631022f1746f8ab8d4b5cdf50404f4b0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Korea-EU FTA - Implications for Global Businesses 2011. 11 United Kingdom Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade The Republic of Korea
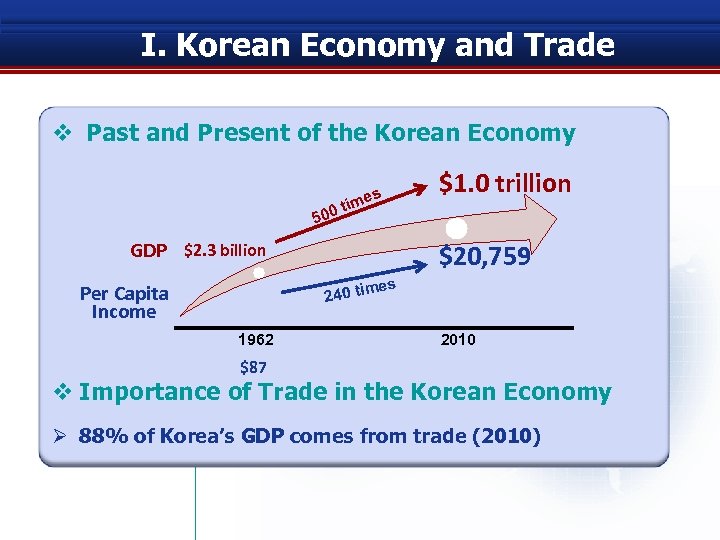
I. Korean Economy and Trade v Past and Present of the Korean Economy s ime t 500 GDP $2. 3 billion $1. 0 trillion $20, 759 es 240 tim Per Capita Income 1962 2010 $87 v Importance of Trade in the Korean Economy Ø 88% of Korea’s GDP comes from trade (2010)

II. Korea’s FTA Policy (1) v Consistent Trade Liberalization policy - based on WTO multilateral system v Policy Environment in 2000’s Ø Stalemate in the WTO DDA negotiations Ø Surge of RTAs after the establishment of WTO in 1995 Ø International trade volume under RTAs : more than 50% of the global trade v FTA Roadmap in 2003
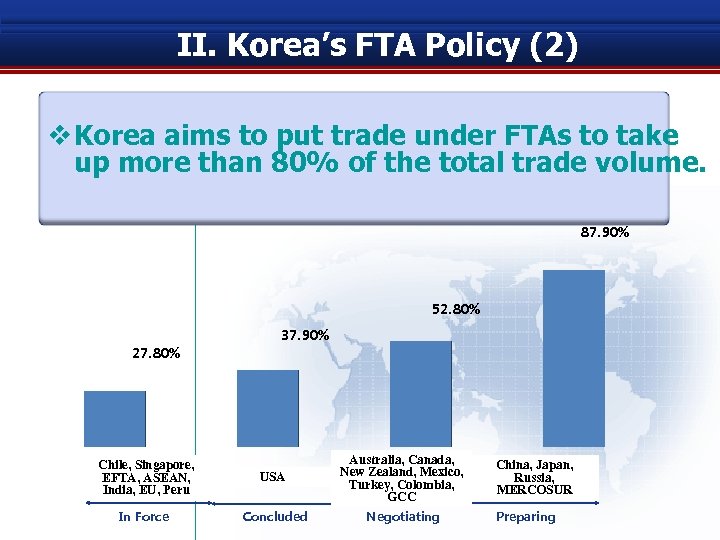
II. Korea’s FTA Policy (2) v Korea aims to put trade under FTAs to take up more than 80% of the total trade volume. 87. 90% 52. 80% 27. 80% 37. 90% Chile, Singapore, EFTA, ASEAN, India, EU, Peru USA Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Mexico, Turkey, Colombia, GCC In Force Concluded Negotiating China, Japan, Russia, MERCOSUR Preparing
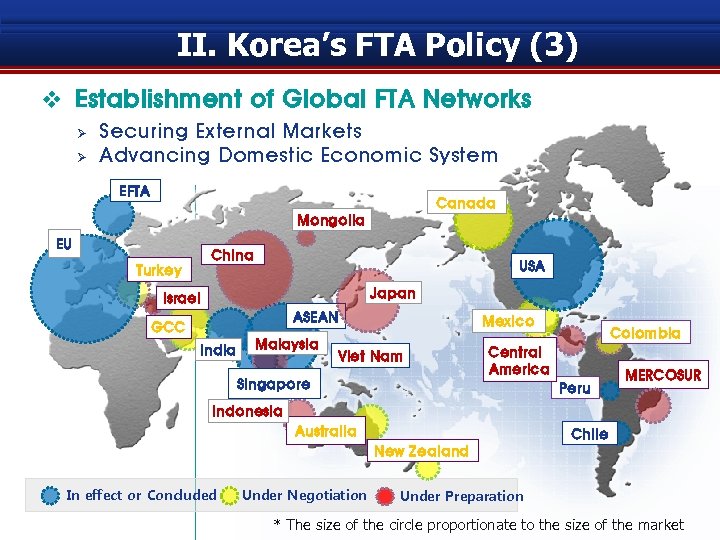
II. Korea’s FTA Policy (3) v Establishment of Global FTA Networks Ø Ø Securing External Markets Advancing Domestic Economic System EFTA Canada Mongolia EU China USA Turkey Japan Israel ASEAN GCC India Malaysia Mexico Viet Nam Colombia Central America Singapore Peru MERCOSUR Indonesia Australia Chile New Zealand In effect or Concluded Under Negotiation Under Preparation * The size of the circle proportionate to the size of the market

III. the Korea-EU FTA: Background Ø Ø Ø Strengthening the Strategic Partnership Korea’s Economic Network with the World’s Largest Market EU’s Springboard into the Asian Market Progress 2007. 5. 6 2009. 7. 13 2009. 10. 15 Launched Concluded Initialed 2010. 6 2011. 7. 1 Officially Signed Provisional Application v Formal Entry into Force (in 2~3 yrs) Ø When all 27 Member States of the EU Completes Domestic Ratification Procedures
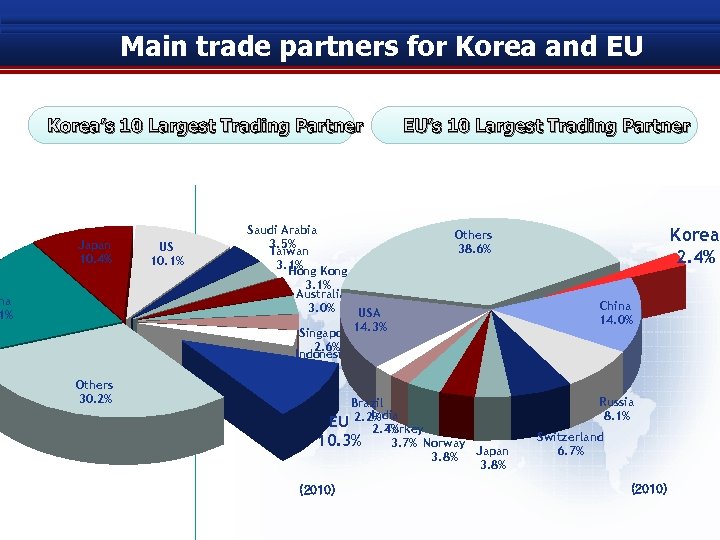
Main trade partners for Korea and EU Korea’s 10 Largest Trading Partner Japan 10. 4% US 10. 1% Saudi Arabia 3. 5% Taiwan 3. 1% Kong Hong EU’s 10 Largest Trading Partner 3. 1% Australia 3. 0% na 1% Korea 2. 4% Others 38. 6% USA 14. 3% Singapore China 14. 0% 2. 6% Indonesia 2. 6% Others 30. 2% Brazil India EU 2. 2% Turkey 2. 4% 10. 3% 3. 7% Norway Japan 3. 8% (2010) Russia 8. 1% Switzerland 6. 7% (2010)
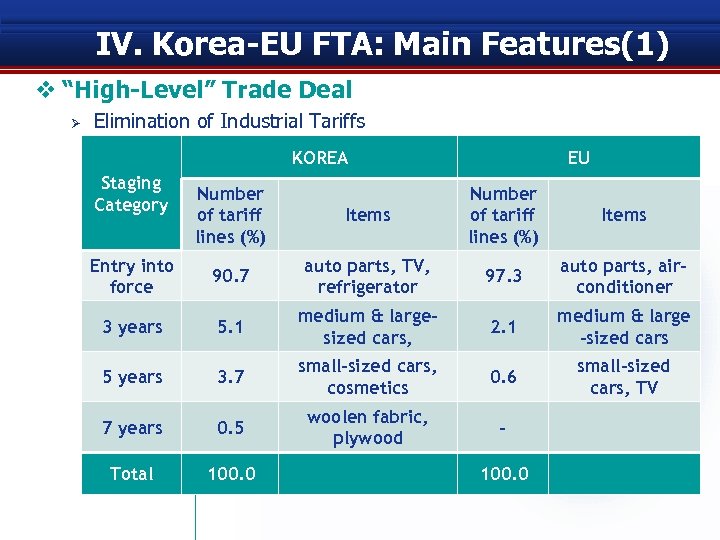
IV. Korea-EU FTA: Main Features(1) v “High-Level” Trade Deal Ø Elimination of Industrial Tariffs KOREA Staging Category Number of tariff lines (%) Entry into force EU Items Number of tariff lines (%) Items 90. 7 auto parts, TV, refrigerator 97. 3 auto parts, airconditioner 3 years 5. 1 medium & largesized cars, 2. 1 medium & large -sized cars 5 years 3. 7 small-sized cars, cosmetics 0. 6 small-sized cars, TV 7 years 0. 5 woolen fabric, plywood - Total 100. 0
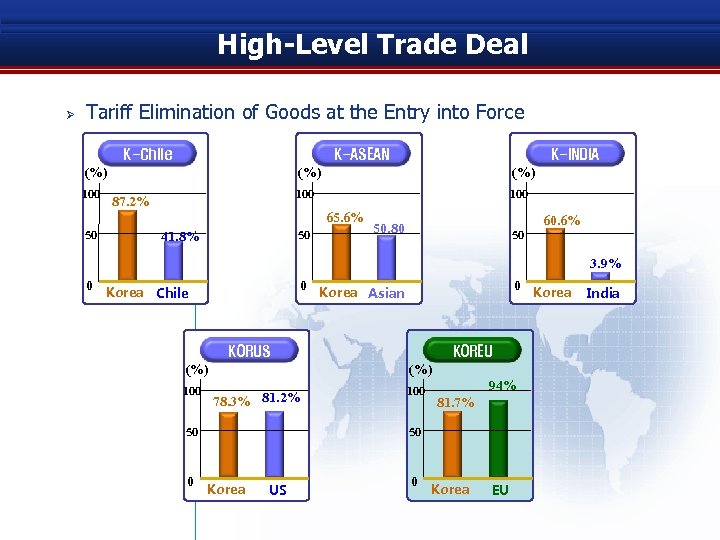
High-Level Trade Deal Ø Tariff Elimination of Goods at the Entry into Force K-Chile K-ASEAN (%) 100 50 K-INDIA (%) 100 87. 2% (%) 100 65. 6% 50 41. 8% 50. 80 50 60. 6% 3. 9% 0 0 Korea Chile 0 Korea Asian KORUS (%) 100 (%) 78. 3% 81. 2% 50 0 KOREU 100 94% 81. 7% 50 Korea US 0 Korea EU Korea India
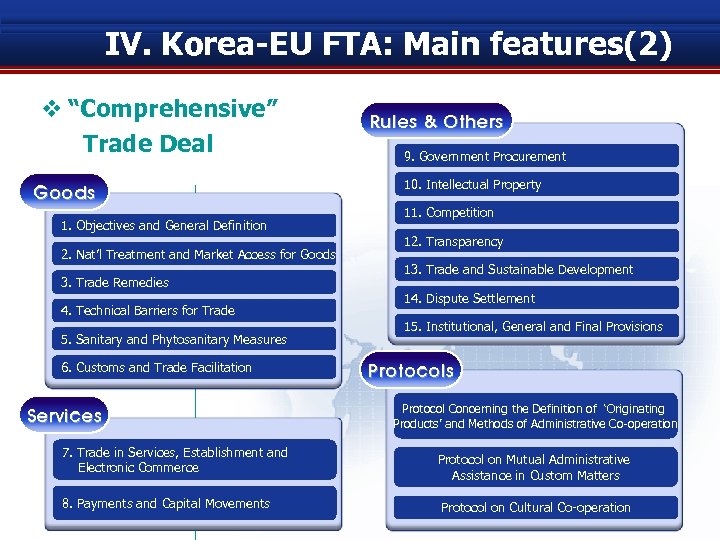
IV. Korea-EU FTA: Main features(2) v “Comprehensive” Trade Deal Goods 1. Objectives and General Definition 2. Nat’l Treatment and Market Access for Goods 3. Trade Remedies 4. Technical Barriers for Trade 5. Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures 6. Customs and Trade Facilitation Services 7. Trade in Services, Establishment and Electronic Commerce 8. Payments and Capital Movements Rules & Others 9. Government Procurement 10. Intellectual Property Rules & Others 11. Competition 12. Transparency 13. Trade and Sustainable Development 14. Dispute Settlement 15. Institutional, General and Final Provisions Protocol Concerning the Definition of ‘Originating Products’ and Methods of Administrative Co-operation Protocol on Mutual Administrative Assistance in Custom Matters Protocol on Cultural Co-operation
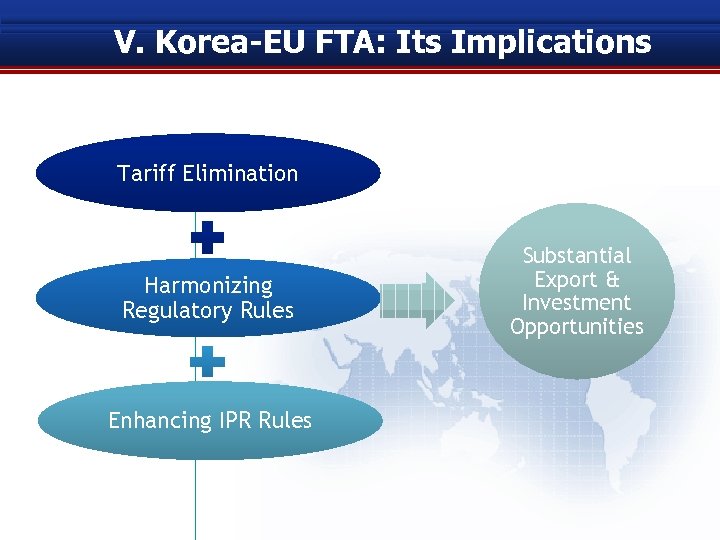
V. Korea-EU FTA: Its Implications Tariff Elimination Harmonizing Regulatory Rules Enhancing IPR Rules Substantial Export & Investment Opportunities
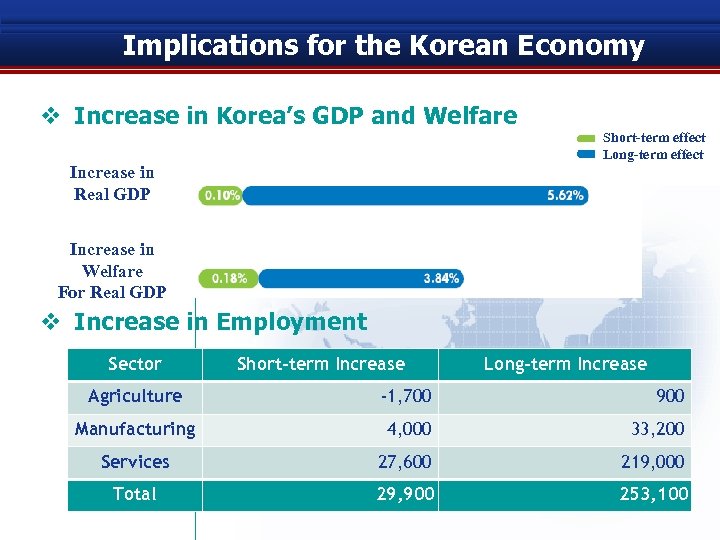
Implications for the Korean Economy v Increase in Korea’s GDP and Welfare Short-term effect Long-term effect Increase in Real GDP Increase in Welfare For Real GDP v Increase in Employment Sector Short-term Increase Long-term Increase Agriculture -1, 700 900 Manufacturing 4, 000 33, 200 Services 27, 600 219, 000 Total 29, 900 253, 100
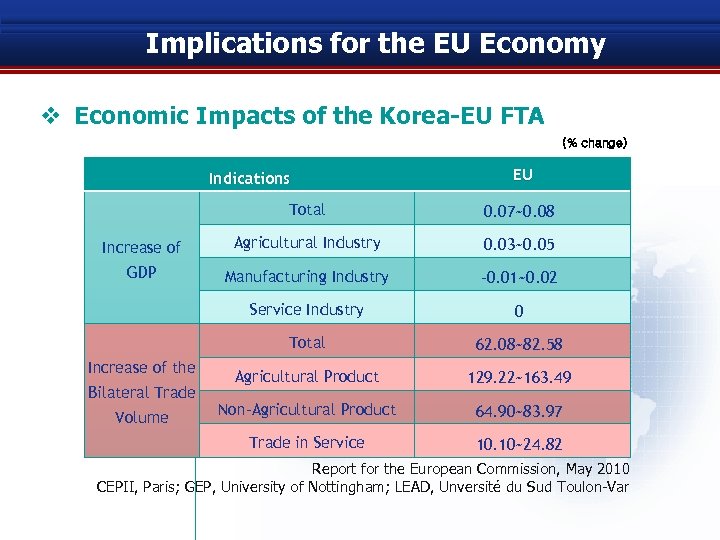
Implications for the EU Economy v Economic Impacts of the Korea-EU FTA (% change) Indications EU Total 0. 07~0. 08 Increase of Agricultural Industry 0. 03~0. 05 GDP Manufacturing Industry -0. 01~0. 02 Service Industry 0 Total 62. 08~82. 58 Agricultural Product 129. 22~163. 49 Non-Agricultural Product 64. 90~83. 97 Trade in Service 10. 10~24. 82 Increase of the Bilateral Trade Volume Report for the European Commission, May 2010 CEPII, Paris; GEP, University of Nottingham; LEAD, Unversité du Sud Toulon-Var
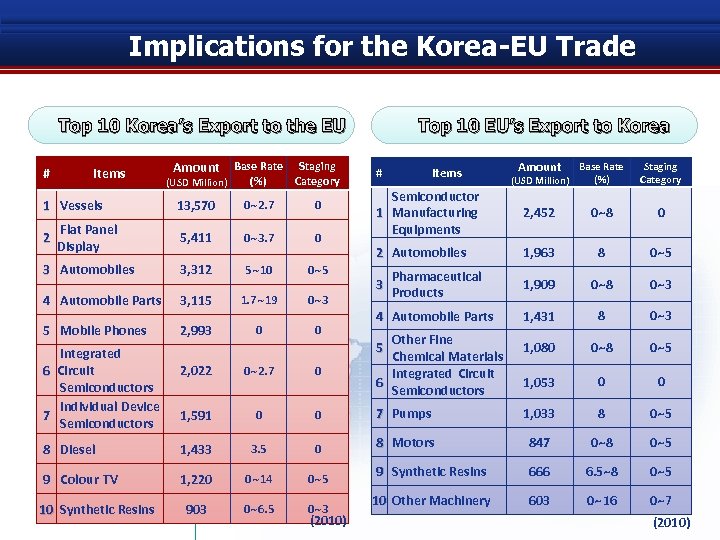
Implications for the Korea-EU Trade Top 10 Korea’s Export to the EU Amount Base Rate (USD Million) (%) Staging Category 13, 570 0~2. 7 0 Flat Panel Display 5, 411 0~3. 7 0 3 Automobiles 3, 312 5~10 0~5 4 Automobile Parts 3, 115 1. 7~19 0~3 5 Mobile Phones 2, 993 0 0 # Items 1 Vessels 2 Integrated 6 Circuit Semiconductors Individual Device 7 Semiconductors Top 10 EU’s Export to Korea (USD Million) Amount Base Rate (%) Staging Category Semiconductor 1 Manufacturing Equipments 2, 452 0~8 0 2 Automobiles 1, 963 8 0~5 Pharmaceutical Products 1, 909 0~8 0~3 4 Automobile Parts 1, 431 8 0~3 1, 080 0~8 0~5 1, 053 0 0 # 3 Items Other Fine Chemical Materials Integrated Circuit 6 Semiconductors 5 2, 022 0~2. 7 0 1, 591 0 0 7 Pumps 1, 033 8 0~5 8 Diesel 1, 433 3. 5 0 8 Motors 847 0~8 0~5 9 Colour TV 1, 220 0~14 0~5 9 Synthetic Resins 666 6. 5~8 0~5 903 0~6. 5 0~3 10 Other Machinery 603 0~16 0~7 10 Synthetic Resins (2010)
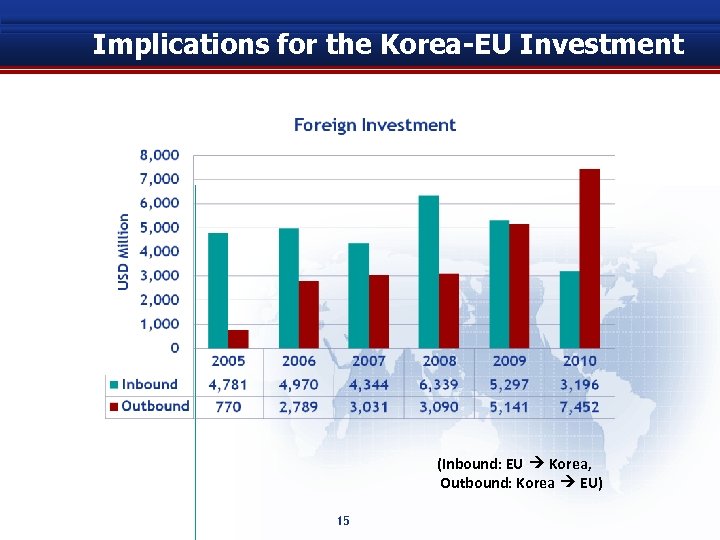
Implications for the Korea-EU Investment (Inbound: EU Korea, Outbound: Korea EU) 15
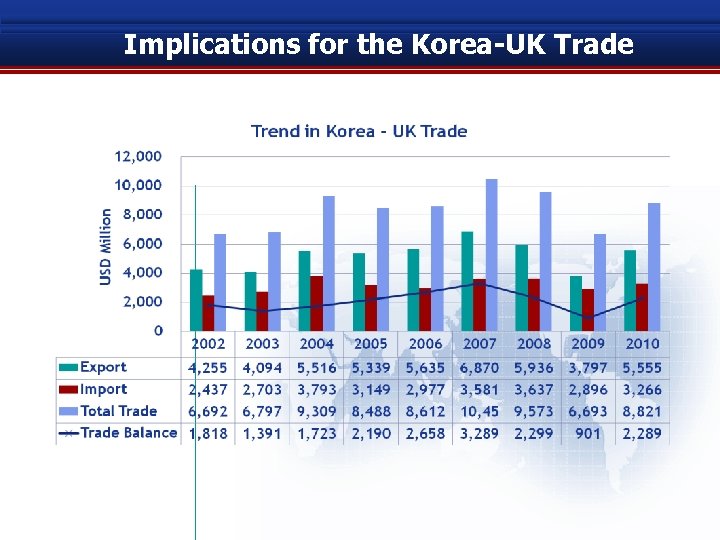
Implications for the Korea-UK Trade
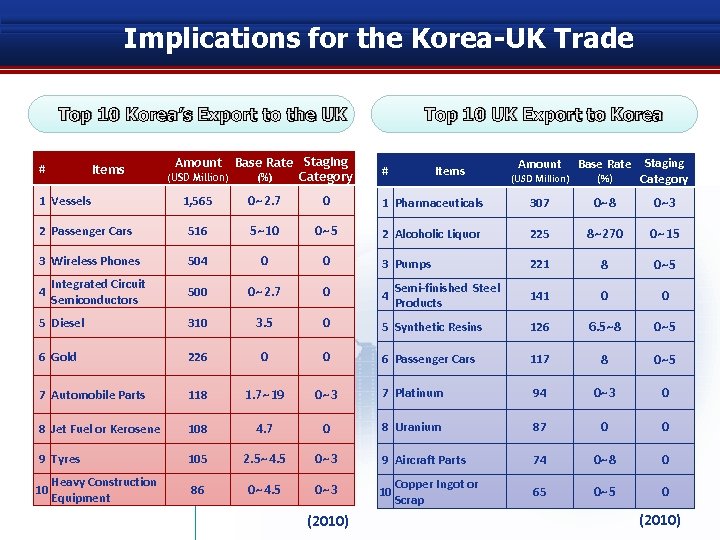
Implications for the Korea-UK Trade Top 10 Korea’s Export to the UK # Items Amount Base Rate Staging (USD Million) (%) Category Top 10 UK Export to Korea # Items Amount Base Rate (USD Million) (%) Staging Category 1, 565 0~2. 7 0 1 Pharmaceuticals 307 0~8 0~3 2 Passenger Cars 516 5~10 0~5 2 Alcoholic Liquor 225 8~270 0~15 3 Wireless Phones 504 0 0 3 Pumps 221 8 0~5 500 0~2. 7 0 4 141 0 0 5 Diesel 310 3. 5 0 5 Synthetic Resins 126 6. 5~8 0~5 6 Gold 226 0 0 6 Passenger Cars 117 8 0~5 7 Automobile Parts 118 1. 7~19 0~3 7 Platinum 94 0~3 0 8 Jet Fuel or Kerosene 108 4. 7 0 8 Uranium 87 0 0 9 Tyres 105 2. 5~4. 5 0~3 9 Aircraft Parts 74 0~8 0 86 0~4. 5 0~3 10 65 0~5 0 1 Vessels 4 10 Integrated Circuit Semiconductors Heavy Construction Equipment (2010) Semi-finished Steel Products Copper Ingot or Scrap (2010)
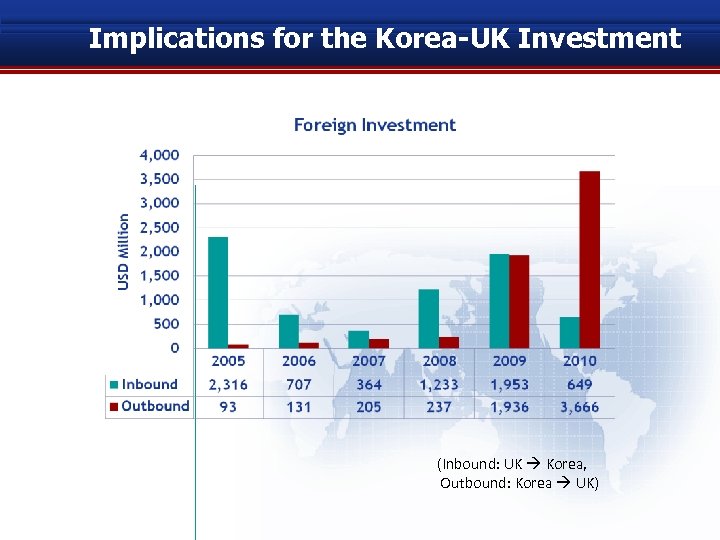
Implications for the Korea-UK Investment (Inbound: UK Korea, Outbound: Korea UK)

VI. Korea-EU FTA: How to make it REAL v Score for the first 100 days Ø Ø Bilateral trade volume: 25. 4 billion US$ = 11. 8% incre The 1 st Trade Committee Meeting: 12 October 2011, Se v FTA is not ending point, but starting point Ø Active participation of Business Community in both Tra and Investment is essential Ø Cooperation between Government and Business Community is also important

631022f1746f8ab8d4b5cdf50404f4b0.ppt