c047b8b7ff75c3c1543cd9c8861c559d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Korea’s Experience Building Intellectual Property Awareness and Economic Development Cairo, March 18, 2010 Won-Kil Yoon Director Technical Cooperation Division Korean Intellectual Property Office
Contents Korea’s Economic Development of IP System in Korea Major Policies of KIPO and its Role in the Economic Development of Korea Conclusion
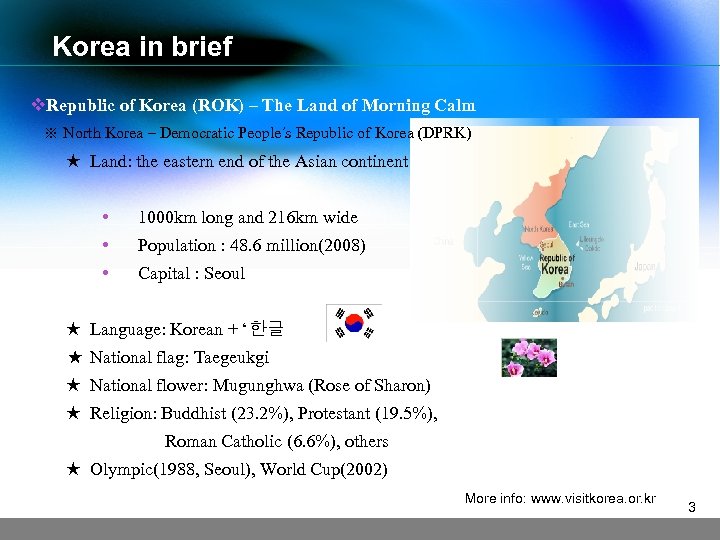
Korea in brief v. Republic of Korea (ROK) – The Land of Morning Calm ※ North Korea – Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) ★ Land: the eastern end of the Asian continent • 1000 km long and 216 km wide • Population : 48. 6 million(2008) • Capital : Seoul ★ Language: Korean + ‘한글 ★ National flag: Taegeukgi ★ National flower: Mugunghwa (Rose of Sharon) ★ Religion: Buddhist (23. 2%), Protestant (19. 5%), Roman Catholic (6. 6%), others ★ Olympic(1988, Seoul), World Cup(2002) More info: www. visitkorea. or. kr 3
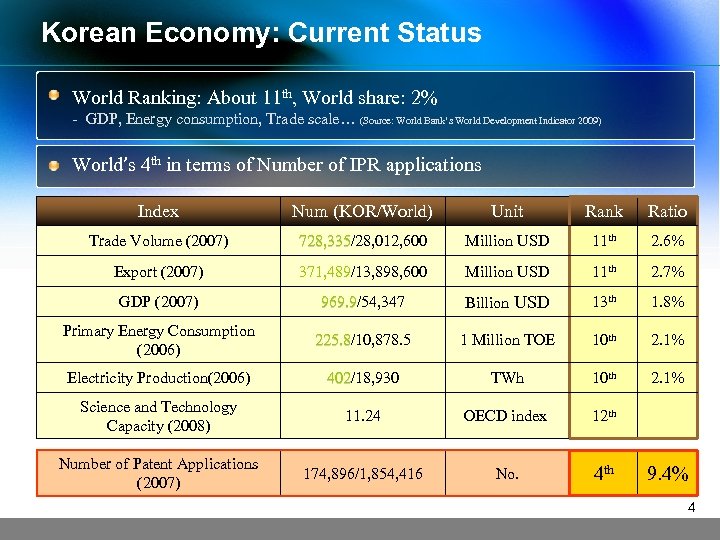
Korean Economy: Current Status World Ranking: About 11 th, World share: 2% - GDP, Energy consumption, Trade scale… (Source: World Bank’s World Development Indicator 2009) World’s 4 th in terms of Number of IPR applications Index Num (KOR/World) Unit Rank Ratio Trade Volume (2007) 728, 335/28, 012, 600 728, 335 Million USD 11 th 2. 6% Export (2007) 371, 489/13, 898, 600 371, 489 Million USD 11 th 2. 7% GDP (2007) 969. 9/54, 347 969. 9 Billion USD 13 th 1. 8% Primary Energy Consumption (2006) 225. 8/10, 878. 5 225. 8 1 Million TOE 10 th 2. 1% Electricity Production(2006) 402/18, 930 402 TWh 10 th 2. 1% Science and Technology Capacity (2008) 11. 24 OECD index 12 th Number of Patent Applications (2007) 174, 896/1, 854, 416 No. 4 th 9. 4% 4
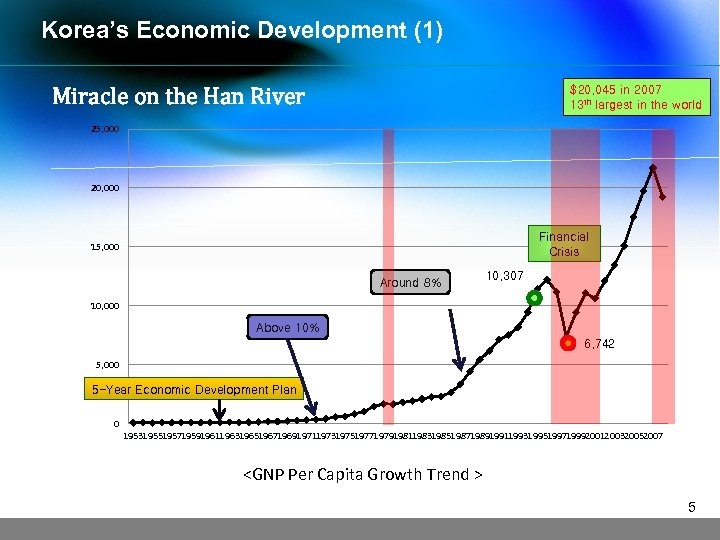
Korea’s Economic Development (1) $20, 045 in 2007 13 th largest in the world Miracle on the Han River 25, 000 20, 000 Financial Crisis 15, 000 Around 8% 10, 307 10, 000 Above 10% 6, 742 5, 000 5 -Year Economic Development Plan 0 1953195519571959196119631965196719691971197319751977197919811983198519871989199119931995199719992001200320052007 <GNP Per Capita Growth Trend > 5

Korea’s Economic Development (2) 1961: One of the Poorest Countries in the World • The Korean War (1950 -1953) : Destruction of industrial faculties • GNP Per Capita : $87 • High population density, lack of natural resources 1970: Start of Economic Development • GNI Per Capita in 1970: $282 (113 th in the world), ü Kenya $215, Zimbabwe $285, North Korea $436 • Small domestic market, weak technology foundation In 1970, the 5 -year Economic Development Plan started yielding desired results • After 1970, average annual economic growth rate: 12. 2% • Major success factors - Government’s will and planning, diligence and entrepreneurship of people, Social atmosphere respecting science, technology, and invention 6

Korea’s Economic Development (3) Before the 1960 s v Farming population: 60% of the total population v Supply of resources almost wholly dependent on foreign aid. 1960 s and beyond v 1960 s • Export-oriented economy v 1970 s • Promotion of labor-intensive industries (Textile, Shoes, Plywood) v 1980 s ~ • Heavy and chemical industries (Cars, Ships, Steel, Oil, Chemical) • Systematic promotion of science and technology 7

Laying the foundation for science and technology development v 1960 s • 1966: Establishment of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) • 1967: Establishment of the Ministry of Science and Technology v 1970 s • Construction of the Daedeok Research Complex, which is the center of science and technology research, a specialized cluster for R&D v 1980 s • Implementation of National R&Ds, such as TDX; and establishment of more private research centers v 1990 s • Fostering of the IT industry, such as semiconductor and communication equipment manufacturing S&T Promotion Policy -> Competitive Technology Base -> Economic Growth 8
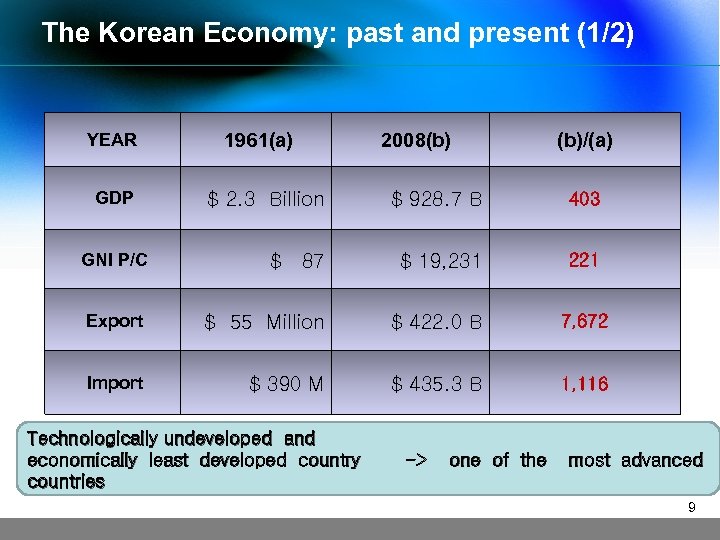
The Korean Economy: past and present (1/2) YEAR GDP 1961(a) 2008(b) (b)/(a) $ 2. 3 Billion $ 928. 7 B 403 GNI P/C $ 87 $ 19, 231 221 Export $ 55 Million $ 422. 0 B 7, 672 Import $ 390 M $ 435. 3 B 1, 116 Technologically undeveloped and economically least developed country countries -> one of the most advanced 9
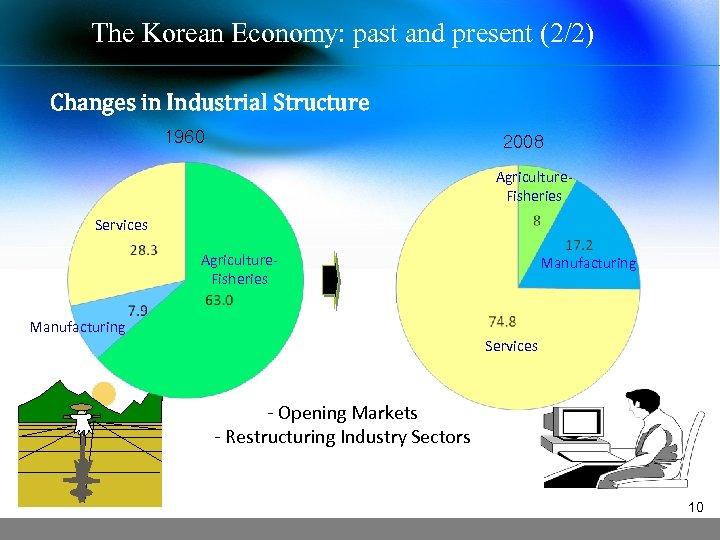
The Korean Economy: past and present (2/2) Changes in Industrial Structure 1960 2008 Agriculture. Fisheries Services Agriculture. Fisheries Manufacturing Services - Opening Markets - Restructuring Industry Sectors 10

Industrial Power of Korea: some facts… Product World market share % (Rank) Semiconductors 49 (1) TFT-LCDs 46. 5 (1) Automobiles 9. 8 (4) 80. 0 (1) LNG carriers Petrochemical products 45 (1) Large diesel engines for ships Refrigerators Air-conditioners 59. 6 (1) 14. 3 (1) 22. 3 (1) Company Samsung Electronics, Hynix Semiconductor Samsung Electronics, LG. Philips LCD Hyundai-Kia Motors, GM Daewoo Hyundai Heavy Industries, Samsung Heavy Industries, Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co. LG Chem, SK Hyundai Heavy Industries, Doosan Engine Co. , STX Heavy Industries Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, Samsung Electronics 11
Ⅱ Development of IP System in Korea
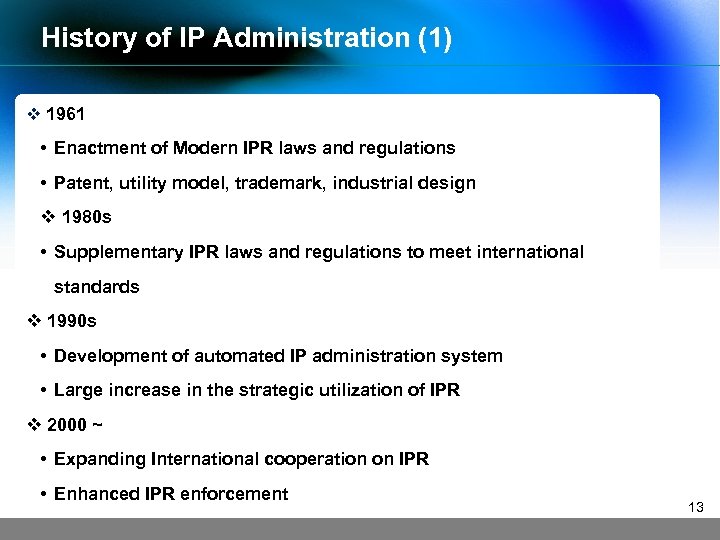
History of IP Administration (1) v 1961 • Enactment of Modern IPR laws and regulations • Patent, utility model, trademark, industrial design v 1980 s • Supplementary IPR laws and regulations to meet international standards v 1990 s • Development of automated IP administration system • Large increase in the strategic utilization of IPR v 2000 ~ • Expanding International cooperation on IPR • Enhanced IPR enforcement 13

History of IP Administration (2) History of KIPO 1908: Enactment of the Patent Decree 1949: Establishment of the Patent Bureau under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry 1977: Establishment of KIPO as an independent office under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry 1998: KIPO moved its headquarters from Seoul to Daejeon 2006: KIPO was transformed into an enterprise-style, performance-based government agency 14
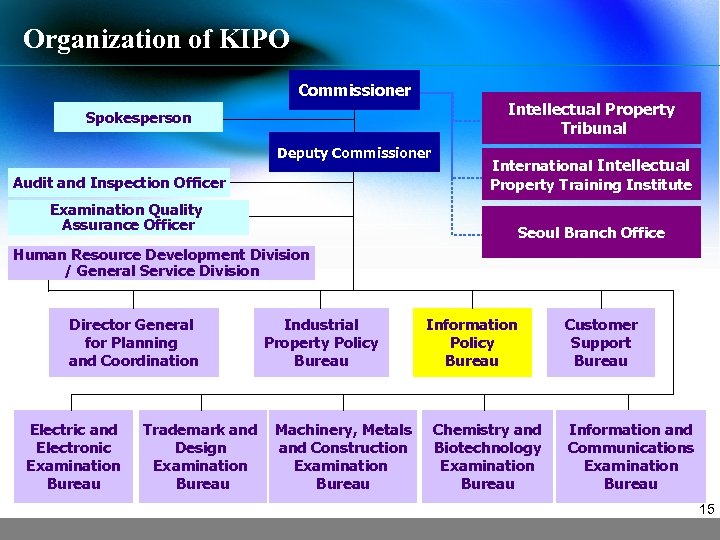
Organization of KIPO Commissioner Intellectual Property Tribunal Spokesperson Deputy Commissioner Audit and Inspection Officer Examination Quality Assurance Officer International Intellectual Property Training Institute Seoul Branch Office Human Resource Development Division / General Service Division Director General for Planning and Coordination Electric and Electronic Examination Bureau Trademark and Design Examination Bureau Industrial Property Policy Bureau Machinery, Metals and Construction Examination Bureau Information Policy Bureau Chemistry and Biotechnology Examination Bureau Customer Support Bureau Information and Communications Examination Bureau 15
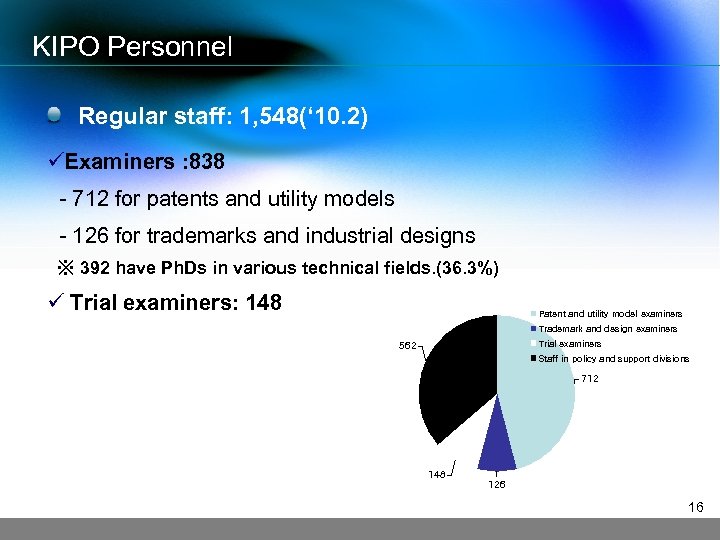
KIPO Personnel Regular staff: 1, 548(‘ 10. 2) üExaminers : 838 - 712 for patents and utility models - 126 for trademarks and industrial designs ※ 392 have Ph. Ds in various technical fields. (36. 3%) ü Trial examiners: 148 Patent and utility model examiners Trademark and design examiners Trial examiners 562 Staff in policy and support divisions 712 148 126 16
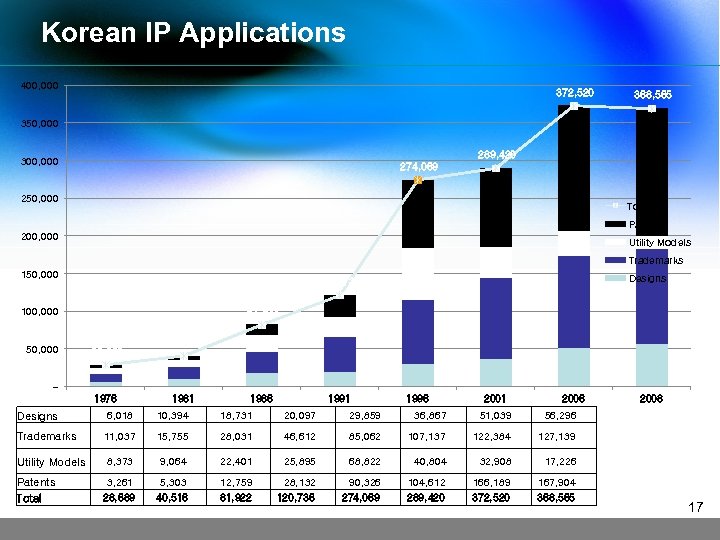
Korean IP Applications 400, 000 372, 520 368, 565 350, 000 289, 420 300, 000 274, 069 250, 000 Total Patents 200, 000 Utility Models Trademarks 150, 000 81, 922 100, 000 50, 000 Designs 120, 736 28, 689 40, 516 1976 Designs 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006 6, 018 10, 394 18, 731 20, 097 29, 859 36, 867 51, 039 56, 296 11, 037 15, 755 28, 031 46, 612 85, 062 107, 137 122, 384 127, 139 Utility Models 8, 373 9, 064 22, 401 25, 895 68, 822 40, 804 32, 908 17, 226 Patents Total 3, 261 5, 303 12, 759 28, 132 90, 326 104, 612 166, 189 167, 904 28, 689 40, 516 81, 922 120, 736 274, 069 289, 420 372, 520 368, 565 2008 Trademarks 17
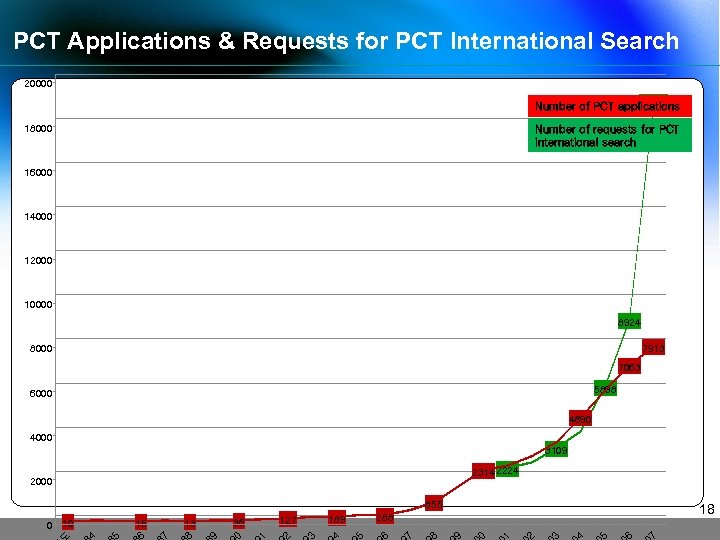
PCT Applications & Requests for PCT International Search 20000 18818 Number of PCT applications Number of requests for PCT international search 18000 16000 14000 12000 10000 8924 8000 7913 7063 5898 6000 4690 4000 3109 2314 2224 2000 855 0 10 15 13 36 127 189 288 18
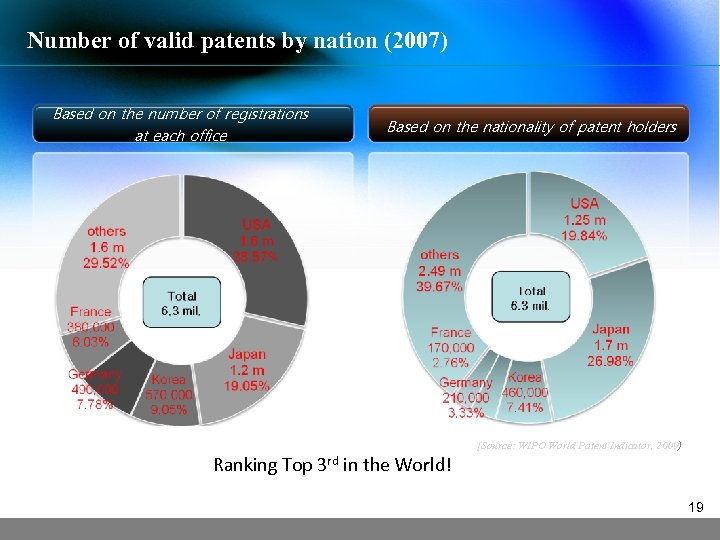
Number of valid patents by nation (2007) Based on the number of registrations at each office Based on the nationality of patent holders Ranking Top 3 rd in the World! [Source: WIPO World Patent Indicator, 2009) 19
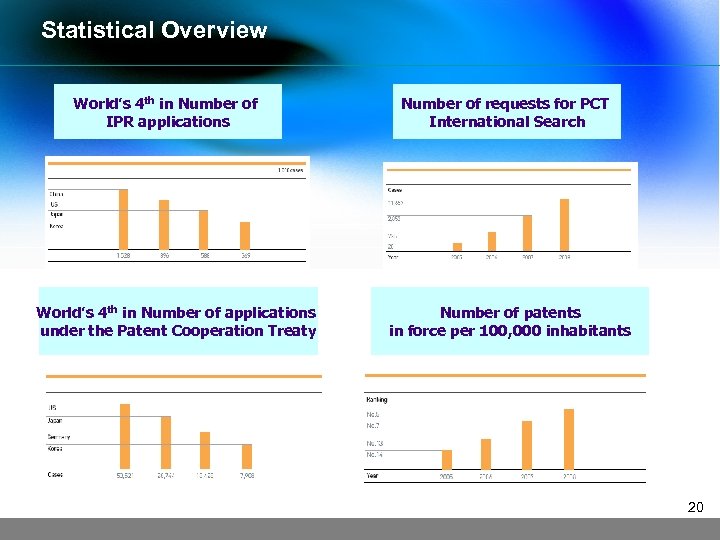
Statistical Overview World’s 4 th in Number of IPR applications World’s 4 th in Number of applications under the Patent Cooperation Treaty Number of requests for PCT International Search Number of patents in force per 100, 000 inhabitants 20
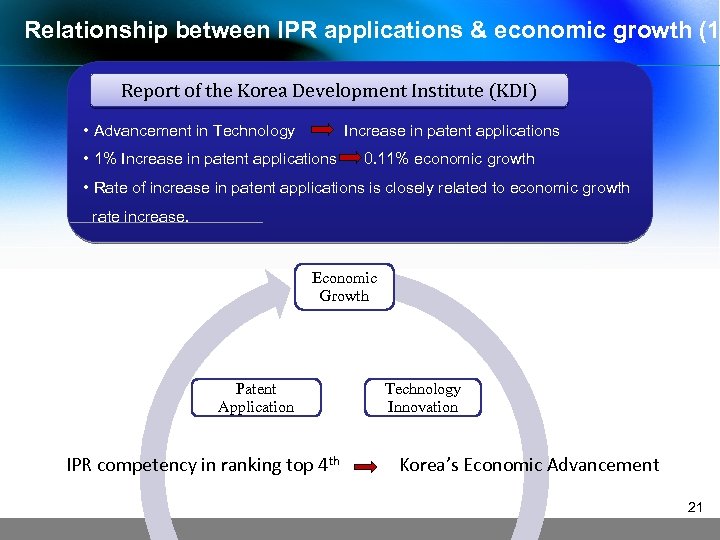
Relationship between IPR applications & economic growth (1 Report of the Korea Development Institute (KDI) • Advancement in Technology Increase in patent applications • 1% Increase in patent applications 0. 11% economic growth • Rate of increase in patent applications is closely related to economic growth rate increase. Economic Growth Patent Application IPR competency in ranking top 4 th Technology Innovation Korea’s Economic Advancement 21
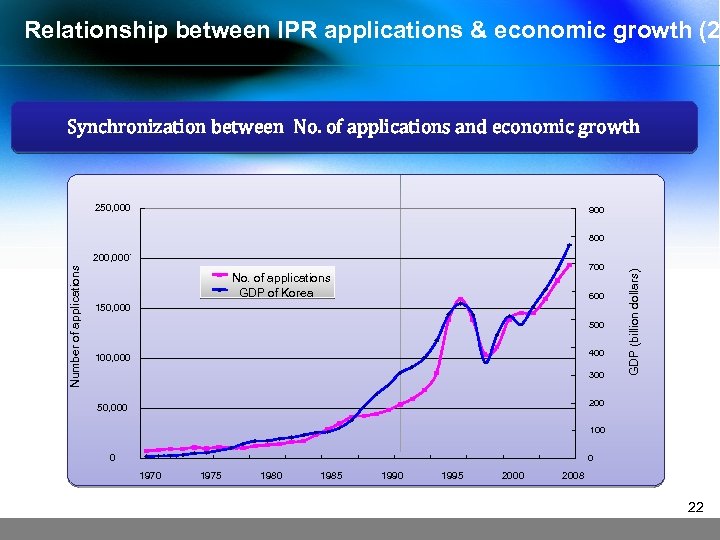
Relationship between IPR applications & economic growth (2 Synchronization between No. of applications and economic growth 250, 000 900 Number of applications 200, 000` 700 No. of applications GDP of Korea 600 150, 000 500 400 100, 000 300 GDP (billion dollars) 800 200 50, 000 100 0 0 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2008 22

Ⅲ Major Policies of KIPO and its Role in the Economic Development of Korea
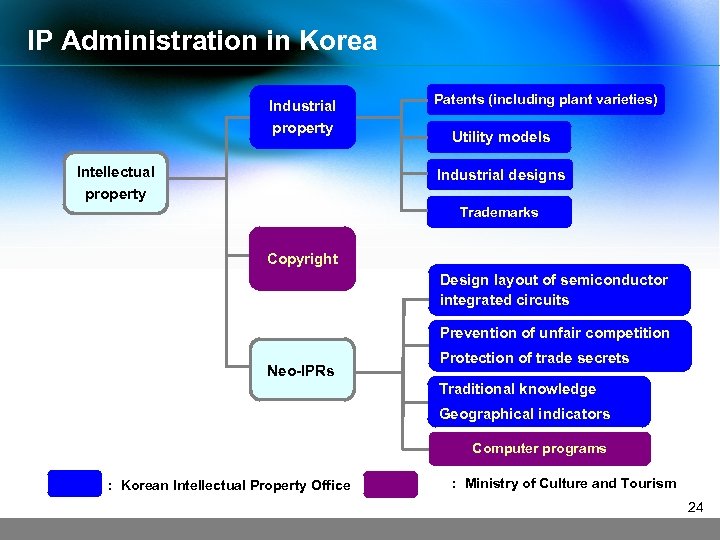
IP Administration in Korea Industrial property Intellectual property Patents (including plant varieties) Utility models Industrial designs Trademarks Copyright Designs of Semiconductor Layout layout of semiconductor integrated circuits Integrated Circuits Prevention of unfair competition Neo-IPRs Protection of trade secrets Traditional knowledge Geographical indicators Computer programs : Korean Intellectual Property Office : Ministry of Culture and Tourism 24
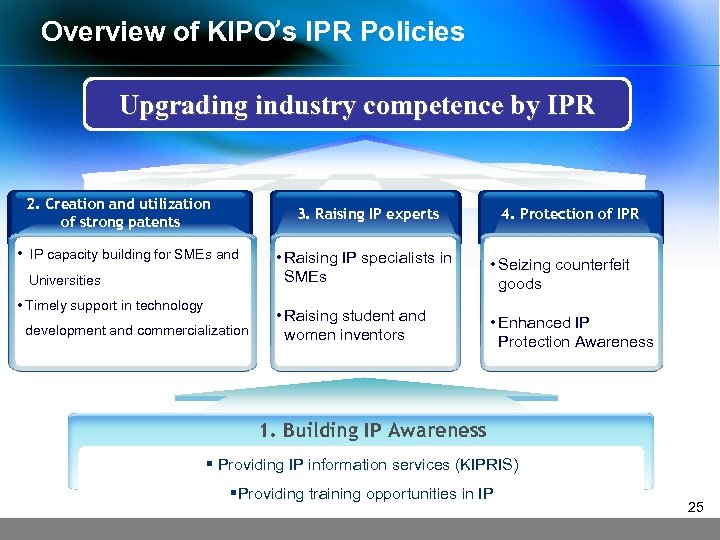
Overview of KIPO’s IPR Policies Upgrading industry competence by IPR 2. Creation and utilization of strong patents 3. Raising IP experts • IP capacity building for SMEs and Universities • Timely support in technology development and commercialization 4. Protection of IPR • Raising IP specialists in SMEs • Seizing counterfeit goods • Raising student and women inventors • Enhanced IP Protection Awareness 1. Building IP Awareness § Providing IP information services (KIPRIS) §Providing training opportunities in IP 25
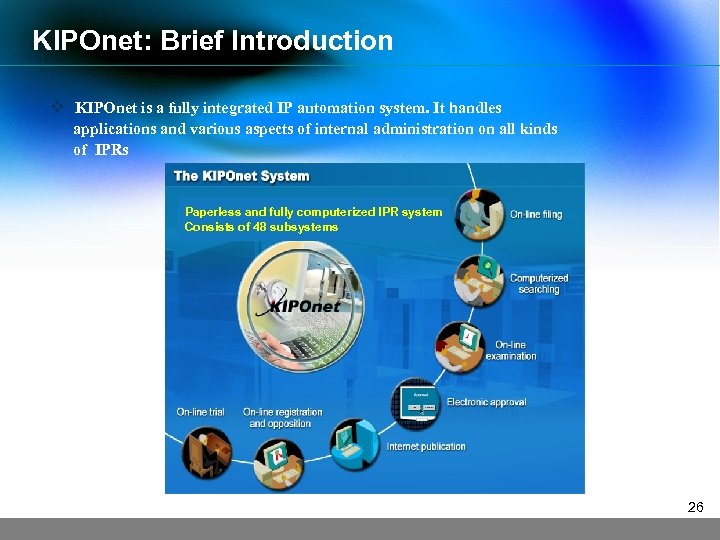
KIPOnet: Brief Introduction v KIPOnet is a fully integrated IP automation system. It handles applications and various aspects of internal administration on all kinds of IPRs Paperless and fully computerized IPR system Consists of 48 subsystems 26
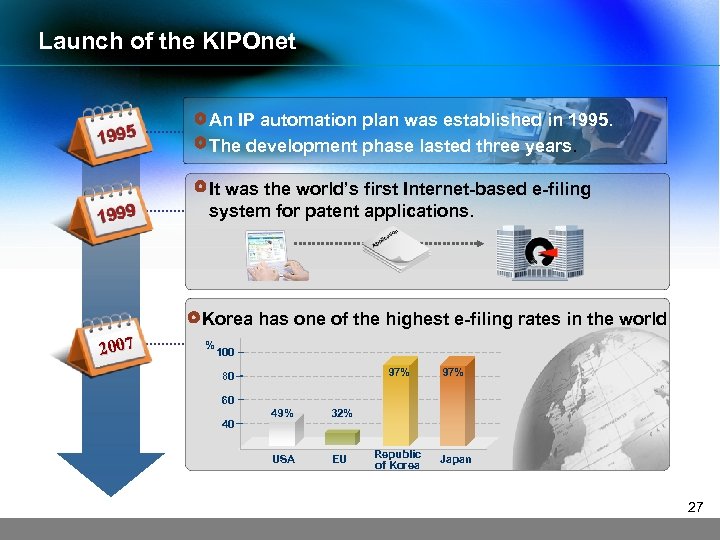
Launch of the KIPOnet An IP automation plan was established in 1995. The development phase lasted three years. It was the world’s first Internet-based e-filing system for patent applications. Korea has one of the highest e-filing rates in the world 2007 % 100 97% 80 97% 60 40 49% 32% USA EU Republic of Korea Japan 27

Major Features of KIPOnet System Work-at-Home System 24 X 7 Non-Stop Service 28

Policy Direction on IPR (1/5) 1. Quality-focused Examinations v Paradigm Shift: Quantity Quality Change in corporate IP strategy ü The focus is on strong, high-quality IPRs rather than the quantity of applications. v Transforming into an IP nation in the 21 st century. 29

Policy Direction on IPR (2/5) 2. EXCEL (EXamination ex. CELlence) Plan Measures to optimize the examination infrastructure ü Putting emphasis on vigorous search of non-patent literature ü Improving the automatic machine translation system Measures to enhance examination quality ü Implementing an individual self-diagnostic system for examination quality ü Establishing new examination divisions dedicated to newly emerging integrated technologies Measures to maximize efficiency in examination quality management ü Systemizing standard operating procedures for searches and examinations in each examination bureau ü Implementing a Responsible Management System, where director generals and directors take full responsibility for the quality of the examination results of their respective bureaus and divisions. 30
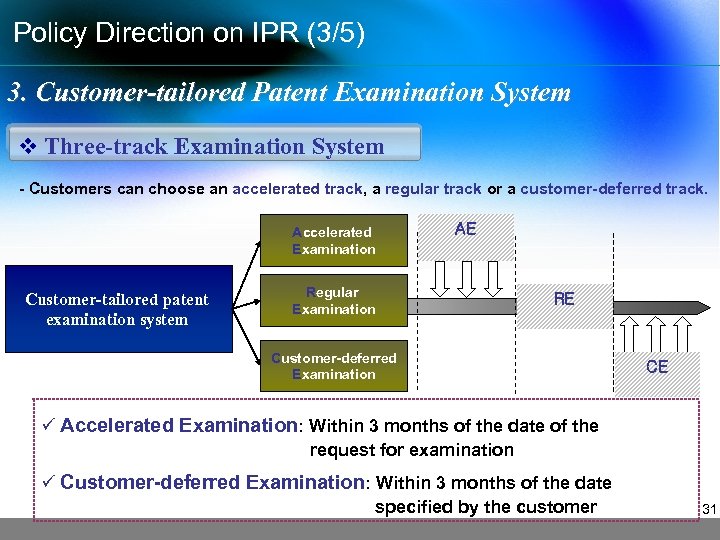
Policy Direction on IPR (3/5) 3. Customer-tailored Patent Examination System v Three-track Examination System - Customers can choose an accelerated track, a regular track or a customer-deferred track. Accelerated Examination Customer-tailored patent examination system Regular Examination AE RE Customer-deferred Examination CE ü Accelerated Examination: Within 3 months of the date of the request for examination ü Customer-deferred Examination: Within 3 months of the date specified by the customer 31

Policy Direction on IPR (4/5) 4. International Cooperation under the new IP 5 Framework Work-Sharing among the IP 5 offices üWork-sharing: a way of tackling examination backlogs Bilateral cooperation and the PPH • Support for SMEs, * Cooperation on IPR education, • Establishing experts meetings * Exchange of staff and examiners, 32

Policy Direction on IPR (5/5) 5. Developing country support using IP Cooperating with WIPO based on Korea Funds-in-Trust üEstablishment of the Korea Funds-in-Trust at WIPO(2004) -To support developing and low income countries in strengthening their IP capacity üAbout 2 Million USD has been spent in 22 fields üPractical support through educational programs on the use of IPR, technology transfer IP-based support programs üObjectives: To help local communities increase their income through the utilization of IP To provide technological solutions to the basic necessities of life One Village One Brand üObjectives: To increase product sales volume through the creation of brands üPilot project (2008): designing a brand securing a trademark for East Timor coffee 33
Conclusion ① Quality focused Examinations and International cooperation ② Creation and promotion of strong IPRs ③ Advancing domestic and foreign protection of IPRs Becoming an advanced IP nation No Patent, No Future! 34

Thank you ﺷﻜﺮﺍ ﺟﺰﻳﻼ Won-Kil YOON Director, Technical Cooperation Division Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPO) Tel. +82 (42) 481 -8254 Fax. +82 (42) 472 -9313 E-mail: wonkil@kipo. go. kr
c047b8b7ff75c3c1543cd9c8861c559d.ppt