5cb3453870bb820f145d7a4fa81e6548.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Knowledge Management, Ethics and Privacy z Define knowledge management, data, information, knowledge, intellectual capital z Compare and contrast tacit and explicit knowledge z Discuss the knowledge management process z Discuss four modes to knowledge conversion z Discuss Mason’s PAPA principles of ethics z Discuss normative theories of business ethics z Describe ways to gather information customer demographics z Discuss the use of privacy policies z Discuss what cookies are and describe their use z Discuss the role of TRUSTe z Discuss approaches to protecting intellectual property
Knowledge Management, Ethics and Privacy z Define knowledge management, data, information, knowledge, intellectual capital z Compare and contrast tacit and explicit knowledge z Discuss the knowledge management process z Discuss four modes to knowledge conversion z Discuss Mason’s PAPA principles of ethics z Discuss normative theories of business ethics z Describe ways to gather information customer demographics z Discuss the use of privacy policies z Discuss what cookies are and describe their use z Discuss the role of TRUSTe z Discuss approaches to protecting intellectual property
 Definitions z. Knowledge management - processes necessary to capture, codify and transfer knowledge across the organization to achieve competitive advantage z. Intellectual capital - knowledge that has been identified, captured and leveraged to produce higher-value goods or services or some other competitive advantage for the firm
Definitions z. Knowledge management - processes necessary to capture, codify and transfer knowledge across the organization to achieve competitive advantage z. Intellectual capital - knowledge that has been identified, captured and leveraged to produce higher-value goods or services or some other competitive advantage for the firm
 Types of Knowledge z. Tacit knowledge ycontext-specific ypersonal yhard to formalize and communicate z. Explicit knowledge yeasily collected, organized and transferred ycan be codified yobjective ytheoretical
Types of Knowledge z. Tacit knowledge ycontext-specific ypersonal yhard to formalize and communicate z. Explicit knowledge yeasily collected, organized and transferred ycan be codified yobjective ytheoretical
 Knowledge Management Process z Knowledge generation - discover new knowledge z Knowledge codification - capture and organize knowledge so it can be found and reused ydefine strategic intent yidentify & evaluate existing knowledge yconsider use z Knowledge transfer- transmitting knowledge from person or group to another and absorbing that knowledge
Knowledge Management Process z Knowledge generation - discover new knowledge z Knowledge codification - capture and organize knowledge so it can be found and reused ydefine strategic intent yidentify & evaluate existing knowledge yconsider use z Knowledge transfer- transmitting knowledge from person or group to another and absorbing that knowledge
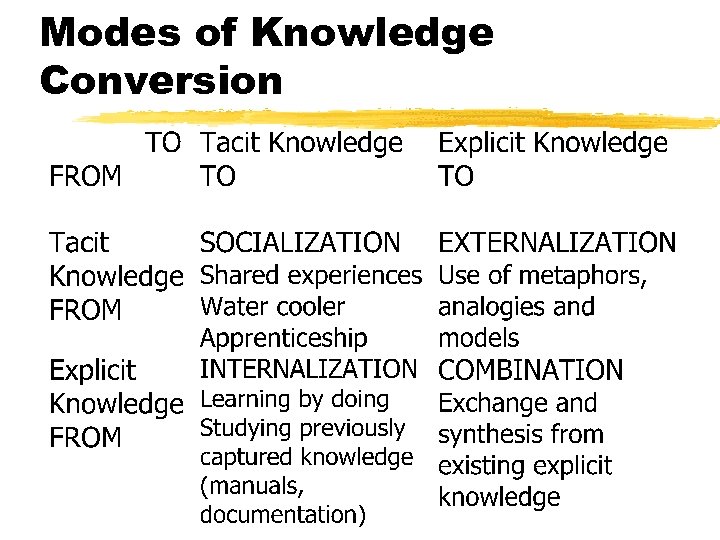 Modes of Knowledge Conversion
Modes of Knowledge Conversion
 Ethics about Information (Mason, MISQ, 1986) z. Privacy z. Accuracy z. Property y. Who owns data about people? y. Who owns intellectual efforts on web? y. Copyrights, watermarks & other protections z. Accessibility y. Haves vs. have nots
Ethics about Information (Mason, MISQ, 1986) z. Privacy z. Accuracy z. Property y. Who owns data about people? y. Who owns intellectual efforts on web? y. Copyrights, watermarks & other protections z. Accessibility y. Haves vs. have nots
 Normative Theories of Business Ethics z. Stockholder theory yemploy legal, non-fraudulent means ytake long view of shareholder interest z. Stakeholder theory yfiduciary responsibility to all those who hold a stake in firm ystockholders, customers, employees, suppliers, local community z. Social contract theory yconsider needs of society (net gain)
Normative Theories of Business Ethics z. Stockholder theory yemploy legal, non-fraudulent means ytake long view of shareholder interest z. Stakeholder theory yfiduciary responsibility to all those who hold a stake in firm ystockholders, customers, employees, suppliers, local community z. Social contract theory yconsider needs of society (net gain)
 Collecting Personal Data on the Web z 93% of 364 commercial sites collect some type of personal information z 66% of these show a warning z. Information collected: y 91%: e-mail address y 81%: name y 63%: postal address y 52%: phone number y 31%: age/birth date y 5%: social security Today USA number
Collecting Personal Data on the Web z 93% of 364 commercial sites collect some type of personal information z 66% of these show a warning z. Information collected: y 91%: e-mail address y 81%: name y 63%: postal address y 52%: phone number y 31%: age/birth date y 5%: social security Today USA number
 Getting Statistics about Usage z. Use HTTPD log files z. Log counts every access z. Logs contain domain names, not user names, of visitors z. Logs also include time, date and accessed URL z. Get logs from ISP z. Logs themselves may be large
Getting Statistics about Usage z. Use HTTPD log files z. Log counts every access z. Logs contain domain names, not user names, of visitors z. Logs also include time, date and accessed URL z. Get logs from ISP z. Logs themselves may be large
 Use of Log Files z. To count visitors ycount users accessing home page ybut, users may skip home page by accessing inside page directly z. To improve pages yaccess patterns by time (may help determine best time for updates) ypages being accessed yaudio, movies or popup images that may be omitted
Use of Log Files z. To count visitors ycount users accessing home page ybut, users may skip home page by accessing inside page directly z. To improve pages yaccess patterns by time (may help determine best time for updates) ypages being accessed yaudio, movies or popup images that may be omitted
 Other Methods of Collecting Demographics z. Page counters yupdatable GIF picture ycgi-bin program z. Cookies z. Web forms and e-mails z. Online focus groups and experiments z. Usenet z. Inducement z. Tracking/Demographic Services
Other Methods of Collecting Demographics z. Page counters yupdatable GIF picture ycgi-bin program z. Cookies z. Web forms and e-mails z. Online focus groups and experiments z. Usenet z. Inducement z. Tracking/Demographic Services
 Cookies z. Built-in feature of browser z. Can refuse to accept y 22% of respondents always accept (8 th GVU) y 23% have computer warn them before cookies are set z. Cookies file: user’s identification codes z. Used to trace where user is at site z. Overt or invisible to user z. Invasion of privacy? y. Good for narrowcasting
Cookies z. Built-in feature of browser z. Can refuse to accept y 22% of respondents always accept (8 th GVU) y 23% have computer warn them before cookies are set z. Cookies file: user’s identification codes z. Used to trace where user is at site z. Overt or invisible to user z. Invasion of privacy? y. Good for narrowcasting
 Cookie Example: C: WINDOWSCookiescsaunder@amazo n(2). txt zsession-idtime 925200000 amazon. com/04071931904 29266051178828716829264692*sessionid 002 -51933732797425 amazon. com/0407193190429266 051178878716829264692*xmain. Wk 2 c. XGW@Wk. Dwf. YSZ 4 vc. L 5 Aamazo n. com/0291634137631961269358702364 829255312*ubid-main 002 -82555885548122 amazon. com/0291634137631961 269379694819229255273*
Cookie Example: C: WINDOWSCookiescsaunder@amazo n(2). txt zsession-idtime 925200000 amazon. com/04071931904 29266051178828716829264692*sessionid 002 -51933732797425 amazon. com/0407193190429266 051178878716829264692*xmain. Wk 2 c. XGW@Wk. Dwf. YSZ 4 vc. L 5 Aamazo n. com/0291634137631961269358702364 829255312*ubid-main 002 -82555885548122 amazon. com/0291634137631961 269379694819229255273*
 Cookie Example z. INTERSE 129115920935528 firefly. com/039 455713282930560774091388829256122*
Cookie Example z. INTERSE 129115920935528 firefly. com/039 455713282930560774091388829256122*
 Tracking/Demographic Services z. I/PRO: Internet Profiles Corporation y. I/Code: universal registration system yleader in web tracking yacquired by Engage Technologies z. Double. Click Inc. z. CMGI
Tracking/Demographic Services z. I/PRO: Internet Profiles Corporation y. I/Code: universal registration system yleader in web tracking yacquired by Engage Technologies z. Double. Click Inc. z. CMGI
 Double. Click, Inc z. Sells advertising space on network of 1400 websites z. Information to better customize ads z. Predicts what you will buy on Web based on what you have purchased online and offline z. Pay $1 billion to buy Abacus Direct ymay need to revise privacy statement z. Plan requires help of online retailer
Double. Click, Inc z. Sells advertising space on network of 1400 websites z. Information to better customize ads z. Predicts what you will buy on Web based on what you have purchased online and offline z. Pay $1 billion to buy Abacus Direct ymay need to revise privacy statement z. Plan requires help of online retailer
 CMGI, Inc. z. Web portals and advertising z. Nearly 50 Internet companies z. Focuses on where you spend your time online z. Acquired Engage Communications to gain access to profiles of 35 million anonymous Web surfers
CMGI, Inc. z. Web portals and advertising z. Nearly 50 Internet companies z. Focuses on where you spend your time online z. Acquired Engage Communications to gain access to profiles of 35 million anonymous Web surfers
 Privacy z. Privacy: the right to be let alone yonly authorized collection, disclosure or other use of information ystatic and dynamic personal information z. Policy about how information will be used y. Example: amazon. com z. Give information provider something in return z. Small bits of information vs. one consolidated database
Privacy z. Privacy: the right to be let alone yonly authorized collection, disclosure or other use of information ystatic and dynamic personal information z. Policy about how information will be used y. Example: amazon. com z. Give information provider something in return z. Small bits of information vs. one consolidated database
 Privacy z. Dangers z. Privacy protections ybrowser standards (Platform for Privacy Preferences) ystandards adopted by sellers and audited by third party (Trust-e) y. Legislation - European Data Protection Directive z. Customer affiliation via tough voluntary standard
Privacy z. Dangers z. Privacy protections ybrowser standards (Platform for Privacy Preferences) ystandards adopted by sellers and audited by third party (Trust-e) y. Legislation - European Data Protection Directive z. Customer affiliation via tough voluntary standard
 Privacy Surveys: GVU (Georgia Tech) 8 th annual, October 1997 z 66% of respondents don’t register w/ web sites that don’t provide clear statement on how the information is going to be used z 63% say giving personal information is not worth access to a site z 58% say they won’t register with a site they don’t trust z 63% say content providers don’t have right to resell information
Privacy Surveys: GVU (Georgia Tech) 8 th annual, October 1997 z 66% of respondents don’t register w/ web sites that don’t provide clear statement on how the information is going to be used z 63% say giving personal information is not worth access to a site z 58% say they won’t register with a site they don’t trust z 63% say content providers don’t have right to resell information
 Privacy Surveys: TRUSTe, March 1997 z. Disclosure of privacy practices would increase by 50% consumer willingness to make net transactions using personal data z 76% of respondents are concerned about sites monitoring their Web browsing z 42% of consumers refuse to give registration info because of privacy concerns z 27% sometimes falsify personal data because of privacy concerns
Privacy Surveys: TRUSTe, March 1997 z. Disclosure of privacy practices would increase by 50% consumer willingness to make net transactions using personal data z 76% of respondents are concerned about sites monitoring their Web browsing z 42% of consumers refuse to give registration info because of privacy concerns z 27% sometimes falsify personal data because of privacy concerns
 How about this one? Amid talk of a possible government crackdown over Internet sites without proper privacy policies, almost two-thirds of federal government Web sites still aren't posting clearly labeled privacy notices linked from their home pages, according to a survey conducted by the Center for Democracy and Technology (CDT).
How about this one? Amid talk of a possible government crackdown over Internet sites without proper privacy policies, almost two-thirds of federal government Web sites still aren't posting clearly labeled privacy notices linked from their home pages, according to a survey conducted by the Center for Democracy and Technology (CDT).
 Government Intervention? z. Clinton administration favors allowing industry to regulate itself z. Department of Commerce and Federal Trade Commission want to encourage privacy protection z. Internet privacy protection legislation? z. EU Directive on Data Protection - blocks transfer of personal information about EU citizens to countries with inadequate privacy protection
Government Intervention? z. Clinton administration favors allowing industry to regulate itself z. Department of Commerce and Federal Trade Commission want to encourage privacy protection z. Internet privacy protection legislation? z. EU Directive on Data Protection - blocks transfer of personal information about EU citizens to countries with inadequate privacy protection
 State Legislation z. Several states considering tough privacy legislation z. California considering identity theft bill yillegal use of someone else’s private information ynew curbs on disclosure of personal data for marketing purposes yprivacy policies ygiving identity-theft victims the right to sue marketers z In February 2000 Federal legislation requiring registrants “opt in” for distribution of driver license information y. Being contested in two states
State Legislation z. Several states considering tough privacy legislation z. California considering identity theft bill yillegal use of someone else’s private information ynew curbs on disclosure of personal data for marketing purposes yprivacy policies ygiving identity-theft victims the right to sue marketers z In February 2000 Federal legislation requiring registrants “opt in” for distribution of driver license information y. Being contested in two states
 Agencies for Privacy z. CASIE yindustry coalition ytwo major advertising trade groups yinform consumer how information will be shared yconsumer be given option that personal information won’t be shared z. World Wide Web Consortium y. P 3: Platform for Privacy Preferences
Agencies for Privacy z. CASIE yindustry coalition ytwo major advertising trade groups yinform consumer how information will be shared yconsumer be given option that personal information won’t be shared z. World Wide Web Consortium y. P 3: Platform for Privacy Preferences
 TRUSTe z. Electronic Frontier Foundation and Commerce. Net Consortium: founders z. Founded in 1997; 1000 seal awarded in January 2000 z. Based on industry-supported selfregulation model z. Independent, non-profit privacy organization www. truste. com z. Privacy quiz: http: //www. truste. org/users_challen
TRUSTe z. Electronic Frontier Foundation and Commerce. Net Consortium: founders z. Founded in 1997; 1000 seal awarded in January 2000 z. Based on industry-supported selfregulation model z. Independent, non-profit privacy organization www. truste. com z. Privacy quiz: http: //www. truste. org/users_challen
 TRUSTe Principles z. Informed consent z. No privacy without appropriate security measures z. Privacy standards vary according to context of use z. Rights to privacy can vary greatly from one country to another
TRUSTe Principles z. Informed consent z. No privacy without appropriate security measures z. Privacy standards vary according to context of use z. Rights to privacy can vary greatly from one country to another
 Informed Consent y. What personal information is being gathered about you y. How the information will be used y. Who the information will be shared with, if anyone is used y. Choices available to you regarding how collected information is used y. Safeguards in place to protect your information from loss, misuse, or alteration y. How you can update or correct inaccuracies in your information
Informed Consent y. What personal information is being gathered about you y. How the information will be used y. Who the information will be shared with, if anyone is used y. Choices available to you regarding how collected information is used y. Safeguards in place to protect your information from loss, misuse, or alteration y. How you can update or correct inaccuracies in your information
 Ensuring Privacy: Ain’t Cheap It E-loan z$250 TRUSTe seal of approval z$520 annual fee for Better Business Bureau seal z$15, 000 Pricewaterhouse Cooper’s Better Web seal z$250, 000 for audit and follow-up y$76, 000 first audit y$28, 000 first update y 700 hours staff time
Ensuring Privacy: Ain’t Cheap It E-loan z$250 TRUSTe seal of approval z$520 annual fee for Better Business Bureau seal z$15, 000 Pricewaterhouse Cooper’s Better Web seal z$250, 000 for audit and follow-up y$76, 000 first audit y$28, 000 first update y 700 hours staff time
 E-Loan - Taking the Challenge z. Its own site ymore consumer education yallowing customers to block future solicitations z. Car. Finance. com’s existing pact re cookie use z. Live. Captial. com’s tracking tool
E-Loan - Taking the Challenge z. Its own site ymore consumer education yallowing customers to block future solicitations z. Car. Finance. com’s existing pact re cookie use z. Live. Captial. com’s tracking tool
 Site Rating Services z. Is this a legitimate business? If so, how good is this company? z. Bizrate: www. bizrate. com yassessment of look and feel of company yreferrals from consumers yreferences from BBB. Local CC ynewspapers and news magazines ysurveys such as J. D. Powers yapprovals from trusted businesses: JD
Site Rating Services z. Is this a legitimate business? If so, how good is this company? z. Bizrate: www. bizrate. com yassessment of look and feel of company yreferrals from consumers yreferences from BBB. Local CC ynewspapers and news magazines ysurveys such as J. D. Powers yapprovals from trusted businesses: JD
 Digital Copyright Wording in On-line Databses z. No downloading at all z. No electronic storage in machine-readable form or transmitted in any means z. No copies or distribution, internally or to third parties z. Limitations on type of use (I. e. , mailing labels)
Digital Copyright Wording in On-line Databses z. No downloading at all z. No electronic storage in machine-readable form or transmitted in any means z. No copies or distribution, internally or to third parties z. Limitations on type of use (I. e. , mailing labels)
 Enforcing Digital Copyrights w/ Technology z. Controlling server access yregistrations and passwords yonce on site may copy yhigher fees for more specialized information z. Controlling document access ysoftware to prevent viewing without authorization yunique file formats requiring certain software yencryption z. Virtual watermarks
Enforcing Digital Copyrights w/ Technology z. Controlling server access yregistrations and passwords yonce on site may copy yhigher fees for more specialized information z. Controlling document access ysoftware to prevent viewing without authorization yunique file formats requiring certain software yencryption z. Virtual watermarks
 Virtual Watermarks z. Work is still visible z. Is not encryption or digital signature z. Watermark may be visible or invisible z. Image watermarking yspatial domain -can flip low order bits of selected pixels ycolor separation - watermark appears only in one color band y. Fast Fourier Transform - changes pixels in lower frequencies z. Can also be applied to text
Virtual Watermarks z. Work is still visible z. Is not encryption or digital signature z. Watermark may be visible or invisible z. Image watermarking yspatial domain -can flip low order bits of selected pixels ycolor separation - watermark appears only in one color band y. Fast Fourier Transform - changes pixels in lower frequencies z. Can also be applied to text
 Watermark Example (visible) zhttp: //www. acm. org/~hlb/publications/dig _wtr/figure 1. jpg zhttp: //www. acm. org/~hlb/publications/dig _wtr/figure 2. jpg
Watermark Example (visible) zhttp: //www. acm. org/~hlb/publications/dig _wtr/figure 1. jpg zhttp: //www. acm. org/~hlb/publications/dig _wtr/figure 2. jpg
 Controlling Use of Work z. Hardware y. Audio Home Recording Act to prevent serial copying z. Software yfiles with instructions governing or controlling distribution ycan limit use with “header” information z. Limited use ynumber of times yperiod of time
Controlling Use of Work z. Hardware y. Audio Home Recording Act to prevent serial copying z. Software yfiles with instructions governing or controlling distribution ycan limit use with “header” information z. Limited use ynumber of times yperiod of time
 Implementing Electronic Contracts z. Software for tracking and monitoring uses z. Software metering use z. Library of Congress Management System yregistration and recording system ydigital library system with repositories of work yrights management system z. Associations to enforce copyrights z. Approaches can’t be too cumbersome
Implementing Electronic Contracts z. Software for tracking and monitoring uses z. Software metering use z. Library of Congress Management System yregistration and recording system ydigital library system with repositories of work yrights management system z. Associations to enforce copyrights z. Approaches can’t be too cumbersome


