7abc7beedea9cbf3a0464e1967ec62fb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Knowledge Management Creating a Dynamic Knowledge Management System for Increased Enterprise Performance and Innovation Knowledge Technologies Conference Austin, Texas March 7, 2001 Charles H. Bixler, D. Sc. charles_h_bixler@keane. com 1
Knowledge Management Creating a Dynamic Knowledge Management System for Increased Enterprise Performance and Innovation Knowledge Technologies Conference Austin, Texas March 7, 2001 Charles H. Bixler, D. Sc. charles_h_bixler@keane. com 1
 Agenda + Knowledge Management 6 Defined 6 The Drivers 6 Application 6 Architecture 6 Body of Knowledge 6 Conceptual Framework + KM Research + KM Implementation + Knowledge Management Enterprise Framework KM-EF 2 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Agenda + Knowledge Management 6 Defined 6 The Drivers 6 Application 6 Architecture 6 Body of Knowledge 6 Conceptual Framework + KM Research + KM Implementation + Knowledge Management Enterprise Framework KM-EF 2 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 Introduction "Knowledge is information that changes something or somebody -either by becoming grounds for actions, or by making an individual (or an institution) capable of different or more effective action. " Peter F. Drucker + Knowledge is information that has value 6 + + relevant, current, and applicable to meeting performance goals The key to unlocking the value of information and knowledge is "action” - it must be dynamic! The active and dynamic implementation and management of knowledge is critical to enabling: 6 6 6 problem solving decision-making organizational learning 3 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Introduction "Knowledge is information that changes something or somebody -either by becoming grounds for actions, or by making an individual (or an institution) capable of different or more effective action. " Peter F. Drucker + Knowledge is information that has value 6 + + relevant, current, and applicable to meeting performance goals The key to unlocking the value of information and knowledge is "action” - it must be dynamic! The active and dynamic implementation and management of knowledge is critical to enabling: 6 6 6 problem solving decision-making organizational learning 3 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 Knowledge Management Defined KM The systematic, explicit, and deliberate building, renewal, and application of knowledge to maximize an enterprise's knowledge-related effectiveness and returns from its knowledge assets. Karl Wiig 1997 Managing the leadership, organization, technology and learning aspects of internal and external intellectual assets through retention and collaborative sharing of knowledge for the purpose of improving performance and inspiring innovation throughout an enterprise. Charlie Bixler 2001 4 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Knowledge Management Defined KM The systematic, explicit, and deliberate building, renewal, and application of knowledge to maximize an enterprise's knowledge-related effectiveness and returns from its knowledge assets. Karl Wiig 1997 Managing the leadership, organization, technology and learning aspects of internal and external intellectual assets through retention and collaborative sharing of knowledge for the purpose of improving performance and inspiring innovation throughout an enterprise. Charlie Bixler 2001 4 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 Knowledge Management - the Drivers Needs in Today’s Enterprises + Preservation of Intellectual Capital 6 + Benefit and Optimize Information Technological (IT) and Communication Technology progress 6 + Ability to deal with global geographical dispersion Competitive Environment 6 6 + Recently evolved and revolutionized the way information is processed and stored New global economy and global proliferation 6 + Enable the ability to sustain and grow the knowledge and skill base Need for performance improvement Need for innovation and technology/process breakthrough The level of sophistication of the client and their expectations 6 Significantly increased 5 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Knowledge Management - the Drivers Needs in Today’s Enterprises + Preservation of Intellectual Capital 6 + Benefit and Optimize Information Technological (IT) and Communication Technology progress 6 + Ability to deal with global geographical dispersion Competitive Environment 6 6 + Recently evolved and revolutionized the way information is processed and stored New global economy and global proliferation 6 + Enable the ability to sustain and grow the knowledge and skill base Need for performance improvement Need for innovation and technology/process breakthrough The level of sophistication of the client and their expectations 6 Significantly increased 5 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 An Example of KM Application The Department of the Navy’s Vision “Knowledge Management is critical to achieving our IM/IT vision” Alex Bennet, Deputy CIO • Integrated, Results-oriented Navy and Marine Corps Team + • Effective, Flexible, and Sustainable DON Enterprise-wide Information and Technology Environment + • Characterized by strategic leadership, ubiquitous communication, and invisible technology Enabling people to make and implement efficient and agile business decisions A Knowledge-Centric Culture + Where trust and respect facilitate information sharing and organizational learning “Knowledge Superiority” 6 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
An Example of KM Application The Department of the Navy’s Vision “Knowledge Management is critical to achieving our IM/IT vision” Alex Bennet, Deputy CIO • Integrated, Results-oriented Navy and Marine Corps Team + • Effective, Flexible, and Sustainable DON Enterprise-wide Information and Technology Environment + • Characterized by strategic leadership, ubiquitous communication, and invisible technology Enabling people to make and implement efficient and agile business decisions A Knowledge-Centric Culture + Where trust and respect facilitate information sharing and organizational learning “Knowledge Superiority” 6 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 Knowledge Management Architecture Strategy Dr. Michael Stankosky’s (GWU) - Four Pillar Approach Environmental Influences Social Economic Political Governmental KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT The Architecture of Enterprise Engineering LEADERSHIP Business Culture Strategic Planning - Vision and Goals Climate Growth Segmentation Communications LEADERSHIP ORGANIZATION BPR - Processes - Procedures Metrics MBO TQM/L Workflow Communications ORGANIZATION TECHNOLOGY E-mail Data Warehousing Search Engines Decision Support Process Modeling Management Tools Communications TECHNOLOGY LEARNING Intuition Innovation vs. Invention Learning Community Virtual Teams Shared Results Exchange Forums Communications LEARNING MULTIPLE DISCIPLINES Systems Engineering Organization Development Systems Management Organization Behavior 7 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Knowledge Management Architecture Strategy Dr. Michael Stankosky’s (GWU) - Four Pillar Approach Environmental Influences Social Economic Political Governmental KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT The Architecture of Enterprise Engineering LEADERSHIP Business Culture Strategic Planning - Vision and Goals Climate Growth Segmentation Communications LEADERSHIP ORGANIZATION BPR - Processes - Procedures Metrics MBO TQM/L Workflow Communications ORGANIZATION TECHNOLOGY E-mail Data Warehousing Search Engines Decision Support Process Modeling Management Tools Communications TECHNOLOGY LEARNING Intuition Innovation vs. Invention Learning Community Virtual Teams Shared Results Exchange Forums Communications LEARNING MULTIPLE DISCIPLINES Systems Engineering Organization Development Systems Management Organization Behavior 7 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
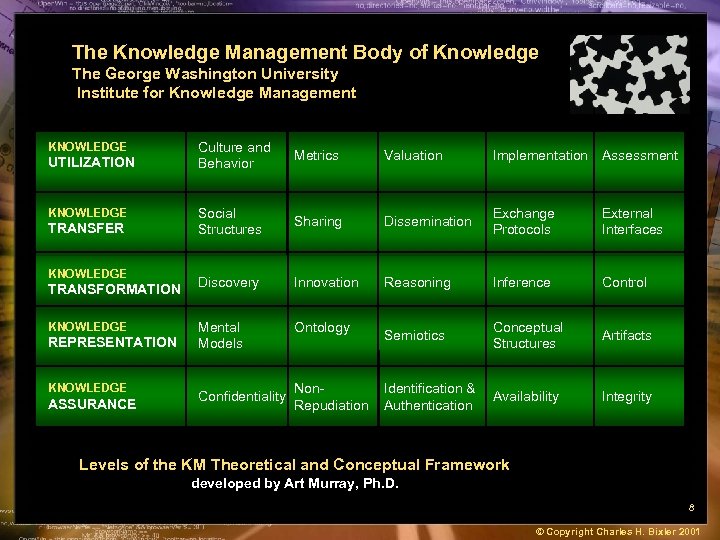 The Knowledge Management Body of Knowledge The George Washington University Institute for Knowledge Management KNOWLEDGE UTILIZATION KNOWLEDGE TRANSFER KNOWLEDGE TRANSFORMATION KNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATION KNOWLEDGE ASSURANCE Culture and Behavior Metrics Valuation Implementation Assessment Social Structures Sharing Dissemination Exchange Protocols External Interfaces Discovery Innovation Reasoning Inference Control Mental Models Ontology Semiotics Conceptual Structures Artifacts Identification & Authentication Availability Integrity Confidentiality Non. Repudiation Levels of the KM Theoretical and Conceptual Framework developed by Art Murray, Ph. D. 8 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
The Knowledge Management Body of Knowledge The George Washington University Institute for Knowledge Management KNOWLEDGE UTILIZATION KNOWLEDGE TRANSFER KNOWLEDGE TRANSFORMATION KNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATION KNOWLEDGE ASSURANCE Culture and Behavior Metrics Valuation Implementation Assessment Social Structures Sharing Dissemination Exchange Protocols External Interfaces Discovery Innovation Reasoning Inference Control Mental Models Ontology Semiotics Conceptual Structures Artifacts Identification & Authentication Availability Integrity Confidentiality Non. Repudiation Levels of the KM Theoretical and Conceptual Framework developed by Art Murray, Ph. D. 8 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
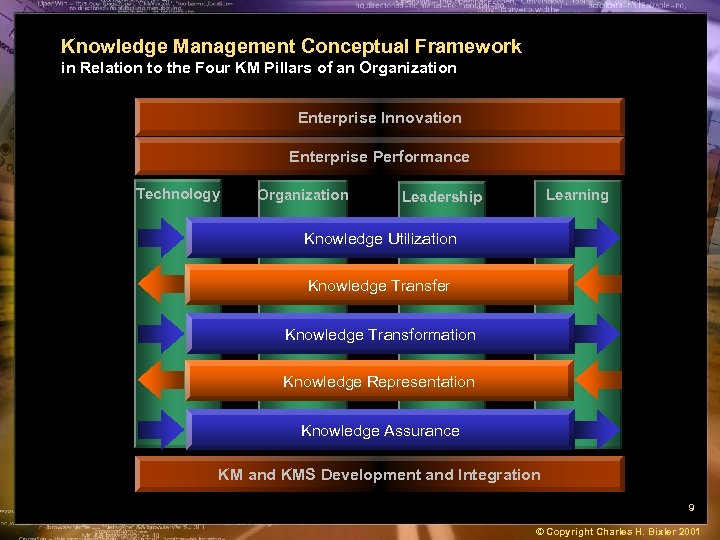 Knowledge Management Conceptual Framework in Relation to the Four KM Pillars of an Organization Enterprise Innovation Enterprise Performance Technology Organization Learning Leadership Knowledge Utilization Knowledge Transfer Knowledge Transformation Knowledge Representation Knowledge Assurance KM and KMS Development and Integration 9 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Knowledge Management Conceptual Framework in Relation to the Four KM Pillars of an Organization Enterprise Innovation Enterprise Performance Technology Organization Learning Leadership Knowledge Utilization Knowledge Transfer Knowledge Transformation Knowledge Representation Knowledge Assurance KM and KMS Development and Integration 9 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
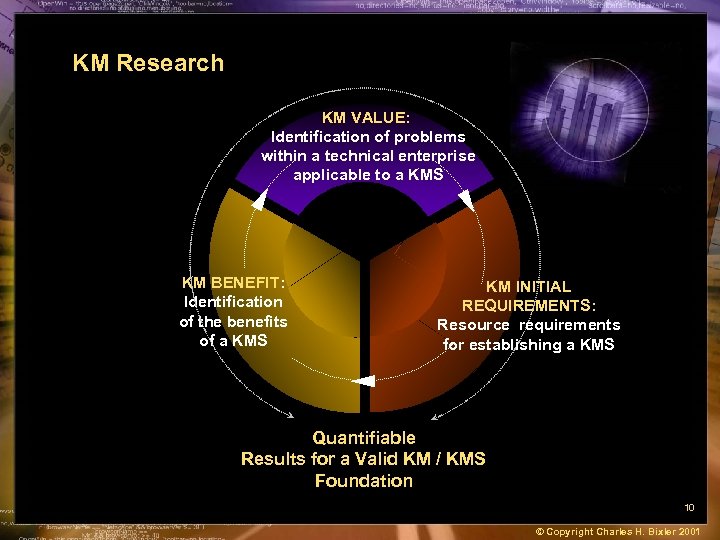 KM Research KM VALUE: Identification of problems within a technical enterprise applicable to a KMS KM BENEFIT: Identification of the benefits of a KMS KM INITIAL REQUIREMENTS: Resource requirements for establishing a KMS Quantifiable Results for a Valid KM / KMS Foundation 10 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
KM Research KM VALUE: Identification of problems within a technical enterprise applicable to a KMS KM BENEFIT: Identification of the benefits of a KMS KM INITIAL REQUIREMENTS: Resource requirements for establishing a KMS Quantifiable Results for a Valid KM / KMS Foundation 10 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 KMS Value: A Set of Problems a KMS Could Help Resolve Category 1 Highest Problem Area for KMS Value Category 2 Moderate Area for KMS Value Proposal / Document Development Quality Management ID of best practices Strategic Planning Stimulate Innovation ID business opportunities Product/Process Planning Continuous Improvement Problem Diagnosis Product/Process Build Strengths and Weaknesses (external) Evaluate for Implementation Training Implement Monitoring CSP Client Satisfaction Assessment Decision Making Strength and Weakness (internal) Risk Management Client Interaction Understanding competition ID Mgt and Leadership Deployment of resources Financial Management 11 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
KMS Value: A Set of Problems a KMS Could Help Resolve Category 1 Highest Problem Area for KMS Value Category 2 Moderate Area for KMS Value Proposal / Document Development Quality Management ID of best practices Strategic Planning Stimulate Innovation ID business opportunities Product/Process Planning Continuous Improvement Problem Diagnosis Product/Process Build Strengths and Weaknesses (external) Evaluate for Implementation Training Implement Monitoring CSP Client Satisfaction Assessment Decision Making Strength and Weakness (internal) Risk Management Client Interaction Understanding competition ID Mgt and Leadership Deployment of resources Financial Management 11 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 KMS Initial Requirements and Conditions: Resource requirements for establishing a KMS Category 2 Highly Necessary Category 1 Very Highly Necessary Gathering and formalizing internal knowledge KM advocates and champions Promoting collaboration and sharing Organizational buy-in and support Gathering and formalizing external knowledge Leadership involvement Allocating necessary resources KM distribution effectiveness KM repository and database Must Have ID core competencies (domains) Should Have Outside the box thinking Continuous education IT infrastructure improvements 12 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
KMS Initial Requirements and Conditions: Resource requirements for establishing a KMS Category 2 Highly Necessary Category 1 Very Highly Necessary Gathering and formalizing internal knowledge KM advocates and champions Promoting collaboration and sharing Organizational buy-in and support Gathering and formalizing external knowledge Leadership involvement Allocating necessary resources KM distribution effectiveness KM repository and database Must Have ID core competencies (domains) Should Have Outside the box thinking Continuous education IT infrastructure improvements 12 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 KMS Benefits: Identification of the benefits of a KMS Category 1 High Value Benefit Expectation Formalized knowledge transfer system Enhance the transfer of knowledge Improve overall performance ID best practices Enhance problem solving Category 2 Some Value Benefit Expectation Enhance strategies Enhance innovation Better on-the-job training Category 3 Nominal Value Benefit Expectation Enhanced client relations Develop an entrepreneurial culture Stimulate and motivate employees Enhance and streamline internal admin processes 13 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
KMS Benefits: Identification of the benefits of a KMS Category 1 High Value Benefit Expectation Formalized knowledge transfer system Enhance the transfer of knowledge Improve overall performance ID best practices Enhance problem solving Category 2 Some Value Benefit Expectation Enhance strategies Enhance innovation Better on-the-job training Category 3 Nominal Value Benefit Expectation Enhanced client relations Develop an entrepreneurial culture Stimulate and motivate employees Enhance and streamline internal admin processes 13 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 Group Differences - Exploratory Study • Overall Group differences were less than expected • Most significant differences were in Management Area + Significant differences in KMS expectations between support managers and operational mangers 9% 4% Service Large Enterprise Size Enterprise Orientation Small Product Enterprise Group Analysis Executive Management Level 5% Middle Line/Operational Management Area Support 16% 14 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Group Differences - Exploratory Study • Overall Group differences were less than expected • Most significant differences were in Management Area + Significant differences in KMS expectations between support managers and operational mangers 9% 4% Service Large Enterprise Size Enterprise Orientation Small Product Enterprise Group Analysis Executive Management Level 5% Middle Line/Operational Management Area Support 16% 14 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
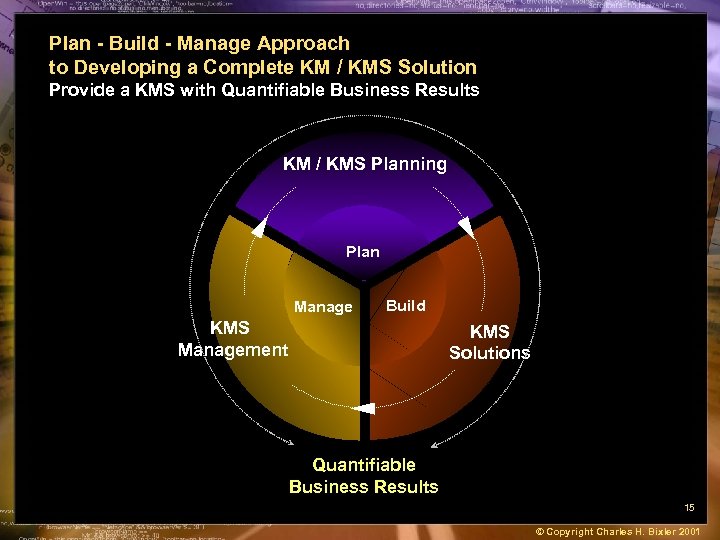 Plan - Build - Manage Approach to Developing a Complete KM / KMS Solution Provide a KMS with Quantifiable Business Results KM / KMS Planning Plan Manage Build KMS Management KMS Solutions Quantifiable Business Results 15 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Plan - Build - Manage Approach to Developing a Complete KM / KMS Solution Provide a KMS with Quantifiable Business Results KM / KMS Planning Plan Manage Build KMS Management KMS Solutions Quantifiable Business Results 15 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
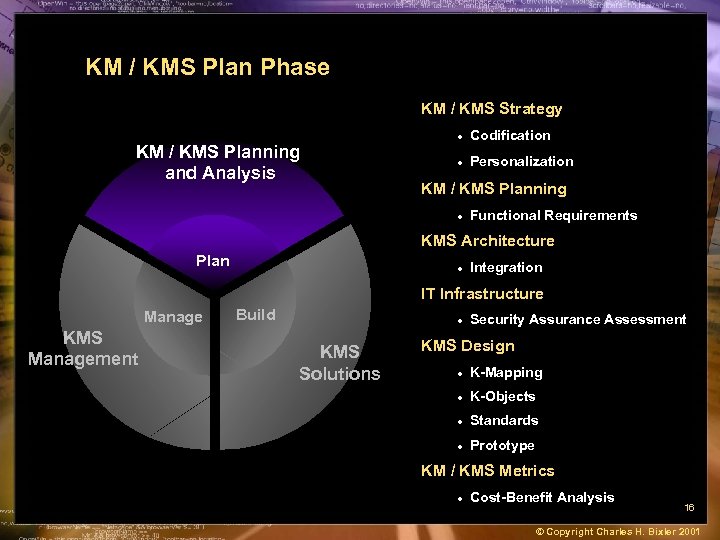 KM / KMS Plan Phase KM / KMS Strategy KM / KMS Planning Business & and Analysis IT Consulting · Codification · Personalization KM / KMS Planning · Functional Requirements KMS Architecture Plan · Integration IT Infrastructure Manage KMS Management Build · KMS Solutions Security Assurance Assessment KMS Design · K-Mapping · K-Objects · Standards · Prototype KM / KMS Metrics · Cost-Benefit Analysis 16 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
KM / KMS Plan Phase KM / KMS Strategy KM / KMS Planning Business & and Analysis IT Consulting · Codification · Personalization KM / KMS Planning · Functional Requirements KMS Architecture Plan · Integration IT Infrastructure Manage KMS Management Build · KMS Solutions Security Assurance Assessment KMS Design · K-Mapping · K-Objects · Standards · Prototype KM / KMS Metrics · Cost-Benefit Analysis 16 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 KMS Planning Strategy considering the Technology enablers Codification Strategy Knowledge Assets / Intellectual Capital Management • • Document Management Systems Data Mining Systems Knowledge Inventory Systems (Search Engines, Knowledge Mapping, and Information Retrieval Systems) Data/Information Knowledge Repositories (Best Practices, Story Telling, and Lessons Learned) Online Training Systems Intranet CBT / IETM / Web-based Training (WBT) Electronic Performance Support Systems (EPSS) Database Management System (DMS) (Oracle, SQL) Personalization Strategy Knowledge Empowerment and Collaboration Management • • • Help Desk Applications Online Workflow / Document Tracking Email and Messaging Systems Groupware (asynchronous) Group Decision Support Systems Yellow Pages - Directory of Knowledge Sources and Thought Leaders Communities of Practice (Online Chat / Electronic Meeting) Communities of Purpose (Online Project/Task Management Meeting) Real-Time (synchronous) Data Conferencing Video / Teleconferencing) Customer Relations Management (CRM) Financial Management Systems Marketing Information System 17 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
KMS Planning Strategy considering the Technology enablers Codification Strategy Knowledge Assets / Intellectual Capital Management • • Document Management Systems Data Mining Systems Knowledge Inventory Systems (Search Engines, Knowledge Mapping, and Information Retrieval Systems) Data/Information Knowledge Repositories (Best Practices, Story Telling, and Lessons Learned) Online Training Systems Intranet CBT / IETM / Web-based Training (WBT) Electronic Performance Support Systems (EPSS) Database Management System (DMS) (Oracle, SQL) Personalization Strategy Knowledge Empowerment and Collaboration Management • • • Help Desk Applications Online Workflow / Document Tracking Email and Messaging Systems Groupware (asynchronous) Group Decision Support Systems Yellow Pages - Directory of Knowledge Sources and Thought Leaders Communities of Practice (Online Chat / Electronic Meeting) Communities of Purpose (Online Project/Task Management Meeting) Real-Time (synchronous) Data Conferencing Video / Teleconferencing) Customer Relations Management (CRM) Financial Management Systems Marketing Information System 17 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 KM Technology and Process Requirements to support the enablers Technology Improvements + + + + + IT Infrastructure Communication Systems Internet / Extranet Servers Application Software Knowledge Nets and Portals Data Warehouses Multimedia Repositories Front-end User Interfaces Business Objects 6 Process Improvements + + + + + IT Standards KM Mapping / Indexing Content Management Content Integrity and Assurance Forms Processing Workflow / Tracking Processing Collaboration Systems Processes Analysis Systems Processes Automation (CRM) Training of K-Workers Rules, Formulas 18 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
KM Technology and Process Requirements to support the enablers Technology Improvements + + + + + IT Infrastructure Communication Systems Internet / Extranet Servers Application Software Knowledge Nets and Portals Data Warehouses Multimedia Repositories Front-end User Interfaces Business Objects 6 Process Improvements + + + + + IT Standards KM Mapping / Indexing Content Management Content Integrity and Assurance Forms Processing Workflow / Tracking Processing Collaboration Systems Processes Analysis Systems Processes Automation (CRM) Training of K-Workers Rules, Formulas 18 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
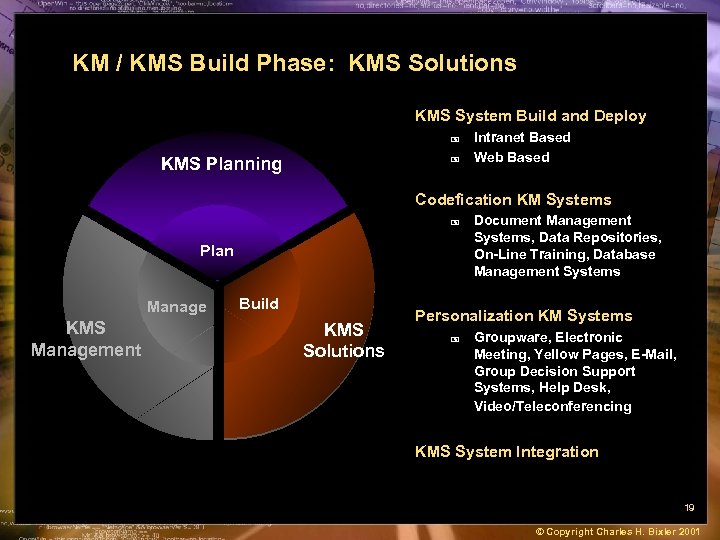 KM / KMS Build Phase: KMS Solutions KMS System Build and Deploy + KMS Planning + Intranet Based Web Based Codefication KM Systems + Plan Manage KMS Management Build KMS Solutions Document Management Systems, Data Repositories, On-Line Training, Database Management Systems Personalization KM Systems + Groupware, Electronic Meeting, Yellow Pages, E-Mail, Group Decision Support Systems, Help Desk, Video/Teleconferencing KMS System Integration 19 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
KM / KMS Build Phase: KMS Solutions KMS System Build and Deploy + KMS Planning + Intranet Based Web Based Codefication KM Systems + Plan Manage KMS Management Build KMS Solutions Document Management Systems, Data Repositories, On-Line Training, Database Management Systems Personalization KM Systems + Groupware, Electronic Meeting, Yellow Pages, E-Mail, Group Decision Support Systems, Help Desk, Video/Teleconferencing KMS System Integration 19 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
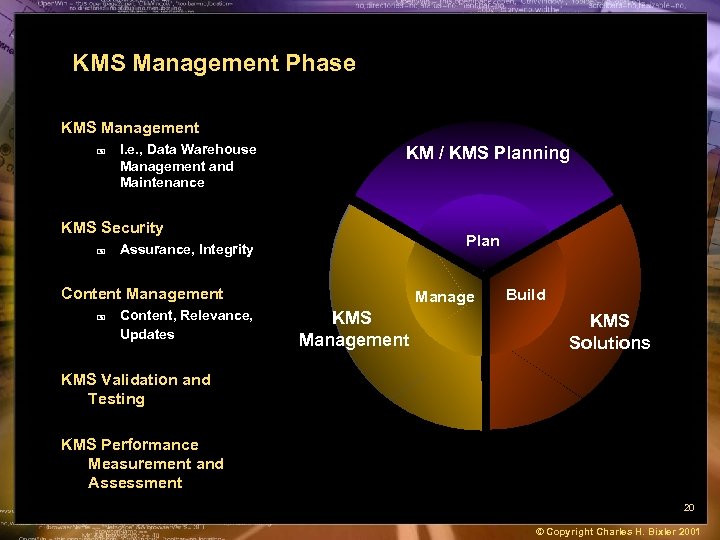 KMS Management Phase KMS Management + I. e. , Data Warehouse Management and Maintenance KM / KMS Planning KMS Security + Plan Assurance, Integrity Content Management + Content, Relevance, Updates Manage KMS Management Build KMS Solutions KMS Validation and Testing KMS Performance Measurement and Assessment 20 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
KMS Management Phase KMS Management + I. e. , Data Warehouse Management and Maintenance KM / KMS Planning KMS Security + Plan Assurance, Integrity Content Management + Content, Relevance, Updates Manage KMS Management Build KMS Solutions KMS Validation and Testing KMS Performance Measurement and Assessment 20 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
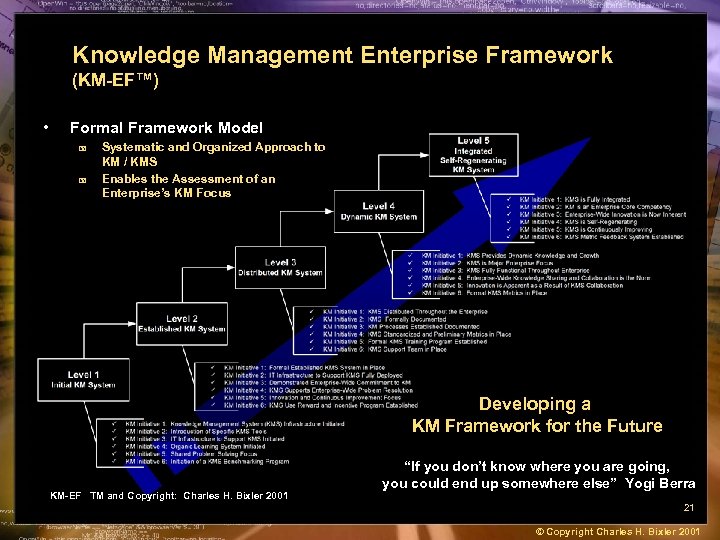 Knowledge Management Enterprise Framework (KM-EF™) • Formal Framework Model + + Systematic and Organized Approach to KM / KMS Enables the Assessment of an Enterprise’s KM Focus Developing a KM Framework for the Future KM-EF TM and Copyright: Charles H. Bixler 2001 “If you don’t know where you are going, you could end up somewhere else” Yogi Berra 21 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Knowledge Management Enterprise Framework (KM-EF™) • Formal Framework Model + + Systematic and Organized Approach to KM / KMS Enables the Assessment of an Enterprise’s KM Focus Developing a KM Framework for the Future KM-EF TM and Copyright: Charles H. Bixler 2001 “If you don’t know where you are going, you could end up somewhere else” Yogi Berra 21 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 Further Research KMS in Government Organizations KMS Tools KMS Metrics KMS Process and Practice Areas KM Enterprise Framework 22 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Further Research KMS in Government Organizations KMS Tools KMS Metrics KMS Process and Practice Areas KM Enterprise Framework 22 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 Final Conclusions KM as a practice will enable the formalizing and integrating of experience, knowledge, and expertise within an enterprise Results: Improved enterprise performance, Innovation, Enhanced customer value KM KMS 23 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Final Conclusions KM as a practice will enable the formalizing and integrating of experience, knowledge, and expertise within an enterprise Results: Improved enterprise performance, Innovation, Enhanced customer value KM KMS 23 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
 Thank you for your time and attention Questions 24 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001
Thank you for your time and attention Questions 24 © Copyright Charles H. Bixler 2001


