89dbfbcd5da7fb10770e6abd2c3deb7a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Knowledge Programme Benefits Realisation Plan January 2013 1

Benefits Management 2
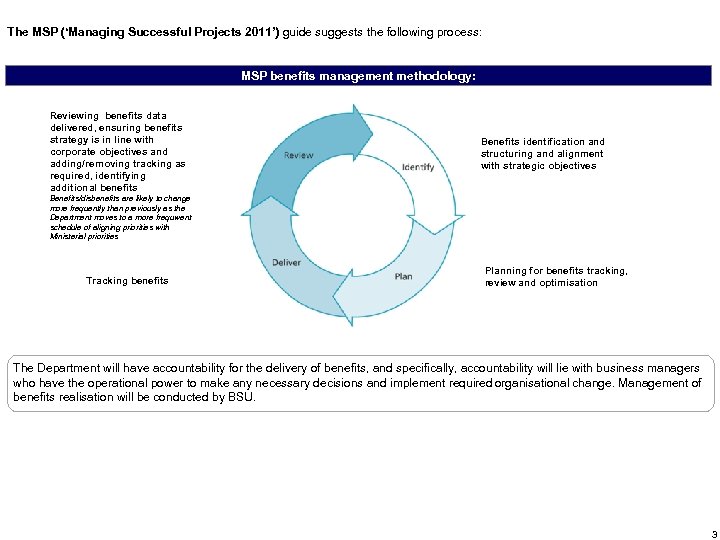
The MSP (‘Managing Successful Projects 2011’) guide suggests the following process: MSP benefits management methodology: Reviewing benefits data delivered, ensuring benefits strategy is in line with corporate objectives and adding/removing tracking as required, identifying additional benefits Benefits identification and structuring and alignment with strategic objectives Benefits/disbenefits are likely to change more frequently than previously as the Department moves to a more frequwent schedule of aligning priorities with Ministerial priorities Tracking benefits Planning for benefits tracking, review and optimisation The Department will have accountability for the delivery of benefits, and specifically, accountability will lie with business managers who have the operational power to make any necessary decisions and implement required organisational change. Management of benefits realisation will be conducted by BSU. 3

Benefits definitions 4
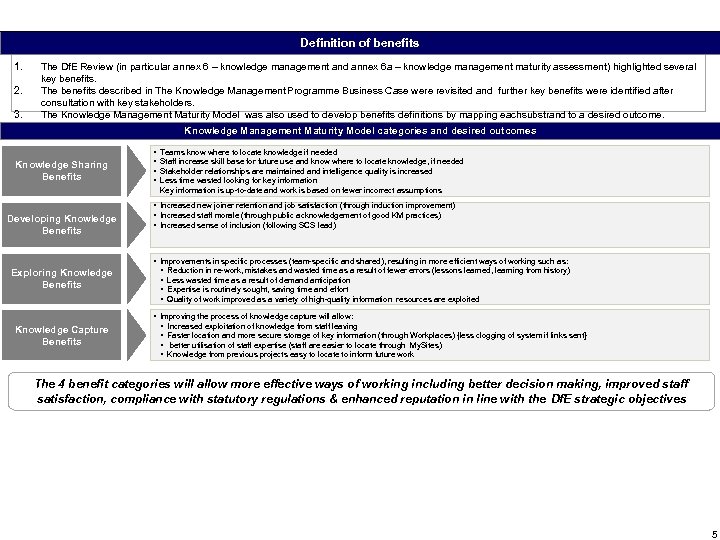
Definition of benefits 1. 2. 3. The Df. E Review (in particular annex 6 – knowledge management and annex 6 a – knowledge management maturity assessment) highlighted several key benefits. The benefits described in The Knowledge Management Programme Business Case were revisited and further key benefits were identified after consultation with key stakeholders. The Knowledge Management Maturity Model was also used to develop benefits definitions by mapping eachsubstrand to a desired outcome. Knowledge Management Maturity Model categories and desired outcomes Knowledge Sharing Benefits Developing Knowledge Benefits Exploring Knowledge Benefits Knowledge Capture Benefits § § Teams know where to locate knowledge if needed Staff increase skill base for future use and know where to locate knowledge, if needed Stakeholder relationships are maintained and intelligence quality is increased Less time wasted looking for key information Key information is up-to-date and work is based on fewer incorrect assumptions § Increased new joiner retention and job satisfaction (through induction improvement) § Increased staff morale (through public acknowledgement of good KM practices) § Increased sense of inclusion (following SCS lead) § Improvements in specific processes (team-specific and shared), resulting in more efficient ways of working such as: § Reduction in re-work, mistakes and wasted time as a result of fewer errors (lessons learned, learning from history) § Less wasted time as a result of demand anticipation § Expertise is routinely sought, saving time and effort § Quality of work improved as a variety of high-quality information resources are exploited § Improving the process of knowledge capture will allow: § Increased exploitation of knowledge from staff leaving § Faster location and more secure storage of key information (through Workplaces) {less clogging of system if links sent} § better utilisation of staff expertise (staff are easier to locate through My. Sites) § Knowledge from previous projects easy to locate to inform future work The 4 benefit categories will allow more effective ways of working including better decision making, improved staff satisfaction, compliance with statutory regulations & enhanced reputation in line with the Df. E strategic objectives 5
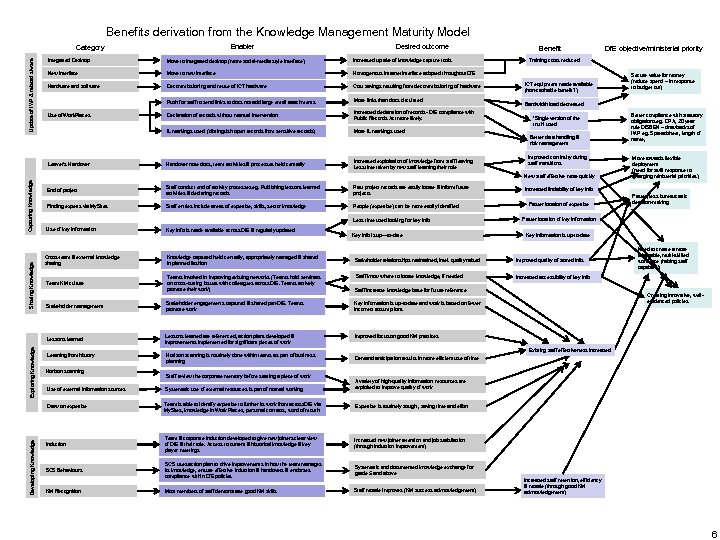
Benefits derivation from the Knowledge Management Maturity Model Enabler Update of IWP & related s/ware Category Desired outcome Integrated Desktop Move to integrated desktop (more social-media style interface) increased uptake of knowledge capture tools New interface Move to new interface Hardware and software Cost savings resulting from decommissioning of hardware Df. E objective/ministerial priority Homogenous Intranet interface adopted throughout Df. E Decommissioning and reuse of ICT hardware Benefit Push for staff to send links to docs not add large email attachments More links than docs circulated Declaration of records without manual intervention Increased declaration of records - Df. E compliance with Public Records Act more likely. IL markings used (distinguish open records from sensitive records) Use of Work. Places Training costs reduced ICT equipment made available (non-cashable benefit? ) Bandwidth load decreased More IL markings used ‘Single version of the truth’ used Better data handling & risk management Leaver’s Handover note docs, team activities & processes held centrally Increased exploitation of knowledge from staff leaving Less time taken by new staff learning their role End of project Staff conduct end of activity processes eg. Publishing lessons learned activities & declaring records Past project records are easily locate & inform future projects Finding experts via My. Sites Staff entries include areas of expertise, skills, sector knowledge People (expertise) can be more easily identified Use of key information Key info is made available across Df. E & regularly updated Improved continuity during staff transitions Capturing Knowledge New staff effective more quickly Less time used looking for key info Sharing Knowledge Key info is up—to-date Cross-team & external knowledge sharing Knowledge captured held centrally, appropriately managed & shared in planned fashion Exploring Knowledge Better compliance with statutory obligations eg. DPA, 20 year rule DISBEN – drawbacks of IWP eg. Spreadsheet, length of name, Move towards flexible deployment (need for swift response to changing ministerial priorities) Increased findability of key info Faster location of expertise Faster, less bureaucratic decision-making Faster location of key information Key information is up-to-date Stakeholder relationships maintained, intel. quality raised Improved quality of stored info. Staff know where to locate knowledge, if needed Need to create a more adaptable, multi-skilled workforce (raising staff capability) Increased accessibility of key info Teams involved in improving existing networks (Teams hold seminars on cross-cutting issues with colleagues across Df. E. Teams actively promote their work) Staff increase knowledge base for future reference Stakeholder management Stakeholder engagements captured & shared pan-Df. E. Teams promote work Key information is up-to-date and work is based on fewer incorrect assumptions Lessons learned are referenced, action plans developed & improvements implemented for significant pieces of work Improved focus on good KM practices Team KM culture Creating innovative, wellevidenced policies Existing staff effectiveness increased Learning from history Horizon scanning is routinely done within teams as part of business planning Demand anticipation results in more efficient use of time Staff review the corporate memory before starting a piece of work A variety of high-quality information resources are exploited to improve quality of work Use of external information sources Systematic use of external resources is part of normal working Draw on expertise Developing Knowledge Secure value for money (reduce spend – in response to budget cut) Team is able to identify expertise to further its work from across Df. E via My. Sites, knowledge in Work Places, personal contacts, word of mouth Expertise is routinely sought, saving time and effort Induction Team & corporate induction developed to give new joiners clear view of Df. E & their role. Access to current & historical knowledge & key player meetings Increased new joiner retention and job satisfaction (through induction improvement) SCS Behaviours SCS uses action plan to drive improvements in how the team manages its knowledge, ensure effective induction & handovers & endorses compliance within Df. E policies Systematic and documented knowledge exchange for grade 5 and above KM Recognition Most members of staff demonstrate good KM skills Staff morale improves (KM success acknowledgement) Increased staff retention, efficiency & morale (through good KM acknowledgement) 6
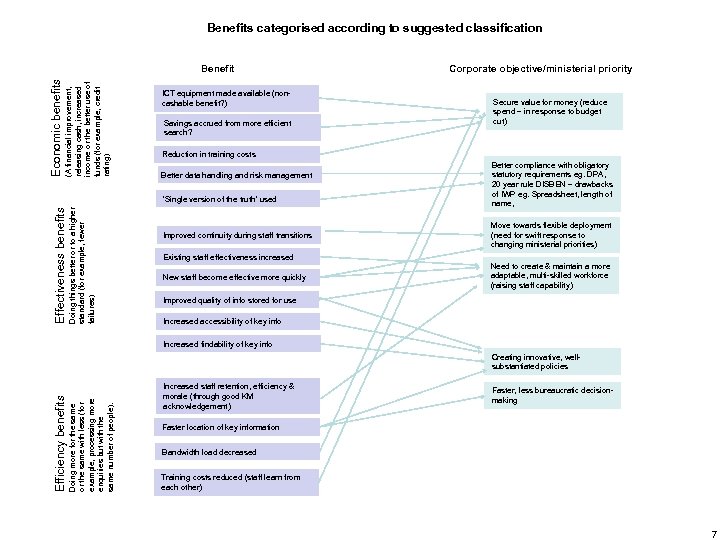
Benefits categorised according to suggested classification (A financial improvement, releasing cash, increased income or the better use of funds (for example, credit rating) Economic benefits Benefit ICT equipment made available (noncashable benefit? ) Savings accrued from more efficient search? Doing things better or to a higher standard (for example, fewer failures) Secure value for money (reduce spend – in response to budget cut) Reduction in training costs Better data handling and risk management ‘Single version of the truth’ used Effectiveness benefits Corporate objective/ministerial priority Improved continuity during staff transitions Better compliance with obligatory statutory requirements eg. DPA, 20 year rule DISBEN – drawbacks of IWP eg. Spreadsheet, length of name, Move towards flexible deployment (need for swift response to changing ministerial priorities) Existing staff effectiveness increased New staff become effective more quickly Need to create & maintain a more adaptable, multi-skilled workforce (raising staff capability) Improved quality of info stored for use Increased accessibility of key info Increased findability of key info Doing more for the same with less (for example, processing more enquiries but with the same number of people). Efficiency benefits Creating innovative, wellsubstantiated policies Increased staff retention, efficiency & morale (through good KM acknowledgement) Faster, less bureaucratic decisionmaking Faster location of key information Bandwidth load decreased Training costs reduced (staff learn from each other) 7
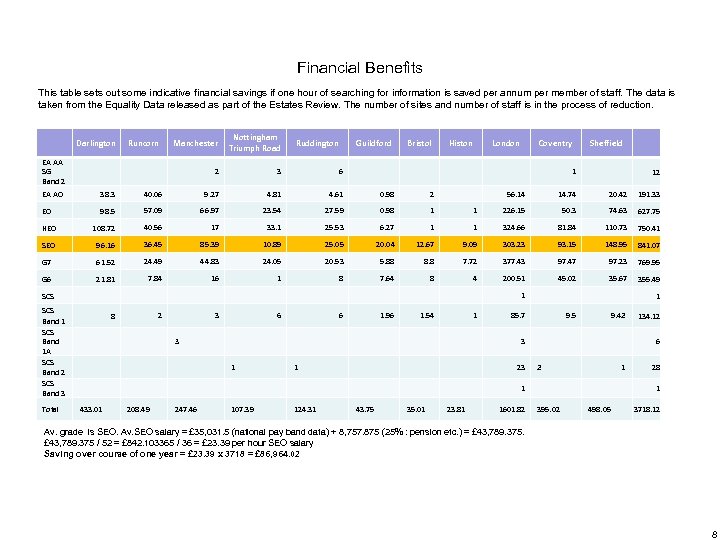
Financial Benefits This table sets out some indicative financial savings if one hour of searching for information is saved per annum per member of staff. The data is taken from the Equality Data released as part of the Estates Review. The number of sites and number of staff is in the process of reduction. Runcorn Manchester Nottingham Triumph Road 2 Darlington 3 6 EA AA SG Band 2 Ruddington Guildford Bristol Histon London Sheffield 1 EA AO 38. 3 40. 06 9. 27 4. 81 4. 61 0. 98 2 EO 98. 5 57. 09 66. 97 23. 54 27. 59 0. 98 1 HEO 108. 72 40. 56 17 33. 1 25. 53 6. 27 SEO 96. 16 36. 45 85. 39 10. 89 25. 05 G 7 61. 52 24. 49 44. 83 24. 05 G 6 21. 81 7. 84 16 1 12 56. 14 14. 74 20. 42 191. 33 1 226. 15 50. 3 74. 63 627. 75 1 1 324. 66 81. 84 110. 73 750. 41 20. 04 12. 67 9. 09 303. 23 93. 15 148. 95 841. 07 20. 53 5. 88 8. 8 7. 72 377. 43 97. 47 97. 23 769. 95 8 7. 64 8 4 200. 51 45. 02 35. 67 355. 49 1 SCS Band 1 A SCS Band 2 SCS Band 3 Total Coventry 2 8 3 6 6 1. 96 1. 54 1 3 1 85. 7 9. 42 9. 5 3 1 1 23 6 2 1 1 433. 01 208. 49 247. 46 107. 39 124. 31 43. 75 35. 01 23. 81 1601. 82 134. 12 28 1 395. 02 498. 05 3718. 12 Av. grade is SEO. Av. SEO salary = £ 35, 031. 5 (national pay band data) + 8, 757. 875 (25% : pension etc. ) = £ 43, 789. 375 / 52 = £ 842. 103365 / 36 = £ 23. 39 per hour SEO salary Saving over course of one year = £ 23. 39 x 3718 = £ 86, 964. 02 8

Identifyng Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics 9
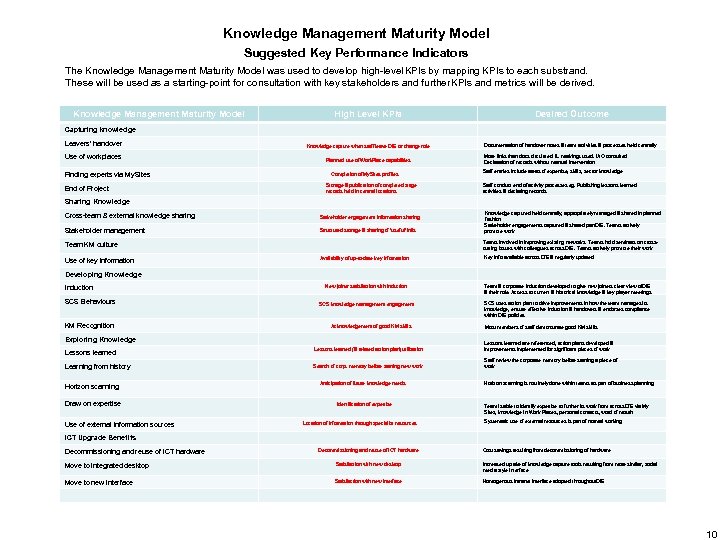
Knowledge Management Maturity Model Suggested Key Performance Indicators The Knowledge Management Maturity Model was used to develop high-level KPIs by mapping KPIs to each substrand. These will be used as a starting-point for consultation with key stakeholders and further KPIs and metrics will be derived. Knowledge Management Maturity Model High Level KPIs Desired Outcome Capturing knowledge Leavers’ handover Use of workplaces Finding experts via My. Sites End of Project Knowledge capture when staff leave Df. E or change role Planned use of Work. Place capabilities Completion of My. Sites profiles Storage & publication of completed stage records held in central locations Documentation of handover notes & team activities & processes held centrally More links than docs circulated. IL markings used. IAO consulted Declaration of records without manual intervention Staff entries include areas of expertise, skills, sector knowledge Staff conduct end of activity processes eg. Publishing lessons learned activities & declaring records Sharing Knowledge Cross-team & external knowledge sharing Stakeholder engagement information sharing Stakeholder management Structured storage & sharing of ‘useful’ info. Teams involved in improving existing networks. Teams hold seminars on crosscutting issues with colleagues across Df. E. Teams actively promote their work Team KM culture Use of key information Knowledge captured held centrally, appropriately managed & shared in planned fashion Stakeholder engagements captured & shared pan-Df. E. Teams actively promote work Availability of up-to-date key information Key info available across Df. E & regularly updated Developing Knowledge Induction SCS Behaviours KM Recognition New joiner satisfaction with induction Team & corporate induction developed to give new joiners clear view of Df. E & their role. Access to current & historical knowledge & key player meetings SCS knowledge management engagement SCS uses action plan to drive improvements in how the team manages its knowledge, ensure effective induction & handovers & endorses compliance within Df. E policies Acknowledgement of good KM skills Exploring Knowledge Most members of staff demonstrate good KM skills Lessons learned (& related action plan) utilisation Lessons learned are referenced, action plans developed & improvements implemented for significant pieces of work Learning from history Search of corp. memory before starting new work Staff review the corporate memory before starting a piece of work Horizon scanning Draw on expertise Use of external information sources Anticipation of future knowledge needs Identification of expertise Location of information through specialist resources Horizon scanning is routinely done within teams as part of business planning Team is able to identify expertise to further its work from across Df. E via My Sites, knowledge in Work Places, personal contacts, word of mouth Systematic use of external resources is part of normal working ICT Upgrade Benefits Decommissioning and reuse of ICT hardware Cost savings resulting from decommissioning of hardware Move to integrated desktop Satisfaction with new desktop increased uptake of knowledge capture tools resulting from more similar, social media style interface Move to new interface Satisfaction with new interface Homogenous Intranet interface adopted throughout Df. E 10
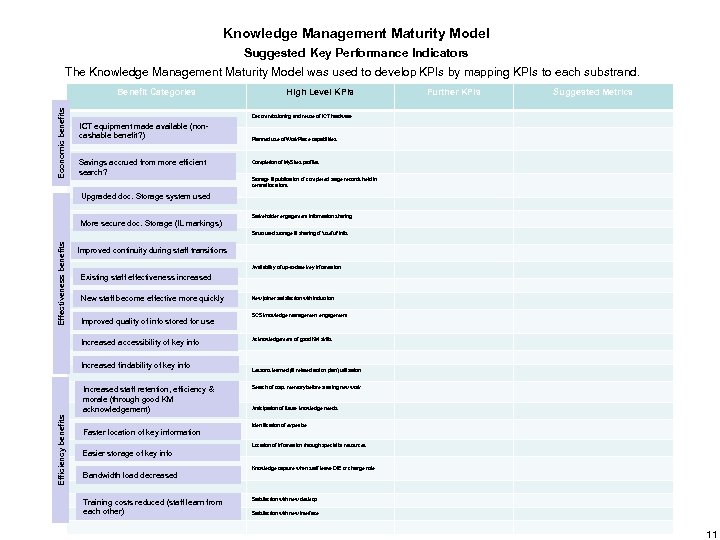
Knowledge Management Maturity Model Suggested Key Performance Indicators The Knowledge Management Maturity Model was used to develop KPIs by mapping KPIs to each substrand. Economic benefits Benefit Categories High Level KPIs Further KPIs Suggested Metrics Decommissioning and reuse of ICT hardware ICT equipment made available (noncashable benefit? ) Savings accrued from more efficient search? Planned use of Work. Place capabilities Completion of My. Sites profiles Storage & publication of completed stage records held in central locations Upgraded doc. Storage system used More secure doc. Storage (IL markings) Stakeholder engagement information sharing Effectiveness benefits Structured storage & sharing of ‘useful’ info. Improved continuity during staff transitions Availability of up-to-date key information Existing staff effectiveness increased New staff become effective more quickly Improved quality of info stored for use Increased accessibility of key info Increased findability of key info Efficiency benefits Increased staff retention, efficiency & morale (through good KM acknowledgement) Faster location of key information New joiner satisfaction with induction SCS knowledge management engagement Acknowledgement of good KM skills Lessons learned (& related action plan) utilisation Search of corp. memory before starting new work Anticipation of future knowledge needs Identification of expertise Location of information through specialist resources Easier storage of key info Bandwidth load decreased Training costs reduced (staff learn from each other) Knowledge capture when staff leave Df. E or change role Satisfaction with new desktop Satisfaction with new interface 11

Baselining indicators 12

Once KPIs and metrics are agreed with BSU stakeholders, baseline data will be collected from across the organisation using a variety of data sources After hand over of benefits tracking in April, BSU will be responsible for benefits tracking including collecting data for future tracking. Baseline Methodology 1. 2. Baseline data for each metric for each KPI will be collected pre- and post 1 month of IWP 2. 0 go live Data will be logged as baseline information 13 Baseline Data Sources* 1. 2. 3. Interviews with key stakeholders Report(s) on Work. Places useage Staff survey 13

Tracking benefits 14
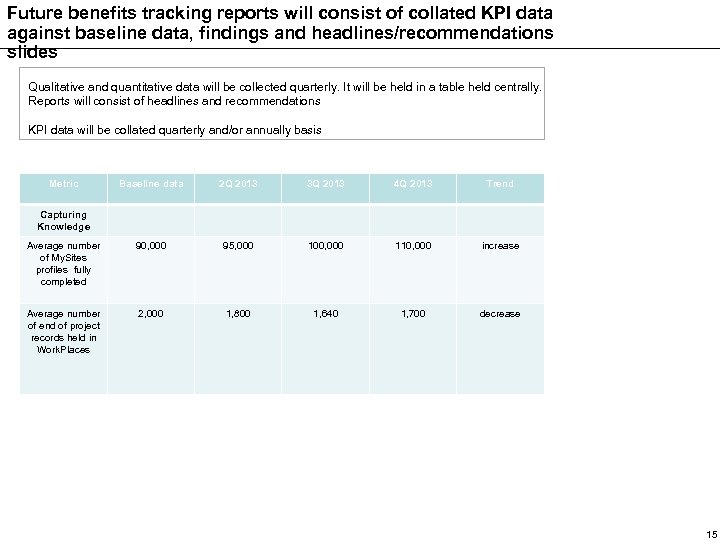
Future benefits tracking reports will consist of collated KPI data against baseline data, findings and headlines/recommendations slides Qualitative and quantitative data will be collected quarterly. It will be held in a table held centrally. Reports will consist of headlines and recommendations KPI data will be collated quarterly and/or annually basis Metric Baseline data 2 Q 2013 3 Q 2013 4 Q 2013 Trend Average number of My. Sites profiles fully completed 90, 000 95, 000 100, 000 110, 000 increase Average number of end of project records held in Work. Places 2, 000 1, 800 1, 640 1, 700 decrease Capturing Knowledge 15

Evaluation 16
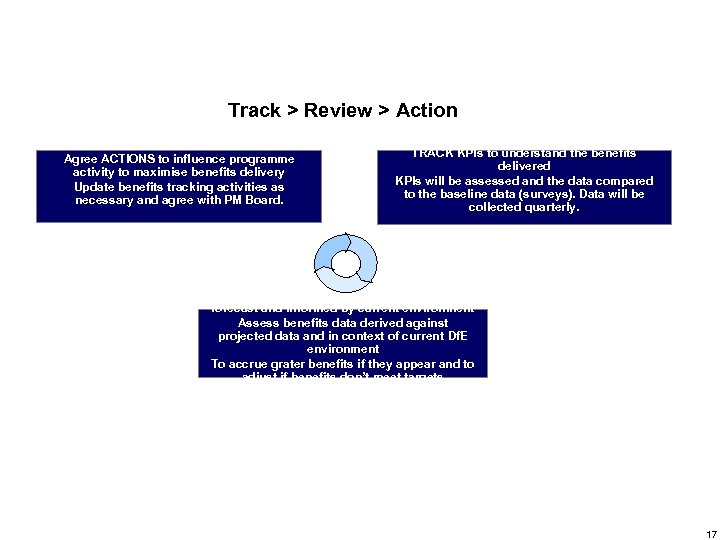
Track > Review > Action Agree ACTIONS to influence programme activity to maximise benefits delivery Update benefits tracking activities as necessary and agree with PM Board. TRACK KPIs to understand the benefits delivered KPIs will be assessed and the data compared to the baseline data (surveys). Data will be collected quarterly. REVIEW the benefits information against forecast and informed by current environment Assess benefits data derived against projected data and in context of current Df. E environment To accrue grater benefits if they appear and to adjust if benefits don’t meet targets 17

Current status 18
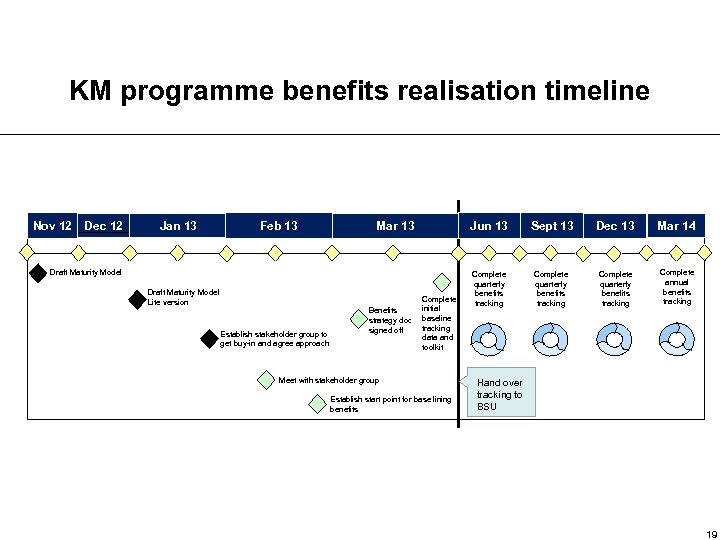
KM programme benefits realisation timeline Nov 12 Dec 12 Jan 13 Feb 13 Jun 13 Mar 13 Draft Maturity Model Lite version Establish stakeholder group to get buy-in and agree approach Benefits strategy doc signed off Complete initial baseline tracking data and toolkit Meet with stakeholder group Establish start point for base lining benefits Sept 13 Dec 13 Mar 14 Complete quarterly benefits tracking Complete annual benefits tracking Hand over tracking to BSU 19
89dbfbcd5da7fb10770e6abd2c3deb7a.ppt