6f093b24f42e0d3a09ff9a432c9fa13d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 kpmg
kpmg
 Reference XXX 2 Information Risk Management E-Commerce Seminar University of Queensland Duncan C Martin KPMG dcmartin@kpmg. com. au kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 2 Information Risk Management E-Commerce Seminar University of Queensland Duncan C Martin KPMG dcmartin@kpmg. com. au kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 3 Disclaimer This presentation has been prepared by Duncan C Martin, of KPMG IRM in Brisbane. The views expressed are those of the author, and not necessarily those of KPMG kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 3 Disclaimer This presentation has been prepared by Duncan C Martin, of KPMG IRM in Brisbane. The views expressed are those of the author, and not necessarily those of KPMG kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 4 Agenda n A few basics n What do we mean by risk? n What’s special about e-Commerce risks? n Approaches to managing certain components of risk n Questions kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 4 Agenda n A few basics n What do we mean by risk? n What’s special about e-Commerce risks? n Approaches to managing certain components of risk n Questions kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 5 What is e-Commerce? n Internet-enabled commerce n ‘Sexy’ - but dangerous - Inward risks - hacking, denial of service - Outward risks - unauthorised disclosure of private information and IP n Global network of computer networks (Comparable to the telephone network) n No owner or single administrative body kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 5 What is e-Commerce? n Internet-enabled commerce n ‘Sexy’ - but dangerous - Inward risks - hacking, denial of service - Outward risks - unauthorised disclosure of private information and IP n Global network of computer networks (Comparable to the telephone network) n No owner or single administrative body kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 6 Types of e-Commerce - 1 n Business to Business (B 2 B) - Internet enabled relationships with business partners, customers, suppliers (extranets) n Business to Consumer (B 2 C) - Relationships with individual customers/end-users n Intra-Business (Intra-B) - Relationships within or between internal businesses/functional areas kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 6 Types of e-Commerce - 1 n Business to Business (B 2 B) - Internet enabled relationships with business partners, customers, suppliers (extranets) n Business to Consumer (B 2 C) - Relationships with individual customers/end-users n Intra-Business (Intra-B) - Relationships within or between internal businesses/functional areas kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 7 Types of e-Commerce - 2 n Customer to Business (C 2 B) - “Reverse” market, where customer dictates product/service and terms of delivery (Priceline) n Customer to Customer (C 2 C) - Consumers interacting directly to create spot markets (e. Bay) kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 7 Types of e-Commerce - 2 n Customer to Business (C 2 B) - “Reverse” market, where customer dictates product/service and terms of delivery (Priceline) n Customer to Customer (C 2 C) - Consumers interacting directly to create spot markets (e. Bay) kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 8 Typical stages of e-Commerce n Stage: 1 - establishing an Internet and e-Commerce presence through e-mail n Stage: 2 - establishing a visual e-Commerce presence with a pre-sale and post-sale web site n Stage: 3 - on-line order entry n Stage: 4 - internal integration of web based e-Commerce activities and “back office” functions n Stage: 5 - external integration of seller and buyer networks to allow automated supply-chain management n Stage: 6 - complete integration of technology including core technologies kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 8 Typical stages of e-Commerce n Stage: 1 - establishing an Internet and e-Commerce presence through e-mail n Stage: 2 - establishing a visual e-Commerce presence with a pre-sale and post-sale web site n Stage: 3 - on-line order entry n Stage: 4 - internal integration of web based e-Commerce activities and “back office” functions n Stage: 5 - external integration of seller and buyer networks to allow automated supply-chain management n Stage: 6 - complete integration of technology including core technologies kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 9 What is risk? “The exposure to the possibility of such things as economic or financial loss or gain, physical damage, injury or delay, as a consequence of pursuing a particular course of action. ” kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 9 What is risk? “The exposure to the possibility of such things as economic or financial loss or gain, physical damage, injury or delay, as a consequence of pursuing a particular course of action. ” kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 10 General risks n Some unique general risks present themselves: - Possible loss of public confidence (if control failures are publicised) - Failure to comply with legal and regulatory requirements (possibly in multiple jurisdictions) - Erosion of traditional control mechanisms (loss of ‘common sense’ and compensating controls) - Technical complexity of infrastructure and systems - High reliance on third-parties (Trust) kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 10 General risks n Some unique general risks present themselves: - Possible loss of public confidence (if control failures are publicised) - Failure to comply with legal and regulatory requirements (possibly in multiple jurisdictions) - Erosion of traditional control mechanisms (loss of ‘common sense’ and compensating controls) - Technical complexity of infrastructure and systems - High reliance on third-parties (Trust) kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 11 Specific risks n Specific e-Commerce risks are many and varied. It is convenient to group them as follows: - Strategic risks - Project and operational risks - Infrastructure risks kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 11 Specific risks n Specific e-Commerce risks are many and varied. It is convenient to group them as follows: - Strategic risks - Project and operational risks - Infrastructure risks kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 12 Strategic risks n Risks to the e-Commerce initiative due to the overall strategy/plan - kpmg E-Commerce strategy itself Senior management support Competing organisational priorities Legal and regulatory issues Invalid assumptions © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 12 Strategic risks n Risks to the e-Commerce initiative due to the overall strategy/plan - kpmg E-Commerce strategy itself Senior management support Competing organisational priorities Legal and regulatory issues Invalid assumptions © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 13 Project/operational risks n Risks due to the implementation project itself, IT operations, and routine use of the system - kpmg Financial and human resources In-house expertise Outsource partners Stakeholders Support processes Monitoring © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 13 Project/operational risks n Risks due to the implementation project itself, IT operations, and routine use of the system - kpmg Financial and human resources In-house expertise Outsource partners Stakeholders Support processes Monitoring © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 14 Infrastructure risks n Risks due to the underlying application and technical (hardware and network) infrastructures - kpmg The technical infrastructure Security over the technical infrastructure System availability/reliability Application security controls Application processing controls Interfaces with other systems © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 14 Infrastructure risks n Risks due to the underlying application and technical (hardware and network) infrastructures - kpmg The technical infrastructure Security over the technical infrastructure System availability/reliability Application security controls Application processing controls Interfaces with other systems © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 15 What and where is the risk? n What is the approach to managing strategic risk? n What is the approach to managing project risk? n What is the approach to managing information and technology risk? kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 15 What and where is the risk? n What is the approach to managing strategic risk? n What is the approach to managing project risk? n What is the approach to managing information and technology risk? kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 16 Assessing the risk n E-Commerce strategy relative to overall business goals n E-Commerce program management n Operations management n Application infrastructure n Technology infrastructure kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 16 Assessing the risk n E-Commerce strategy relative to overall business goals n E-Commerce program management n Operations management n Application infrastructure n Technology infrastructure kpmg © 1999 KPMG
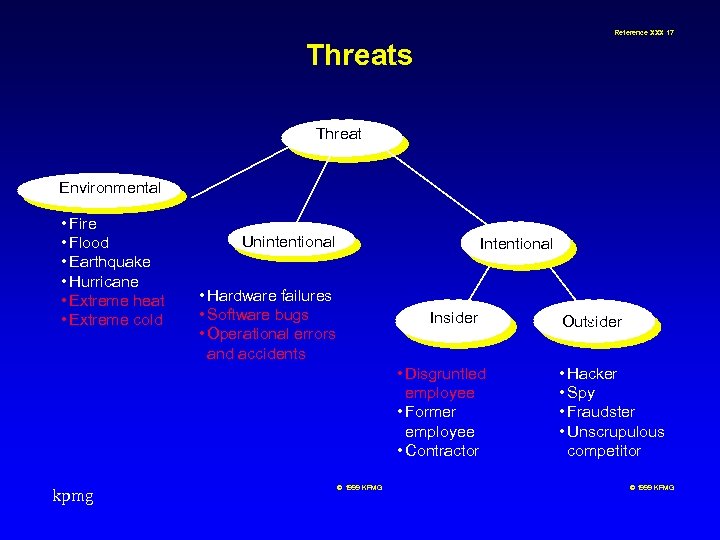 Reference XXX 17 Threats Threat Environmental • Fire • Flood • Earthquake • Hurricane • Extreme heat • Extreme cold Unintentional Intentional • Hardware failures • Software bugs • Operational errors and accidents Insider • Disgruntled employee • Former employee • Contractor kpmg © 1999 KPMG Outsider • Hacker • Spy • Fraudster • Unscrupulous competitor © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 17 Threats Threat Environmental • Fire • Flood • Earthquake • Hurricane • Extreme heat • Extreme cold Unintentional Intentional • Hardware failures • Software bugs • Operational errors and accidents Insider • Disgruntled employee • Former employee • Contractor kpmg © 1999 KPMG Outsider • Hacker • Spy • Fraudster • Unscrupulous competitor © 1999 KPMG
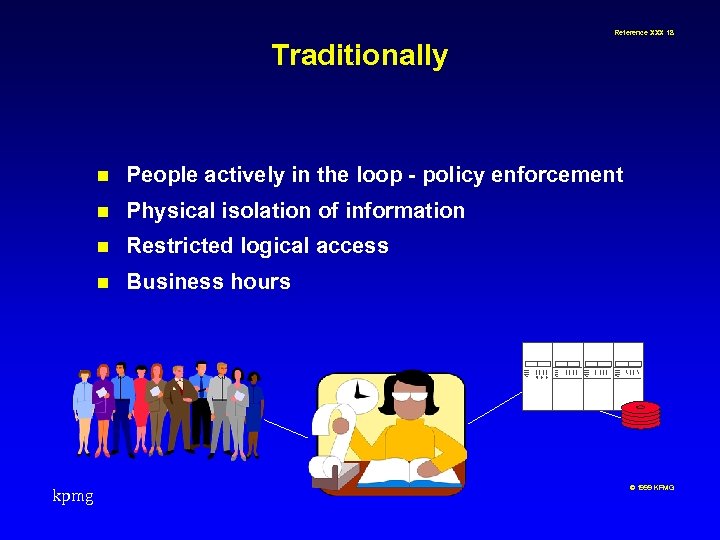 Reference XXX 18 Traditionally n n Physical isolation of information n Restricted logical access n kpmg People actively in the loop - policy enforcement Business hours © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 18 Traditionally n n Physical isolation of information n Restricted logical access n kpmg People actively in the loop - policy enforcement Business hours © 1999 KPMG
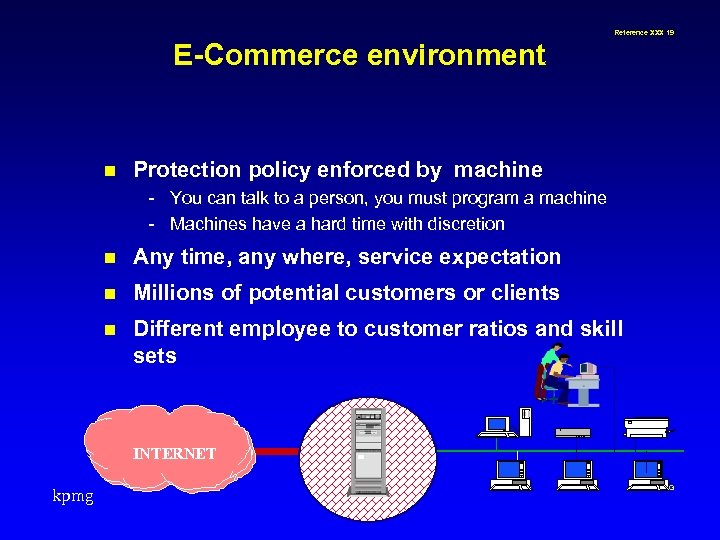 Reference XXX 19 E-Commerce environment n Protection policy enforced by machine - You can talk to a person, you must program a machine - Machines have a hard time with discretion n Any time, any where, service expectation n Millions of potential customers or clients n Different employee to customer ratios and skill sets INTERNET kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 19 E-Commerce environment n Protection policy enforced by machine - You can talk to a person, you must program a machine - Machines have a hard time with discretion n Any time, any where, service expectation n Millions of potential customers or clients n Different employee to customer ratios and skill sets INTERNET kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 20 Objectives n Making sure the data is not altered as it passes between one end point and another - The use of signatures to ensure the data stream is not altered n Making sure you know who it is you're talking to at the other end - Authentication to verify the remote user n Preventing unauthorised third parties from eavesdropping on your conversation - Encryption to prevent eavesdropping kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 20 Objectives n Making sure the data is not altered as it passes between one end point and another - The use of signatures to ensure the data stream is not altered n Making sure you know who it is you're talking to at the other end - Authentication to verify the remote user n Preventing unauthorised third parties from eavesdropping on your conversation - Encryption to prevent eavesdropping kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 21 Traditional security mechanisms n Confidentiality -Locked file cabinets, drawers, safes, envelopes, personnel, service counters n Integrity -Product seals, shrink-wrap, signatures, barcodes n Availability -Multiple locations, personnel, alternate delivery options n Non-repudiation -Signatures, confirmations, receipts kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 21 Traditional security mechanisms n Confidentiality -Locked file cabinets, drawers, safes, envelopes, personnel, service counters n Integrity -Product seals, shrink-wrap, signatures, barcodes n Availability -Multiple locations, personnel, alternate delivery options n Non-repudiation -Signatures, confirmations, receipts kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 22 E-Commerce mechanisms n Confidentiality - Data encryption, automated access controls, access control lists, passwords, tokens, biometrics n Integrity - Digital signatures, permissions, hash algorithms, audit trails n Availability - System redundancies, back-ups, off-site storage, hot/cold recovery sites, fail-over n Non-repudiation - Audit trails and logs, digital signatures and certificates kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 22 E-Commerce mechanisms n Confidentiality - Data encryption, automated access controls, access control lists, passwords, tokens, biometrics n Integrity - Digital signatures, permissions, hash algorithms, audit trails n Availability - System redundancies, back-ups, off-site storage, hot/cold recovery sites, fail-over n Non-repudiation - Audit trails and logs, digital signatures and certificates kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 23 Encryption n Plaintext to ciphertext n Renders message unreadable n Secret key method - same key to encrypts and decrypts n Public key method - two keys, one kept secret and never transmitted, and the other made public. (Public key method is used to safely send the secret key to the recipient so that the message can be encrypted using the faster secret key algorithm). kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 23 Encryption n Plaintext to ciphertext n Renders message unreadable n Secret key method - same key to encrypts and decrypts n Public key method - two keys, one kept secret and never transmitted, and the other made public. (Public key method is used to safely send the secret key to the recipient so that the message can be encrypted using the faster secret key algorithm). kpmg © 1999 KPMG
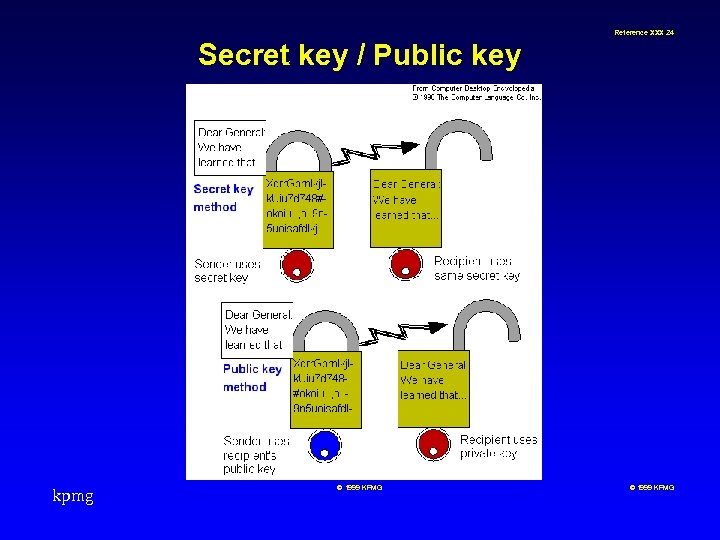 Reference XXX 24 Secret key / Public key kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 24 Secret key / Public key kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 25 Authentication The truth is not always out there! Can I trust you ? Who are you ? What can you do ? kpmg Is anybody listening ? © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 25 Authentication The truth is not always out there! Can I trust you ? Who are you ? What can you do ? kpmg Is anybody listening ? © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 26 Authentication kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 26 Authentication kpmg © 1999 KPMG
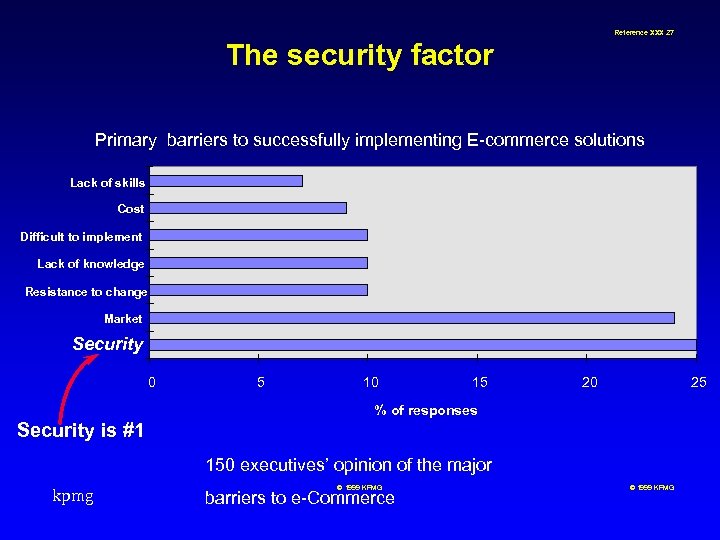 Reference XXX 27 The security factor Primary barriers to successfully implementing E-commerce solutions Lack of skills Cost Difficult to implement Lack of knowledge Resistance to change Market Security 0 5 10 15 20 25 % of responses Security is #1 150 executives’ opinion of the major kpmg © 1999 KPMG barriers to e-Commerce © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 27 The security factor Primary barriers to successfully implementing E-commerce solutions Lack of skills Cost Difficult to implement Lack of knowledge Resistance to change Market Security 0 5 10 15 20 25 % of responses Security is #1 150 executives’ opinion of the major kpmg © 1999 KPMG barriers to e-Commerce © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 28 How real is the risk? n Of approximately 643 Surveyed organisations - 90% detected security breaches in last 12 months 85% detected computer virii 79% detected employee abuse of Internet privileges 70% reported serious breaches, (inc. Theft of I. P. Financial Loss, System Penetration and Do. S Attacks) - 74% acknowledged loss due to computer breaches n Only 42% (273) could quantify loss - this was a total of US$266 million Source: “The Computer Security Institute - “ 2000 Computer Crime Security Survey” - March 2000 kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 28 How real is the risk? n Of approximately 643 Surveyed organisations - 90% detected security breaches in last 12 months 85% detected computer virii 79% detected employee abuse of Internet privileges 70% reported serious breaches, (inc. Theft of I. P. Financial Loss, System Penetration and Do. S Attacks) - 74% acknowledged loss due to computer breaches n Only 42% (273) could quantify loss - this was a total of US$266 million Source: “The Computer Security Institute - “ 2000 Computer Crime Security Survey” - March 2000 kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 29 And in the e-Commerce environment n 61 respondents had experienced sabotage of networks at an estimated loss of US$27 Million - (Last year US$11 Million) n E-Commerce - kpmg 93% of respondents have www sites 64% of those attacked reported Web-site vandalism 60% reported Denial of Service (Do. S) attacks 43% conduct e-Commerce (30% in 1999) 19% had unauthorised access 32% didn’t know if their systems had been misused 3% reported financial fraud © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 29 And in the e-Commerce environment n 61 respondents had experienced sabotage of networks at an estimated loss of US$27 Million - (Last year US$11 Million) n E-Commerce - kpmg 93% of respondents have www sites 64% of those attacked reported Web-site vandalism 60% reported Denial of Service (Do. S) attacks 43% conduct e-Commerce (30% in 1999) 19% had unauthorised access 32% didn’t know if their systems had been misused 3% reported financial fraud © 1999 KPMG
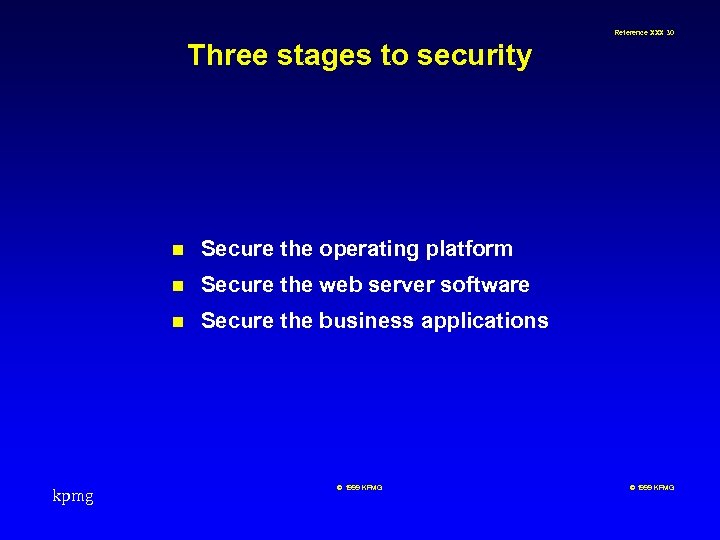 Reference XXX 30 Three stages to security n n Secure the web server software n kpmg Secure the operating platform Secure the business applications © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 30 Three stages to security n n Secure the web server software n kpmg Secure the operating platform Secure the business applications © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 31 Secure the operating environment n Remove unnecessary services n Restrict access - physical - logical - ‘two out of three’ n n kpmg Keep the OS up to date Keep it simple © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 31 Secure the operating environment n Remove unnecessary services n Restrict access - physical - logical - ‘two out of three’ n n kpmg Keep the OS up to date Keep it simple © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 32 Secure the web server n n Keep the web server software updated n kpmg Change the shipped/standard defaults Audit web server logs © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 32 Secure the web server n n Keep the web server software updated n kpmg Change the shipped/standard defaults Audit web server logs © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 33 Secure the application n n Keep up to date - bug alerts n Security awareness n Segregation of duties n kpmg Test the software Knowledgable staff © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 33 Secure the application n n Keep up to date - bug alerts n Security awareness n Segregation of duties n kpmg Test the software Knowledgable staff © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 34 Firewalls n Additional protection (never run the web server on the Firewall itself) n Configurations - Sacrificial lamb - network-firewall-web server-Internet - DMZ (De. Militarised Zone) - n Internal network-firewall-web server-firewall-Internet Policies - “Except for” - academia - “Only” - corporations n kpmg Audit firewall logs © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 34 Firewalls n Additional protection (never run the web server on the Firewall itself) n Configurations - Sacrificial lamb - network-firewall-web server-Internet - DMZ (De. Militarised Zone) - n Internal network-firewall-web server-firewall-Internet Policies - “Except for” - academia - “Only” - corporations n kpmg Audit firewall logs © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 35 Securing web servers n Security tools - Security scanners - Intrusion detection systems - File modification monitors n Hacker deception tools - Dynamic memory buffering - False responses n Third party services - Penetration testing - Certification kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 35 Securing web servers n Security tools - Security scanners - Intrusion detection systems - File modification monitors n Hacker deception tools - Dynamic memory buffering - False responses n Third party services - Penetration testing - Certification kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 36 Security policy n Responsibility and accountability - kpmg Internet related Use of tools & review of logs Incident handling and response Recovery procedures Communication and update Dedicated security resources Expert resources and reviews © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 36 Security policy n Responsibility and accountability - kpmg Internet related Use of tools & review of logs Incident handling and response Recovery procedures Communication and update Dedicated security resources Expert resources and reviews © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 37 Summary n Multi-layered approach - Platform - Web server - Web applications n n Security policy n Security is the continuous assessment of risk against expense n kpmg Firewalls and tools Security is an enabling technology for Commerce © 1999 KPMG e- © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 37 Summary n Multi-layered approach - Platform - Web server - Web applications n n Security policy n Security is the continuous assessment of risk against expense n kpmg Firewalls and tools Security is an enabling technology for Commerce © 1999 KPMG e- © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 38 Common KPMG findings n Blind reliance on the technology - plug and play n Inadequate network intrusion monitoring controls n Policies and procedures are incomplete or weak kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 38 Common KPMG findings n Blind reliance on the technology - plug and play n Inadequate network intrusion monitoring controls n Policies and procedures are incomplete or weak kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 39 Key messages n Security & e-Commerce have a symbiotic relationship n Risks cannot be totally eliminated but controlled with solutions and procedures n Clients are evaluating PKI solutions for e. Commerce needs n Security risks in e-Commerce are real kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 39 Key messages n Security & e-Commerce have a symbiotic relationship n Risks cannot be totally eliminated but controlled with solutions and procedures n Clients are evaluating PKI solutions for e. Commerce needs n Security risks in e-Commerce are real kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 Reference XXX 40 Questions kpmg © 1999 KPMG
Reference XXX 40 Questions kpmg © 1999 KPMG
 kpmg
kpmg


