544c12fc6b7f5842aab688cbff162784.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Terminology, Interactive Media and Standards - A Scenario toward Personalized Interactive Knowledge Services Key-Sun Choi and Yeun-Bae Kim* KAIST Korterm, NHK STRL* kschoi@cs. kaist. ac. kr http: //www. korterm. org/
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Terminology, Interactive Media and Standards - A Scenario toward Personalized Interactive Knowledge Services Key-Sun Choi and Yeun-Bae Kim* KAIST Korterm, NHK STRL* kschoi@cs. kaist. ac. kr http: //www. korterm. org/
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Outline q. Integrating the multiple number of lexical knowledge base q. Question-answering for what-, and why-type question q. By causality probing q. Integration of Video clipping of answer segments
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Outline q. Integrating the multiple number of lexical knowledge base q. Question-answering for what-, and why-type question q. By causality probing q. Integration of Video clipping of answer segments
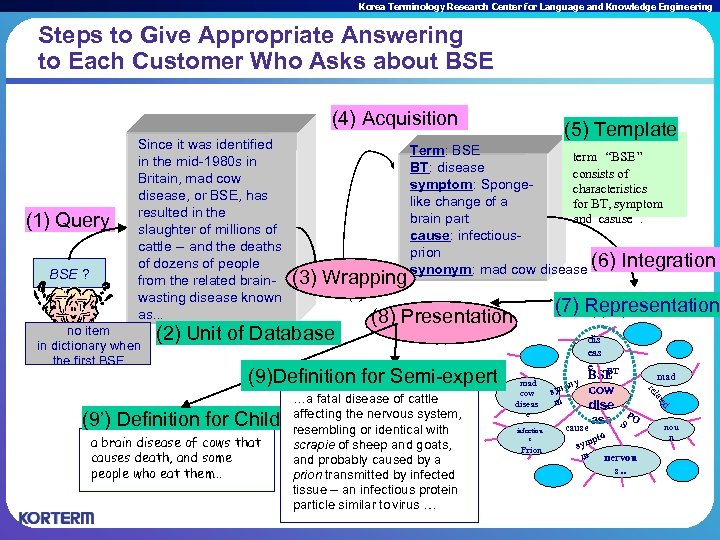 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Steps to Give Appropriate Answering to Each Customer Who Asks about BSE (4) Acquisition (1) Query BSE ? Since it was identified in the mid-1980 s in Britain, mad cow disease, or BSE, has resulted in the slaughter of millions of cattle -- and the deaths of dozens of people from the related brainwasting disease known as. . . no item in dictionary when the first BSE (5) template : (3) Wrapping Term: BSE term “BSE ” BT: disease consists of symptom: Spongecharacteristics like change of a for BT, symptom and casuse. brain part cause: infectiousprion synonym: mad cow disease (6) Integration synonym: mad cow (3) (2) unit of (2) Unit of Database Prion cow dise ase cause mad S PO pto sym m nervou s. . d infectiou s ny syno m t t ate …a fatal disease of cattle affecting the nervous system, resembling or identical with scrapie of sheep and goats, and probably caused by a prion transmitted by infected tissue -- an infectious protein particle similar to virus … mad cow diseas e dis eas e BT BSE rl rl rel a brain disease of cows that causes death, and some people who eat them… (7) Representation (7) representation (8) Presentation (9) definition for semi-expert (9)Definition for Semi-expert (9’) definition for child (9’) Definition for Child (5) Template nou n
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Steps to Give Appropriate Answering to Each Customer Who Asks about BSE (4) Acquisition (1) Query BSE ? Since it was identified in the mid-1980 s in Britain, mad cow disease, or BSE, has resulted in the slaughter of millions of cattle -- and the deaths of dozens of people from the related brainwasting disease known as. . . no item in dictionary when the first BSE (5) template : (3) Wrapping Term: BSE term “BSE ” BT: disease consists of symptom: Spongecharacteristics like change of a for BT, symptom and casuse. brain part cause: infectiousprion synonym: mad cow disease (6) Integration synonym: mad cow (3) (2) unit of (2) Unit of Database Prion cow dise ase cause mad S PO pto sym m nervou s. . d infectiou s ny syno m t t ate …a fatal disease of cattle affecting the nervous system, resembling or identical with scrapie of sheep and goats, and probably caused by a prion transmitted by infected tissue -- an infectious protein particle similar to virus … mad cow diseas e dis eas e BT BSE rl rl rel a brain disease of cows that causes death, and some people who eat them… (7) Representation (7) representation (8) Presentation (9) definition for semi-expert (9)Definition for Semi-expert (9’) definition for child (9’) Definition for Child (5) Template nou n
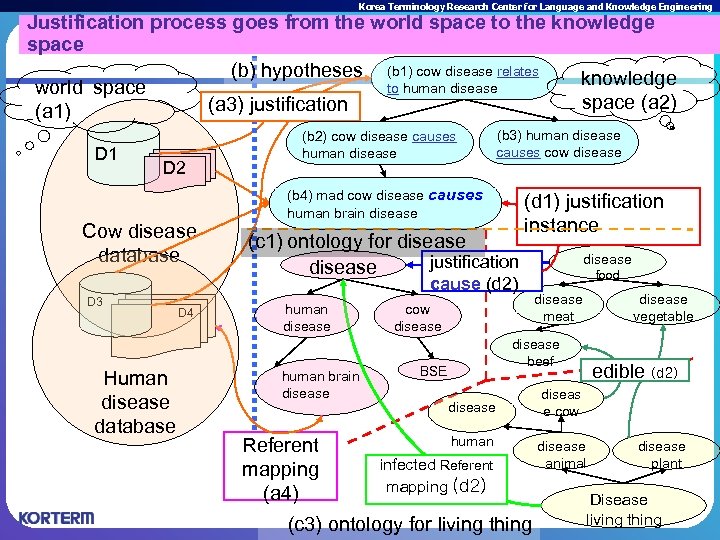 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Justification process goes from the world space to the knowledge space (b) hypotheses (b 1) cow disease relates knowledge to human disease world space (a 2) (a 3) justification (a 1) D 1 D 2 Cow disease database (b 2) cow disease causes human disease (b 3) human disease causes cow disease (b 4) mad cow disease causes human brain disease (d 1) justification instance (c 1) ontology for disease justification disease cause (d 2) D 3 Human disease database D 4 human disease human brain disease Referent mapping (a 4) cow disease food disease meat disease beef BSE disease human infected Referent mapping (d 2) (c 3) ontology for living thing disease vegetable edible (d 2) diseas e cow disease animal disease plant Disease living thing
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Justification process goes from the world space to the knowledge space (b) hypotheses (b 1) cow disease relates knowledge to human disease world space (a 2) (a 3) justification (a 1) D 1 D 2 Cow disease database (b 2) cow disease causes human disease (b 3) human disease causes cow disease (b 4) mad cow disease causes human brain disease (d 1) justification instance (c 1) ontology for disease justification disease cause (d 2) D 3 Human disease database D 4 human disease human brain disease Referent mapping (a 4) cow disease food disease meat disease beef BSE disease human infected Referent mapping (d 2) (c 3) ontology for living thing disease vegetable edible (d 2) diseas e cow disease animal disease plant Disease living thing
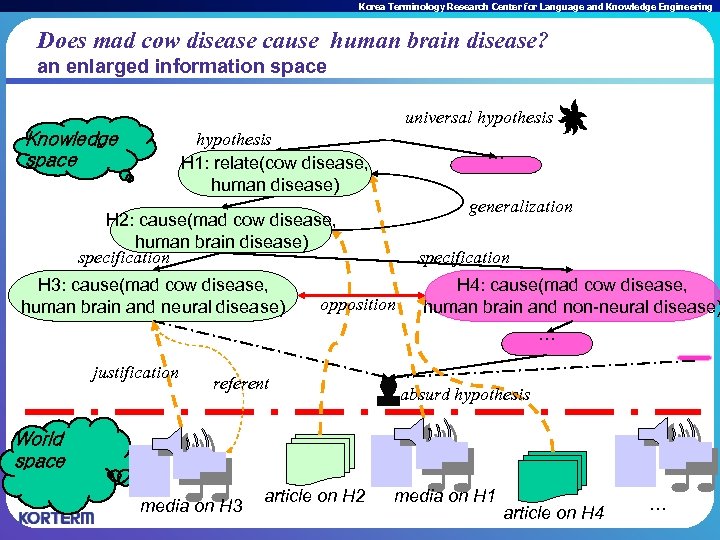 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Does mad cow disease cause human brain disease? an enlarged information space universal hypothesis Knowledge space hypothesis H 1: relate(cow disease, human disease) … generalization H 2: cause(mad cow disease, human brain disease) specification H 3: cause(mad cow disease, human brain and neural disease) specification opposition H 4: cause(mad cow disease, human brain and non-neural disease) … justification referent absurd hypothesis World space media on H 3 article on H 2 media on H 1 article on H 4 …
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Does mad cow disease cause human brain disease? an enlarged information space universal hypothesis Knowledge space hypothesis H 1: relate(cow disease, human disease) … generalization H 2: cause(mad cow disease, human brain disease) specification H 3: cause(mad cow disease, human brain and neural disease) specification opposition H 4: cause(mad cow disease, human brain and non-neural disease) … justification referent absurd hypothesis World space media on H 3 article on H 2 media on H 1 article on H 4 …
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Construction of knowledge space q How to construct the knowledge space and its linkage to the associated justification world space q By Experienced humans or (Semi-)automatic machines q Knowledge Discovery from Text
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Construction of knowledge space q How to construct the knowledge space and its linkage to the associated justification world space q By Experienced humans or (Semi-)automatic machines q Knowledge Discovery from Text
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Tell me whether a mad cow disease will cause a human brain disease. v Where is relevant resources in response to a given knowledge request? Ø v How to meta-data catalogs by categorizing the information content in each repository Information Seeking Problem
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Tell me whether a mad cow disease will cause a human brain disease. v Where is relevant resources in response to a given knowledge request? Ø v How to meta-data catalogs by categorizing the information content in each repository Information Seeking Problem
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Does the “mad cow disease” cause the “human brain disease”? q What is the correlation between “mad cow disease” and “human disease”? Where is the related repository? the human disease repository, and The mad cow disease repository. q Knowledge Seeking Problem
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Does the “mad cow disease” cause the “human brain disease”? q What is the correlation between “mad cow disease” and “human disease”? Where is the related repository? the human disease repository, and The mad cow disease repository. q Knowledge Seeking Problem
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Tell me whether a mad cow disease will cause a human brain disease. q How to correlate concepts - Find possible relationships between animal disease and human disease Ø Ø Link a animal disease record with the corresponding a human disease report. What is shared ontology? Ø Ø What is related contextual ontology? Ø Ø Disease, virus, … Food chain, time period How to standardize that? Ø Ø ISO/TC 37 MPEG 7
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Tell me whether a mad cow disease will cause a human brain disease. q How to correlate concepts - Find possible relationships between animal disease and human disease Ø Ø Link a animal disease record with the corresponding a human disease report. What is shared ontology? Ø Ø What is related contextual ontology? Ø Ø Disease, virus, … Food chain, time period How to standardize that? Ø Ø ISO/TC 37 MPEG 7
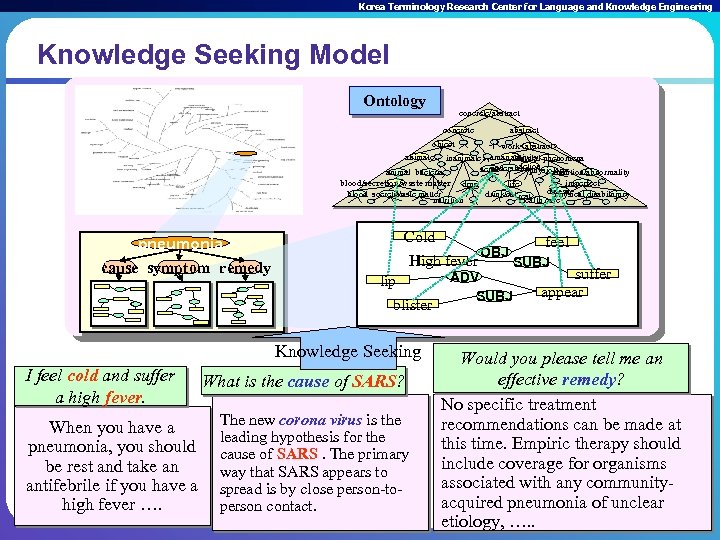 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Knowledge Seeking Model Ontology concrete/abstract concrete abstract object work
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Knowledge Seeking Model Ontology concrete/abstract concrete abstract object work
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Knowledge Seeking q Necessity of Knowledge Seeking Questions requiring -- "why", "what" , "how“ type questions q Problems of Knowledge Seeking Justification Probing on knowledge How to utilize various Knowledge resources q Goal Building an algorithm for searching some topical paths in order to find causal explanations for questions E. g. , “Why do patients pay money to doctors? ”
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Knowledge Seeking q Necessity of Knowledge Seeking Questions requiring -- "why", "what" , "how“ type questions q Problems of Knowledge Seeking Justification Probing on knowledge How to utilize various Knowledge resources q Goal Building an algorithm for searching some topical paths in order to find causal explanations for questions E. g. , “Why do patients pay money to doctors? ”
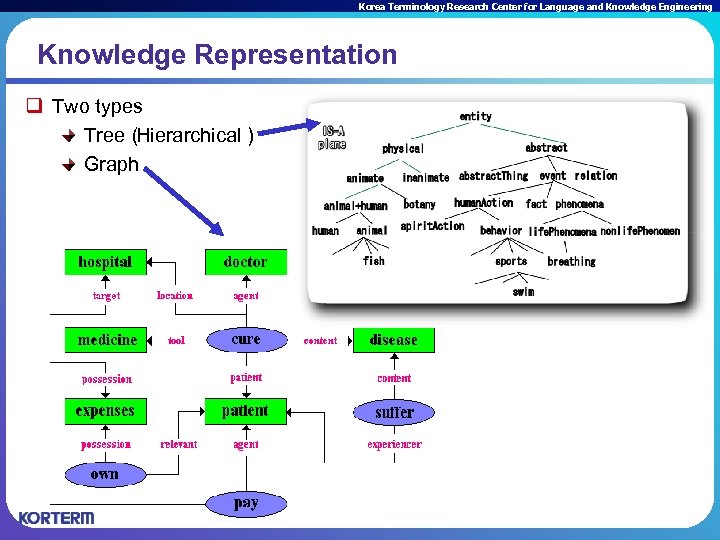 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Knowledge Representation q Two types Tree( Hierarchical) Graph
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Knowledge Representation q Two types Tree( Hierarchical) Graph
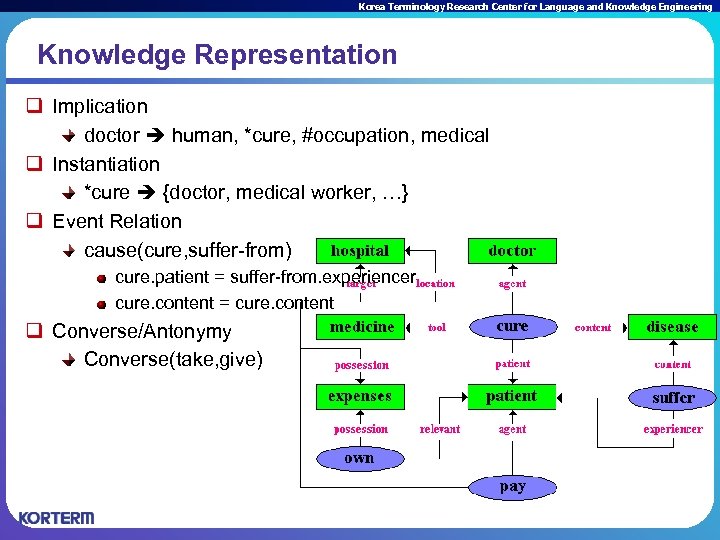 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Knowledge Representation q Implication doctor human, *cure, #occupation, medical q Instantiation *cure {doctor, medical worker, …} q Event Relation cause(cure, suffer-from) cure. patient = suffer-from. experiencer cure. content = cure. content q Converse/Antonymy Converse(take, give)
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Knowledge Representation q Implication doctor human, *cure, #occupation, medical q Instantiation *cure {doctor, medical worker, …} q Event Relation cause(cure, suffer-from) cure. patient = suffer-from. experiencer cure. content = cure. content q Converse/Antonymy Converse(take, give)
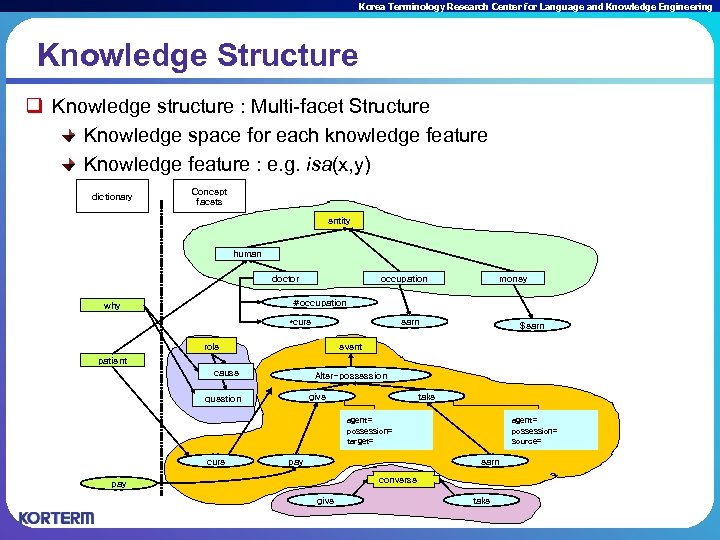 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Knowledge Structure q Knowledge structure : Multi-facet Structure Knowledge space for each knowledge feature Knowledge feature : e. g. isa(x, y) dictionary Concept facets entity human 人間 doctor money occupation #occupation why *cure earn role $earn event patient cause Alter-possession give question take agent= possession= target= cure pay 支払い agent= possession= source= earn converse pay give take
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Knowledge Structure q Knowledge structure : Multi-facet Structure Knowledge space for each knowledge feature Knowledge feature : e. g. isa(x, y) dictionary Concept facets entity human 人間 doctor money occupation #occupation why *cure earn role $earn event patient cause Alter-possession give question take agent= possession= target= cure pay 支払い agent= possession= source= earn converse pay give take
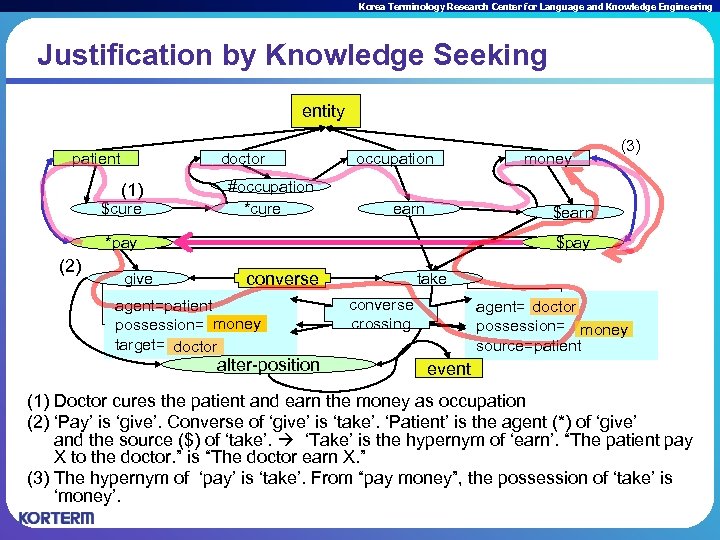 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Justification by Knowledge Seeking entity patient doctor (1) $cure #occupation *cure occupation earn give (3) $earn *pay (2) money $pay converse agent=patient possession= money target= doctor alter-position take converse crossing agent= doctor possession= money source=patient event (1) Doctor cures the patient and earn the money as occupation (2) ‘Pay’ is ‘give’. Converse of ‘give’ is ‘take’. ‘Patient’ is the agent (*) of ‘give’ and the source ($) of ‘take’. ‘Take’ is the hypernym of ‘earn’. “The patient pay X to the doctor. ” is “The doctor earn X. ” (3) The hypernym of ‘pay’ is ‘take’. From “pay money”, the possession of ‘take’ is ‘money’.
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Justification by Knowledge Seeking entity patient doctor (1) $cure #occupation *cure occupation earn give (3) $earn *pay (2) money $pay converse agent=patient possession= money target= doctor alter-position take converse crossing agent= doctor possession= money source=patient event (1) Doctor cures the patient and earn the money as occupation (2) ‘Pay’ is ‘give’. Converse of ‘give’ is ‘take’. ‘Patient’ is the agent (*) of ‘give’ and the source ($) of ‘take’. ‘Take’ is the hypernym of ‘earn’. “The patient pay X to the doctor. ” is “The doctor earn X. ” (3) The hypernym of ‘pay’ is ‘take’. From “pay money”, the possession of ‘take’ is ‘money’.
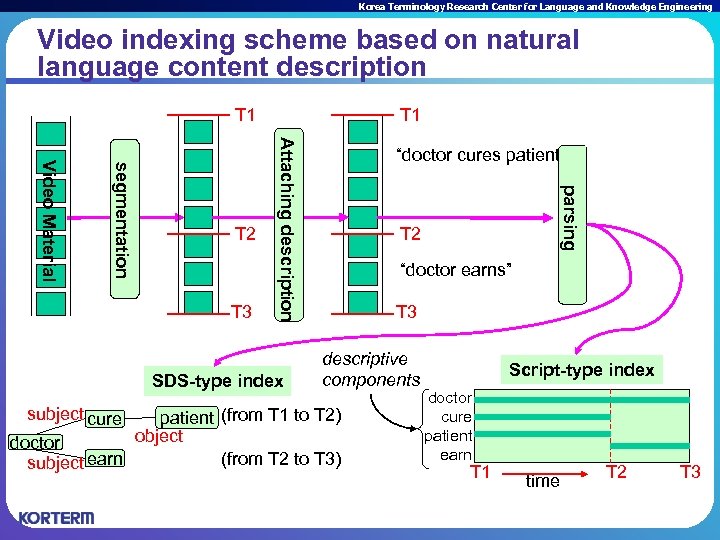 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Video indexing scheme based on natural language content description T 1 SDS-type index subject cure “doctor cures patient” parsing T 3 Attaching description segmentation Video Material T 2 T 1 T 2 “doctor earns” T 3 descriptive components patient (from T 1 to T 2) object doctor (from T 2 to T 3) subject earn Script-type index doctor cure patient earn T 1 time T 2 T 3
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Video indexing scheme based on natural language content description T 1 SDS-type index subject cure “doctor cures patient” parsing T 3 Attaching description segmentation Video Material T 2 T 1 T 2 “doctor earns” T 3 descriptive components patient (from T 1 to T 2) object doctor (from T 2 to T 3) subject earn Script-type index doctor cure patient earn T 1 time T 2 T 3
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Gaps in possible syllogism q Syllogism If pay(human 2, money, to-human 1) is earn(human 1, money, fromhuman 2), and earn(doctor, money, from-human 2), Then pay(human 2, money, to-doctor). Axiom-1 Converse (antonymy) event role inter-relation § pay(agent=human 2, content=X, target=human 1) iff earn(agent=human 1, content=X, source=human 2) q Axiom-2 If cure(doctor, human 2) and occupation(doctor), then earn(doctor, money, source=human 2) q Extended syllogism If Axiom-2 and cure(doctor, human 2) and occupation(doctor), then earn(doctor, money, from-human 2).
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Gaps in possible syllogism q Syllogism If pay(human 2, money, to-human 1) is earn(human 1, money, fromhuman 2), and earn(doctor, money, from-human 2), Then pay(human 2, money, to-doctor). Axiom-1 Converse (antonymy) event role inter-relation § pay(agent=human 2, content=X, target=human 1) iff earn(agent=human 1, content=X, source=human 2) q Axiom-2 If cure(doctor, human 2) and occupation(doctor), then earn(doctor, money, source=human 2) q Extended syllogism If Axiom-2 and cure(doctor, human 2) and occupation(doctor), then earn(doctor, money, from-human 2).
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Gaps in Linguistic Knowledge Base q Query: Why doctor cure patient? Why doctor earn money? Why patient pay money to doctor? q Extended syllogism Axiom-2 § If cure(doctor, human 2) and occupation(doctor), then earn(doctor, money, source=human 2) If Axiom-2 and cure(doctor, human 2) and occupation(doctor), then earn(doctor, money, from-human 2). q Gaps in Linguistic Knowledge Base No axiom q Motivation of Crossover algorithm: causal linking to link the gaps in linguistic knowledge base to find possible axioms
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Gaps in Linguistic Knowledge Base q Query: Why doctor cure patient? Why doctor earn money? Why patient pay money to doctor? q Extended syllogism Axiom-2 § If cure(doctor, human 2) and occupation(doctor), then earn(doctor, money, source=human 2) If Axiom-2 and cure(doctor, human 2) and occupation(doctor), then earn(doctor, money, from-human 2). q Gaps in Linguistic Knowledge Base No axiom q Motivation of Crossover algorithm: causal linking to link the gaps in linguistic knowledge base to find possible axioms
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Motivation of Crossover algorithm q. Motivation of Crossover algorithm: causal linking to link the gaps in linguistic knowledge base to find possible axioms
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Motivation of Crossover algorithm q. Motivation of Crossover algorithm: causal linking to link the gaps in linguistic knowledge base to find possible axioms
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Similarity: mission q Mission for two nodes, check the connectability between two nodes if sense ambiguities for a word, select the best sense. if there are multiple expansion possibilities in the next step, select the best node. q Final goal to find a causal linkage
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Similarity: mission q Mission for two nodes, check the connectability between two nodes if sense ambiguities for a word, select the best sense. if there are multiple expansion possibilities in the next step, select the best node. q Final goal to find a causal linkage
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Similarity: motivated example q For query: “Why does doctor cures patient? ” similarity guides to find all kinds of possible situation between doctor and patient before/during/after “doctor cures patient”. for example, § § § Patient suffers from a disease. Doctor cures the patient. Doctor is an occupation. Occupation is to earn money for living. All properties of doctor (e. g. , cure) is relevant to the occupation. § Curing is to earn the money. § Doctor earns the money. § Patient pays the money to the doctor.
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Similarity: motivated example q For query: “Why does doctor cures patient? ” similarity guides to find all kinds of possible situation between doctor and patient before/during/after “doctor cures patient”. for example, § § § Patient suffers from a disease. Doctor cures the patient. Doctor is an occupation. Occupation is to earn money for living. All properties of doctor (e. g. , cure) is relevant to the occupation. § Curing is to earn the money. § Doctor earns the money. § Patient pays the money to the doctor.
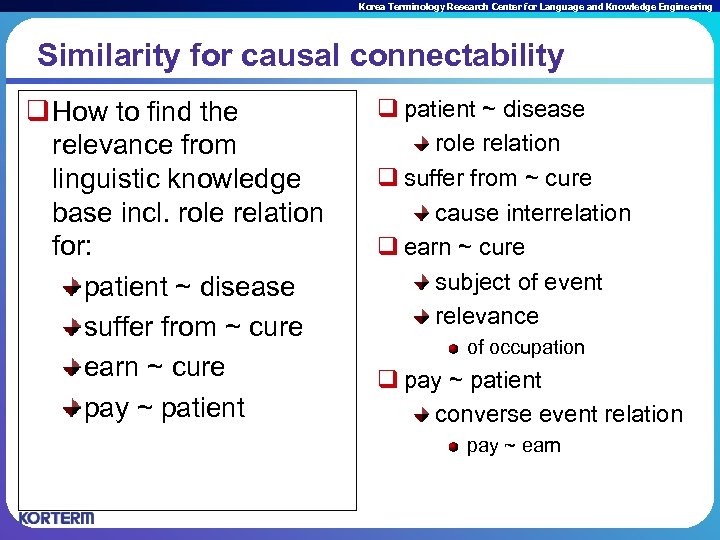 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Similarity for causal connectability q How to find the relevance from linguistic knowledge base incl. role relation for: patient ~ disease suffer from ~ cure earn ~ cure pay ~ patient q patient ~ disease role relation q suffer from ~ cure cause interrelation q earn ~ cure subject of event relevance of occupation q pay ~ patient converse event relation pay ~ earn
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Similarity for causal connectability q How to find the relevance from linguistic knowledge base incl. role relation for: patient ~ disease suffer from ~ cure earn ~ cure pay ~ patient q patient ~ disease role relation q suffer from ~ cure cause interrelation q earn ~ cure subject of event relevance of occupation q pay ~ patient converse event relation pay ~ earn
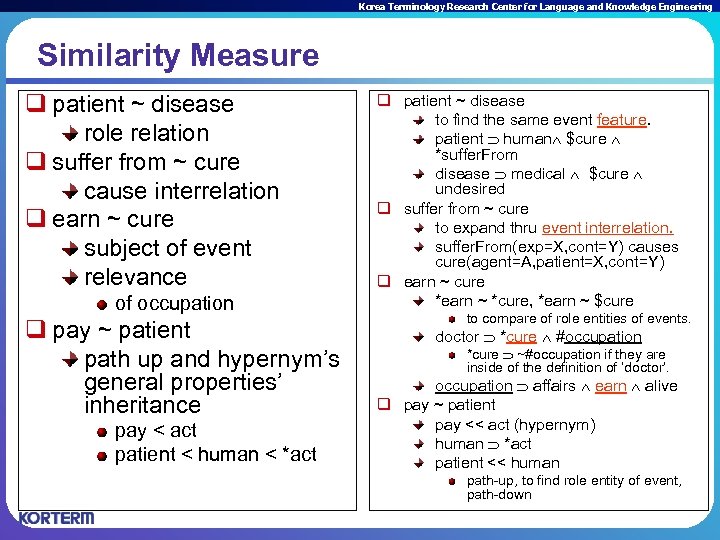 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Similarity Measure q patient ~ disease role relation q suffer from ~ cure cause interrelation q earn ~ cure subject of event relevance of occupation q pay ~ patient path up and hypernym’s general properties’ inheritance pay < act patient < human < *act q patient ~ disease to find the same event feature. patient human $cure *suffer. From disease medical $cure undesired q suffer from ~ cure to expand thru event interrelation. suffer. From(exp=X, cont=Y) causes cure(agent=A, patient=X, cont=Y) q earn ~ cure *earn ~ *cure, *earn ~ $cure to compare of role entities of events. doctor *cure #occupation *cure ~#occupation if they are inside of the definition of ‘doctor’. occupation affairs earn alive q pay ~ patient pay << act (hypernym) human *act patient << human path-up, to find role entity of event, path-down
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Similarity Measure q patient ~ disease role relation q suffer from ~ cure cause interrelation q earn ~ cure subject of event relevance of occupation q pay ~ patient path up and hypernym’s general properties’ inheritance pay < act patient < human < *act q patient ~ disease to find the same event feature. patient human $cure *suffer. From disease medical $cure undesired q suffer from ~ cure to expand thru event interrelation. suffer. From(exp=X, cont=Y) causes cure(agent=A, patient=X, cont=Y) q earn ~ cure *earn ~ *cure, *earn ~ $cure to compare of role entities of events. doctor *cure #occupation *cure ~#occupation if they are inside of the definition of ‘doctor’. occupation affairs earn alive q pay ~ patient pay << act (hypernym) human *act patient << human path-up, to find role entity of event, path-down
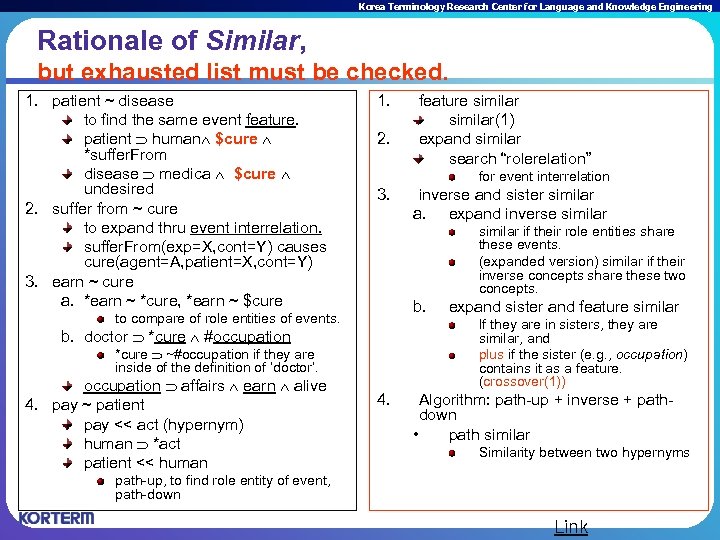 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Rationale of Similar, but exhausted list must be checked. 1. patient ~ disease to find the same event feature. patient human $cure *suffer. From disease medica $cure undesired 2. suffer from ~ cure to expand thru event interrelation. suffer. From(exp=X, cont=Y) causes cure(agent=A, patient=X, cont=Y) 3. earn ~ cure a. *earn ~ *cure, *earn ~ $cure 1. 2. for event interrelation 3. inverse and sister similar a. expand inverse similar if their role entities share these events. (expanded version) similar if their inverse concepts share these two concepts. b. to compare of role entities of events. expand sister and feature similar If they are in sisters, they are similar, and plus if the sister (e. g. , occupation) contains it as a feature. (crossover(1)) b. doctor *cure #occupation *cure ~#occupation if they are inside of the definition of ‘doctor’. occupation affairs earn alive 4. pay ~ patient pay << act (hypernym) human *act patient << human feature similar(1) expand similar search “rolerelation” 4. Algorithm: path-up + inverse + pathdown • path similar Similarity between two hypernyms path-up, to find role entity of event, path-down Link
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Rationale of Similar, but exhausted list must be checked. 1. patient ~ disease to find the same event feature. patient human $cure *suffer. From disease medica $cure undesired 2. suffer from ~ cure to expand thru event interrelation. suffer. From(exp=X, cont=Y) causes cure(agent=A, patient=X, cont=Y) 3. earn ~ cure a. *earn ~ *cure, *earn ~ $cure 1. 2. for event interrelation 3. inverse and sister similar a. expand inverse similar if their role entities share these events. (expanded version) similar if their inverse concepts share these two concepts. b. to compare of role entities of events. expand sister and feature similar If they are in sisters, they are similar, and plus if the sister (e. g. , occupation) contains it as a feature. (crossover(1)) b. doctor *cure #occupation *cure ~#occupation if they are inside of the definition of ‘doctor’. occupation affairs earn alive 4. pay ~ patient pay << act (hypernym) human *act patient << human feature similar(1) expand similar search “rolerelation” 4. Algorithm: path-up + inverse + pathdown • path similar Similarity between two hypernyms path-up, to find role entity of event, path-down Link
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering similar(Level) q. Goal to merge all of similarity measures path similar feature similar crossover similar (not yet fixed) to give Level of Similarity Notation: similar(Level)
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering similar(Level) q. Goal to merge all of similarity measures path similar feature similar crossover similar (not yet fixed) to give Level of Similarity Notation: similar(Level)
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Level of Similarity q Motivation: to be able to compare the similarity levels to be dynamically adaptable to the knowledge levels q Levels of details Level 0: based on itself and its top path = path similar Level 1: to expand to the features =feature similar Level 2:
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Level of Similarity q Motivation: to be able to compare the similarity levels to be dynamically adaptable to the knowledge levels q Levels of details Level 0: based on itself and its top path = path similar Level 1: to expand to the features =feature similar Level 2:
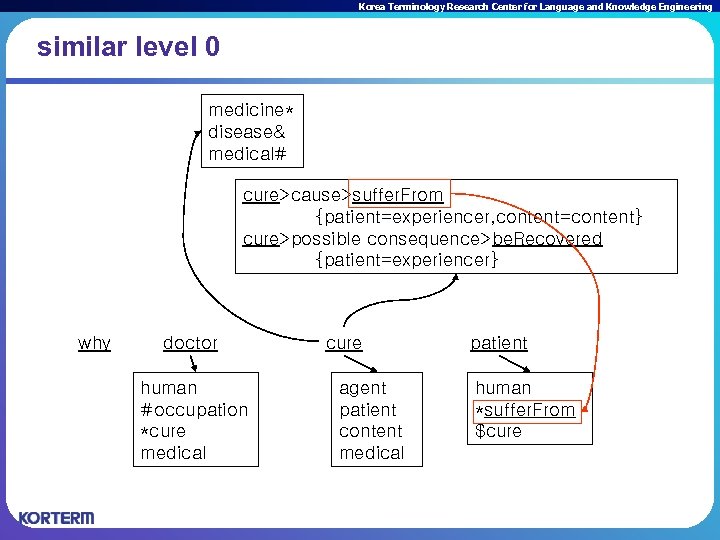 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering similar level 0 medicine* disease& medical# cure>cause>suffer. From {patient=experiencer, content=content} cure>possible consequence>be. Recovered {patient=experiencer} why doctor human #occupation *cure medical cure agent patient content medical patient human *suffer. From $cure
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering similar level 0 medicine* disease& medical# cure>cause>suffer. From {patient=experiencer, content=content} cure>possible consequence>be. Recovered {patient=experiencer} why doctor human #occupation *cure medical cure agent patient content medical patient human *suffer. From $cure
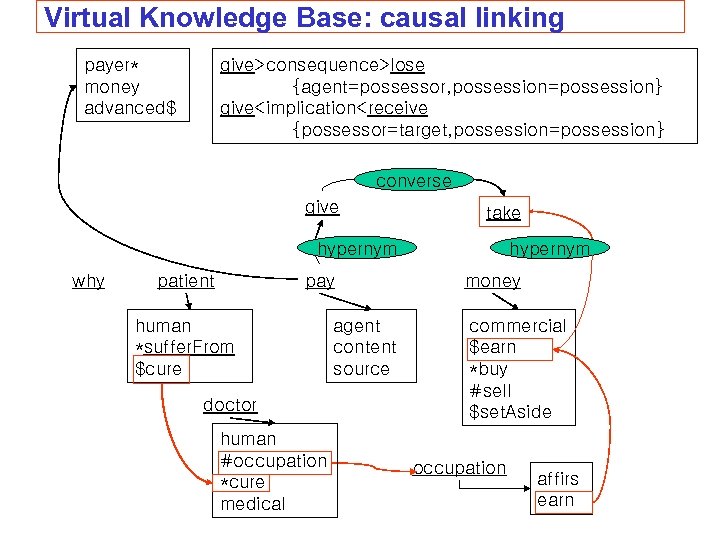 Virtual Knowledge Base: causal linking payer* money advanced$ give>consequence>lose {agent=possessor, possession=possession} give
Virtual Knowledge Base: causal linking payer* money advanced$ give>consequence>lose {agent=possessor, possession=possession} give
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering A Snapshot
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering A Snapshot
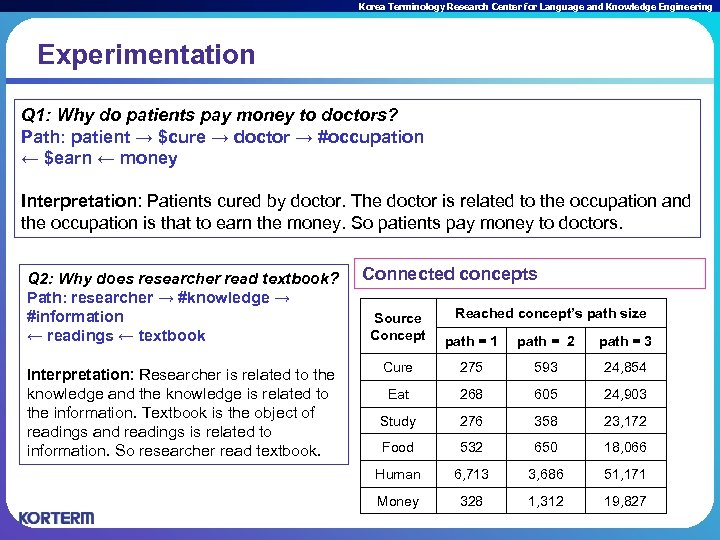 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Experimentation Q 1: Why do patients pay money to doctors? Path: patient → $cure → doctor → #occupation ← $earn ← money Interpretation: Patients cured by doctor. The doctor is related to the occupation and the occupation is that to earn the money. So patients pay money to doctors. Q 2: Why does researcher read textbook? Path: researcher → #knowledge → #information ← readings ← textbook Interpretation: Researcher is related to the knowledge and the knowledge is related to the information. Textbook is the object of readings and readings is related to information. So researcher read textbook. Connected concepts Reached concept’s path size Source Concept path = 1 path = 2 path = 3 Cure 275 593 24, 854 Eat 268 605 24, 903 Study 276 358 23, 172 Food 532 650 18, 066 Human 6, 713 3, 686 51, 171 Money 328 1, 312 19, 827
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Experimentation Q 1: Why do patients pay money to doctors? Path: patient → $cure → doctor → #occupation ← $earn ← money Interpretation: Patients cured by doctor. The doctor is related to the occupation and the occupation is that to earn the money. So patients pay money to doctors. Q 2: Why does researcher read textbook? Path: researcher → #knowledge → #information ← readings ← textbook Interpretation: Researcher is related to the knowledge and the knowledge is related to the information. Textbook is the object of readings and readings is related to information. So researcher read textbook. Connected concepts Reached concept’s path size Source Concept path = 1 path = 2 path = 3 Cure 275 593 24, 854 Eat 268 605 24, 903 Study 276 358 23, 172 Food 532 650 18, 066 Human 6, 713 3, 686 51, 171 Money 328 1, 312 19, 827
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Future Works q Resources EDR, Word. Net, Cyc How. Net based q Algorithm and Representation Lexical Chain Interpretation as Abduction Bayesian Belief Net q Causality Stopping Condition What is “Causality” and “Explanation”? q Automatic Video Synchronization with Causal Justification Path
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Future Works q Resources EDR, Word. Net, Cyc How. Net based q Algorithm and Representation Lexical Chain Interpretation as Abduction Bayesian Belief Net q Causality Stopping Condition What is “Causality” and “Explanation”? q Automatic Video Synchronization with Causal Justification Path
 Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Conclusion q How to link the already existing linguistic knowledge base q To be tested for the definition and the causality link. q To be adapted for the user knowledge level to find more causality link. q How to link the video archive to linguistic causal path Dependency structure MPEG 7
Korea Terminology Research Center for Language and Knowledge Engineering Conclusion q How to link the already existing linguistic knowledge base q To be tested for the definition and the causality link. q To be adapted for the user knowledge level to find more causality link. q How to link the video archive to linguistic causal path Dependency structure MPEG 7


