62ce94244494cf643e24015040caf40d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63
 “Kuality” Assurance What does that look like? Scott Heise Indiana University KFS - Quality Assurance Manager Kymber Horn University of Arizona KFS - Lead Testing Coordinator Paul Sandoval University of Arizona KRA – Lead Testing Coordinator Lora O’Connor Indiana University KRA – Quality Assurance Manager Jennifer Flach Coeus Consortium Coeus. TM – Quality Assurance Manager
“Kuality” Assurance What does that look like? Scott Heise Indiana University KFS - Quality Assurance Manager Kymber Horn University of Arizona KFS - Lead Testing Coordinator Paul Sandoval University of Arizona KRA – Lead Testing Coordinator Lora O’Connor Indiana University KRA – Quality Assurance Manager Jennifer Flach Coeus Consortium Coeus. TM – Quality Assurance Manager
 What does QA mean to you? Have you heard these phrases before? • • • We don’t need documentation. The developers can test it. We don’t have time. How hard could it be? We don’t need Unit Tests. We have functional testers. I thought the spec was just a guideline. We don’t have time for a QA period.
What does QA mean to you? Have you heard these phrases before? • • • We don’t need documentation. The developers can test it. We don’t have time. How hard could it be? We don’t need Unit Tests. We have functional testers. I thought the spec was just a guideline. We don’t have time for a QA period.
 Introduction • What is QA? – The process for defining techniques, procedures, and methodologies that will be used to assure timely delivery of the software that meets specified requirements. • What are the benefits of QA? – Improved utilization of time and resources – Improved efficiency – Consistent quality and timely delivery
Introduction • What is QA? – The process for defining techniques, procedures, and methodologies that will be used to assure timely delivery of the software that meets specified requirements. • What are the benefits of QA? – Improved utilization of time and resources – Improved efficiency – Consistent quality and timely delivery
 Introduction • What are the benefits of QA, continued…? – Increased stakeholder satisfaction – Improved control of processes – Improved performance of software – Documented system provides useful reference – Lower rejection rates, rework, and implementation costs – Improved control during periods of change or growth – Plus, many more…….
Introduction • What are the benefits of QA, continued…? – Increased stakeholder satisfaction – Improved control of processes – Improved performance of software – Documented system provides useful reference – Lower rejection rates, rework, and implementation costs – Improved control during periods of change or growth – Plus, many more…….
 Scott Heise Indiana University Kuali Financial System (KFS) Quality Assurance Manager
Scott Heise Indiana University Kuali Financial System (KFS) Quality Assurance Manager
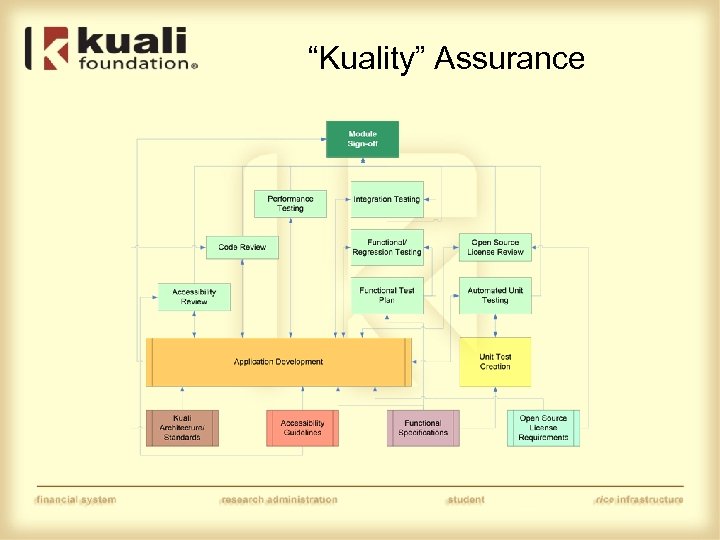 “Kuality” Assurance
“Kuality” Assurance
 Automated Unit Testing
Automated Unit Testing
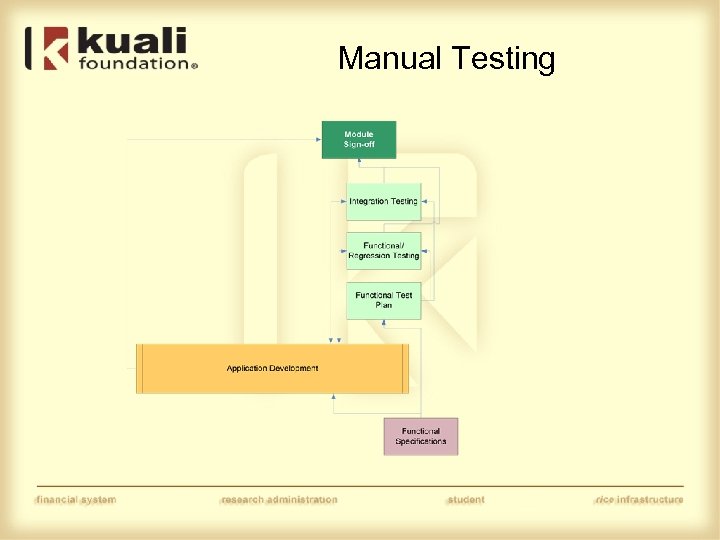 Manual Testing
Manual Testing
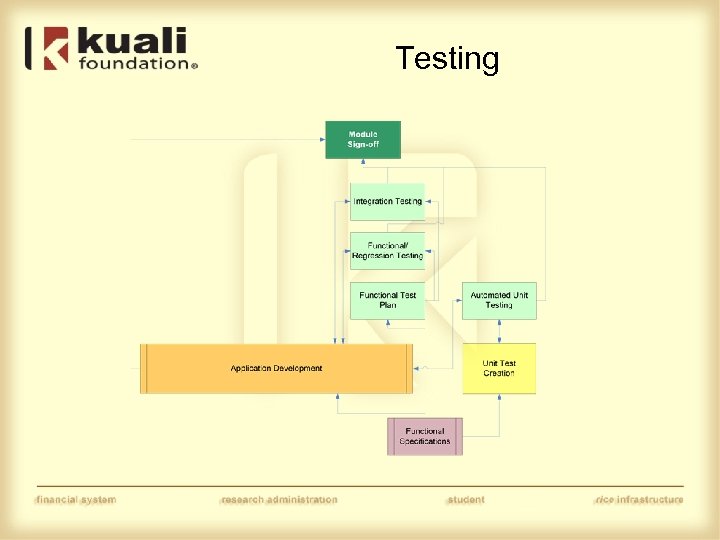 Testing
Testing
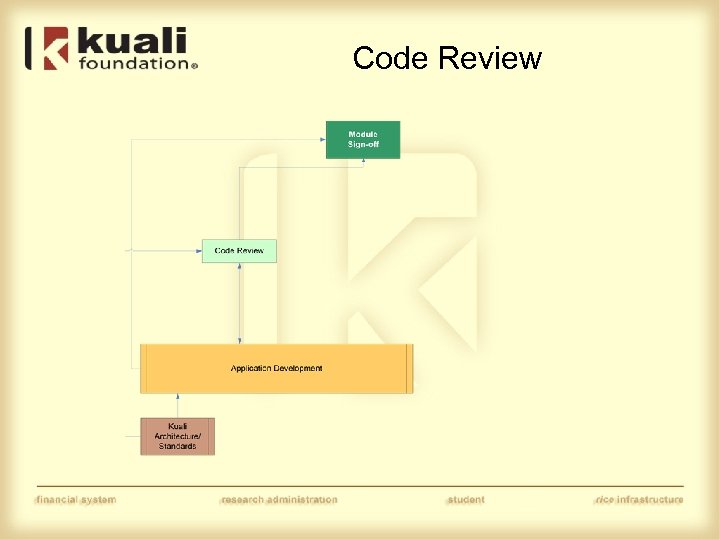 Code Review
Code Review
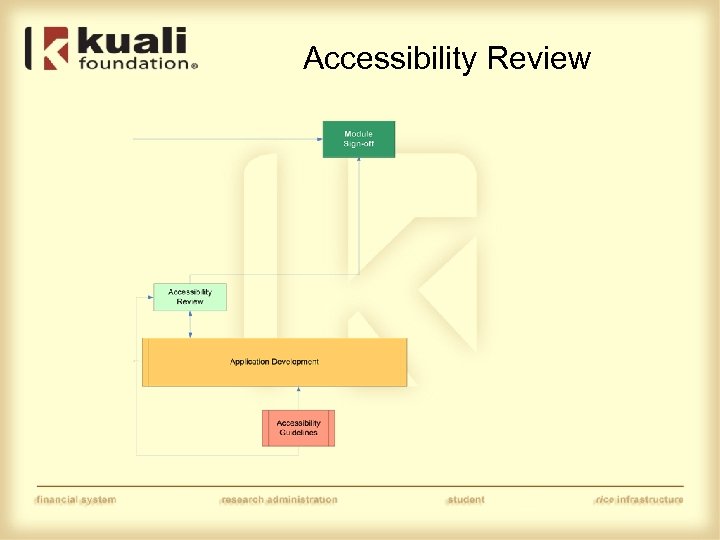 Accessibility Review
Accessibility Review
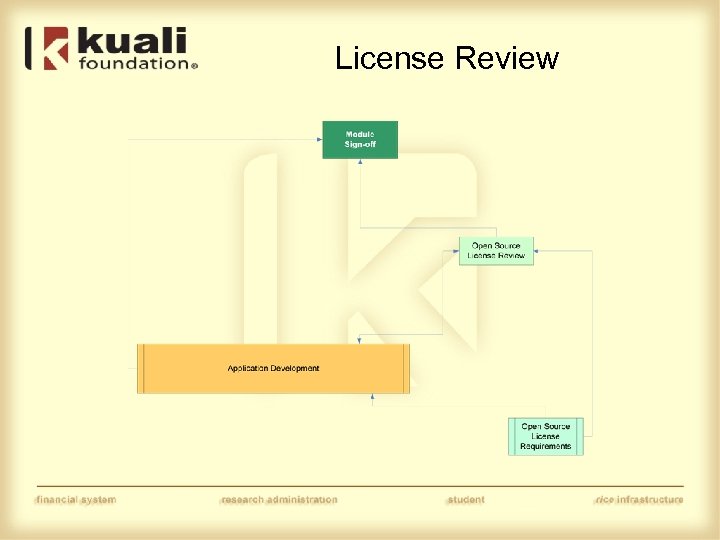 License Review
License Review
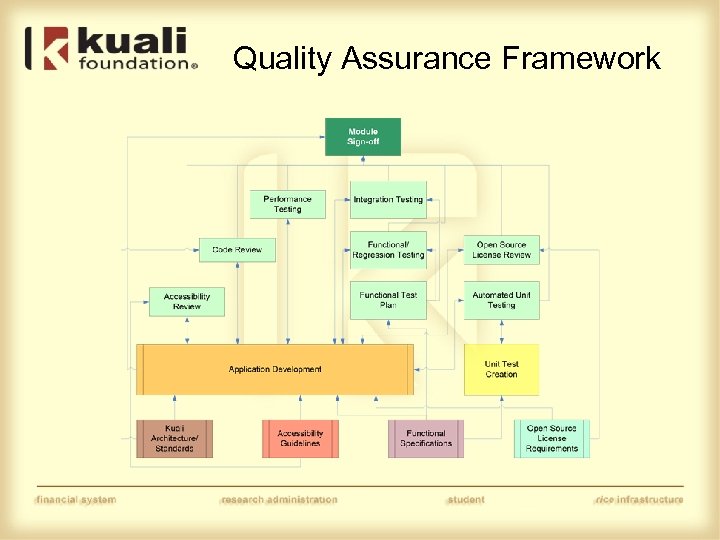 Quality Assurance Framework
Quality Assurance Framework
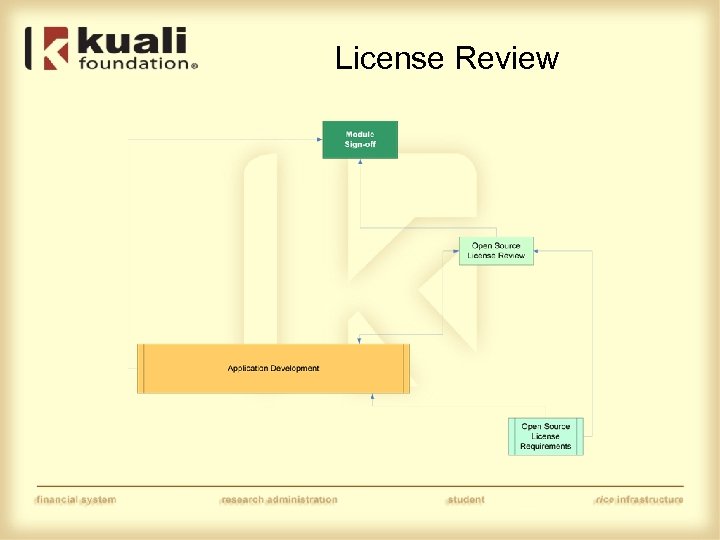 License Review
License Review
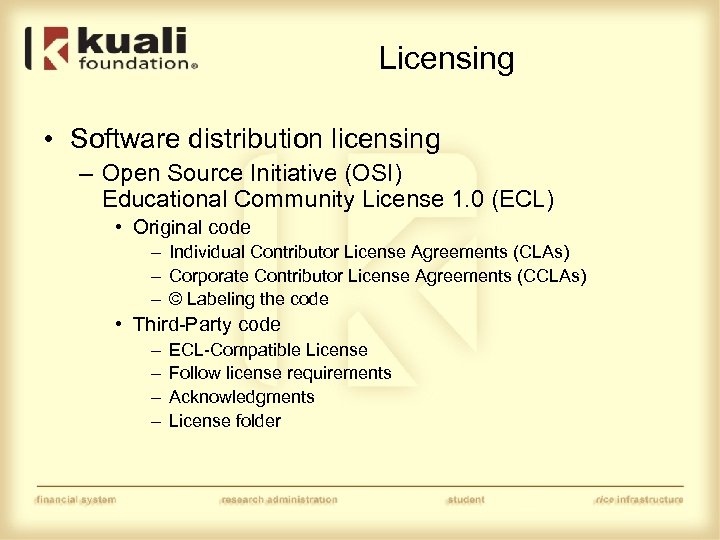 Licensing • Software distribution licensing – Open Source Initiative (OSI) Educational Community License 1. 0 (ECL) • Original code – Individual Contributor License Agreements (CLAs) – Corporate Contributor License Agreements (CCLAs) – © Labeling the code • Third-Party code – – ECL-Compatible License Follow license requirements Acknowledgments License folder
Licensing • Software distribution licensing – Open Source Initiative (OSI) Educational Community License 1. 0 (ECL) • Original code – Individual Contributor License Agreements (CLAs) – Corporate Contributor License Agreements (CCLAs) – © Labeling the code • Third-Party code – – ECL-Compatible License Follow license requirements Acknowledgments License folder
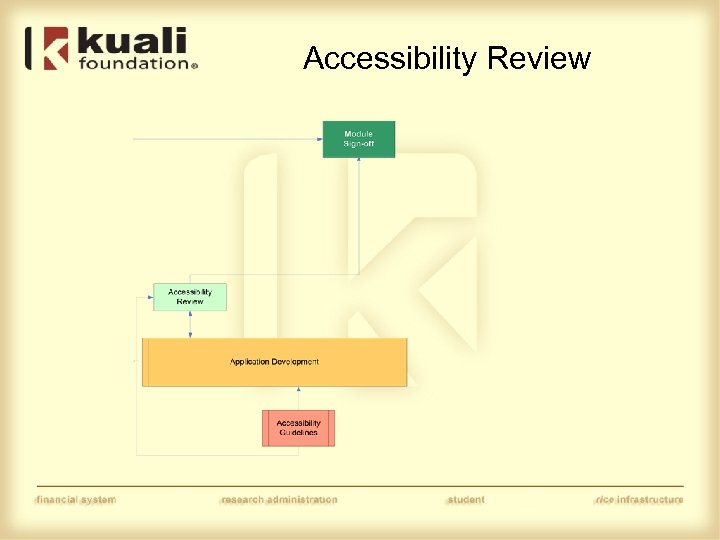 Accessibility Review
Accessibility Review
 Accessibility • Guidelines • Test by sampling • “Issues” approach to resolution
Accessibility • Guidelines • Test by sampling • “Issues” approach to resolution
 Kymber Horn University of Arizona Kuali Financial System (KFS) Lead Testing Coordinator
Kymber Horn University of Arizona Kuali Financial System (KFS) Lead Testing Coordinator
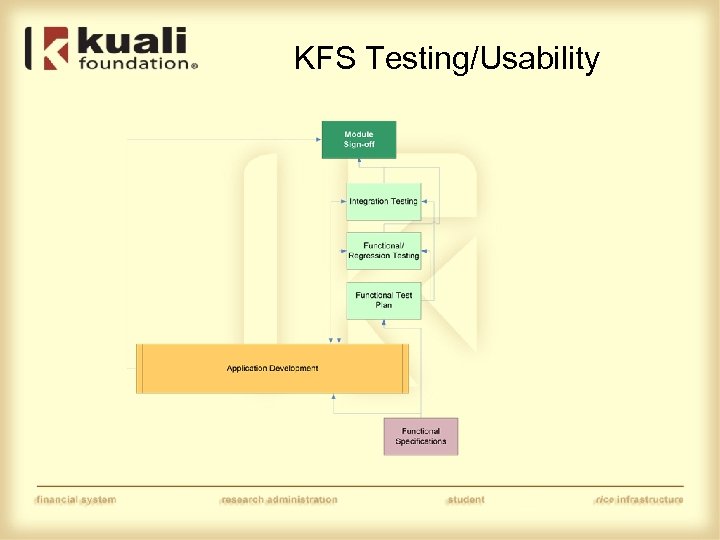 KFS Testing/Usability
KFS Testing/Usability
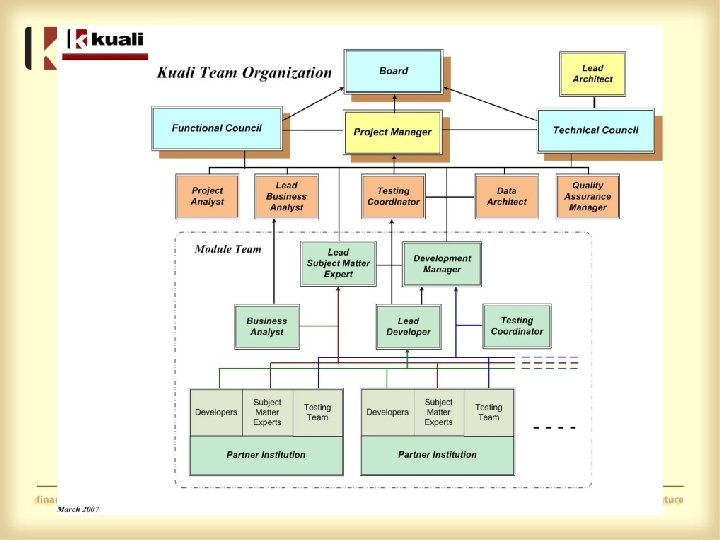
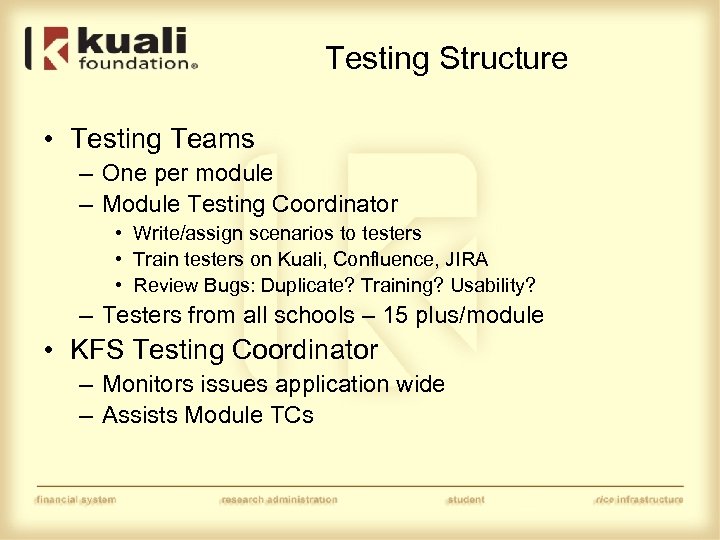 Testing Structure • Testing Teams – One per module – Module Testing Coordinator • Write/assign scenarios to testers • Train testers on Kuali, Confluence, JIRA • Review Bugs: Duplicate? Training? Usability? – Testers from all schools – 15 plus/module • KFS Testing Coordinator – Monitors issues application wide – Assists Module TCs
Testing Structure • Testing Teams – One per module – Module Testing Coordinator • Write/assign scenarios to testers • Train testers on Kuali, Confluence, JIRA • Review Bugs: Duplicate? Training? Usability? – Testers from all schools – 15 plus/module • KFS Testing Coordinator – Monitors issues application wide – Assists Module TCs
 Process • • e. Doc/process ready for testing Scenario created/assigned – JIRA Bugs reported in JIRA Issues fixed marked as resolved Testing environment released weekly Release notes created - Confluence Testers test close/reopen Rinse and Repeat!
Process • • e. Doc/process ready for testing Scenario created/assigned – JIRA Bugs reported in JIRA Issues fixed marked as resolved Testing environment released weekly Release notes created - Confluence Testers test close/reopen Rinse and Repeat!
 Tools - JIRA
Tools - JIRA
 Tools - Confluence
Tools - Confluence
 Usability – Before Coding • Indiana UXG – Usability Group – Developed Standards/Guidelines for the UI – Initial Mocks reviewed by Kuali Financial Functional Council • Decisions made: – Editable data entry lines – Page Level Help – no field level help – Usability sessions with users from each school via Breeze
Usability – Before Coding • Indiana UXG – Usability Group – Developed Standards/Guidelines for the UI – Initial Mocks reviewed by Kuali Financial Functional Council • Decisions made: – Editable data entry lines – Page Level Help – no field level help – Usability sessions with users from each school via Breeze
 Usability – During/After • Marked as Usability • Reviewed and Prioritized by Usability Prioritization Committee • Usability Dev team formed during QA • Usability issues that affect infrastructure, reviewed and time allocated during next release, e. g. – error handling framework
Usability – During/After • Marked as Usability • Reviewed and Prioritized by Usability Prioritization Committee • Usability Dev team formed during QA • Usability issues that affect infrastructure, reviewed and time allocated during next release, e. g. – error handling framework
 Lessons Learned • • Face to Face sessions Never too many testers Training for testers Pre-Testing to ensure a fairly stable environment • Weekly meetings with testers • Testing is the BEST way to learn!
Lessons Learned • • Face to Face sessions Never too many testers Training for testers Pre-Testing to ensure a fairly stable environment • Weekly meetings with testers • Testing is the BEST way to learn!
 Paul Sandoval University of Arizona Kuali Research Administration System (KRA) Lead Testing Coordinator
Paul Sandoval University of Arizona Kuali Research Administration System (KRA) Lead Testing Coordinator
 KRA Testing and Usability
KRA Testing and Usability
 Process • Functional Specs (SMEs) • Code (Developers) • Testing (Developers, Lead Testing Coordinator, Module Testing Coordinator, SMEs, Testers – includes Coeus consortium members)
Process • Functional Specs (SMEs) • Code (Developers) • Testing (Developers, Lead Testing Coordinator, Module Testing Coordinator, SMEs, Testers – includes Coeus consortium members)
 Testing • Module Testing Coordinators – One per module – Write/assign scenarios to testers from each school in JIRA – Train testers • Testers test – report bugs in JIRA • Module Testing Coordinators review – Bug, Duplicate, Training opp, Usability
Testing • Module Testing Coordinators – One per module – Write/assign scenarios to testers from each school in JIRA – Train testers • Testers test – report bugs in JIRA • Module Testing Coordinators review – Bug, Duplicate, Training opp, Usability
 Bugs • • Reported in JIRA Fixed by Developers Resolved with next Build Confluence used to help testers keep track of resolved bugs ready to be tested • Testers Test – Close/Reopen
Bugs • • Reported in JIRA Fixed by Developers Resolved with next Build Confluence used to help testers keep track of resolved bugs ready to be tested • Testers Test – Close/Reopen
 Lessons Learned • One person was designated to write Spec Docs in the SME group in KFS. In KRA, everyone is taking an active role in writing Spec Docs. This promotes ownership in the process!! • SME Members are going to take a more active role in testing. • Face to Face testing – Training
Lessons Learned • One person was designated to write Spec Docs in the SME group in KFS. In KRA, everyone is taking an active role in writing Spec Docs. This promotes ownership in the process!! • SME Members are going to take a more active role in testing. • Face to Face testing – Training
 Lora O’Connor Indiana University Kuali Research Administration System (KRA) Quality Assurance Manager
Lora O’Connor Indiana University Kuali Research Administration System (KRA) Quality Assurance Manager
 KRA Quality, Timelines and Synergy
KRA Quality, Timelines and Synergy
 QA is Continuous! • QA exists throughout the entire software development life cycle! – Planning and Communication Tools • Microsoft Project, Confluence and Jira, Breeze, Skype, Face-to-face meetings – Analysis • Functional and Technical – Licensing – Coding • Code Reviews, Development Standards
QA is Continuous! • QA exists throughout the entire software development life cycle! – Planning and Communication Tools • Microsoft Project, Confluence and Jira, Breeze, Skype, Face-to-face meetings – Analysis • Functional and Technical – Licensing – Coding • Code Reviews, Development Standards
 QA is Continuous! – Testing • Unit Testing, Regression Testing, Integration Testing – Usability and Accessibility • HTML Mock Development, Focus Groups, Design Critiques, W 3 C Priorities, Accessibility Testing – Documentation • Functional and Technical – Builds and Releases
QA is Continuous! – Testing • Unit Testing, Regression Testing, Integration Testing – Usability and Accessibility • HTML Mock Development, Focus Groups, Design Critiques, W 3 C Priorities, Accessibility Testing – Documentation • Functional and Technical – Builds and Releases
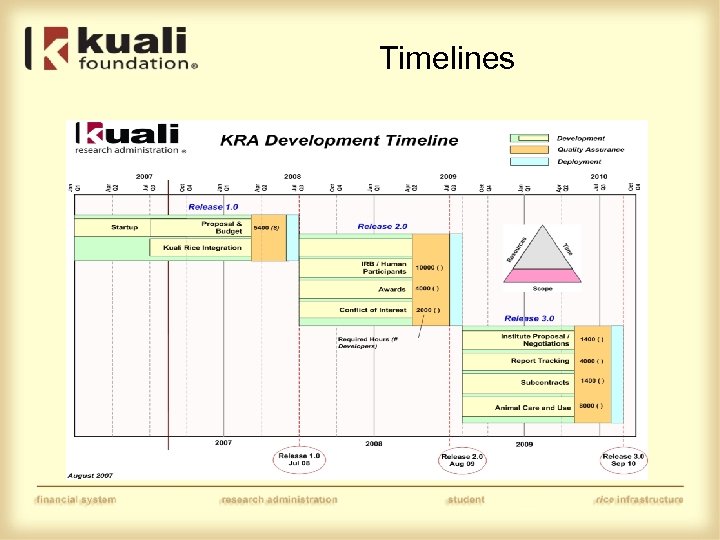 Timelines
Timelines
 QA impacts Timelines • Project planning is continuous along with QA • Coeus represents the base functionality that will be delivered in KRA • Enhancements are reviewed, estimated and submitted for functional approval. If accepted, the project plan is adjusted. • Functional specifications are standard • SME groups follow similar processes when interacting with SME group members and the development team • A user interface group monitors HTML mock development and usability/accessibility issues
QA impacts Timelines • Project planning is continuous along with QA • Coeus represents the base functionality that will be delivered in KRA • Enhancements are reviewed, estimated and submitted for functional approval. If accepted, the project plan is adjusted. • Functional specifications are standard • SME groups follow similar processes when interacting with SME group members and the development team • A user interface group monitors HTML mock development and usability/accessibility issues
 QA impacts Timelines • Focus groups and design critiques are conducted with Faculty and staff roles across multiple schools • HTML mocks and jsps are validated for W 3 C Priority 1 and 2 issues and corrected • Code reviews are standard and code is reviewed weekly • Unit testing is standard and a continuous test process runs daily • Multiple test environments exist to ensure that automated and manual testing is performed • Documentation is standard – functional specifications, technical gap documents, integration documents, user and help documents
QA impacts Timelines • Focus groups and design critiques are conducted with Faculty and staff roles across multiple schools • HTML mocks and jsps are validated for W 3 C Priority 1 and 2 issues and corrected • Code reviews are standard and code is reviewed weekly • Unit testing is standard and a continuous test process runs daily • Multiple test environments exist to ensure that automated and manual testing is performed • Documentation is standard – functional specifications, technical gap documents, integration documents, user and help documents
 QA Tracking
QA Tracking
 QA Tracking
QA Tracking
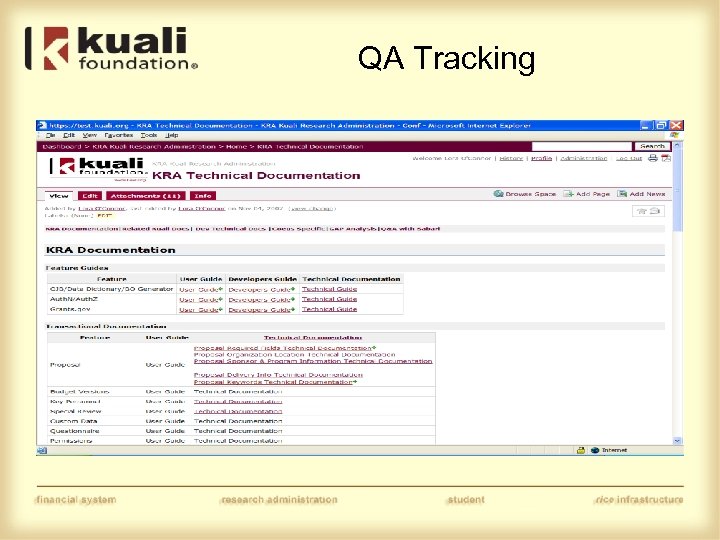 QA Tracking
QA Tracking
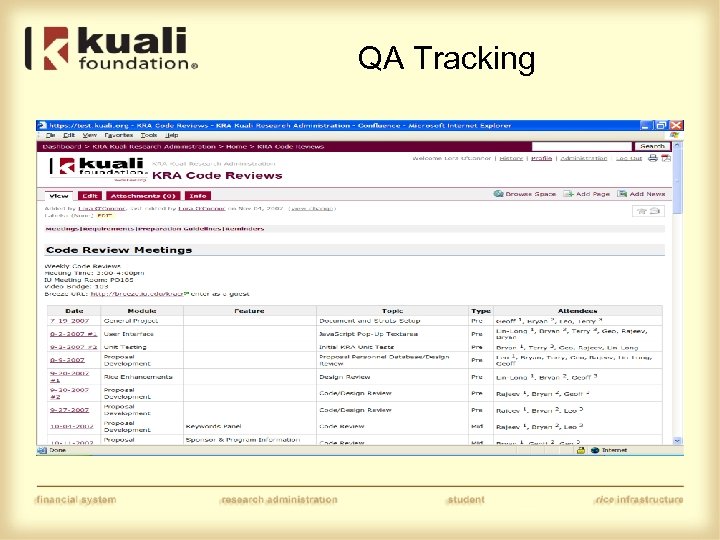 QA Tracking
QA Tracking
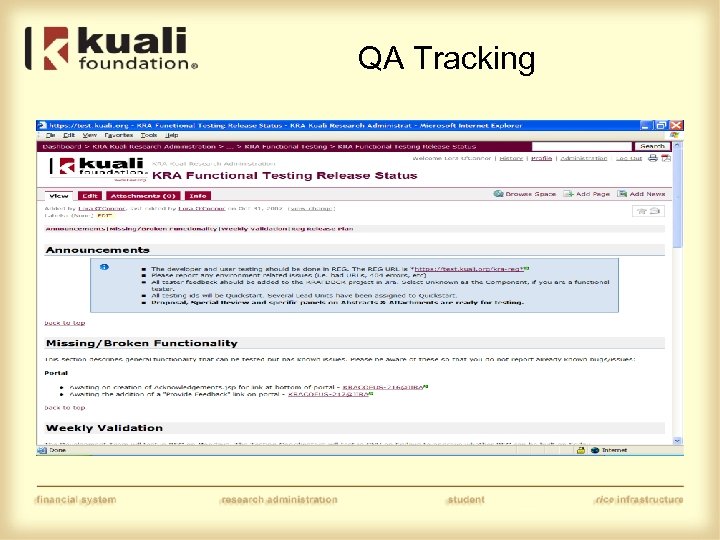 QA Tracking
QA Tracking
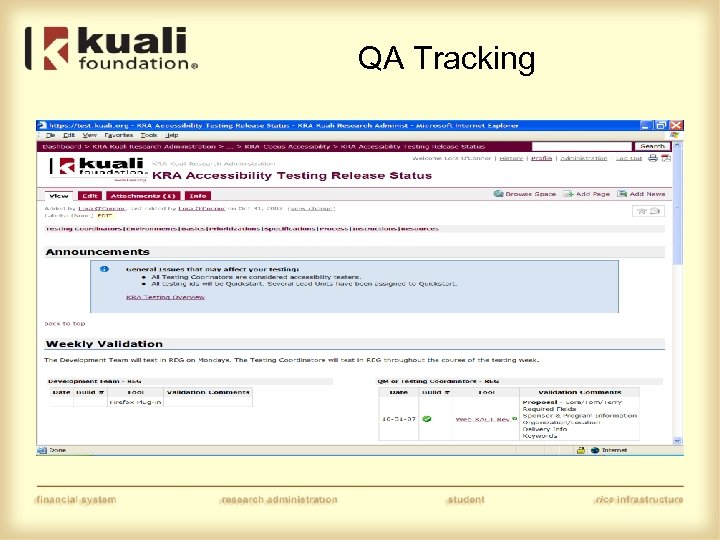 QA Tracking
QA Tracking
 Synergy From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia – Synergy (from the Greek synergos, συνεργός meaning working together, circa 1660) From Merriam-Webster – syn·er·gy • 1: synergism; broadly : combined action or operation • 2: a mutually advantageous conjunction or compatibility of distinct business participants or elements (as resources or efforts)Synergy with other Kuali Projects
Synergy From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia – Synergy (from the Greek synergos, συνεργός meaning working together, circa 1660) From Merriam-Webster – syn·er·gy • 1: synergism; broadly : combined action or operation • 2: a mutually advantageous conjunction or compatibility of distinct business participants or elements (as resources or efforts)Synergy with other Kuali Projects
 Synergy • Synergy with other Kuali Projects – KFS, Rice, KEW, KEN • Synergy within KRA modules – Proposal, Budget, Award, IRB and future modules • Synergy with Coeus – Share architecture and tools moving forward – Assess Coeus enhancements & bug fixes
Synergy • Synergy with other Kuali Projects – KFS, Rice, KEW, KEN • Synergy within KRA modules – Proposal, Budget, Award, IRB and future modules • Synergy with Coeus – Share architecture and tools moving forward – Assess Coeus enhancements & bug fixes
 Lessons Learned • Developers should test the web application on a regular basis • Code should be reviewed as functionality is developed and a final code review should be required for completion • Unit Testing guidelines should be set early and followed • Functional testers should test functionality as early as possible • Project team members must embrace QA processes • Coeus participation is essential! Coeus documentation is essential
Lessons Learned • Developers should test the web application on a regular basis • Code should be reviewed as functionality is developed and a final code review should be required for completion • Unit Testing guidelines should be set early and followed • Functional testers should test functionality as early as possible • Project team members must embrace QA processes • Coeus participation is essential! Coeus documentation is essential
 Jennifer Flach Coeus Consortium TM Quality Assurance Manager
Jennifer Flach Coeus Consortium TM Quality Assurance Manager
 Coeus. TM Quality Assurance
Coeus. TM Quality Assurance
 Coeus and Kuali KRA Joint QA Ongoing collaboration (synergy) between Coeus and Kuali KRA through all phases of the software development life cycle results in a Win/Win for Quality!
Coeus and Kuali KRA Joint QA Ongoing collaboration (synergy) between Coeus and Kuali KRA through all phases of the software development life cycle results in a Win/Win for Quality!
 Coeus QA Process • • • Enhancement requested and assigned to Subcommittee prioritizes and Steering Committee votes Bugs follow a shorter, parallel path Scope of release finalized Users drive analysis and design of new functionality Code developed iteratively Test…Fix bugs…Test…. Fix bugs…. Point releases made at MIT frequently After QA complete, release is made available to the Consortium
Coeus QA Process • • • Enhancement requested and assigned to Subcommittee prioritizes and Steering Committee votes Bugs follow a shorter, parallel path Scope of release finalized Users drive analysis and design of new functionality Code developed iteratively Test…Fix bugs…Test…. Fix bugs…. Point releases made at MIT frequently After QA complete, release is made available to the Consortium
 Coeus Testing • • • Developer Testing Automated Regression Testing Integration Testing User verification QA sessions Beta testing
Coeus Testing • • • Developer Testing Automated Regression Testing Integration Testing User verification QA sessions Beta testing
 Key Coeus QA documents • • • Enhancement Request Form Functional Design Specification Technical Design Specification Test Plans Test Cases
Key Coeus QA documents • • • Enhancement Request Form Functional Design Specification Technical Design Specification Test Plans Test Cases
 Coeus QA Tools • Perfect Tracker – Bug and enhancement request tracking tool • Coeus Project Wiki – Release Information – Subcommittee Pages – Links to QA documents • Coeus Consortium Instance – Testing – Demo
Coeus QA Tools • Perfect Tracker – Bug and enhancement request tracking tool • Coeus Project Wiki – Release Information – Subcommittee Pages – Links to QA documents • Coeus Consortium Instance – Testing – Demo
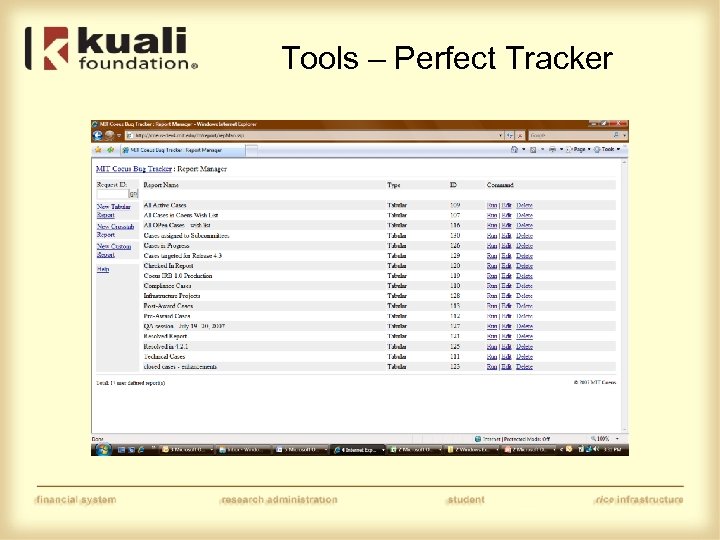 Tools – Perfect Tracker
Tools – Perfect Tracker
 Tools – Wiki
Tools – Wiki
 Coeus and KRA Joint QA Kuali KRA contributes to Coeus QA by: • Developing functional specs that can be used supplement Coeus documentation • Providing feedback into existing and planned functionality • Suggesting enhancements to Coeus functionality • Reporting bugs found in Coeus test/demo environment • Identifying areas of improvement in Coeus user documentation • Sharing approaches for technical implementation
Coeus and KRA Joint QA Kuali KRA contributes to Coeus QA by: • Developing functional specs that can be used supplement Coeus documentation • Providing feedback into existing and planned functionality • Suggesting enhancements to Coeus functionality • Reporting bugs found in Coeus test/demo environment • Identifying areas of improvement in Coeus user documentation • Sharing approaches for technical implementation
 Coeus and KRA Joint QA Coeus contributes to Kuali KRA QA by: • Participating in SME calls • Reviewing specs, screen mocks, and other documents for accuracy and usability • Keeping KRA informed about Coeus release plans and known bugs • Attending KRA technical and functional retreats • Responding to SME queries about Coeus functionality • Participating in KRA testing efforts
Coeus and KRA Joint QA Coeus contributes to Kuali KRA QA by: • Participating in SME calls • Reviewing specs, screen mocks, and other documents for accuracy and usability • Keeping KRA informed about Coeus release plans and known bugs • Attending KRA technical and functional retreats • Responding to SME queries about Coeus functionality • Participating in KRA testing efforts
 “Kuality” Conclusions • QA exists throughout the software development life cycle • While processes may vary between projects, the goal is to ensure that the software is built in a timely manner and meets specified functional requirements • Reviewing and making changes based upon lessons learned can improve the project • Synergy must exist for success!
“Kuality” Conclusions • QA exists throughout the software development life cycle • While processes may vary between projects, the goal is to ensure that the software is built in a timely manner and meets specified functional requirements • Reviewing and making changes based upon lessons learned can improve the project • Synergy must exist for success!
 Questions?
Questions?
 Contacts Please feel free to contact the following individuals about the KFS, KRA or Coeus projects: • Jim Thomas, Project Manager Indiana University – jthomas@indiana. edu • Andy Slusar, Senior Project Manager Cornell University – as 833@cornell. edu • Steve Dowdy, Director of Electronic Research Administration MIT – sdowdy@mit. edu
Contacts Please feel free to contact the following individuals about the KFS, KRA or Coeus projects: • Jim Thomas, Project Manager Indiana University – jthomas@indiana. edu • Andy Slusar, Senior Project Manager Cornell University – as 833@cornell. edu • Steve Dowdy, Director of Electronic Research Administration MIT – sdowdy@mit. edu


