16f0453b8e3d01d9f8378b1929be3ec2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 KWAZULU NATAL INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY 2012 Presentation for the National Skills Development Framework on 8 November 2012 at ICC
KWAZULU NATAL INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY 2012 Presentation for the National Skills Development Framework on 8 November 2012 at ICC
 Content • • • What is Industrialisation Key Success Factors to Industrialisation Industrial Sectors identified by KZN IDS Industrial Sectors Skills Gap Recommendations Discussion
Content • • • What is Industrialisation Key Success Factors to Industrialisation Industrial Sectors identified by KZN IDS Industrial Sectors Skills Gap Recommendations Discussion
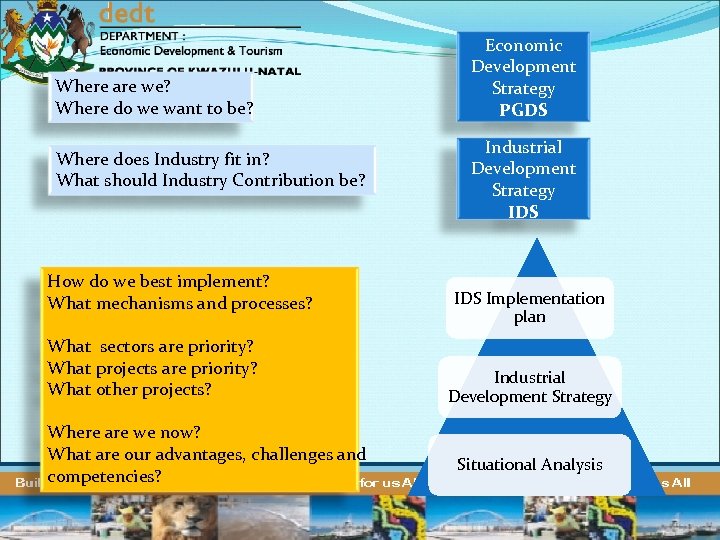 Where are we? Where do we want to be? Where does Industry fit in? What should Industry Contribution be? How do we best implement? What mechanisms and processes? What sectors are priority? What projects are priority? What other projects? Where are we now? What are our advantages, challenges and competencies? Economic Development Strategy PGDS Industrial Development Strategy IDS Implementation plan Industrial Development Strategy Situational Analysis
Where are we? Where do we want to be? Where does Industry fit in? What should Industry Contribution be? How do we best implement? What mechanisms and processes? What sectors are priority? What projects are priority? What other projects? Where are we now? What are our advantages, challenges and competencies? Economic Development Strategy PGDS Industrial Development Strategy IDS Implementation plan Industrial Development Strategy Situational Analysis
 Challenges to Industrial Growth Infrastructure • Uncertain policy environment (Mining, Land) • Poor working relationship between business and government affects propensity to invest • Poor and unreliable infrastructure increases costs along many value chains • Need for improved and efficient rail and port logistics broadband electrical energy infrastructure • • • Skills • Perceptions of high net labour cost ( removing non performers, training, low productivity etc. ) • No/low/inappropriate skills means higher costs as businesses must retrain • Need for improved • technical and professional skills
Challenges to Industrial Growth Infrastructure • Uncertain policy environment (Mining, Land) • Poor working relationship between business and government affects propensity to invest • Poor and unreliable infrastructure increases costs along many value chains • Need for improved and efficient rail and port logistics broadband electrical energy infrastructure • • • Skills • Perceptions of high net labour cost ( removing non performers, training, low productivity etc. ) • No/low/inappropriate skills means higher costs as businesses must retrain • Need for improved • technical and professional skills
 KZN Economic Development Strategy and Constraints • • • Pre conditions for Economic Growth – Leverage agriculture- must resolve land issues. – Improve strategic infrastructure. – Build human capital. Spatial Development – Focus on Nodes and Corridors. – Spread economic activity efficiently. Key Constraints – Lack of industrial land. – No finalisation of land issues. – Rising costs of capital and input costs (electricity, transport etc. ) – Skills shortages and labour inflexibility – Inadequate infrastructure
KZN Economic Development Strategy and Constraints • • • Pre conditions for Economic Growth – Leverage agriculture- must resolve land issues. – Improve strategic infrastructure. – Build human capital. Spatial Development – Focus on Nodes and Corridors. – Spread economic activity efficiently. Key Constraints – Lack of industrial land. – No finalisation of land issues. – Rising costs of capital and input costs (electricity, transport etc. ) – Skills shortages and labour inflexibility – Inadequate infrastructure
 South Africa Current Scarce Skills According to the Home Affairs 34 825 Scarce skills are required and the country is recruiting from other nations Example Engineers 415 o Agricultural technicians 5000 Clinical & Biomedical Engineers and Technologists 5000 Building and Engineering technicians 5000 Natural & Physical Professionals 3500 Mechanical & Fabrication Engineering trade works 5500
South Africa Current Scarce Skills According to the Home Affairs 34 825 Scarce skills are required and the country is recruiting from other nations Example Engineers 415 o Agricultural technicians 5000 Clinical & Biomedical Engineers and Technologists 5000 Building and Engineering technicians 5000 Natural & Physical Professionals 3500 Mechanical & Fabrication Engineering trade works 5500
 KWAZULU NATAL PROPOSED REVISED INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY 2012 - 2016
KWAZULU NATAL PROPOSED REVISED INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY 2012 - 2016
 IDS 2012 • Vision “A Productive and competitive Kwa. Zulu Natal that creates employment for all” • Mission “To ensure a competitive economy that provides sustainable employment for all through improved infrastructure, skills entrepreneurial development and productive growth”
IDS 2012 • Vision “A Productive and competitive Kwa. Zulu Natal that creates employment for all” • Mission “To ensure a competitive economy that provides sustainable employment for all through improved infrastructure, skills entrepreneurial development and productive growth”
 Objectives of the Industrial Development Strategy • To Stimulate and Fast Track Productive Growth and Job Creation in Kwa. Zulu Natal by: – Providing an Industrial Development Strategy for Kwa. Zulu Natal in order to focus resources for the best return. – Providing a Framework for Implementation which will ensure prioritisation, accountability and measurement.
Objectives of the Industrial Development Strategy • To Stimulate and Fast Track Productive Growth and Job Creation in Kwa. Zulu Natal by: – Providing an Industrial Development Strategy for Kwa. Zulu Natal in order to focus resources for the best return. – Providing a Framework for Implementation which will ensure prioritisation, accountability and measurement.
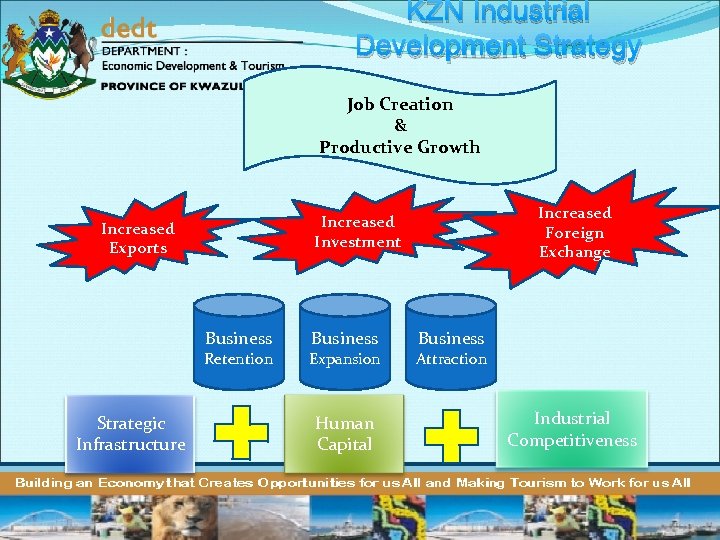 KZN Industrial Development Strategy Job Creation & Productive Growth Increased Exports Business Retention Strategic Infrastructure Increased Foreign Exchange Increased Investment Business Expansion Human Capital Business Attraction Industrial Competitiveness
KZN Industrial Development Strategy Job Creation & Productive Growth Increased Exports Business Retention Strategic Infrastructure Increased Foreign Exchange Increased Investment Business Expansion Human Capital Business Attraction Industrial Competitiveness

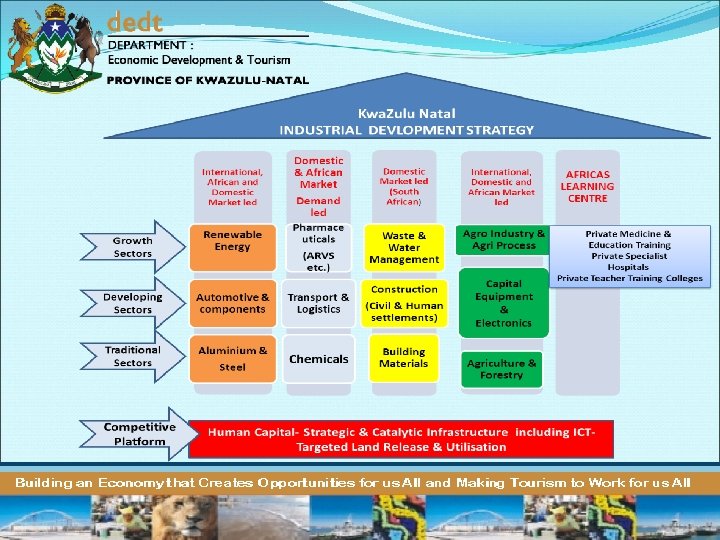
 INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY FOCUS New Industries Attract New Investment Green Economy, Pharmaneuticals, Agro Industry and Agri processing, Water & Waste Management Focus on start up efficiencies, specialised infrastructure and market s Developing Industries Expand Attract New Investment Automotive, Transport & Logistics, Construction, Capital Equipment & Green Electronics Training Service Industry- Nurses, Teachers, Artisans Focus on support for existing growth clusters Traditional Industries Retain and Expand Metals, Chemicals, Building Materials, Agriculture Focus on cost chain efficiencies Enabling Platform Strategic Infrastructure Rail, ports, road, SEZ, IDZ and Broadband Enabling Platform Skills Development Artisans, Engineers, Teachers, Nurses Foundations for success of IDS
INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY FOCUS New Industries Attract New Investment Green Economy, Pharmaneuticals, Agro Industry and Agri processing, Water & Waste Management Focus on start up efficiencies, specialised infrastructure and market s Developing Industries Expand Attract New Investment Automotive, Transport & Logistics, Construction, Capital Equipment & Green Electronics Training Service Industry- Nurses, Teachers, Artisans Focus on support for existing growth clusters Traditional Industries Retain and Expand Metals, Chemicals, Building Materials, Agriculture Focus on cost chain efficiencies Enabling Platform Strategic Infrastructure Rail, ports, road, SEZ, IDZ and Broadband Enabling Platform Skills Development Artisans, Engineers, Teachers, Nurses Foundations for success of IDS
 SECTOR IDENTIFIED FOR SKILLS New Industries Attract New Investment Green Economy, Pharmaneuticals, Agro Industry and Agri processing, Water & Waste Management Focus on start up efficiencies, specialised infrastructure and markets Developing Industries Expand Attract New Investment Automotive, Transport & Logistics, Construction, Capital Equipment & Green Electronics Training Service Industry- Nurses, Teachers, Artisans, Engineers Focus on support for existing growth clusters Traditional Industries Retain and Expand Metals, Chemicals, Building Materials, Agriculture Focus on cost chain efficiencies
SECTOR IDENTIFIED FOR SKILLS New Industries Attract New Investment Green Economy, Pharmaneuticals, Agro Industry and Agri processing, Water & Waste Management Focus on start up efficiencies, specialised infrastructure and markets Developing Industries Expand Attract New Investment Automotive, Transport & Logistics, Construction, Capital Equipment & Green Electronics Training Service Industry- Nurses, Teachers, Artisans, Engineers Focus on support for existing growth clusters Traditional Industries Retain and Expand Metals, Chemicals, Building Materials, Agriculture Focus on cost chain efficiencies
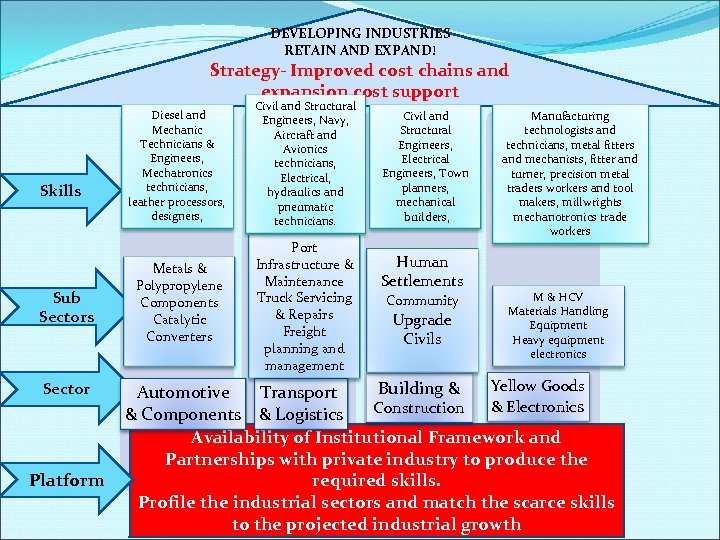 DEVELOPING INDUSTRIES RETAIN AND EXPAND! Strategy- Improved cost chains and expansion cost support Skills Sub Sectors Sector Platform Diesel and Mechanic Technicians & Engineers, Mechatronics technicians, leather processors, designers, Civil and Structural Engineers, Navy, Aircraft and Avionics technicians, Electrical, hydraulics and pneumatic technicians. Metals & Polypropylene Components Catalytic Converters Port Infrastructure & Maintenance Truck Servicing & Repairs Freight planning and management Civil and Structural Engineers, Electrical Engineers, Town planners, mechanical builders, Human Settlements Community Upgrade Civils Manufacturing technologists and technicians, metal fitters and mechanists, fitter and turner, precision metal traders workers and tool makers, millwrights mechanotronics trade workers M & HCV Materials Handling Equipment Heavy equipment electronics Yellow Goods Building & Automotive Transport & Electronics Construction & Components & Logistics Availability of Institutional Framework and Partnerships with private industry to produce the required skills. Profile the industrial sectors and match the scarce skills to the projected industrial growth
DEVELOPING INDUSTRIES RETAIN AND EXPAND! Strategy- Improved cost chains and expansion cost support Skills Sub Sectors Sector Platform Diesel and Mechanic Technicians & Engineers, Mechatronics technicians, leather processors, designers, Civil and Structural Engineers, Navy, Aircraft and Avionics technicians, Electrical, hydraulics and pneumatic technicians. Metals & Polypropylene Components Catalytic Converters Port Infrastructure & Maintenance Truck Servicing & Repairs Freight planning and management Civil and Structural Engineers, Electrical Engineers, Town planners, mechanical builders, Human Settlements Community Upgrade Civils Manufacturing technologists and technicians, metal fitters and mechanists, fitter and turner, precision metal traders workers and tool makers, millwrights mechanotronics trade workers M & HCV Materials Handling Equipment Heavy equipment electronics Yellow Goods Building & Automotive Transport & Electronics Construction & Components & Logistics Availability of Institutional Framework and Partnerships with private industry to produce the required skills. Profile the industrial sectors and match the scarce skills to the projected industrial growth
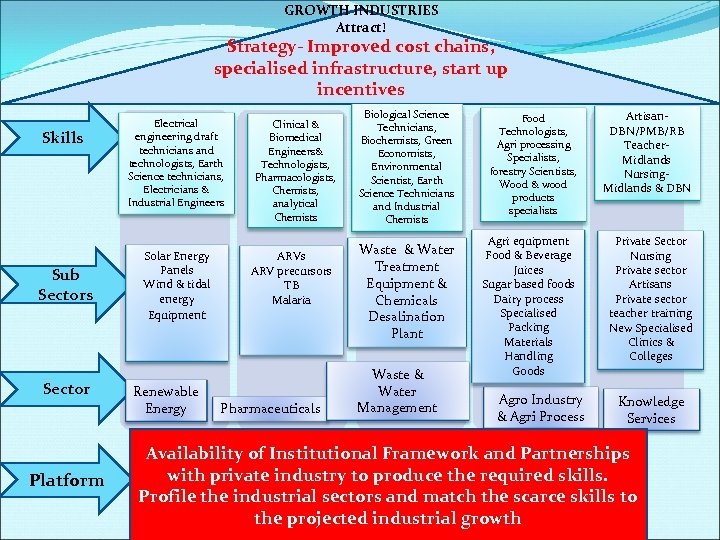 GROWTH INDUSTRIES Attract! Strategy- Improved cost chains, specialised infrastructure, start up incentives Skills Sub Sectors Sector Platform Electrical engineering draft technicians and technologists, Earth Science technicians, Electricians & Industrial Engineers Solar Energy Panels Wind & tidal energy Equipment Renewable Energy Clinical & Biomedical Engineers& Technologists, Pharmacologists, Chemists, analytical Chemists ARV precursors TB Malaria Pharmaceuticals Biological Science Technicians, Biochemists, Green Economists, Environmental Scientist, Earth Science Technicians and Industrial Chemists Waste & Water Treatment Equipment & Chemicals Desalination Plant Waste & Water Management Food Technologists, Agri processing Specialists, forestry Scientists, Wood & wood products specialists Artisan. DBN/PMB/RB Teacher. Midlands Nursing. Midlands & DBN Agri equipment Food & Beverage Juices Sugar based foods Dairy process Specialised Packing Materials Handling Goods Private Sector Nursing Private sector Artisans Private sector teacher training New Specialised Clinics & Colleges Agro Industry & Agri Process Knowledge Services Availability of Institutional Framework and Partnerships with private industry to produce the required skills. Profile the industrial sectors and match the scarce skills to the projected industrial growth
GROWTH INDUSTRIES Attract! Strategy- Improved cost chains, specialised infrastructure, start up incentives Skills Sub Sectors Sector Platform Electrical engineering draft technicians and technologists, Earth Science technicians, Electricians & Industrial Engineers Solar Energy Panels Wind & tidal energy Equipment Renewable Energy Clinical & Biomedical Engineers& Technologists, Pharmacologists, Chemists, analytical Chemists ARV precursors TB Malaria Pharmaceuticals Biological Science Technicians, Biochemists, Green Economists, Environmental Scientist, Earth Science Technicians and Industrial Chemists Waste & Water Treatment Equipment & Chemicals Desalination Plant Waste & Water Management Food Technologists, Agri processing Specialists, forestry Scientists, Wood & wood products specialists Artisan. DBN/PMB/RB Teacher. Midlands Nursing. Midlands & DBN Agri equipment Food & Beverage Juices Sugar based foods Dairy process Specialised Packing Materials Handling Goods Private Sector Nursing Private sector Artisans Private sector teacher training New Specialised Clinics & Colleges Agro Industry & Agri Process Knowledge Services Availability of Institutional Framework and Partnerships with private industry to produce the required skills. Profile the industrial sectors and match the scarce skills to the projected industrial growth
 Strategic Interventions & Industrial S Development Strategic Interventions Development of a detailed skills profile per industry in partnership with private sector Quantification and projections of skills needed by each sector and subsector; Value chain analysis of skills requirements at each value node. Development of vocational lifelong training & skills strategy for each sector in collaboration with the private sector, with clear implementation plan and M& E measures. Development & revamping of training institutions new and exisiting with emphasis on Higher vocational institutions Advanced technical schools Secondary Polytechnic Schools Employment training centers
Strategic Interventions & Industrial S Development Strategic Interventions Development of a detailed skills profile per industry in partnership with private sector Quantification and projections of skills needed by each sector and subsector; Value chain analysis of skills requirements at each value node. Development of vocational lifelong training & skills strategy for each sector in collaboration with the private sector, with clear implementation plan and M& E measures. Development & revamping of training institutions new and exisiting with emphasis on Higher vocational institutions Advanced technical schools Secondary Polytechnic Schools Employment training centers
 Strategic Interventions & Industrial Sk Development Strategic Interventions Development & revamping of training institutions new and exisiting with emphasis on Higher vocational institutions Advanced technical schools Secondary Polytechnic Schools Employment training centers Non- governmental Vocational Training Institutions Enterprise based Employee Training centres Design and implementation of skills hub to address reskilling , upskilling in various sectors e. g clothing and textiles Implementation of improved and world class technical centres, innovation hubs , incubators and centres for excellence for identified industrial sector s training artisans, industrial technicians, biotechnicians ets
Strategic Interventions & Industrial Sk Development Strategic Interventions Development & revamping of training institutions new and exisiting with emphasis on Higher vocational institutions Advanced technical schools Secondary Polytechnic Schools Employment training centers Non- governmental Vocational Training Institutions Enterprise based Employee Training centres Design and implementation of skills hub to address reskilling , upskilling in various sectors e. g clothing and textiles Implementation of improved and world class technical centres, innovation hubs , incubators and centres for excellence for identified industrial sector s training artisans, industrial technicians, biotechnicians ets
 Strategic Interventions & Industrial Sk Development Strategic Interventions Reinstate artisanal training centres with Transnet, Eskom and Water Utilities. Focus areas on the skills development should include Strengthening pre-employment training Strengthening labour skills training Strengthening re-employment training Developing long distance training and on the job training Implementing the vocational qualification certificate system in an integrated way Launching skills competitions and activities honouring technical experts.
Strategic Interventions & Industrial Sk Development Strategic Interventions Reinstate artisanal training centres with Transnet, Eskom and Water Utilities. Focus areas on the skills development should include Strengthening pre-employment training Strengthening labour skills training Strengthening re-employment training Developing long distance training and on the job training Implementing the vocational qualification certificate system in an integrated way Launching skills competitions and activities honouring technical experts.
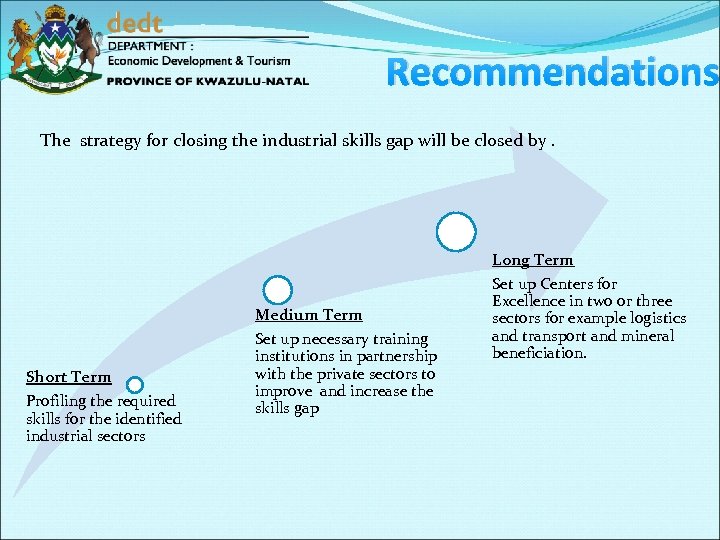 Recommendations The strategy for closing the industrial skills gap will be closed by. Short Term Profiling the required skills for the identified industrial sectors Medium Term Set up necessary training institutions in partnership with the private sectors to improve and increase the skills gap Long Term Set up Centers for Excellence in two or three sectors for example logistics and transport and mineral beneficiation.
Recommendations The strategy for closing the industrial skills gap will be closed by. Short Term Profiling the required skills for the identified industrial sectors Medium Term Set up necessary training institutions in partnership with the private sectors to improve and increase the skills gap Long Term Set up Centers for Excellence in two or three sectors for example logistics and transport and mineral beneficiation.
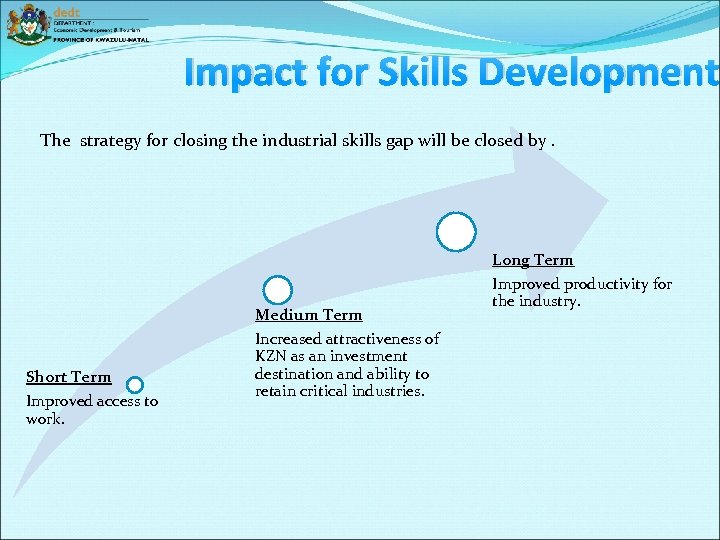 Impact for Skills Development The strategy for closing the industrial skills gap will be closed by. Short Term Improved access to work. Medium Term Increased attractiveness of KZN as an investment destination and ability to retain critical industries. Long Term Improved productivity for the industry.
Impact for Skills Development The strategy for closing the industrial skills gap will be closed by. Short Term Improved access to work. Medium Term Increased attractiveness of KZN as an investment destination and ability to retain critical industries. Long Term Improved productivity for the industry.
 THANK YOU
THANK YOU


