ba103b6cecea63737c702420f21ac0bb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

Labor Policy Keiichiro HAMAGUCHI

Chapter 2 Labor Market Policy

Section 2 Employment insurance system

(1) Unemployment Benefit (a) Historical Overview • ILO Convention No. 44 on unemployment benefit adopted in 1934. • Retirement Funds and Retirement Allowances Law enacted in 1936. • Unemployment Insurance Law enacted in 1947. • Term of benefit: 180 days.

• 1955 revised UI Law distributed the term of benefit from 90 to 270 days according to length of service. • 1974 Employment Insurance Law distributed the term of benefit from 90 to 300 days according to age. • 1984 revised EI Law introduced length of service again. • 2000 revised EI Law introduced reason of job loss (voluntary quit: 180 days).

(b) Legal nature of unemployment benefit • As a social insurance scheme: to compensate the lost income of the jobless • As an employment policy instrument: to assist the jobless to be re-employed • Subjective requirement of willing to work is difficult to distinguish from pretending. • Moral hazard has been the central issue.
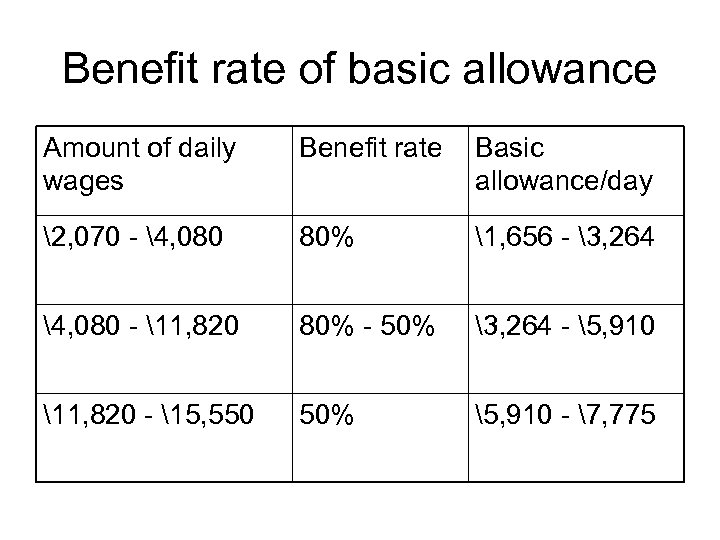
Benefit rate of basic allowance Amount of daily wages Benefit rate Basic allowance/day 2, 070 - 4, 080 80% 1, 656 - 3, 264 4, 080 - 11, 820 80% - 50% 3, 264 - 5, 910 11, 820 - 15, 550 50% 5, 910 - 7, 775
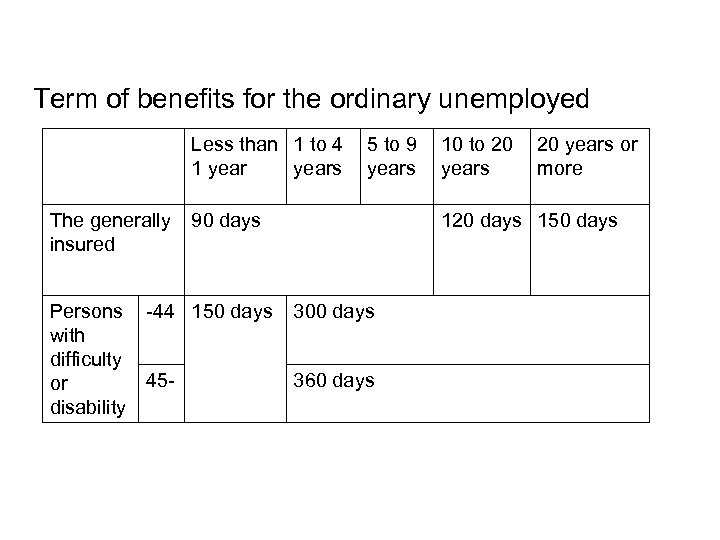
Term of benefits for the ordinary unemployed Less than 1 to 4 1 years The generally insured 5 to 9 years 90 days Persons -44 150 days with difficulty 45 or disability 10 to 20 years or more 120 days 150 days 300 days 360 days
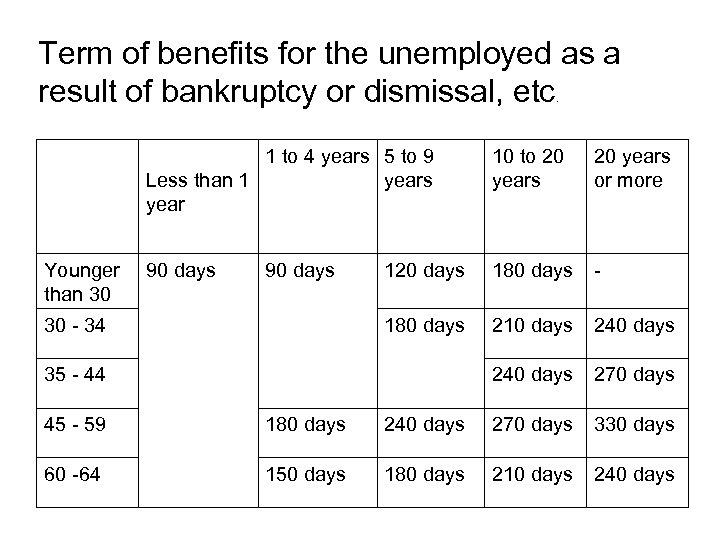
Term of benefits for the unemployed as a result of bankruptcy or dismissal, etc. 1 to 4 years 5 to 9 Less than 1 years year Younger than 30 10 to 20 years or more 90 days 120 days 180 days - 180 days 210 days 240 days 270 days 90 days 30 - 34 35 - 44 45 - 59 180 days 240 days 270 days 330 days 60 -64 150 days 180 days 210 days 240 days

(2) Employment-related benefits • Childcare Leave Benefits are paid to workers who take childcare leave under 1 (benefit rate: 25%, 40% in 2000, 50% in 2007 revision). • Continued Employment Benefits for Older Workers are paid to older workers working after mandatory retirement age (benefit rate: 25%, down to 15% in 2003). • Educational Training Benefits are paid to workers who take training course (benefit rate: 80%, 40% in 2003, 20% in 2007 revision).

(3) Employment subsidies • Employment Adjustment Subsidy is paid to employers who, without dismissals, adopt measures as temporary leave with pay, in-house training, temporary transfer to other companies (half of paid wages). • Specified Job Applicant Employment Development Subsidy • Regional Employment Development Subsidy • Career Formation Promotion Subsidy
ba103b6cecea63737c702420f21ac0bb.ppt