f4ae77b50d90d6d86e137e78127e98d3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

l. Understanding Problem Solving Reminder: student learning activities are at the end of this power point.

Next Generation Science/Common Core Standards Addressed! l CCSS. Math. Content. 8. EE. B. 5 Graph proportional relationships, interpreting the unit rate as the slope of the graph. Compare two different proportional relationships represented in different ways. For example, compare a distance-time graph to a distance-time equation to determine which of two moving objects has greater speed l WHST. 6‐ 8. 8 Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources; assess the credibility of each source; and quote or paraphrase the data and conclusions of others while avoiding plagiarism and providing basic bibliographic information for sources. (MS-LS 1 -8)

Agriculture, Food and Natural Resource Standards Addressed! l l l CRP. 02. Apply appropriate academic and technical skills. Career-ready individuals readily access and use the knowledge and skills acquired through experience and education to be more productive. They make connections between abstract concepts with real-world applications, and they make correct insights about when it is appropriate to apply the use of an academic skill in a workplace situation. CRP. 02. 01. Use strategic thinking to connect and apply academic learning, knowledge and skills to solve problems in the workplace and community. Sample Measurement: The following sample measurement strands are provided to guide the development of measurable activities (at different levels of proficiency) to assess students’ attainment of knowledge and skills related to the above performance indicator. The topics represented by each strand are not all-encompassing. – CRP. 02. 01. a. Distinguish opportunities to apply academic learning to solve problems in the workplace (e. g. , identify how to: increase productivity, reduce costs, lower inputs, etc. ).

Bell Work! 1. Describe the problem-solving process. 2. Explain the decision-making process. 3. Describe the similarities and differences of problem solving and decision making. 4. Understand the scientific method.

Terms Conclusion Data Hypothesis Problem solving l Evaluate Summarize l Hypothesis l Goal l Alternative l Methodical l Consequences

Interest Approach Imagine that you are driving in your car about 15 miles from home and your car dies. It will crank, but will not start. You are due at dinner at your girlfriend or boyfriends house in 30 minutes. What should you do? ?

Describe the problem-solving process l A problem is a life situation which creates a difficulty, a state of suspense, confusion, and doubt. – Problem solving is the process of attempting to deal with problems. – It involves eight steps.

Problem Solving 1. Identify the problem 2. Evaluate the problem. 3. Gather information about the problem. 4. Generate alternatives. 5. Decide on an appropriate plan. 6. Select and plan a course of action. 7. Carry out the plan of action. 8. Evaluate the results.

The decision-making process. l A methodical process should be followed when making decisions. – State the desired goal or condition. – Identify the obstacles to realizing the goal or condition.

The decision-making process. Examine alternatives available for overcoming each obstacle. l Rank the alternatives in terms of their probable consequences. l Choose the best alternative. l

Describe the similarities and differences of problem solving and decision making. l Problem solving and decision making involve similar goals. – Problem solving focuses on problems and their solutions – decision making focuses on desired goals or conditions.

Describe the similarities and differences of problem solving and decision making. l Decision making involves problem solving to a large degree.

Describe the similarities and differences of problem solving and decision making. l Problem solving usually occurs in response to a specific situation; decision making is usually initiated to create a desired condition.

Describe the similarities and differences of problem solving and decision making. l Problem solving usually focuses on recent events; decision making usually deals with future, planned events. l Both problem solving and decision making involve the examination of alternative action, choosing the optimal action, and evaluating the results.

The scientific method. l The scientific method is used to find answers to scientific problems.

The scientific method has five steps 1. Define the problem - usually stated as a question. 2. Gather data (facts and information) about the problem. a. Summarize past experiences. b. Review other research results.

3. Suggest possible answers or solutions. a. A hypothesis is a prediction of the results of an experiment. b. Write the hypothesis before beginning the experiment.
4. Test the hypothesis. a. Conduct an experiment to test the hypothesis. b. Summarize the data collected in organized charts or tables.

5. Evaluate the results. a. Examine the findings of the experiment. b. Draw conclusions or judgments made on the basis of the findings.

Review / Summary l Describe the problem-solving process. l Explain the decision-making process. l Describe the similarities and differences of problem solving and decision making. l Understand the scientific method.
The End! NEXT: Student Learning Activities

Student Learning Activities l Sample tests are available in the Lesson Plan tab.


l Here is a foldable that you can make with your students on the scientific method. On the out side write the steps of the scientific method. On the inside write what that step means. Outside Inside

l Have students write a one to two page paper explaining how they use or can use the scientific method in their everyday lives.

l Have students create a poster explaining the scientific method. Below are some example posters.

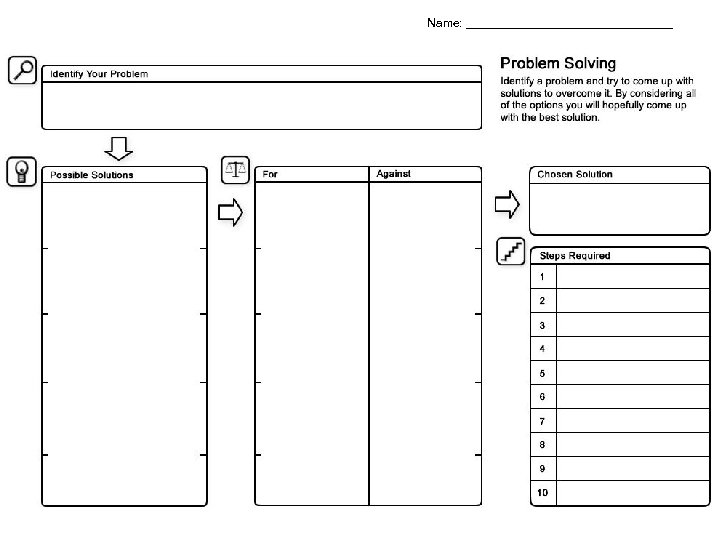
Name: ________________
KEY

f4ae77b50d90d6d86e137e78127e98d3.ppt