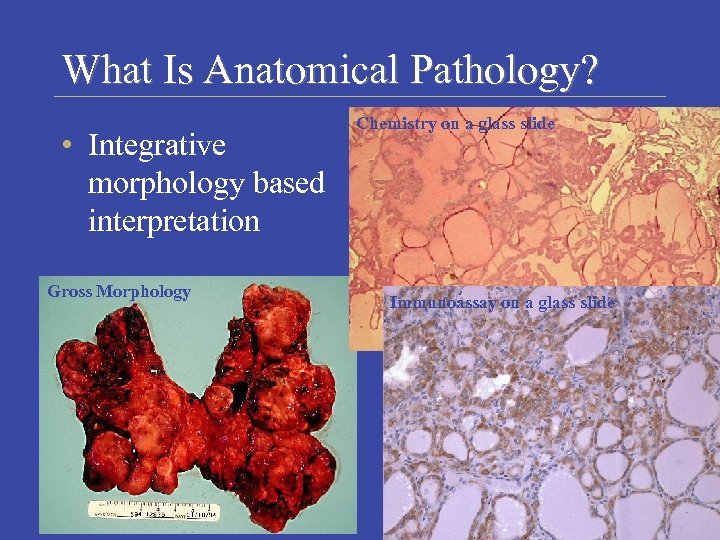
What Is Anatomical Pathology? • Integrative morphology based interpretation Gross Morphology Chemistry on a glass slide Immunoassay on a glass slide Laboratory Medicine Program

Garbage In – Garbage Out • We have the technical capacity to produce low quality data from low quality analytes with unprecedented efficiency • We arrive at the wrong answer with unprecedented speed Laboratory Medicine Program

The New Paradigm: Innovative • Pathology / Laboratory Medicine – critical players in ensuring the highest quality of translational research: • The right specimen, the right test, the right interpretation • Biobanking in Translational Research – Value is in the technical and diagnostic excellence of the specimens The “Biobank” is the current phraseology for the “Department of Pathology” Laboratory Medicine Program
The Expanding Role of Lab Medicine • To provide the right diagnosis • To provide the right material • To provide the right leads • To provide the right experiments • To evaluate the consequences of genetic manipulation Laboratory Medicine Program 36

Where Are We Heading? • Predictive genetics/epigenetics will define individual risk and prognosis • Targeted prevention • Monitoring for onset with multimodal biomarkers • Targeted therapies based on host genetics and epigenetics • Signatures of stage-specific progression • Mechanisms of escape Laboratory Medicine Program

The Uncontestable Trends • Clinicians want increasingly detailed, reliable and relevant information from specimen analyses that can be translated into optimal treatments • Pathology must re-educate and re-invent itself if it is to maintain the central role it plays as the ultimate arbiter of treatment “As is your pathology, so goes your clinical care” Sir William Osler Laboratory Medicine Program 38

The New Paradigm • Pathology labs must be faster and better – QA is the sine qua non • Pathology reports must be comprehensive – Incorporation of molecular, biochemical and other data is critical to the consultative value of the report • Pathology data must be synoptic and database-oriented • Pathology must be innovative Laboratory Medicine Program 39

The Virtual Autopsy Laboratory Medicine Program

After “The Anatomy Lecture of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp” – Rembrandt, 1632 (Courtesy of Dr. Carlos Cordón, New York, Laboratory Medicine Program USA)

2020 Vision • Large automated core laboratories • Electronic support for specimen tracking and handling, QMS • Highly subspecialized teams providing a matrix of subject and technical expertise – Biochemistry - Microbiology – Hematology, Transfusion & Hematopathology – Subspecialty Anatomical Pathology – Molecular/Genetics “Blurring the lines between AP and CP” Laboratory Medicine Program 42

Laboratory Management in the Electronic Era • Specimen tracking • Workload tracking and personnel • Supplies and equipment • QA processes “………sophisticated refrigerators and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology will be able to monitor the products household members use, create shopping lists, and even communicate with other networked devices to arrange deliveries” Laboratory Medicine Program 43
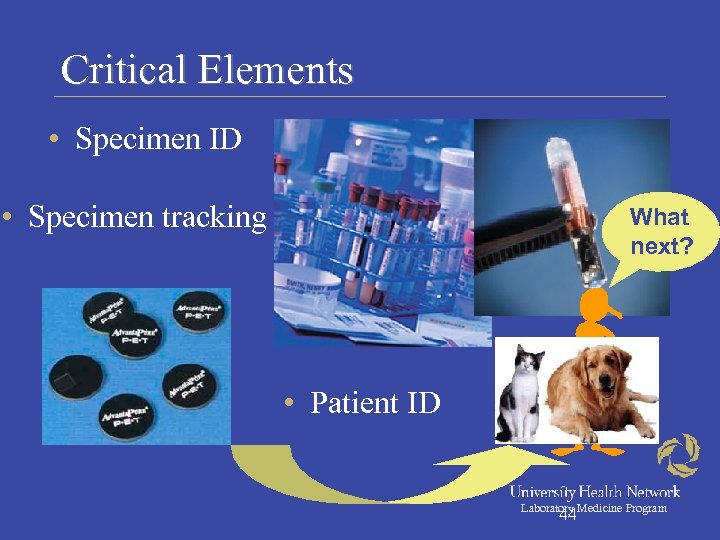
Critical Elements • Specimen ID • Specimen tracking What next? • Patient ID Laboratory Medicine Program 44

The 2020 Paradigm • Comprehensive pathology reports – Incorporation and integration of radiologic, biochemical, morphologic , molecular, cytogenetic and epigenetic data Biochemistry Radiology Gross Pathology Biomarkers Histopathology Molecular Pathology • The Pathologist’s Cockpit Laboratory Medicine Program
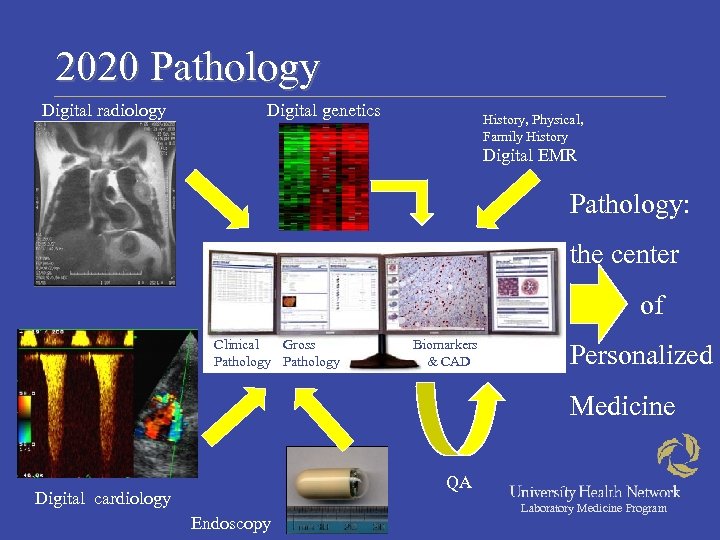
2020 Pathology Digital radiology Digital genetics History, Physical, Family History Digital EMR Pathology: the center of Clinical Gross Pathology Biomarkers & CAD Personalized Medicine QA Digital cardiology Endoscopy Laboratory Medicine Program

2020 Pathologist Laboratory Medicine Program

The Philosophical Response In a time of drastic change it is the learners who inherit the future. The learned usually find themselves equipped to live in a world that no longer exists. Eric Hoffer Laboratory Medicine Program 48

The Future of Pathology The best way to predict the future is to invent it Alan Kay Laboratory Medicine Program 49
eda7df09bd74e03de2a9c882bad6cddb.ppt