610cb01b375a8d6683c3981c5f691c5c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 KOREA’s Initiative for IT Application and the Development of Internet March 1998 WAN-IL CHOI National Computerization Agency
KOREA’s Initiative for IT Application and the Development of Internet March 1998 WAN-IL CHOI National Computerization Agency
 Contents • Current Status of Information Infrastructures • National IT Initiatives and Policy • Internet Development and Policy National Computerization Agency
Contents • Current Status of Information Infrastructures • National IT Initiatives and Policy • Internet Development and Policy National Computerization Agency
 Current Status of Information Infrastructures • IT Production • PC Diffusion • Telecommunications • CATV • Internet • Informatization Index National Computerization Agency
Current Status of Information Infrastructures • IT Production • PC Diffusion • Telecommunications • CATV • Internet • Informatization Index National Computerization Agency
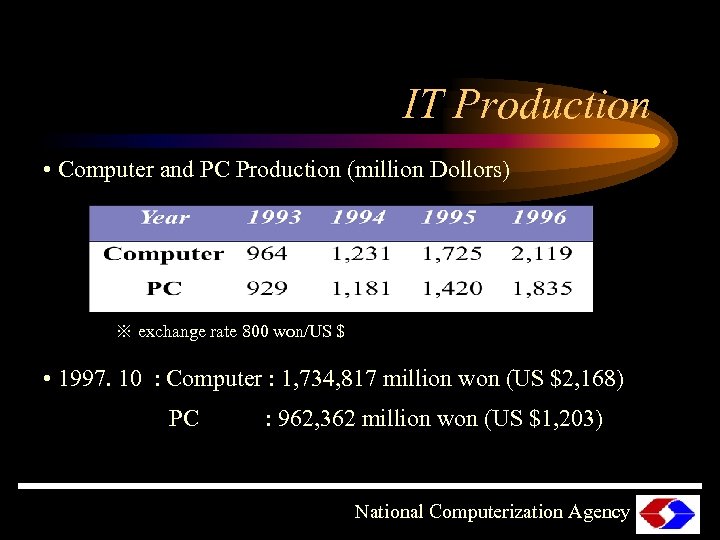 IT Production • Computer and PC Production (million Dollors) ※ exchange rate 800 won/US $ • 1997. 10 : Computer : 1, 734, 817 million won (US $2, 168) PC : 962, 362 million won (US $1, 203) National Computerization Agency
IT Production • Computer and PC Production (million Dollors) ※ exchange rate 800 won/US $ • 1997. 10 : Computer : 1, 734, 817 million won (US $2, 168) PC : 962, 362 million won (US $1, 203) National Computerization Agency
 PC Diffusion • Number of PCs Sold Domestically(thousands) • Number of PCs in Use : 7 Million (as of the end of 1997) • Goal set in NBIS (National Basic Information System) - One PC per household by the Year 2000 - 10 mil PC’s diffused to offices and homes National Computerization Agency
PC Diffusion • Number of PCs Sold Domestically(thousands) • Number of PCs in Use : 7 Million (as of the end of 1997) • Goal set in NBIS (National Basic Information System) - One PC per household by the Year 2000 - 10 mil PC’s diffused to offices and homes National Computerization Agency
 Telecommunications • Market Structure for Basic Service - KT Monopoly Broken at the Mid, 1991 - International Call Carrier : Oligopoly (KT, Dacom, Onse) - Domestic Long Distance : Jan ‘ 96. Duopoly (KT, Dacom) - Local Calls : Duopoly (KT, Dacom) • Telephone Lines per 100 population(1996) : 44. 4 - U. S. : 62. 5 (1995) - Japan : 48. 8 (1995) - U. K. : 50. 5 (1995) • Subscribers of Mobile Communications (thousands) National Computerization Agency
Telecommunications • Market Structure for Basic Service - KT Monopoly Broken at the Mid, 1991 - International Call Carrier : Oligopoly (KT, Dacom, Onse) - Domestic Long Distance : Jan ‘ 96. Duopoly (KT, Dacom) - Local Calls : Duopoly (KT, Dacom) • Telephone Lines per 100 population(1996) : 44. 4 - U. S. : 62. 5 (1995) - Japan : 48. 8 (1995) - U. K. : 50. 5 (1995) • Subscribers of Mobile Communications (thousands) National Computerization Agency
 CATV • New Service : on Mar 1995 • Number of Subscribers - 500, 000 (Jan 1996) : 5% of households - 1, 700, 000 (Mar 1997) : 13. 1% of households - 2, 000 (Jun 1997) : 15. 4% of households - 2, 452, 000 (Feb 1998) : 19% of households - 6, 500, 000 (by the year 2000, Projection) : 50% of households • Time for Diffusion of CATV - 10% of households : 8 ∼ 10 years (Canada, U. S. A. ) - 6% of households : 8 years (Japan) National Computerization Agency
CATV • New Service : on Mar 1995 • Number of Subscribers - 500, 000 (Jan 1996) : 5% of households - 1, 700, 000 (Mar 1997) : 13. 1% of households - 2, 000 (Jun 1997) : 15. 4% of households - 2, 452, 000 (Feb 1998) : 19% of households - 6, 500, 000 (by the year 2000, Projection) : 50% of households • Time for Diffusion of CATV - 10% of households : 8 ∼ 10 years (Canada, U. S. A. ) - 6% of households : 8 years (Japan) National Computerization Agency
 Internet • Number of Internet Host Computers (thousands, Jan 1997) ※ 131 : Dec ’ 97 National Computerization Agency
Internet • Number of Internet Host Computers (thousands, Jan 1997) ※ 131 : Dec ’ 97 National Computerization Agency
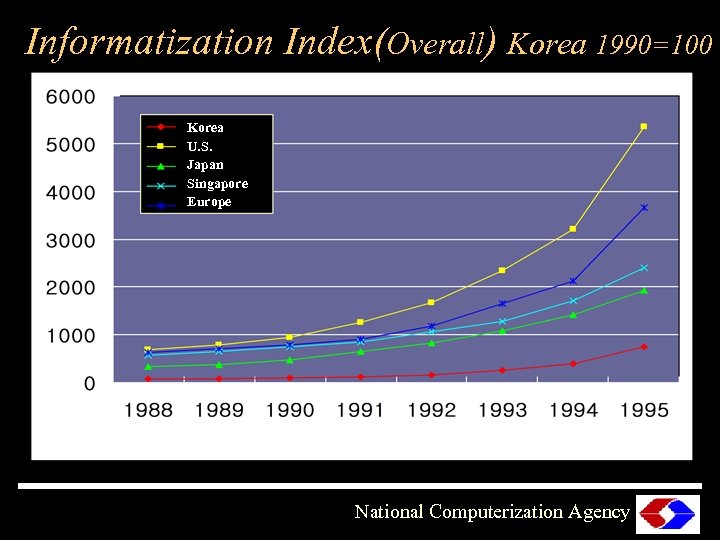 Informatization Index(Overall) Korea 1990=100 Korea U. S. Japan Singapore Europe National Computerization Agency
Informatization Index(Overall) Korea 1990=100 Korea U. S. Japan Singapore Europe National Computerization Agency
 National IT Initiatives and Policy • NBIS, NAIS • Master Plan and Strategy for Information Society • Korea Information Infrastructure • Policy Issues National Computerization Agency
National IT Initiatives and Policy • NBIS, NAIS • Master Plan and Strategy for Information Society • Korea Information Infrastructure • Policy Issues National Computerization Agency
 NBIS (National Basic Information System) • First National Initiative of IT Use and Production – 1 st Five-Year Plan (1987 - 1991) – 2 nd Five-Year Plan (1992 - 1996) • Consensus on the Potentials of IT – Industrial Revolution vs. Information Revolution • Strong Support by Government – Funding Schedule – NCB (National Computerization Board) • Under the Executive Office of the President • Effective Coordination among Government Agencies • Computerization Promotion Meeting (Presidential) National Computerization Agency
NBIS (National Basic Information System) • First National Initiative of IT Use and Production – 1 st Five-Year Plan (1987 - 1991) – 2 nd Five-Year Plan (1992 - 1996) • Consensus on the Potentials of IT – Industrial Revolution vs. Information Revolution • Strong Support by Government – Funding Schedule – NCB (National Computerization Board) • Under the Executive Office of the President • Effective Coordination among Government Agencies • Computerization Promotion Meeting (Presidential) National Computerization Agency
 NBIS (National Basic Information System) • Objective – – – Economic Growth in “Information Age” Use IT to Improve Competitiveness Take a Position of Developed Nation in 21 st Century Improve Quality of Life Provide Initial Markets for IT Industries • Implementation – – – Administrations Financial Institutions Education and Research National Defense National Security National Computerization Agency
NBIS (National Basic Information System) • Objective – – – Economic Growth in “Information Age” Use IT to Improve Competitiveness Take a Position of Developed Nation in 21 st Century Improve Quality of Life Provide Initial Markets for IT Industries • Implementation – – – Administrations Financial Institutions Education and Research National Defense National Security National Computerization Agency
 NAIS (National Administration Information System) • Small and Efficient Government – 1 st Stage : Developing the Separate Systems – 2 nd Stage : Sharing Information among Agencies • Pre-assigned Fund : US $ 200 million (1987 - 1991) • Six Subsystems – – – Resident Vehicle Hose and Land Employment Customs Clearance Economic Statistics National Computerization Agency
NAIS (National Administration Information System) • Small and Efficient Government – 1 st Stage : Developing the Separate Systems – 2 nd Stage : Sharing Information among Agencies • Pre-assigned Fund : US $ 200 million (1987 - 1991) • Six Subsystems – – – Resident Vehicle Hose and Land Employment Customs Clearance Economic Statistics National Computerization Agency
 Master Plan and Strategy for Information Society • Legal Ground – Basic Act on Informatization Promotion(1995) • Basic guiding principles on building KII and creating information society • Basic plan for informatization and implementation • Establishment and operation of Informatization Promotion Committee • Operation of Informatization Promotion Fund National Computerization Agency
Master Plan and Strategy for Information Society • Legal Ground – Basic Act on Informatization Promotion(1995) • Basic guiding principles on building KII and creating information society • Basic plan for informatization and implementation • Establishment and operation of Informatization Promotion Committee • Operation of Informatization Promotion Fund National Computerization Agency
 Master Plan • 1 st phase(1996 -2000): – laying the foundation for building a national information network • 2 nd phase(2001 -2005) – Spreading the usage of information networks • 3 rd phase(2006 -2010) – Promoting a higher level of information network usage National Computerization Agency
Master Plan • 1 st phase(1996 -2000): – laying the foundation for building a national information network • 2 nd phase(2001 -2005) – Spreading the usage of information networks • 3 rd phase(2006 -2010) – Promoting a higher level of information network usage National Computerization Agency
 Major programs • Promoting projects aimed at accelerated usage of the information network in the public sector • Building an information superhighway • Creating the desirable environment for the information and communication industry • Establishing a legal framework • Ensuring information security and standardization National Computerization Agency
Major programs • Promoting projects aimed at accelerated usage of the information network in the public sector • Building an information superhighway • Creating the desirable environment for the information and communication industry • Establishing a legal framework • Ensuring information security and standardization National Computerization Agency
 Korea Information Infrastructure • Aim: To construct high-speed government and public information networks – KII-G: needs of public administration, research institutes, and universities – KII-P : needs of industry and general public • Construction – Operator: Korea Telecommunication, Dacom – Fund : US $ 580 million – Schedule: completed by 2010 National Computerization Agency
Korea Information Infrastructure • Aim: To construct high-speed government and public information networks – KII-G: needs of public administration, research institutes, and universities – KII-P : needs of industry and general public • Construction – Operator: Korea Telecommunication, Dacom – Fund : US $ 580 million – Schedule: completed by 2010 National Computerization Agency
 KII and Internet • KII promotes the usage of Internet services • Internet becomes the integral part of KII • Vitalization of Internet as a basis of implementing Electronic government • Development of Web based application in the KII National Computerization Agency
KII and Internet • KII promotes the usage of Internet services • Internet becomes the integral part of KII • Vitalization of Internet as a basis of implementing Electronic government • Development of Web based application in the KII National Computerization Agency
 Policy Issues • Demand-Pull vs. Supply-Push – KII Plan coordinated by Government : Supply-Push Model – Experience of Failed System in NBIS due to Insufficient Demand – Shifts of Interest to Demand Side – Nature of IT • Consumer’s potential needs and market demand to be developed • Unforeseen yet popular services generated by enabling technologies – Interaction and Synergy Effects of Demand Supply National Computerization Agency
Policy Issues • Demand-Pull vs. Supply-Push – KII Plan coordinated by Government : Supply-Push Model – Experience of Failed System in NBIS due to Insufficient Demand – Shifts of Interest to Demand Side – Nature of IT • Consumer’s potential needs and market demand to be developed • Unforeseen yet popular services generated by enabling technologies – Interaction and Synergy Effects of Demand Supply National Computerization Agency
 Policy Issues • Roles of Government – Strong Leadership in Economic Development Plan – Different Environments in Managing the KII Plan – Limited Roles of Government – Bureaucratic Attitudes Are Still Alive – Mixed Attittudes Held by Private Sectors • Preferring liberalized business environment • Seeking for direct government supports National Computerization Agency
Policy Issues • Roles of Government – Strong Leadership in Economic Development Plan – Different Environments in Managing the KII Plan – Limited Roles of Government – Bureaucratic Attitudes Are Still Alive – Mixed Attittudes Held by Private Sectors • Preferring liberalized business environment • Seeking for direct government supports National Computerization Agency
 Internet Development and Policy History of Internet use in Korea o 1982 Installment of SDN(System Development Network) between Seoul National University and Korea Institute of Electronics and Telecommunication o 1986 Establishment of KRNIC(Korea Network Information Center) at KAIST o 1987 Interoperation of SDN with CSNet (9. 6 Kbps) extending to Research and Education Network o 1994 Starting ISP Businesses, Providing Internet services to the Public o 1994 KRNIC move to NCA(National Computerization Agency) o 1997 Establishment of Commerce Network in KOREA, stimulating Internet Commerce National Computerization Agency
Internet Development and Policy History of Internet use in Korea o 1982 Installment of SDN(System Development Network) between Seoul National University and Korea Institute of Electronics and Telecommunication o 1986 Establishment of KRNIC(Korea Network Information Center) at KAIST o 1987 Interoperation of SDN with CSNet (9. 6 Kbps) extending to Research and Education Network o 1994 Starting ISP Businesses, Providing Internet services to the Public o 1994 KRNIC move to NCA(National Computerization Agency) o 1997 Establishment of Commerce Network in KOREA, stimulating Internet Commerce National Computerization Agency
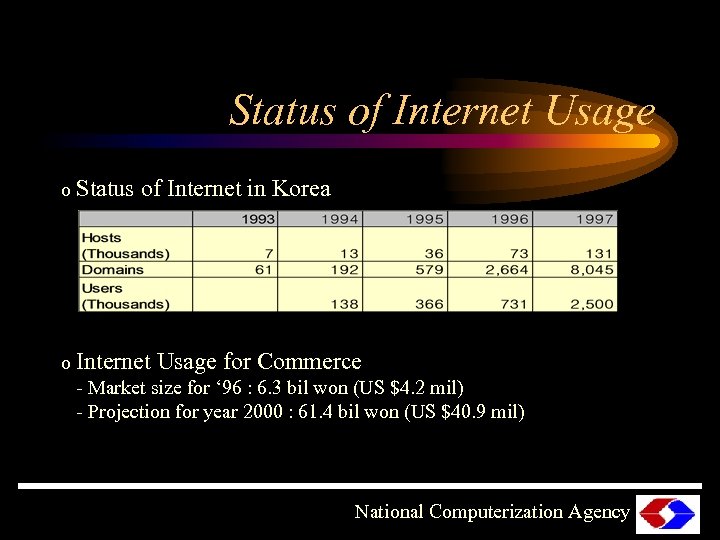 Status of Internet Usage o Status of Internet in Korea o Internet Usage for Commerce - Market size for ‘ 96 : 6. 3 bil won (US $4. 2 mil) - Projection for year 2000 : 61. 4 bil won (US $40. 9 mil) National Computerization Agency
Status of Internet Usage o Status of Internet in Korea o Internet Usage for Commerce - Market size for ‘ 96 : 6. 3 bil won (US $4. 2 mil) - Projection for year 2000 : 61. 4 bil won (US $40. 9 mil) National Computerization Agency
 Internet and New Businesses • Application of Internet Technology to existing Businesses - Banking, Shopping, Distribution, Retailing, etc - Improving Efficiency and Productivity • Intra-firms • Between Producers and consumers • Generation of New Businesses - Huge Business opportunities provided by Large number of Users connected to the Internet - New production system and distribution channels - Access to cyber market requiring Small Investment National Computerization Agency
Internet and New Businesses • Application of Internet Technology to existing Businesses - Banking, Shopping, Distribution, Retailing, etc - Improving Efficiency and Productivity • Intra-firms • Between Producers and consumers • Generation of New Businesses - Huge Business opportunities provided by Large number of Users connected to the Internet - New production system and distribution channels - Access to cyber market requiring Small Investment National Computerization Agency
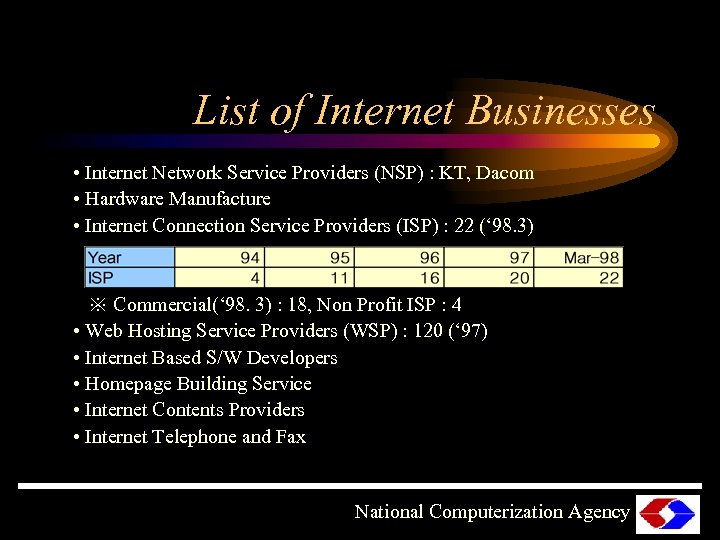 List of Internet Businesses • Internet Network Service Providers (NSP) : KT, Dacom • Hardware Manufacture • Internet Connection Service Providers (ISP) : 22 (‘ 98. 3) ※ Commercial(‘ 98. 3) : 18, Non Profit ISP : 4 • Web Hosting Service Providers (WSP) : 120 (‘ 97) • Internet Based S/W Developers • Homepage Building Service • Internet Contents Providers • Internet Telephone and Fax National Computerization Agency
List of Internet Businesses • Internet Network Service Providers (NSP) : KT, Dacom • Hardware Manufacture • Internet Connection Service Providers (ISP) : 22 (‘ 98. 3) ※ Commercial(‘ 98. 3) : 18, Non Profit ISP : 4 • Web Hosting Service Providers (WSP) : 120 (‘ 97) • Internet Based S/W Developers • Homepage Building Service • Internet Contents Providers • Internet Telephone and Fax National Computerization Agency
 Restructuring of Industrial Organization and Internet Business • Overrule of Large Businesses and Economic Crisis • Strategic Shift toward SME’s and Internet Businesses – New Government Strategy in favor of Small Businesses – Recognition of Internet as a means of Supporting Small Businesses – Easy Access to World Market with Modest Investment – Internet Technology enabling New Ideas into Businesses along with Venture Capital National Computerization Agency
Restructuring of Industrial Organization and Internet Business • Overrule of Large Businesses and Economic Crisis • Strategic Shift toward SME’s and Internet Businesses – New Government Strategy in favor of Small Businesses – Recognition of Internet as a means of Supporting Small Businesses – Easy Access to World Market with Modest Investment – Internet Technology enabling New Ideas into Businesses along with Venture Capital National Computerization Agency
 Strategies for Development of Internet Businesses • Improvement of Internet Backbone Network • Development of Internet Business Services on the CATV Network • Government Support for Internet Businesses • Promotion of R&D Investment for Internet Technologies • Government role in Electronic Commerce • Reformation of Regulations, Rules for Promotion of Internet Businesses National Computerization Agency
Strategies for Development of Internet Businesses • Improvement of Internet Backbone Network • Development of Internet Business Services on the CATV Network • Government Support for Internet Businesses • Promotion of R&D Investment for Internet Technologies • Government role in Electronic Commerce • Reformation of Regulations, Rules for Promotion of Internet Businesses National Computerization Agency
 Improvement of Internet Backbone network • For the Short term : Examine traffic on the existing Internet backbone to solve bottleneck point. • For the long term : Use PUBNET and ATM to build Superhigh speed Internet backbone - build more IX (Internet exchange point) - 33. 6 Kbps → 56 K bps National Computerization Agency
Improvement of Internet Backbone network • For the Short term : Examine traffic on the existing Internet backbone to solve bottleneck point. • For the long term : Use PUBNET and ATM to build Superhigh speed Internet backbone - build more IX (Internet exchange point) - 33. 6 Kbps → 56 K bps National Computerization Agency
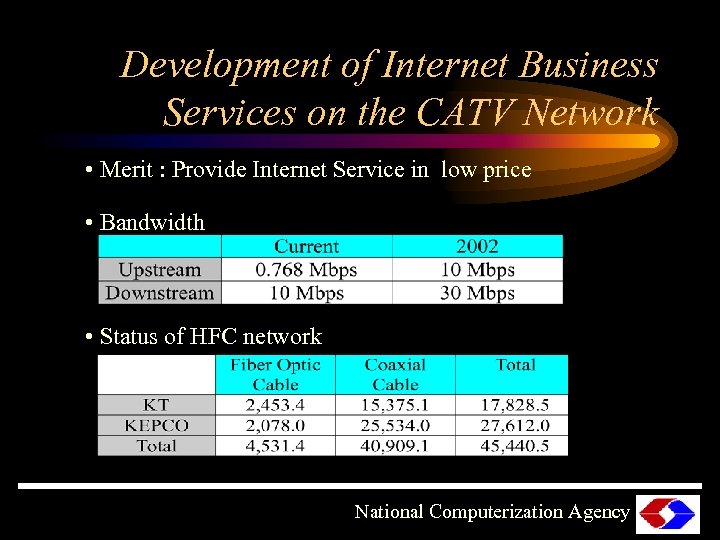 Development of Internet Business Services on the CATV Network • Merit : Provide Internet Service in low price • Bandwidth • Status of HFC network National Computerization Agency
Development of Internet Business Services on the CATV Network • Merit : Provide Internet Service in low price • Bandwidth • Status of HFC network National Computerization Agency
 Government Support for Internet Businesses • Support Model Project of Commercial Activity based on Internet • Support Next generation Internet Pilot Project • Support APAN (Asia Pacific Advanced network) Activity National Computerization Agency
Government Support for Internet Businesses • Support Model Project of Commercial Activity based on Internet • Support Next generation Internet Pilot Project • Support APAN (Asia Pacific Advanced network) Activity National Computerization Agency
 Promotion of R&D Investment for Internet Technologies • Direction - Driving force to develop new technology through Industrial-educational cooperation - positive utilization of Forward Delivery Trial Network to verify Internet technology which will be developed - Reinforce exchange information between Standardization and R& D National Computerization Agency
Promotion of R&D Investment for Internet Technologies • Direction - Driving force to develop new technology through Industrial-educational cooperation - positive utilization of Forward Delivery Trial Network to verify Internet technology which will be developed - Reinforce exchange information between Standardization and R& D National Computerization Agency
 Government Roles in EC • Constructing technical infrastructure – EC related technology – Standards for electronic document – Physical network infrastructure • Preparing legal and institutional arrangement • Constructing the environment for elevating the social acknowledgement on EC • Establishing the national strategy for issues on global EC and internal cooperation National Computerization Agency
Government Roles in EC • Constructing technical infrastructure – EC related technology – Standards for electronic document – Physical network infrastructure • Preparing legal and institutional arrangement • Constructing the environment for elevating the social acknowledgement on EC • Establishing the national strategy for issues on global EC and internal cooperation National Computerization Agency
 Government initiatives for EC In Korea • Government took full initiatives in major areas during the introduction of EDI in Korea – logistics, customs, taxation, procurement • Market formation as a investor and a user • Promulgated independent EDI law for the first time in the world(1992) • EDI is considered an integral part of the major social overhead capital • MOTI(Ministry of Trade and Industry) and MIC(Ministry of Information) are major actors in EC policy. National Computerization Agency
Government initiatives for EC In Korea • Government took full initiatives in major areas during the introduction of EDI in Korea – logistics, customs, taxation, procurement • Market formation as a investor and a user • Promulgated independent EDI law for the first time in the world(1992) • EDI is considered an integral part of the major social overhead capital • MOTI(Ministry of Trade and Industry) and MIC(Ministry of Information) are major actors in EC policy. National Computerization Agency
 Policy direction in Internet based EC • Foster market mechanism and private sector initiatives • More focus on production and logistics than consumption • Active participation to Int’l cooperation • Effective division of responsibility among government and private sector National Computerization Agency
Policy direction in Internet based EC • Foster market mechanism and private sector initiatives • More focus on production and logistics than consumption • Active participation to Int’l cooperation • Effective division of responsibility among government and private sector National Computerization Agency
 Some Measure for Expansion of EC over the Internet • Tariffs on Internet transaction – Visible merchandise : tariff as present – Invisible product : tentatively tariff-free • Regulation on Contents – Development of consumer protect measure – Self regulation against harmful contents • Preparation of Electronic Fund Transfer Act (during 1998) • Operation of EC supporting Center for SME’s • Launching and supporting EC pilot project in the public & private sector – Risk taking and awareness elevation National Computerization Agency
Some Measure for Expansion of EC over the Internet • Tariffs on Internet transaction – Visible merchandise : tariff as present – Invisible product : tentatively tariff-free • Regulation on Contents – Development of consumer protect measure – Self regulation against harmful contents • Preparation of Electronic Fund Transfer Act (during 1998) • Operation of EC supporting Center for SME’s • Launching and supporting EC pilot project in the public & private sector – Risk taking and awareness elevation National Computerization Agency
 Thank you ! National Computerization Agency
Thank you ! National Computerization Agency


