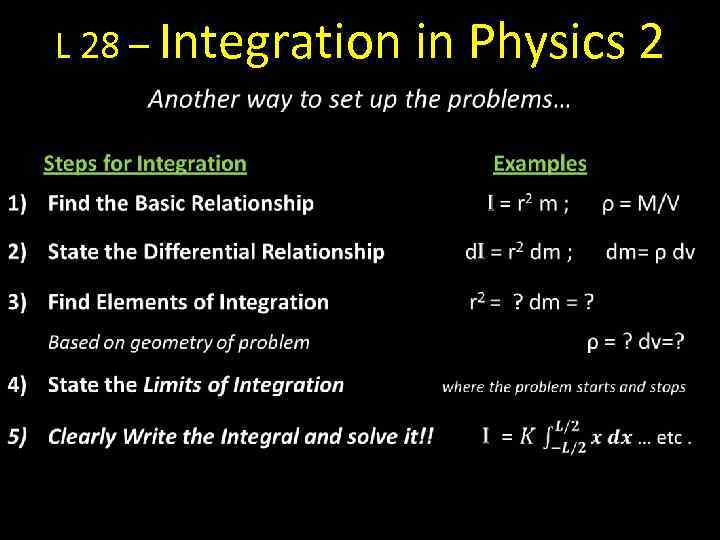
 L 28 – Integration in Physics 2
L 28 – Integration in Physics 2
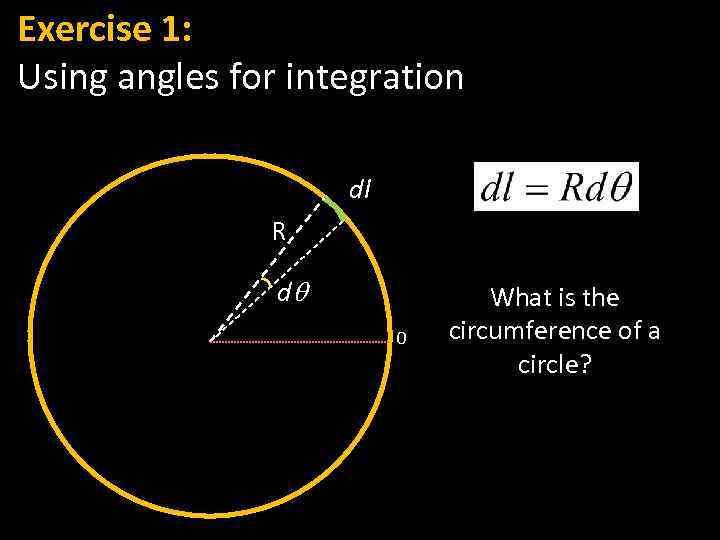 Exercise 1: Using angles for integration dl R dq 0 What is the circumference of a circle?
Exercise 1: Using angles for integration dl R dq 0 What is the circumference of a circle?
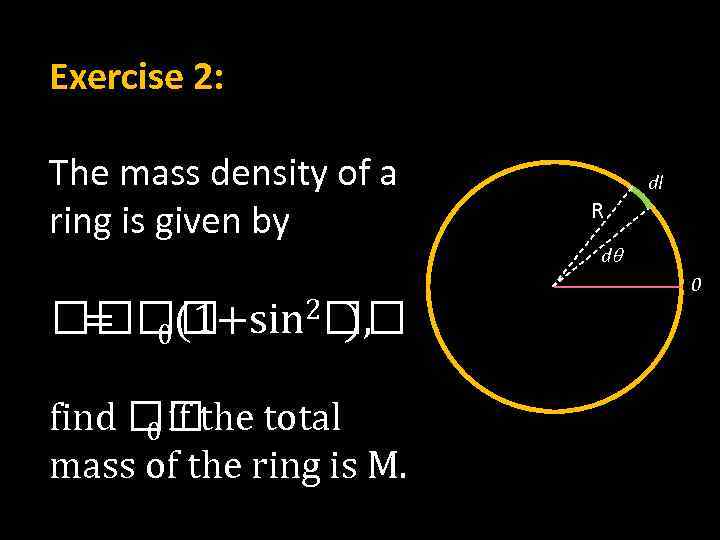 Exercise 2: The mass density of a ring is given by 2 0(1+sin ), = find the total 0 if mass of the ring is M. dl R dq 0
Exercise 2: The mass density of a ring is given by 2 0(1+sin ), = find the total 0 if mass of the ring is M. dl R dq 0
 Exercise 3: One end of a rod of length 4. 00 m of non uniform mass distribution is placed at the origin. Find the position of center of mass of the rod whose density varies as 2 (x) = 1+x
Exercise 3: One end of a rod of length 4. 00 m of non uniform mass distribution is placed at the origin. Find the position of center of mass of the rod whose density varies as 2 (x) = 1+x
 Exercise 4: A piece of glass, 5. 00 cm thick, is made such that its refractive index is 1. 50 on the front surface, and varies with the distance x (in cm) from the front surface, according to the following equation: Find the time in seconds for light normally incident on the glass to pass through it. Hint: consider time taken for light travel a distance dx at x.
Exercise 4: A piece of glass, 5. 00 cm thick, is made such that its refractive index is 1. 50 on the front surface, and varies with the distance x (in cm) from the front surface, according to the following equation: Find the time in seconds for light normally incident on the glass to pass through it. Hint: consider time taken for light travel a distance dx at x.
 Exercise 5: A small object of mass m, initially at rest, is falling in the fluid. The fluid resistance force acting on the object is directly proportional to the speed of the object. Find the speed of the object as a function of time. What happens to the speed when t is large and define terminal velocity? Find the time dependence of the vertical position and acceleration of the object.
Exercise 5: A small object of mass m, initially at rest, is falling in the fluid. The fluid resistance force acting on the object is directly proportional to the speed of the object. Find the speed of the object as a function of time. What happens to the speed when t is large and define terminal velocity? Find the time dependence of the vertical position and acceleration of the object.
 Additional Resources: • http: //www. karlscalculus. org/calc 12_0. html • Link to a worked example involving Gravitation (click on this sentence) • http: //www. onlinemathlearning. com/work-done-calculus-2. html • http: //www. themathpage. com/acalc/instantaneous-velocity. htm
Additional Resources: • http: //www. karlscalculus. org/calc 12_0. html • Link to a worked example involving Gravitation (click on this sentence) • http: //www. onlinemathlearning. com/work-done-calculus-2. html • http: //www. themathpage. com/acalc/instantaneous-velocity. htm