fac9f3751360d4c6f9e9e29a05cd0b4e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 KT-EQUAL/ CARDI Workshop: ‘Lost in Translation’ 23 June 2011 Communicating research results to policy makers: A practitioner’s perspective.
KT-EQUAL/ CARDI Workshop: ‘Lost in Translation’ 23 June 2011 Communicating research results to policy makers: A practitioner’s perspective.
 Structure 1. What do policy practitioners expect from researchers? 2. The policy process - Implications for: 3. Communicating research results to policy makers 4. Opportunities for improving links between research & policy practitioners
Structure 1. What do policy practitioners expect from researchers? 2. The policy process - Implications for: 3. Communicating research results to policy makers 4. Opportunities for improving links between research & policy practitioners
 Better policy-making agenda: Aims: To improve the capacity to address strategic, cross-cutting issues; To promote innovation in the development & delivery of policy; To promote evidence-based policy making, including the dissemination of relevant information and research.
Better policy-making agenda: Aims: To improve the capacity to address strategic, cross-cutting issues; To promote innovation in the development & delivery of policy; To promote evidence-based policy making, including the dissemination of relevant information and research.
 10 Features of Good Policy Making (OFMDFM, 2003) Evidence-based Joined up Outward looking Learns lessons Innovative, flexible & creative Communication Forward looking Inclusive Review Evaluation
10 Features of Good Policy Making (OFMDFM, 2003) Evidence-based Joined up Outward looking Learns lessons Innovative, flexible & creative Communication Forward looking Inclusive Review Evaluation
 The policy process (1) ØMay not always proceed as neatly as suggested; ØNo two policies will need exactly the same process; ØSources of policy making will vary from case to case; ØExisting state of policy and its complexity will vary; ØPolicy process can be blown off course; ØImplementation and evaluation stages can be neglected.
The policy process (1) ØMay not always proceed as neatly as suggested; ØNo two policies will need exactly the same process; ØSources of policy making will vary from case to case; ØExisting state of policy and its complexity will vary; ØPolicy process can be blown off course; ØImplementation and evaluation stages can be neglected.
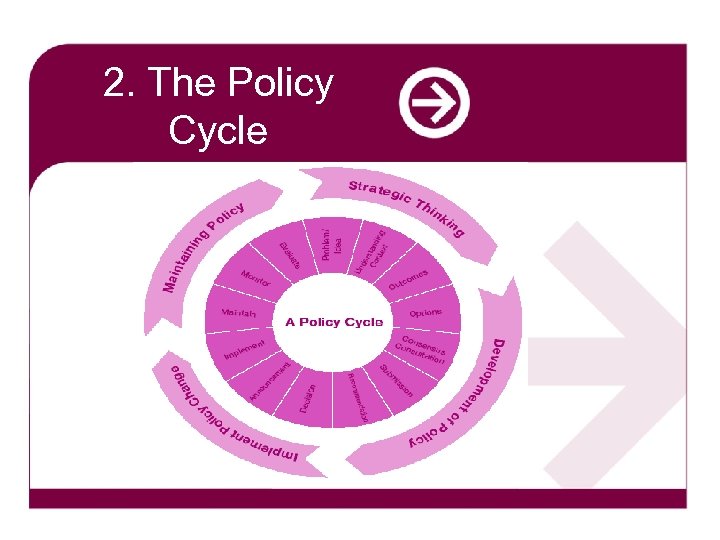 2. The Policy Cycle
2. The Policy Cycle
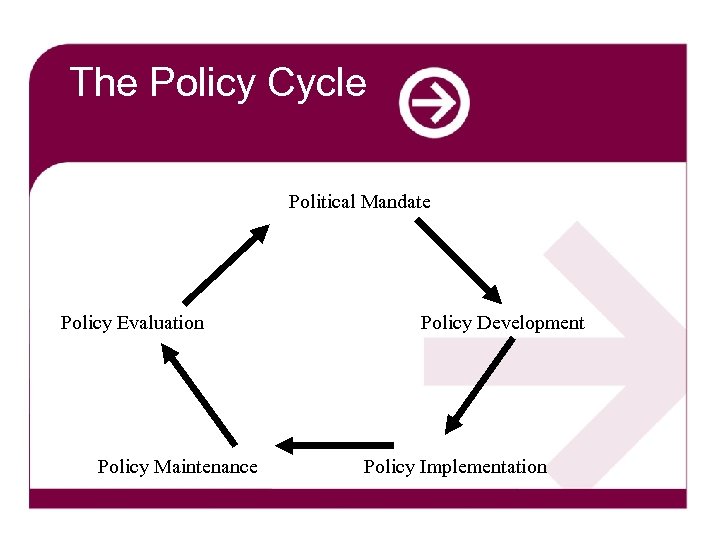 The Policy Cycle Political Mandate Policy Evaluation Policy Maintenance Policy Development Policy Implementation
The Policy Cycle Political Mandate Policy Evaluation Policy Maintenance Policy Development Policy Implementation
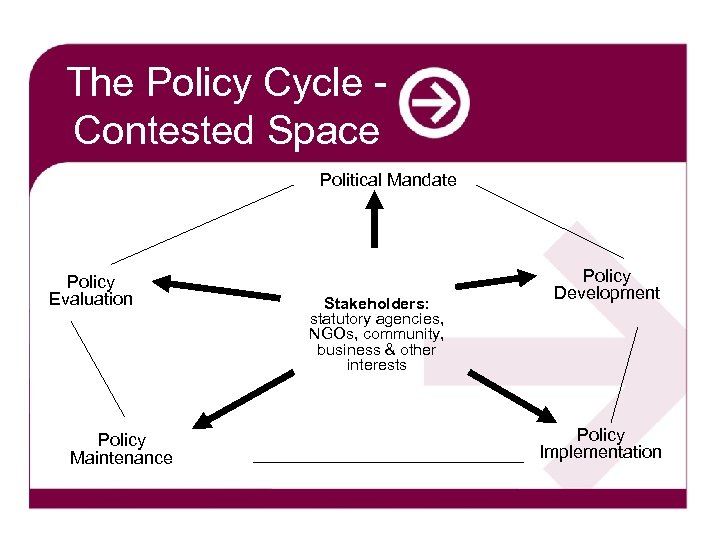 The Policy Cycle Contested Space Political Mandate Policy Evaluation Policy Maintenance Stakeholders: statutory agencies, NGOs, community, business & other interests Policy Development Policy Implementation
The Policy Cycle Contested Space Political Mandate Policy Evaluation Policy Maintenance Stakeholders: statutory agencies, NGOs, community, business & other interests Policy Development Policy Implementation
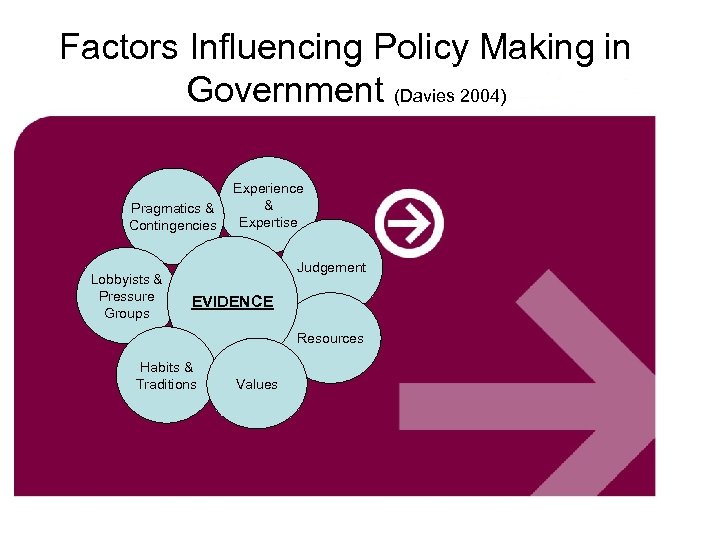 Factors Influencing Policy Making in Government (Davies 2004) Pragmatics & Contingencies Lobbyists & Pressure Groups Experience & Expertise Judgement EVIDENCE Resources Habits & Traditions Values
Factors Influencing Policy Making in Government (Davies 2004) Pragmatics & Contingencies Lobbyists & Pressure Groups Experience & Expertise Judgement EVIDENCE Resources Habits & Traditions Values
 The policy process (2) ØTime pressures ØUse of in-house expertise at branch level ØRole of economists / statisticians and other experts ØFocus on ‘policy development’ ØIdentified training needs ØPolicy networks at different levels – EU / Regional / Local
The policy process (2) ØTime pressures ØUse of in-house expertise at branch level ØRole of economists / statisticians and other experts ØFocus on ‘policy development’ ØIdentified training needs ØPolicy networks at different levels – EU / Regional / Local
 Communicating research results to policy makers Ø Essential to develop & sustain a dialogue Ø Language Ø Make it policy relevant. Examples: ‘Patterns of demographic ageing and related aspects’; ‘Sustainable Regional development from Rhetoric to Practice’; ‘Social impact Assessment in Regional & Land Use planning’ Ø Nature of the policy process
Communicating research results to policy makers Ø Essential to develop & sustain a dialogue Ø Language Ø Make it policy relevant. Examples: ‘Patterns of demographic ageing and related aspects’; ‘Sustainable Regional development from Rhetoric to Practice’; ‘Social impact Assessment in Regional & Land Use planning’ Ø Nature of the policy process
 Communicating research results to policy makers Ø Theory & Practice Ø Transfer of Learning Ø Consider a variety of communication formats to promote research findings: Examples: ‘Britain in 2011: Annual Magazine of the ESRC Community newsletters / Alumni news / www. Ø Think of How the research will be used and quoted. Ø Early dissemination of research e. g. Working papers.
Communicating research results to policy makers Ø Theory & Practice Ø Transfer of Learning Ø Consider a variety of communication formats to promote research findings: Examples: ‘Britain in 2011: Annual Magazine of the ESRC Community newsletters / Alumni news / www. Ø Think of How the research will be used and quoted. Ø Early dissemination of research e. g. Working papers.
 Communicating research results to policy makers Ø Quality is important: Need for internal & external validity. Ø Policy cycle: how do the research findings relate to the policy cycle? (see next slide). Ø Facilitate collaboration & multi – disciplinarity. Ø Utilise or develop policy networks.
Communicating research results to policy makers Ø Quality is important: Need for internal & external validity. Ø Policy cycle: how do the research findings relate to the policy cycle? (see next slide). Ø Facilitate collaboration & multi – disciplinarity. Ø Utilise or develop policy networks.
 Communicating research results to policy makers Ø Perceptions: Consider how different research disciplines may be perceived: (e. g. Economics / Sociology / Occupational Psychology / Political Science / Public Health /Science / Law). Ø Policy evaluation: Maximise utility of evaluation findings. Ø Highlight innovation & creativity: identify the value added contribution of the research. Define the policy challenge – make clear the policy recommendations but outline the limitations of the work.
Communicating research results to policy makers Ø Perceptions: Consider how different research disciplines may be perceived: (e. g. Economics / Sociology / Occupational Psychology / Political Science / Public Health /Science / Law). Ø Policy evaluation: Maximise utility of evaluation findings. Ø Highlight innovation & creativity: identify the value added contribution of the research. Define the policy challenge – make clear the policy recommendations but outline the limitations of the work.
 Communicating research results to policy makers Examples of research findings presented to policy officials Ø Fuel poverty Ø Devolution in practice Ø Implication of the ageing population Ø Equality issues Ø Early childhood disadvantage
Communicating research results to policy makers Examples of research findings presented to policy officials Ø Fuel poverty Ø Devolution in practice Ø Implication of the ageing population Ø Equality issues Ø Early childhood disadvantage
 Communicating research results to policy makers CONCLUSIONS Ø Identify policy implications of research findings in a comprehensible way. Ø Recognise the difficult choices policy makers have to make. Ø Be clear on the key messages for policy makers and other key stakeholders. Ø Need for ongoing dialogue - from design to dissemination.
Communicating research results to policy makers CONCLUSIONS Ø Identify policy implications of research findings in a comprehensible way. Ø Recognise the difficult choices policy makers have to make. Ø Be clear on the key messages for policy makers and other key stakeholders. Ø Need for ongoing dialogue - from design to dissemination.
 Communicating research results to policy makers CONCLUSIONS continued. . . Ø Recognise the complexity of the policy process: ‘…the complex interplay between political interests, competing discourse and the agency of multiple actors’. Ø Enhancing communications skills for researchers Ø Encourage the utilisation of research by policy practitioners
Communicating research results to policy makers CONCLUSIONS continued. . . Ø Recognise the complexity of the policy process: ‘…the complex interplay between political interests, competing discourse and the agency of multiple actors’. Ø Enhancing communications skills for researchers Ø Encourage the utilisation of research by policy practitioners
 Improving the links between research and policy Ø Devolution - opportunity for differentiated policy making Ø Professionalisation of policy making function Ø Potential for collaborative approaches Ø Dissemination of research results Ø Engagement of specialist staff in policy process Ø Utility of Research programmes Ø Contribution to ‘joined up’ thinking Ø Sustainable development agenda
Improving the links between research and policy Ø Devolution - opportunity for differentiated policy making Ø Professionalisation of policy making function Ø Potential for collaborative approaches Ø Dissemination of research results Ø Engagement of specialist staff in policy process Ø Utility of Research programmes Ø Contribution to ‘joined up’ thinking Ø Sustainable development agenda
 A Policymakers view of issues
A Policymakers view of issues
 policylink www. ofmdfmni. gov. uk/policylink
policylink www. ofmdfmni. gov. uk/policylink


