KB&M (Week13, Global challenge).ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Korean Business & Management: global challenge of Korean firms Week 13

Table of content 1. The global challenge of Korean firms 2. How Korean firms deal with globalization 3. Global coordination and control 4. Conclusion 2

1. The global challenge of Korean firms n n n The outstanding of performance many Korean firms was due to their peculiar management systems Peculiar management systems are in three core areas: Strategy, leadership and HRM The three cores were highly related to the home country’s history, culture, and society 3

1. The global challenge of Korean firms (Cont. ) However, two basic questions remain - They are how and to what extent can Korean management systems can be transferred to other countries and - How can Korean firms maintain their organizational efficiency and effectiveness when going global? n 4

1. The global challenge of Korean firms (Cont. ) However, two basic questions remain - They are how and to what extent can Korean management systems can be transferred to other countries and - How can Korean firms maintain their organizational efficiency and effectiveness when going global? n 5

1. The global challenge of Korean firms (Cont. ) Koreans firms face two global challenges: - They need to be responsive to local environment in each country and region and - They have to maintain high efficiency level in the world wide operation n Unfortunately, many Korean firms face difficulties of meeting both global responsiveness and global efficiency 6

1. The global challenge of Korean firms (Cont. ) Koreans firms’ global responsiveness is particularly in great challenge - They mostly operated in Asian countries - When going into other western world where culturally and institutionally different environment, Korean firms should recognize that there will be huge managerial and customer differences n 7

1. The global challenge of Korean firms (Cont. ) The need for localization has two main aspects: - First, Korean firms need to understand specific needs and requirements of various external stakeholders such as customer, suppliers, government agencies, labor unions and the media - Second, need to develop policies in order to manage their international subsidiaries and local workforces in each countries effectively n 8

1. The global challenge of Korean firms (Cont. ) The need for global efficiency is more challeging to Korean firms - They have been used to operating in rather small countries, relying heavily on face-to-face communications - It constitutes huge task for them to operate in complex networks in geographically dispersed locations n 9

2. How Korean firms deal with globalization The need for localization of supplier and customer linkages - Korean firms’ global operation tend to be wholly own subsidiaries - Major Korean Chaebols’ localization efforts were facilitated by existence of major suppliers within their groups - Finding the right foreign local partners are essential in the global business n 10

2. How Korean firms deal with globalization (cont. ) The clear priority should be creating reliable local supply chains - When internal suppliers are not available, Korean firms should flexibly be engaged with local external partners - The supply chain localization has proven to be a major asset in customer relations, in emerging market in particular n 11

2. How Korean firms deal with globalization (cont. ) The Korean firms have to customize their product and service according to the local need and preferences - A good example is LG’s Mecca phone in Muslim countries, Prada Phone in Europe, etc. - Hyundai Motor’s tailor made marketing practice in the US n 12

2. How Korean firms deal with globalization n n (cont. ) So far, the Korean firms engaged in continuously localizing customer relationships in different countries by intensive R&D, marketing and service efforts However, the localization efforts are still far way to go and should concern more on transferring important aspects of their management aspects to other countries 13

2. How Korean firms deal with globalization (cont. ) Management of international subsidiaries - Many Korean firms tend to replicate home operation with the foreign subsidiaries - Seniority and strict organizational hierarchy tend to be pronounced in foreign operation - Some of the leading firms try to change the old and classic foreign subsidiary management n 14
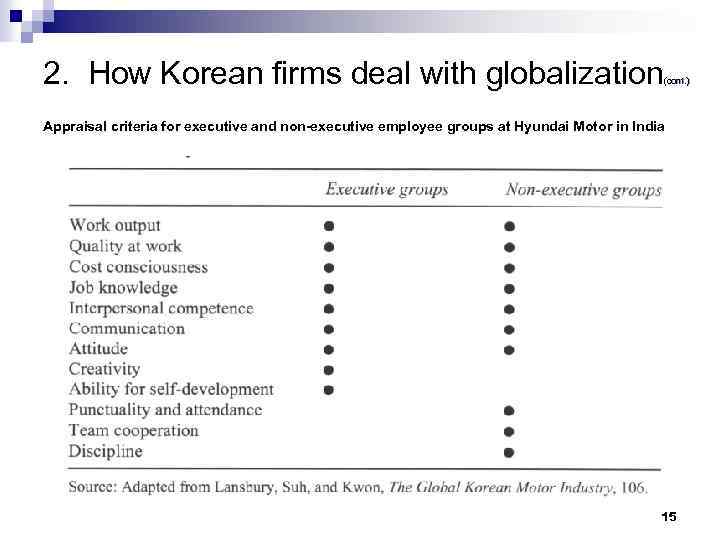
2. How Korean firms deal with globalization (cont. ) Appraisal criteria for executive and non-executive employee groups at Hyundai Motor in India 15

2. How Korean firms deal with globalization (cont. ) When transferring Korean management style to foreign subsidiaries, they should remind the cultural distance - Western culture may be hard to accept hierarchical culture and strong teamwork - Flexible management is necessary in other culture n 16

2. How Korean firms deal with globalization n n (cont. ) Elevating foreign language proficiency and cross -cultural competence of expatriate managers are essential In addition, Korean companies should also make intense efforts to recruit outstanding local talent for managerial positions at their international subsidiaries 17

2. How Korean firms deal with globalization n (cont. ) Taken together, Most Korean firms tend to follow the model of their domestic operation in their international operation Instead of this, they should build more global operational competencies by increasingly relying on local managers in international operation At the same time, extensive training them to make them familiar with Korean management system and corporate culture should follow 18

3. Global coordination and control Companies need to coordinate and control their global operations on several levels - First, to determine which activities are conducted where - Second, to develop appropriate organizational structures for the activities n 19

3. Global coordination and control (cont. ) Korean firms tend to replicate their integrated domestic operation by building large manufacturing complex in foreign countries - ex. , Lotte Towns in n Korean firms are also pursuing flexible design of overseas operations - ex. , Hyundai in US n But, Korean firms prefer centralized control system from the HQ n 20

3. Global coordination and control (cont. ) Some companies, however, have given more autonomy to international subsidiaries - The HQ only gives the guidelines and sets the business targets, giving subsidiary managers a free hand in day-to-day operation on how to achieve the targets n Establishing the regional headquarter is popular these days n 21

3. Global coordination and control n n n (cont. ) Overall, gradual decentralization of control can be observed in the global operations of Korean firms However, compared with western companies, Korean ones are still centralized and hierarchical Korean firms are willing to change their global structure and coordination by imposing more role on expatriate managers and frequent communications with int’l subsidiaries 22

4. Conclusion n Korean firms are facing global efficiency and local responsiveness in their int’l operation When setting int’l production subsidiaries, Korean firms used to prefer vertically integrated SCM using internal suppliers However, this classical method confronted Korean firms with lack of meeting global-local dilemma 23

4. Conclusion n (cont. ) Localization of the int’l subsidiaries was also the challenging issue of Korean firms Insufficient knowledge of local knowledge and language have been the key problems of localization However, these problems are diminishing in recent years by conducting extensive training programs 24

4. Conclusion n (cont. ) The characteristics of Korean firms in int’l operation is to place high value on integrating global operation and achieving efficiency Although not all their int’l operation successful, their attempts to adjust to ever changing global environment continue In this sense, they are now gearing towards more on swift, flexible and decisive strategic responses in the world market 25
KB&M (Week13, Global challenge).ppt