246596fb0d630c24a39a182a2d0acf03.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 141
 "Knowledge in IS/IT processes and standards" Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporters:GROUP 5 組員名單: 970431 王樂瑄 971626 劉建旻 971648 李東樺 971663 蔡志良 971611 胡仲康 971635 王政欽 971654 林建順 971707 洪至柔 1
"Knowledge in IS/IT processes and standards" Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporters:GROUP 5 組員名單: 970431 王樂瑄 971626 劉建旻 971648 李東樺 971663 蔡志良 971611 胡仲康 971635 王政欽 971654 林建順 971707 洪至柔 1
 What are the existing IS/IT standards available for n System development Ø ISO/IEC 15288 Ø ISO/IEC 12207 n System Maintenance Ø ISO/IEC 12207 Ø IEEE 1219 n Software process improvement Ø CMMI Ø ISO/IEC TR 15504 n IT Governance Ø COBIT Ø ITIL 2
What are the existing IS/IT standards available for n System development Ø ISO/IEC 15288 Ø ISO/IEC 12207 n System Maintenance Ø ISO/IEC 12207 Ø IEEE 1219 n Software process improvement Ø CMMI Ø ISO/IEC TR 15504 n IT Governance Ø COBIT Ø ITIL 2
 System development ISO/IEC 15288 System Life Cycle Process standard (International Standards Organization / International Electro technical Commission) Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971611 胡仲康 3
System development ISO/IEC 15288 System Life Cycle Process standard (International Standards Organization / International Electro technical Commission) Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971611 胡仲康 3
 Contents n n What is ISO/IEC 15288 Life cycle stages The system life cycle processes System Development processes 971611胡仲康
Contents n n What is ISO/IEC 15288 Life cycle stages The system life cycle processes System Development processes 971611胡仲康
 What is ISO/IEC 15288 n n a Systems Engineering standard covering processes and life cycle stages. It establishes a common framework for describing the life cycle of systems created by humans and defines a set of processes and associated terminology within that framework. 971611胡仲康 http: //www. 15288. com/about_standards. php
What is ISO/IEC 15288 n n a Systems Engineering standard covering processes and life cycle stages. It establishes a common framework for describing the life cycle of systems created by humans and defines a set of processes and associated terminology within that framework. 971611胡仲康 http: //www. 15288. com/about_standards. php
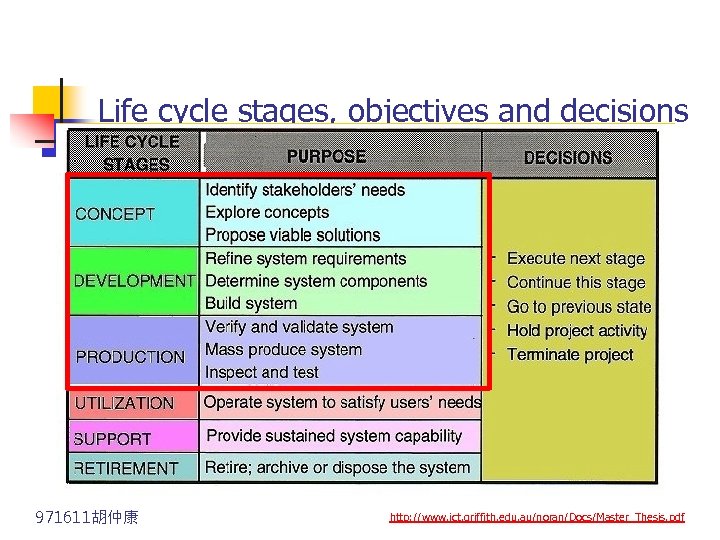 Life cycle stages, objectives and decisions 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
Life cycle stages, objectives and decisions 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
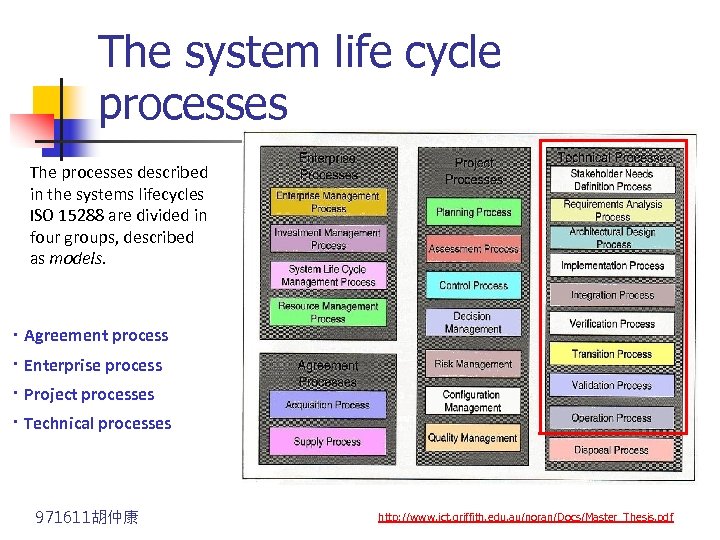 The system life cycle processes The processes described in the systems lifecycles ISO 15288 are divided in four groups, described as models. ‧ Agreement process ‧ Enterprise process ‧ Project processes ‧ Technical processes 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
The system life cycle processes The processes described in the systems lifecycles ISO 15288 are divided in four groups, described as models. ‧ Agreement process ‧ Enterprise process ‧ Project processes ‧ Technical processes 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
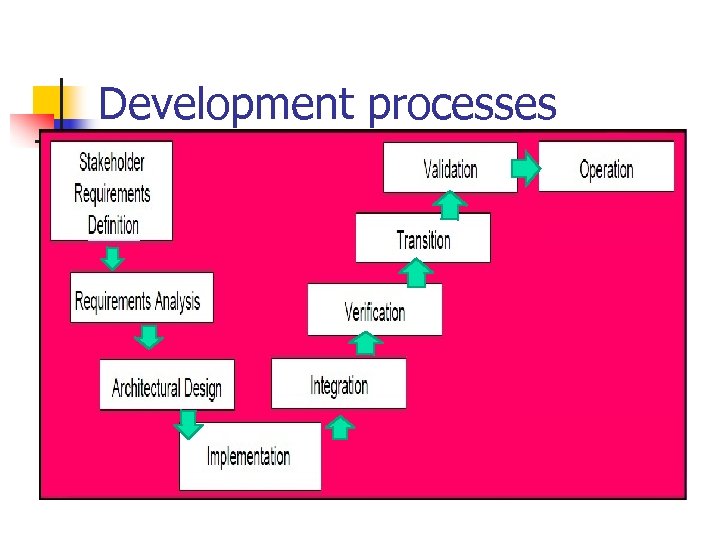 Development processes
Development processes
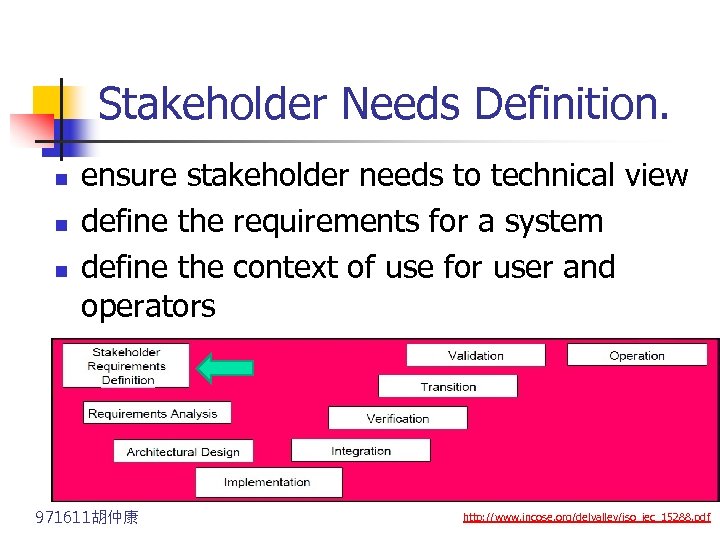 Stakeholder Needs Definition. n n n ensure stakeholder needs to technical view define the requirements for a system define the context of use for user and operators 971611胡仲康 http: //www. incose. org/delvalley/iso_iec_15288. pdf
Stakeholder Needs Definition. n n n ensure stakeholder needs to technical view define the requirements for a system define the context of use for user and operators 971611胡仲康 http: //www. incose. org/delvalley/iso_iec_15288. pdf
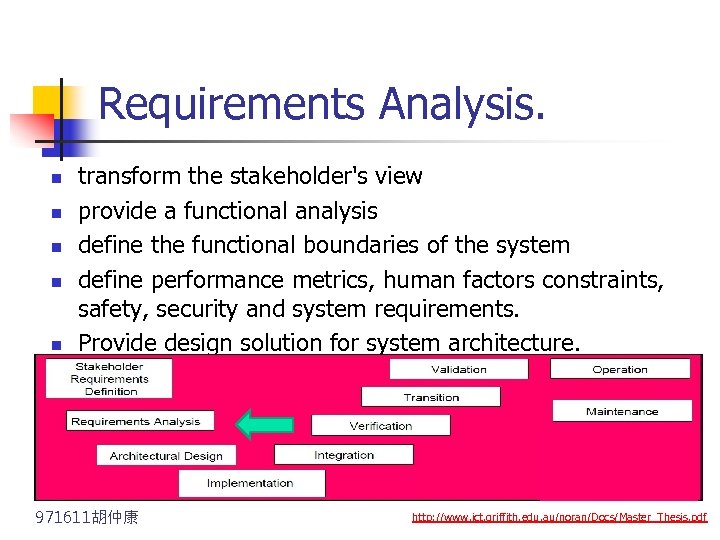 Requirements Analysis. n n n transform the stakeholder's view provide a functional analysis define the functional boundaries of the system define performance metrics, human factors constraints, safety, security and system requirements. Provide design solution for system architecture. 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
Requirements Analysis. n n n transform the stakeholder's view provide a functional analysis define the functional boundaries of the system define performance metrics, human factors constraints, safety, security and system requirements. Provide design solution for system architecture. 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
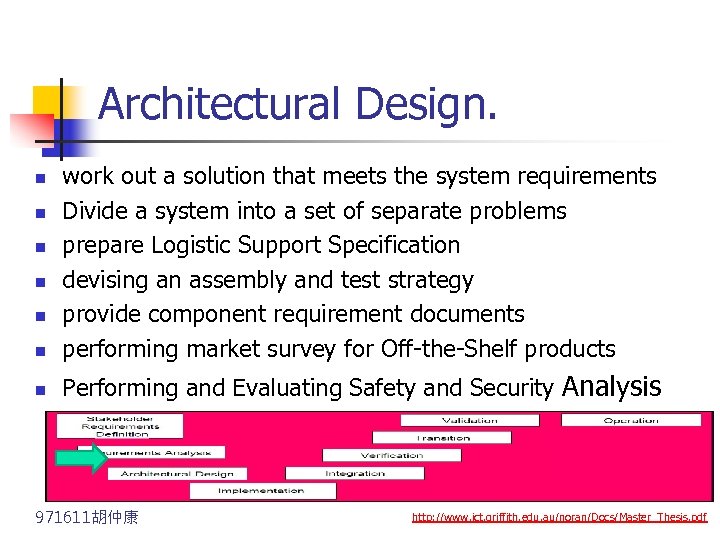 Architectural Design. n work out a solution that meets the system requirements Divide a system into a set of separate problems prepare Logistic Support Specification devising an assembly and test strategy provide component requirement documents performing market survey for Off-the-Shelf products n Performing and Evaluating Safety and Security Analysis n n n 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
Architectural Design. n work out a solution that meets the system requirements Divide a system into a set of separate problems prepare Logistic Support Specification devising an assembly and test strategy provide component requirement documents performing market survey for Off-the-Shelf products n Performing and Evaluating Safety and Security Analysis n n n 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
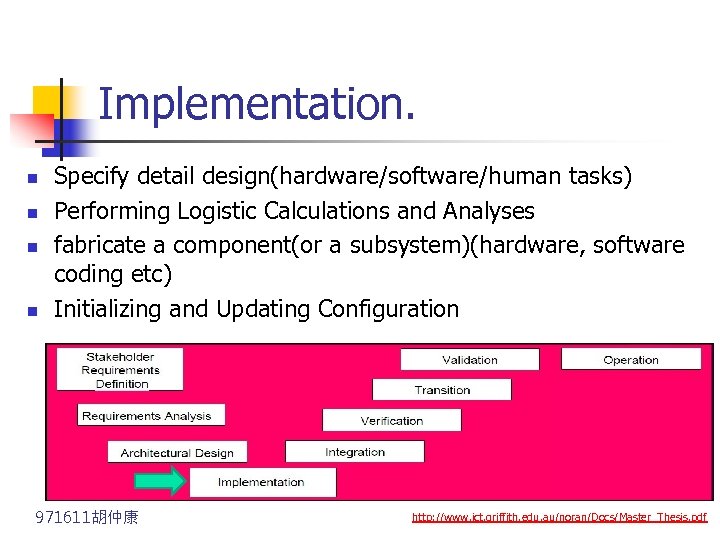 Implementation. n n Specify detail design(hardware/software/human tasks) Performing Logistic Calculations and Analyses fabricate a component(or a subsystem)(hardware, software coding etc) Initializing and Updating Configuration 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
Implementation. n n Specify detail design(hardware/software/human tasks) Performing Logistic Calculations and Analyses fabricate a component(or a subsystem)(hardware, software coding etc) Initializing and Updating Configuration 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
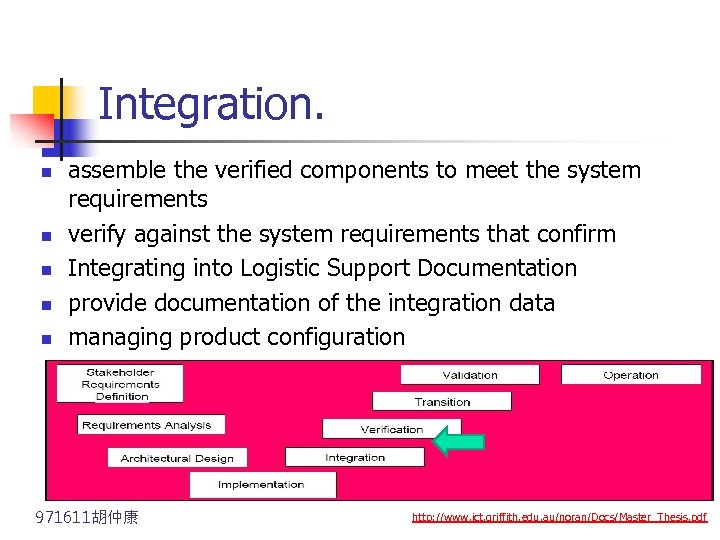 Integration. n n n assemble the verified components to meet the system requirements verify against the system requirements that confirm Integrating into Logistic Support Documentation provide documentation of the integration data managing product configuration 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
Integration. n n n assemble the verified components to meet the system requirements verify against the system requirements that confirm Integrating into Logistic Support Documentation provide documentation of the integration data managing product configuration 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
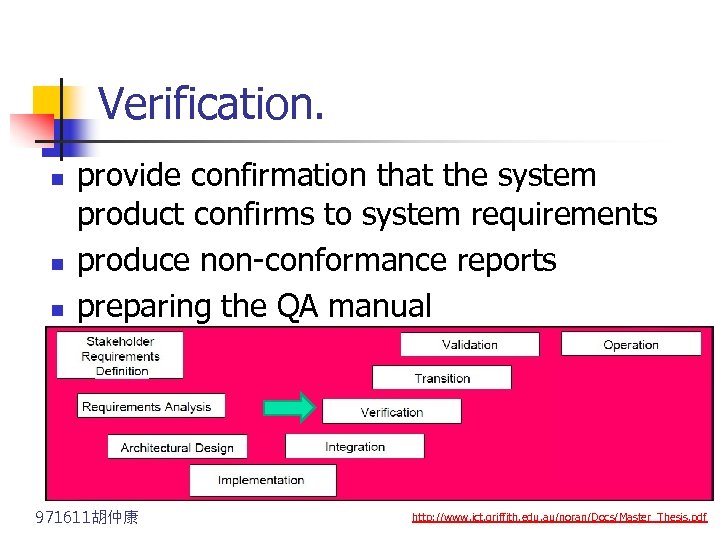 Verification. n n n provide confirmation that the system product confirms to system requirements produce non-conformance reports preparing the QA manual 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
Verification. n n n provide confirmation that the system product confirms to system requirements produce non-conformance reports preparing the QA manual 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
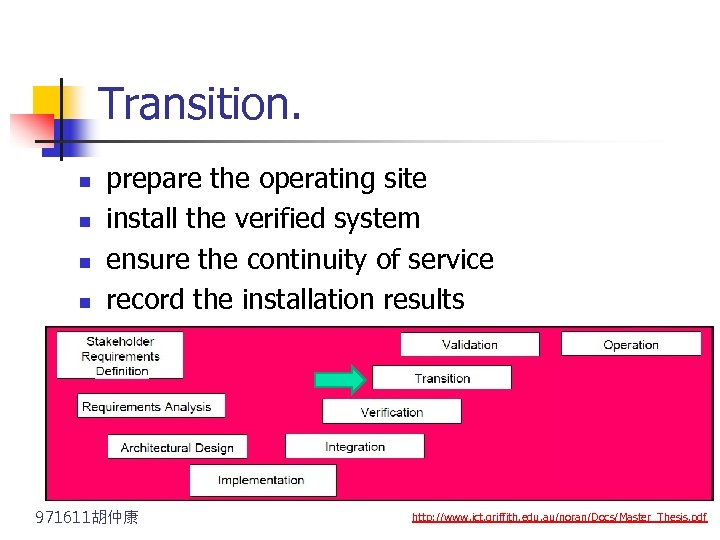 Transition. n n prepare the operating site install the verified system ensure the continuity of service record the installation results 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
Transition. n n prepare the operating site install the verified system ensure the continuity of service record the installation results 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
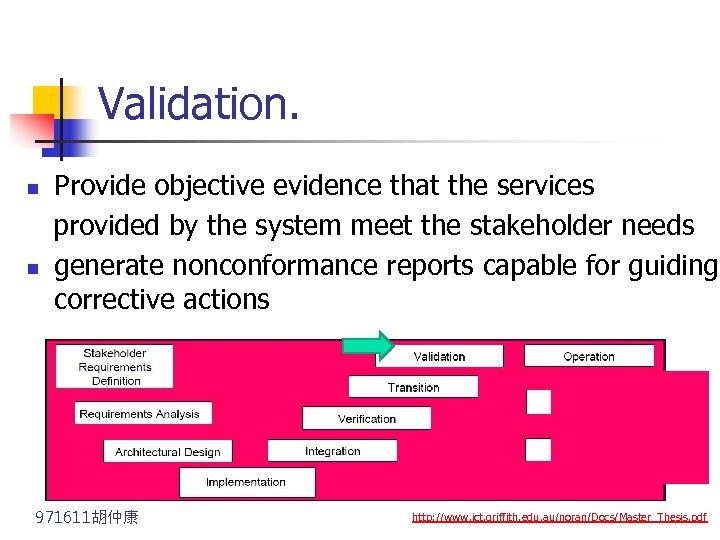 Validation. Provide objective evidence that the services provided by the system meet the stakeholder needs n generate nonconformance reports capable for guiding corrective actions n 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
Validation. Provide objective evidence that the services provided by the system meet the stakeholder needs n generate nonconformance reports capable for guiding corrective actions n 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
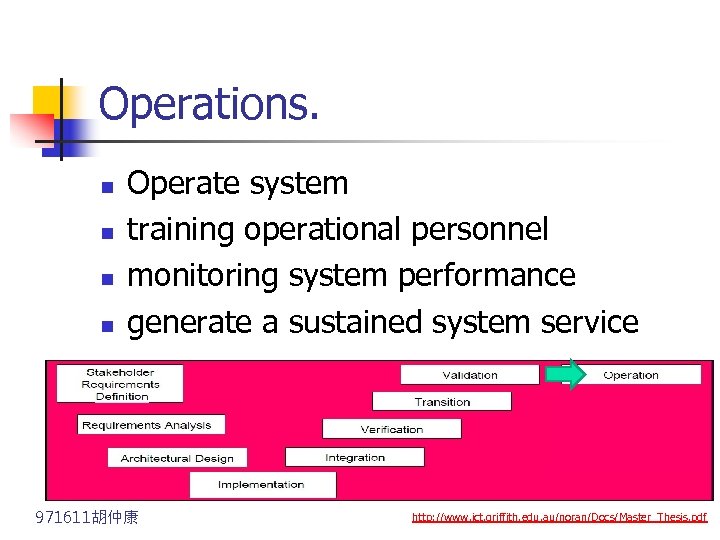 Operations. n n Operate system training operational personnel monitoring system performance generate a sustained system service 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
Operations. n n Operate system training operational personnel monitoring system performance generate a sustained system service 971611胡仲康 http: //www. ict. griffith. edu. au/noran/Docs/Master_Thesis. pdf
 Operations. (2) n n n Preparing Logistic Support Specification Defining In-Service Documentation Preparing Training Documentation Preparing Problem Report/Change Request Maintaining Change Status List Preparing Logistic Support Concept 971611胡仲康
Operations. (2) n n n Preparing Logistic Support Specification Defining In-Service Documentation Preparing Training Documentation Preparing Problem Report/Change Request Maintaining Change Status List Preparing Logistic Support Concept 971611胡仲康
 Key business domain n n n Aerospace Telecommunications Transportation systems Military systems Ship building Finance and Administrative systems Information Technology systems 971611胡仲康 http: //www. incose. org/delvalley/iso_iec_15288. pdf
Key business domain n n n Aerospace Telecommunications Transportation systems Military systems Ship building Finance and Administrative systems Information Technology systems 971611胡仲康 http: //www. incose. org/delvalley/iso_iec_15288. pdf
 Q&A Thanks 971611胡仲康 20
Q&A Thanks 971611胡仲康 20
 System development ISO/IEC 12207 software lifecycle processes Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 970431 王樂瑄 21
System development ISO/IEC 12207 software lifecycle processes Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 970431 王樂瑄 21
 What is ISO/IEC 12207 n An standard for software lifecycle processes. n The standard that defines all the tasks required for developing and maintaining software. 970431 王樂瑄 http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ISO_12207#Example 22
What is ISO/IEC 12207 n An standard for software lifecycle processes. n The standard that defines all the tasks required for developing and maintaining software. 970431 王樂瑄 http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ISO_12207#Example 22
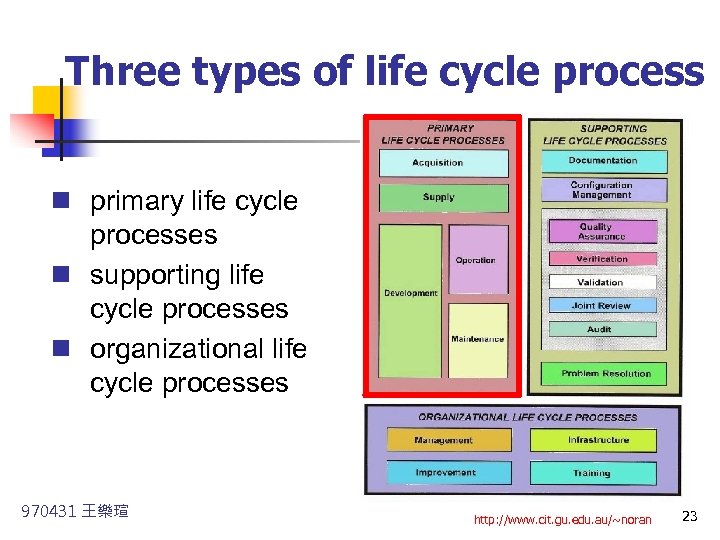 Three types of life cycle process n primary life cycle processes n supporting life cycle processes n organizational life cycle processes 970431 王樂瑄 http: //www. cit. gu. edu. au/~noran 23
Three types of life cycle process n primary life cycle processes n supporting life cycle processes n organizational life cycle processes 970431 王樂瑄 http: //www. cit. gu. edu. au/~noran 23
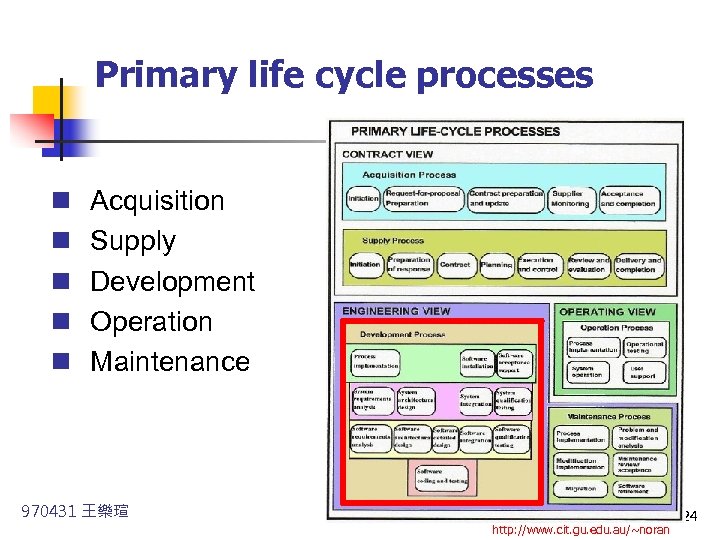 Primary life cycle processes n n n Acquisition Supply Development Operation Maintenance 970431 王樂瑄 http: //www. cit. gu. edu. au/~noran 24
Primary life cycle processes n n n Acquisition Supply Development Operation Maintenance 970431 王樂瑄 http: //www. cit. gu. edu. au/~noran 24
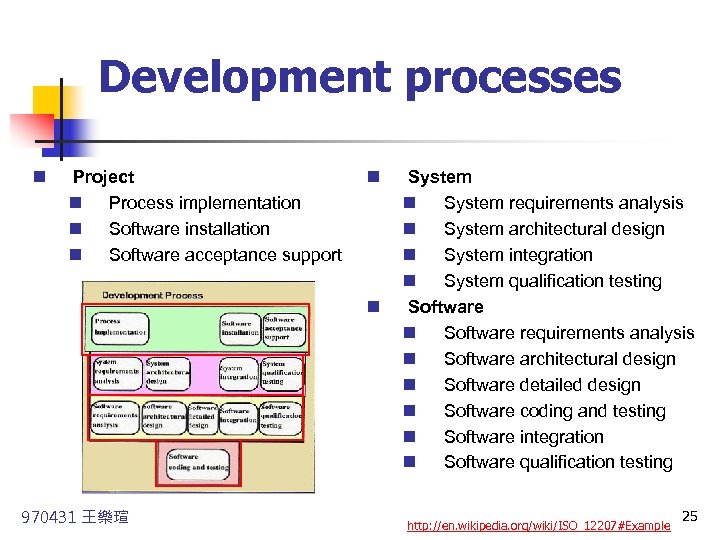 Development processes n Project n Process implementation n Software installation n Software acceptance support n n 970431 王樂瑄 System n System requirements analysis n System architectural design n System integration n System qualification testing Software n Software requirements analysis n Software architectural design n Software detailed design n Software coding and testing n Software integration n Software qualification testing http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ISO_12207#Example 25
Development processes n Project n Process implementation n Software installation n Software acceptance support n n 970431 王樂瑄 System n System requirements analysis n System architectural design n System integration n System qualification testing Software n Software requirements analysis n Software architectural design n Software detailed design n Software coding and testing n Software integration n Software qualification testing http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ISO_12207#Example 25
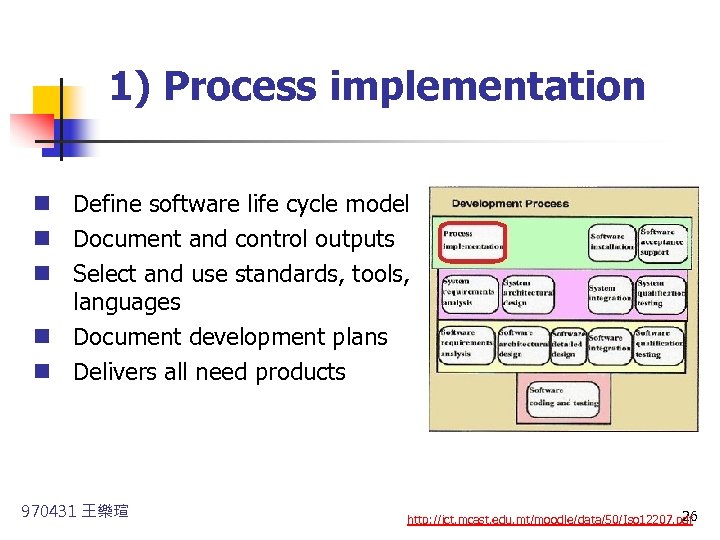 1) Process implementation n Define software life cycle model n Document and control outputs n Select and use standards, tools, languages n Document development plans n Delivers all need products 970431 王樂瑄 26 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf
1) Process implementation n Define software life cycle model n Document and control outputs n Select and use standards, tools, languages n Document development plans n Delivers all need products 970431 王樂瑄 26 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf
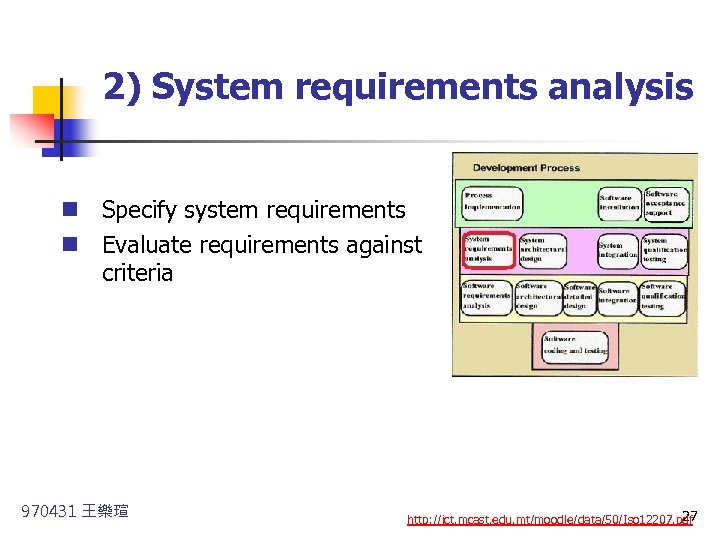 2) System requirements analysis n Specify system requirements n Evaluate requirements against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 27 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf
2) System requirements analysis n Specify system requirements n Evaluate requirements against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 27 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf
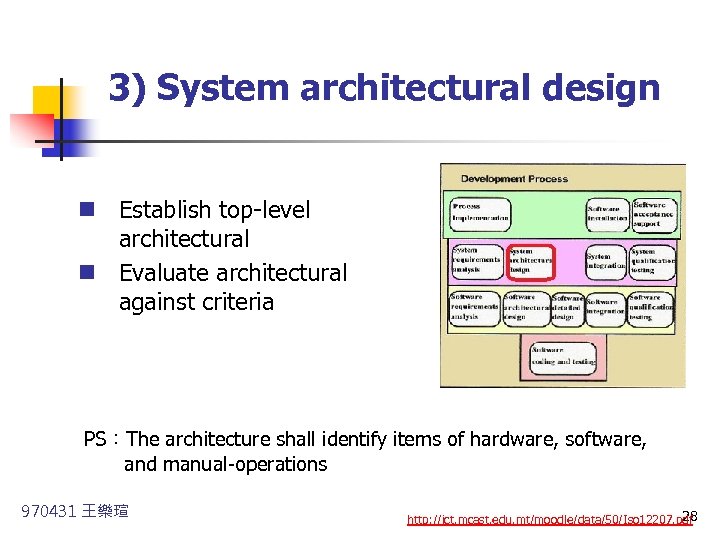 3) System architectural design n Establish top-level architectural n Evaluate architectural against criteria PS:The architecture shall identify items of hardware, software, and manual-operations 970431 王樂瑄 28 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf
3) System architectural design n Establish top-level architectural n Evaluate architectural against criteria PS:The architecture shall identify items of hardware, software, and manual-operations 970431 王樂瑄 28 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf
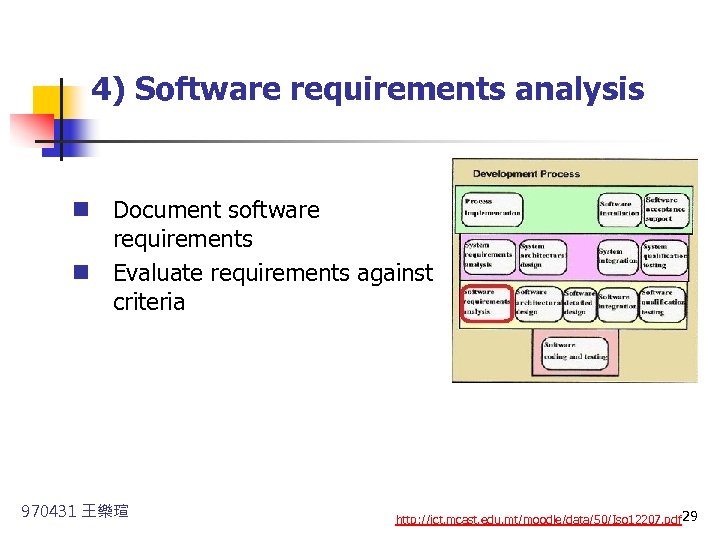 4) Software requirements analysis n Document software requirements n Evaluate requirements against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 29
4) Software requirements analysis n Document software requirements n Evaluate requirements against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 29
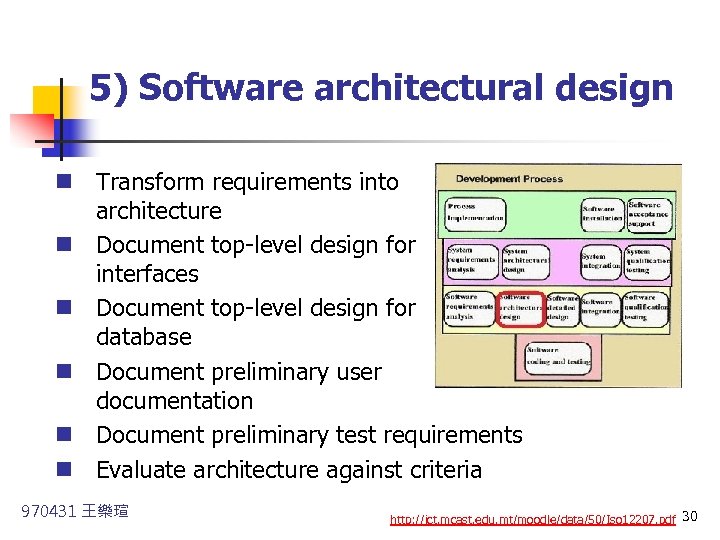 5) Software architectural design n Transform requirements into architecture n Document top-level design for interfaces n Document top-level design for database n Document preliminary user documentation n Document preliminary test requirements n Evaluate architecture against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 30
5) Software architectural design n Transform requirements into architecture n Document top-level design for interfaces n Document top-level design for database n Document preliminary user documentation n Document preliminary test requirements n Evaluate architecture against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 30
 6) Software detailed design n Document design for each component n Document design for interfaces n Document design for database n Update user documentation n Document unit test requirements n Update integration test requirements n Evaluate detailed design against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 31
6) Software detailed design n Document design for each component n Document design for interfaces n Document design for database n Update user documentation n Document unit test requirements n Update integration test requirements n Evaluate detailed design against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 31
 7) Software coding and testing n Document each unit, database and tests n Conduct and document unit testing n Update user documentation n Update integration test requirements n Evaluate code and test results 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 32
7) Software coding and testing n Document each unit, database and tests n Conduct and document unit testing n Update user documentation n Update integration test requirements n Evaluate code and test results 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 32
 8) Software integration n Document integration plans n Conduct and document integration tests n Update user documentation n Document qualification tests n Evaluate plans and tests against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 33
8) Software integration n Document integration plans n Conduct and document integration tests n Update user documentation n Document qualification tests n Evaluate plans and tests against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 33
 9) Software qualification testing n Conduct and document qualification testing n Update user documentation n Evaluate tests against criteria n Prepare product for next phase 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 34
9) Software qualification testing n Conduct and document qualification testing n Update user documentation n Evaluate tests against criteria n Prepare product for next phase 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 34
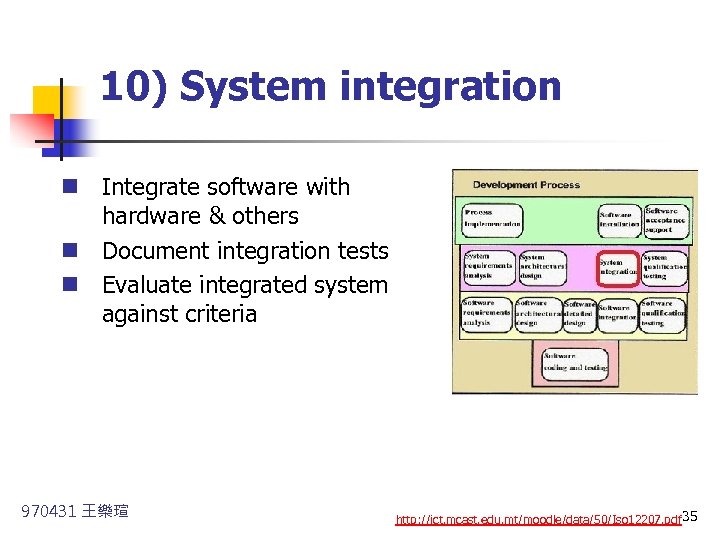 10) System integration n Integrate software with hardware & others n Document integration tests n Evaluate integrated system against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 35
10) System integration n Integrate software with hardware & others n Document integration tests n Evaluate integrated system against criteria 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 35
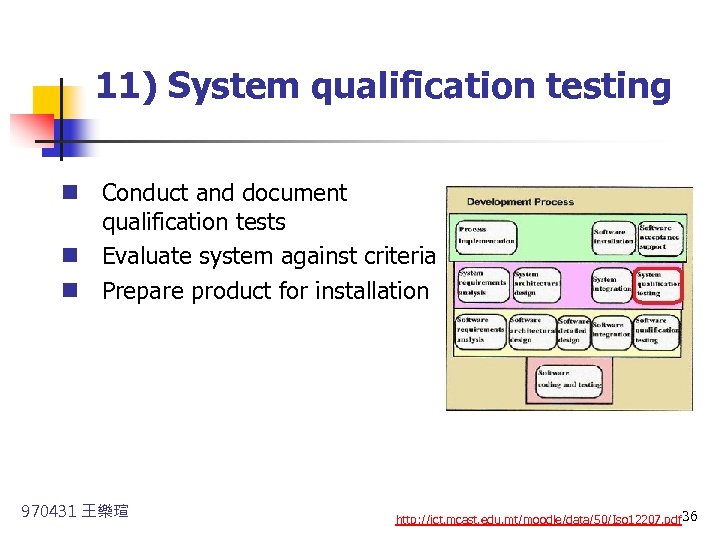 11) System qualification testing n Conduct and document qualification tests n Evaluate system against criteria n Prepare product for installation 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 36
11) System qualification testing n Conduct and document qualification tests n Evaluate system against criteria n Prepare product for installation 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 36
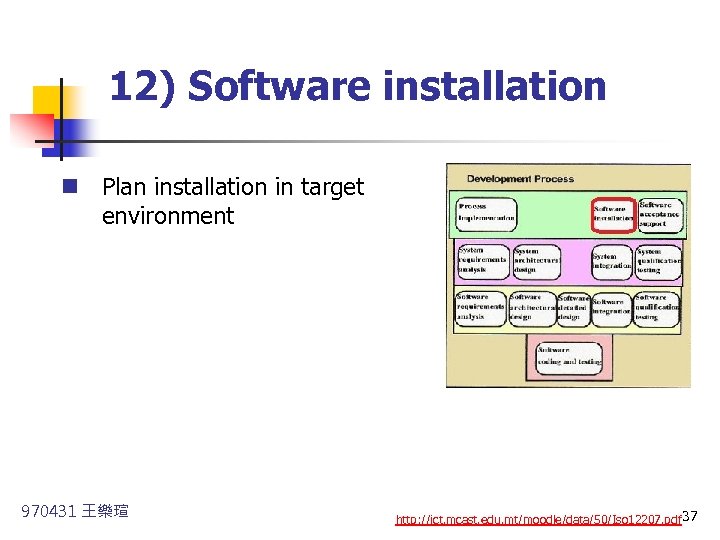 12) Software installation n Plan installation in target environment 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 37
12) Software installation n Plan installation in target environment 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 37
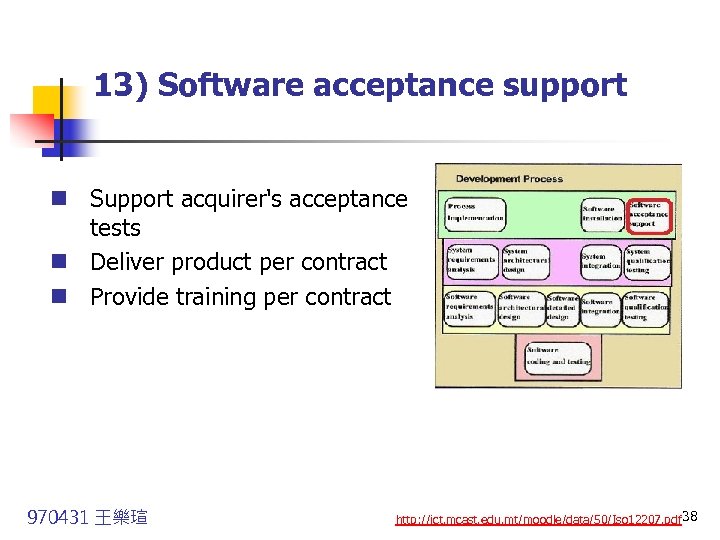 13) Software acceptance support n Support acquirer's acceptance tests n Deliver product per contract n Provide training per contract 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 38
13) Software acceptance support n Support acquirer's acceptance tests n Deliver product per contract n Provide training per contract 970431 王樂瑄 http: //ict. mcast. edu. mt/moodle/data/50/Iso 12207. pdf 38
 Q&A Thanks 970431 王樂瑄 39
Q&A Thanks 970431 王樂瑄 39
 System Maintenance ISO/IEC 12207 software lifecycle processes Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971707 洪至柔
System Maintenance ISO/IEC 12207 software lifecycle processes Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971707 洪至柔
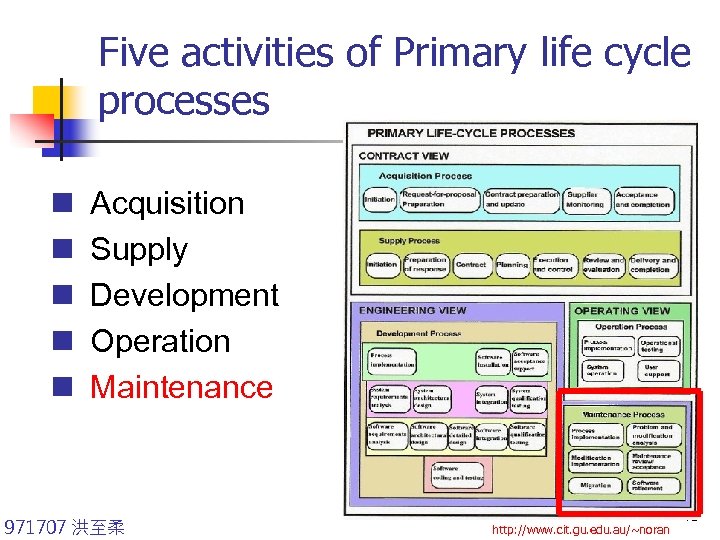 Five activities of Primary life cycle processes n n n Acquisition Supply Development Operation Maintenance 971707 洪至柔 http: //www. cit. gu. edu. au/~noran 41
Five activities of Primary life cycle processes n n n Acquisition Supply Development Operation Maintenance 971707 洪至柔 http: //www. cit. gu. edu. au/~noran 41
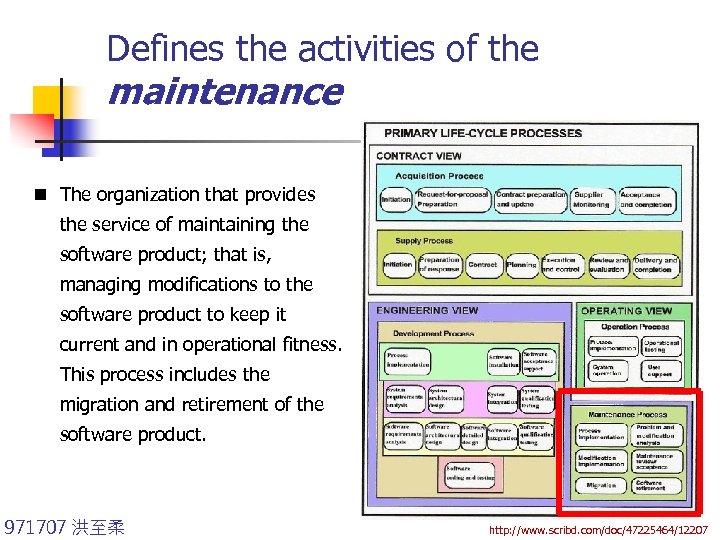 Defines the activities of the maintenance n The organization that provides the service of maintaining the software product; that is, managing modifications to the software product to keep it current and in operational fitness. This process includes the migration and retirement of the software product. 971707 洪至柔 http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
Defines the activities of the maintenance n The organization that provides the service of maintaining the software product; that is, managing modifications to the software product to keep it current and in operational fitness. This process includes the migration and retirement of the software product. 971707 洪至柔 http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
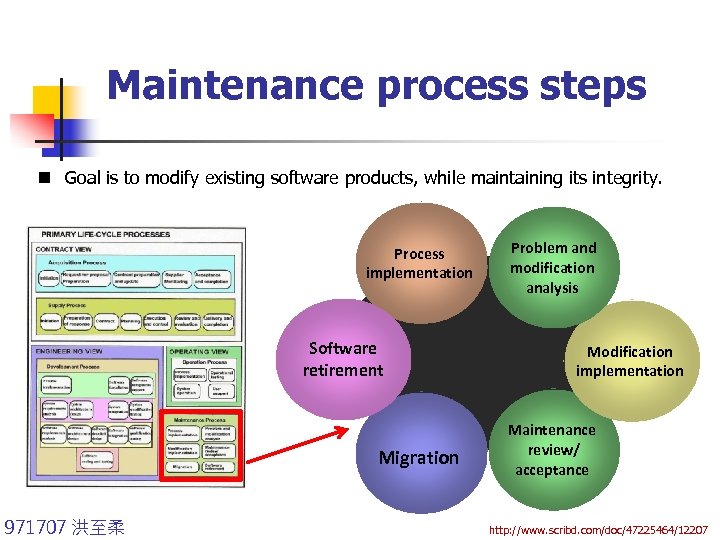 Maintenance process steps n Goal is to modify existing software products, while maintaining its integrity. Process implementation Software retirement Migration 971707 洪至柔 Problem and modification analysis Modification implementation Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
Maintenance process steps n Goal is to modify existing software products, while maintaining its integrity. Process implementation Software retirement Migration 971707 洪至柔 Problem and modification analysis Modification implementation Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
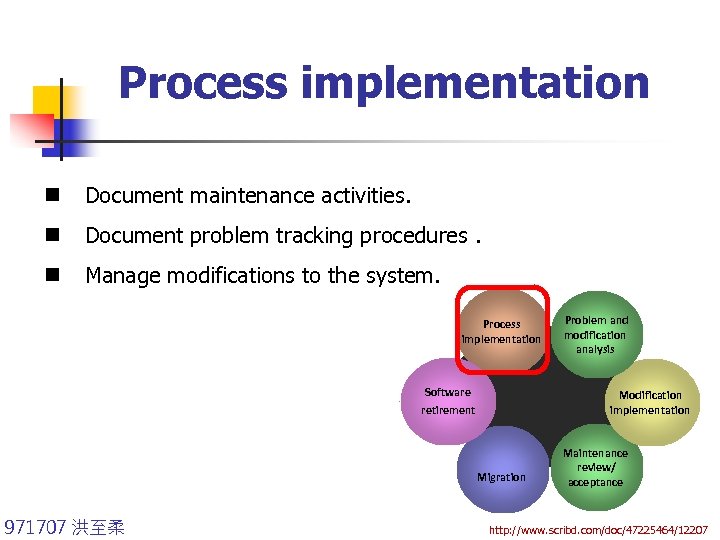 Process implementation n Document maintenance activities. n Document problem tracking procedures. n Manage modifications to the system. Process implementation Software retirement Modification implementation Migration 971707 洪至柔 Problem and modification analysis Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
Process implementation n Document maintenance activities. n Document problem tracking procedures. n Manage modifications to the system. Process implementation Software retirement Modification implementation Migration 971707 洪至柔 Problem and modification analysis Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
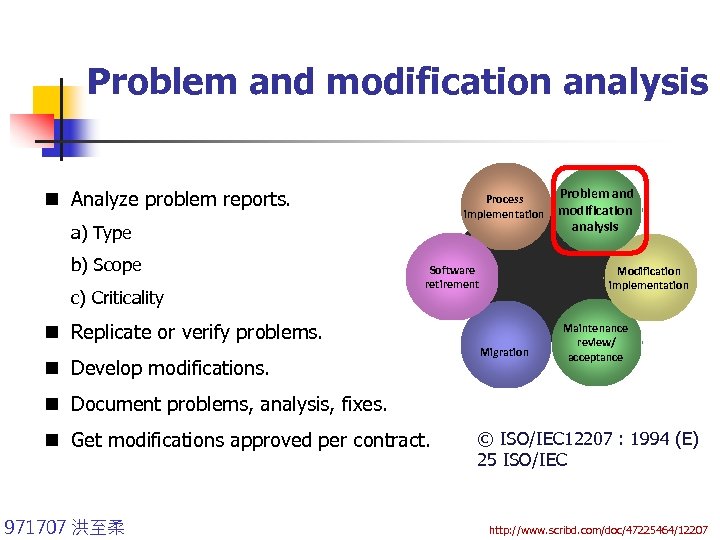 Problem and modification analysis n Analyze problem reports. Process implementation a) Type b) Scope c) Criticality Software retirement Modification implementation n Replicate or verify problems. n Develop modifications. Problem and modification analysis Migration Maintenance review/ acceptance n Document problems, analysis, fixes. n Get modifications approved per contract. 971707 洪至柔 © ISO/IEC 12207 : 1994 (E) 25 ISO/IEC http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
Problem and modification analysis n Analyze problem reports. Process implementation a) Type b) Scope c) Criticality Software retirement Modification implementation n Replicate or verify problems. n Develop modifications. Problem and modification analysis Migration Maintenance review/ acceptance n Document problems, analysis, fixes. n Get modifications approved per contract. 971707 洪至柔 © ISO/IEC 12207 : 1994 (E) 25 ISO/IEC http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
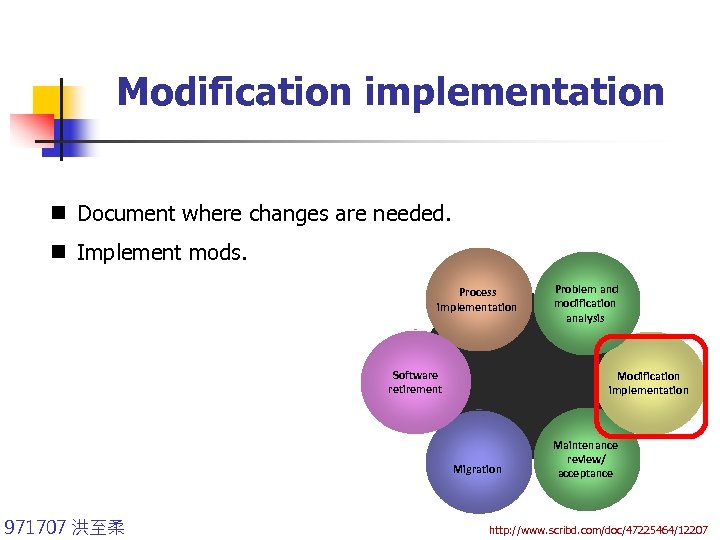 Modification implementation n Document where changes are needed. n Implement mods. Process implementation Software retirement Modification implementation Migration 971707 洪至柔 Problem and modification analysis Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
Modification implementation n Document where changes are needed. n Implement mods. Process implementation Software retirement Modification implementation Migration 971707 洪至柔 Problem and modification analysis Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
 Maintenance review/acceptance n Review integrity of modified system. n Get approval for modifications per contract. Process implementation Software retirement Modification implementation Migration 971707 洪至柔 Problem and modification analysis Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
Maintenance review/acceptance n Review integrity of modified system. n Get approval for modifications per contract. Process implementation Software retirement Modification implementation Migration 971707 洪至柔 Problem and modification analysis Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
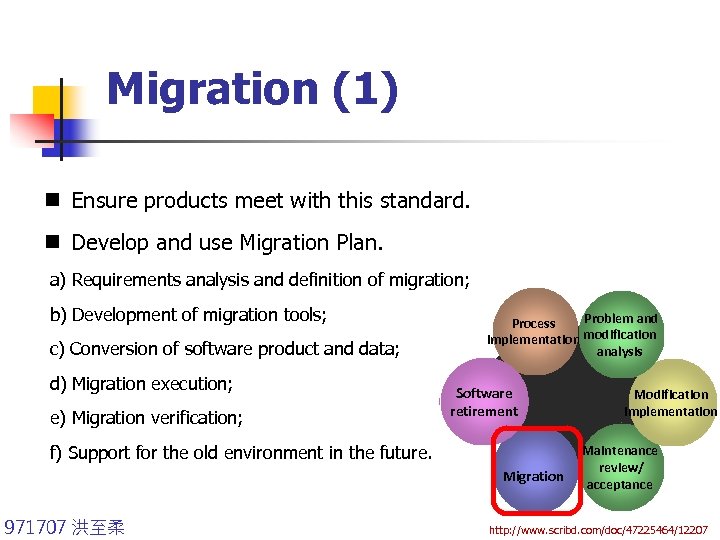 Migration (1) n Ensure products meet with this standard. n Develop and use Migration Plan. a) Requirements analysis and definition of migration; b) Development of migration tools; c) Conversion of software product and data; d) Migration execution; e) Migration verification; Problem and Process implementation modification analysis Software retirement f) Support for the old environment in the future. Migration 971707 洪至柔 Modification implementation Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
Migration (1) n Ensure products meet with this standard. n Develop and use Migration Plan. a) Requirements analysis and definition of migration; b) Development of migration tools; c) Conversion of software product and data; d) Migration execution; e) Migration verification; Problem and Process implementation modification analysis Software retirement f) Support for the old environment in the future. Migration 971707 洪至柔 Modification implementation Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
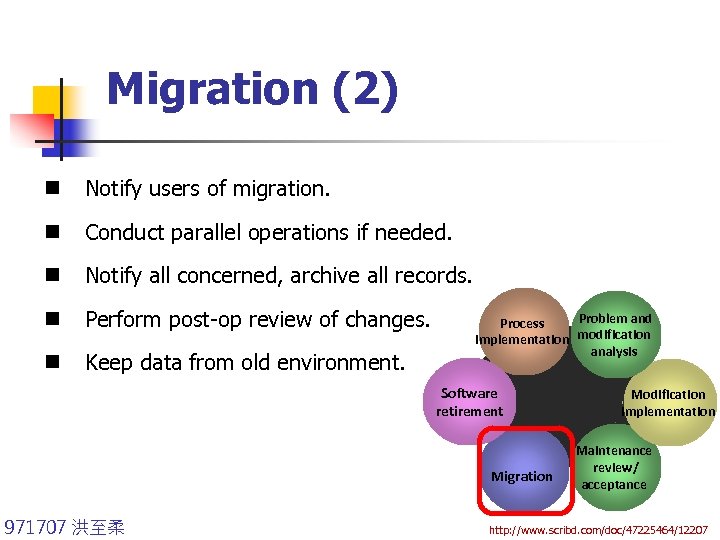 Migration (2) n Notify users of migration. n Conduct parallel operations if needed. n Notify all concerned, archive all records. n Perform post-op review of changes. n Keep data from old environment. Problem and Process implementation modification analysis Software retirement Migration 971707 洪至柔 Modification implementation Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
Migration (2) n Notify users of migration. n Conduct parallel operations if needed. n Notify all concerned, archive all records. n Perform post-op review of changes. n Keep data from old environment. Problem and Process implementation modification analysis Software retirement Migration 971707 洪至柔 Modification implementation Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
 Software retirement n Document plans for retirement. n Notify all users of plans and activities. n Conduct parallel operations. n Notify all concerned, archive all records. n Keep data from retired product per contract. Problem and Process implementation modification analysis Software retirement Migration 971707 洪至柔 Modification implementation Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
Software retirement n Document plans for retirement. n Notify all users of plans and activities. n Conduct parallel operations. n Notify all concerned, archive all records. n Keep data from retired product per contract. Problem and Process implementation modification analysis Software retirement Migration 971707 洪至柔 Modification implementation Maintenance review/ acceptance http: //www. scribd. com/doc/47225464/12207
 Q&A Thanks 971707 洪至柔 51
Q&A Thanks 971707 洪至柔 51
 System Maintenance IEEE 1219 software lifecycle processes Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971663 蔡志良 52
System Maintenance IEEE 1219 software lifecycle processes Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971663 蔡志良 52
 Introduction of IEEE 1219 n An iterative process for managing and executing software maintenance activities. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 53
Introduction of IEEE 1219 n An iterative process for managing and executing software maintenance activities. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 53
 Requirements n This standards prescribes requirements: Process Control Management of planning Execution Documentation of software maintenance 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 54
Requirements n This standards prescribes requirements: Process Control Management of planning Execution Documentation of software maintenance 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 54
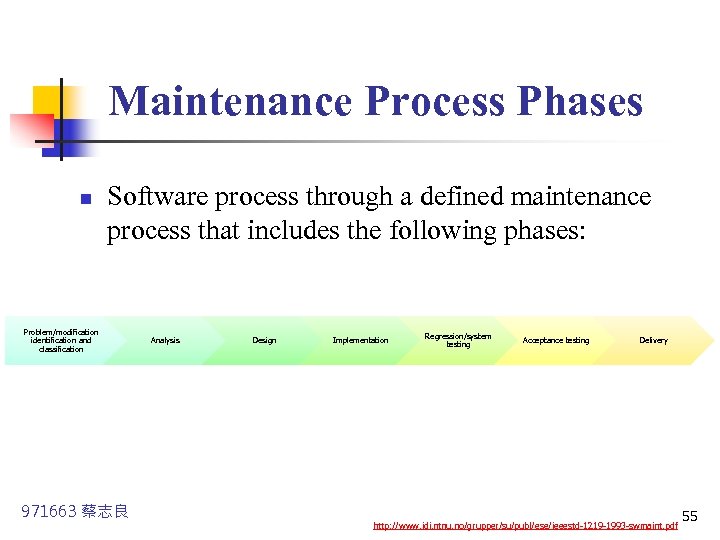 Maintenance Process Phases n Software process through a defined maintenance process that includes the following phases: Problem/modification identification and classification 971663 蔡志良 Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 55
Maintenance Process Phases n Software process through a defined maintenance process that includes the following phases: Problem/modification identification and classification 971663 蔡志良 Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 55
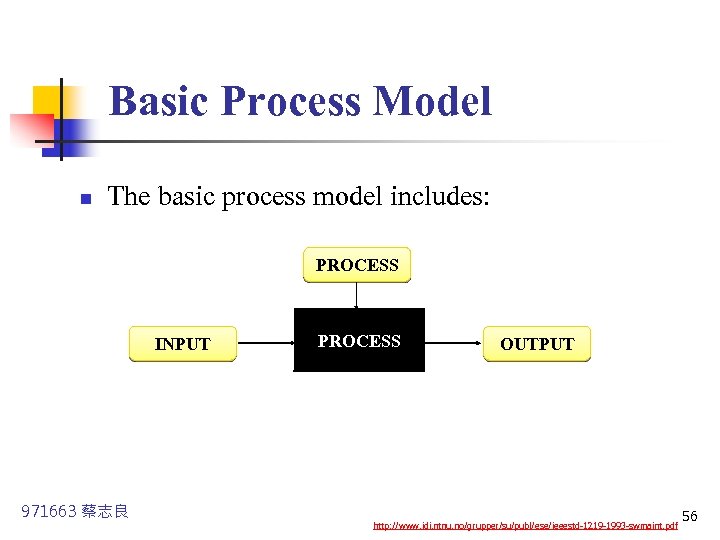 Basic Process Model n The basic process model includes: PROCESS INPUT 971663 蔡志良 PROCESS OUTPUT http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 56
Basic Process Model n The basic process model includes: PROCESS INPUT 971663 蔡志良 PROCESS OUTPUT http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 56
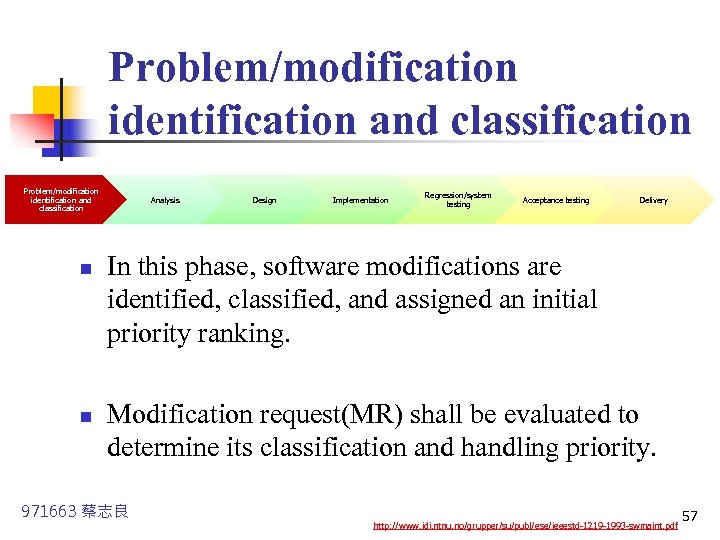 Problem/modification identification and classification n n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery In this phase, software modifications are identified, classified, and assigned an initial priority ranking. Modification request(MR) shall be evaluated to determine its classification and handling priority. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 57
Problem/modification identification and classification n n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery In this phase, software modifications are identified, classified, and assigned an initial priority ranking. Modification request(MR) shall be evaluated to determine its classification and handling priority. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 57
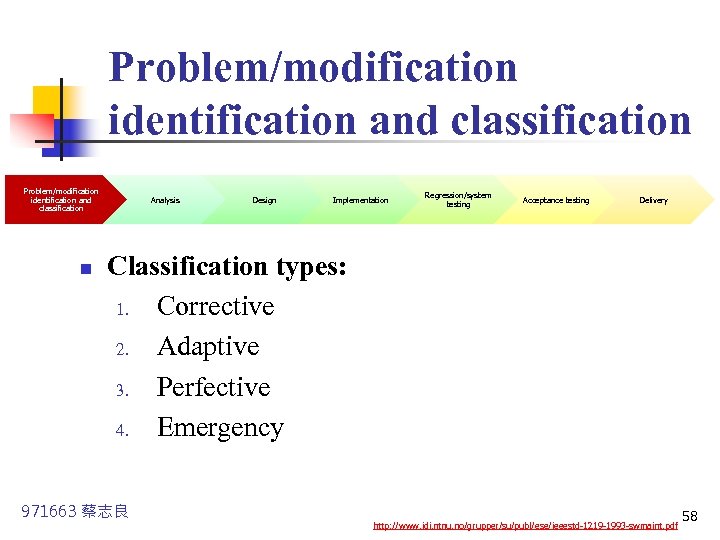 Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Classification types: 1. Corrective 2. Adaptive 3. Perfective 4. Emergency 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 58
Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Classification types: 1. Corrective 2. Adaptive 3. Perfective 4. Emergency 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 58
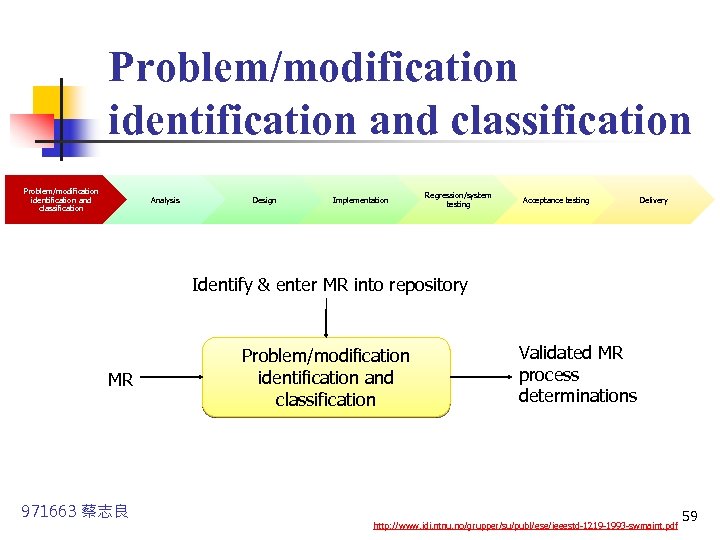 Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Identify & enter MR into repository MR 971663 蔡志良 Problem/modification identification and classification Validated MR process determinations http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 59
Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Identify & enter MR into repository MR 971663 蔡志良 Problem/modification identification and classification Validated MR process determinations http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 59
 Analysis Problem/modification identification and classification n n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Use the repository information and the MR validated in the modification identification and classification phase. Study the feasibility and scope of the modification and to devise a preliminary plan for Design, Implementation, Testing and Delivery 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 60
Analysis Problem/modification identification and classification n n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Use the repository information and the MR validated in the modification identification and classification phase. Study the feasibility and scope of the modification and to devise a preliminary plan for Design, Implementation, Testing and Delivery 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 60
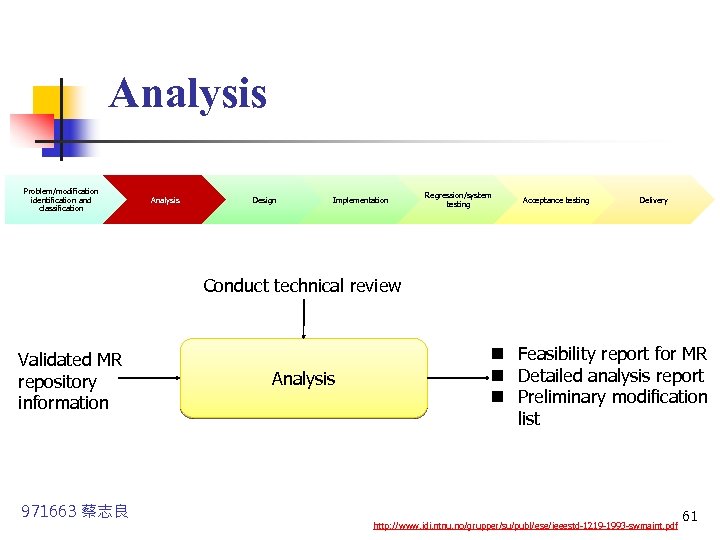 Analysis Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Conduct technical review Validated MR repository information 971663 蔡志良 Analysis n Feasibility report for MR n Detailed analysis report n Preliminary modification list http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 61
Analysis Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Conduct technical review Validated MR repository information 971663 蔡志良 Analysis n Feasibility report for MR n Detailed analysis report n Preliminary modification list http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 61
 Design Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery All current system and project documentation, existing software and database, and the output of analysis phase shall be using to design the modification to the system. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 62
Design Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery All current system and project documentation, existing software and database, and the output of analysis phase shall be using to design the modification to the system. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 62
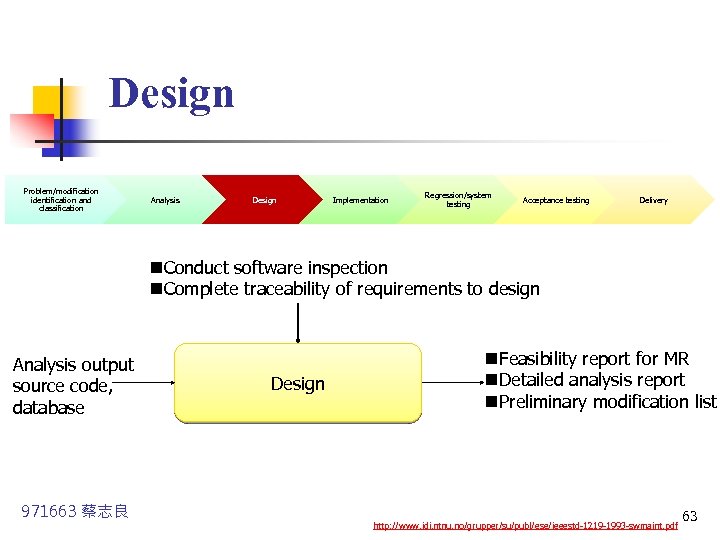 Design Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery n. Conduct software inspection n. Complete traceability of requirements to design Analysis output source code, database 971663 蔡志良 Design n. Feasibility report for MR n. Detailed analysis report n. Preliminary modification list http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 63
Design Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery n. Conduct software inspection n. Complete traceability of requirements to design Analysis output source code, database 971663 蔡志良 Design n. Feasibility report for MR n. Detailed analysis report n. Preliminary modification list http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 63
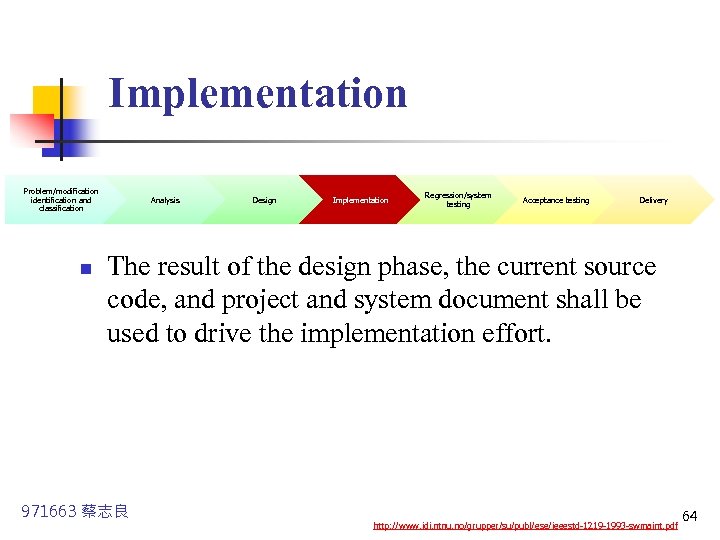 Implementation Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery The result of the design phase, the current source code, and project and system document shall be used to drive the implementation effort. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 64
Implementation Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery The result of the design phase, the current source code, and project and system document shall be used to drive the implementation effort. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 64
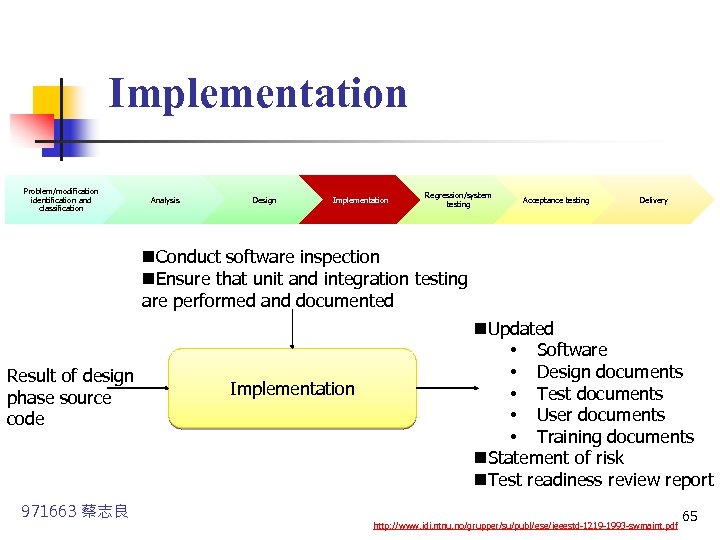 Implementation Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery n. Conduct software inspection n. Ensure that unit and integration testing are performed and documented Result of design phase source code 971663 蔡志良 Implementation n. Updated • Software • Design documents • Test documents • User documents • Training documents n. Statement of risk n. Test readiness review report http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 65
Implementation Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery n. Conduct software inspection n. Ensure that unit and integration testing are performed and documented Result of design phase source code 971663 蔡志良 Implementation n. Updated • Software • Design documents • Test documents • User documents • Training documents n. Statement of risk n. Test readiness review report http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 65
 Regression/System testing Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Regression testing is a part of system testing and shall be performed to validate that the modified code does not introduce faults that did not exist prior to maintenance activity. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 66
Regression/System testing Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Regression testing is a part of system testing and shall be performed to validate that the modified code does not introduce faults that did not exist prior to maintenance activity. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 66
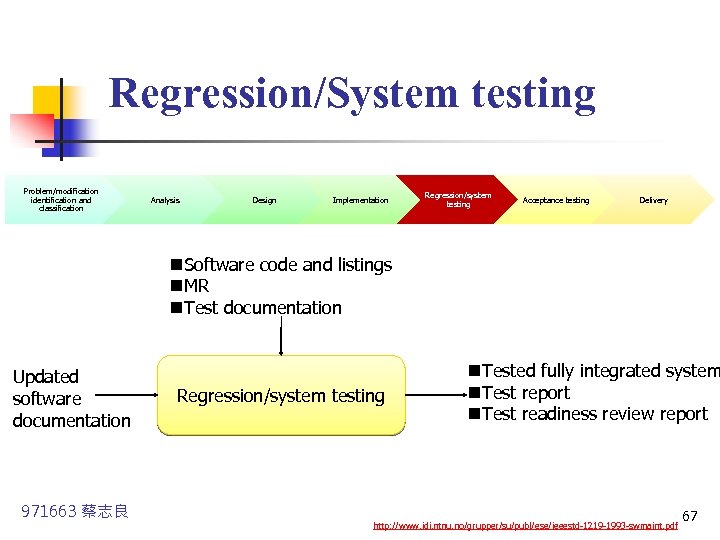 Regression/System testing Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery n. Software code and listings n. MR n. Test documentation Updated software documentation 971663 蔡志良 Regression/system testing n. Tested fully integrated system n. Test report n. Test readiness review report http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 67
Regression/System testing Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery n. Software code and listings n. MR n. Test documentation Updated software documentation 971663 蔡志良 Regression/system testing n. Tested fully integrated system n. Test report n. Test readiness review report http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 67
 Acceptance testing Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Performed by either the customer, the user of the modification package, or a third party designated by the customer. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 68
Acceptance testing Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Performed by either the customer, the user of the modification package, or a third party designated by the customer. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 68
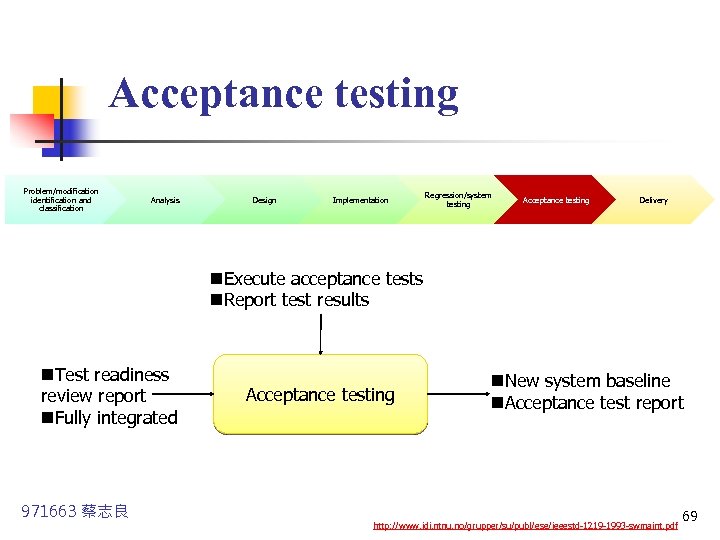 Acceptance testing Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery n. Execute acceptance tests n. Report test results n. Test readiness review report n. Fully integrated 971663 蔡志良 Acceptance testing n. New system baseline n. Acceptance test report http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 69
Acceptance testing Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery n. Execute acceptance tests n. Report test results n. Test readiness review report n. Fully integrated 971663 蔡志良 Acceptance testing n. New system baseline n. Acceptance test report http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 69
 Delivery Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Complete acceptance testing phase and delivery new system to the customer. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 70
Delivery Problem/modification identification and classification n Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery Complete acceptance testing phase and delivery new system to the customer. 971663 蔡志良 http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 70
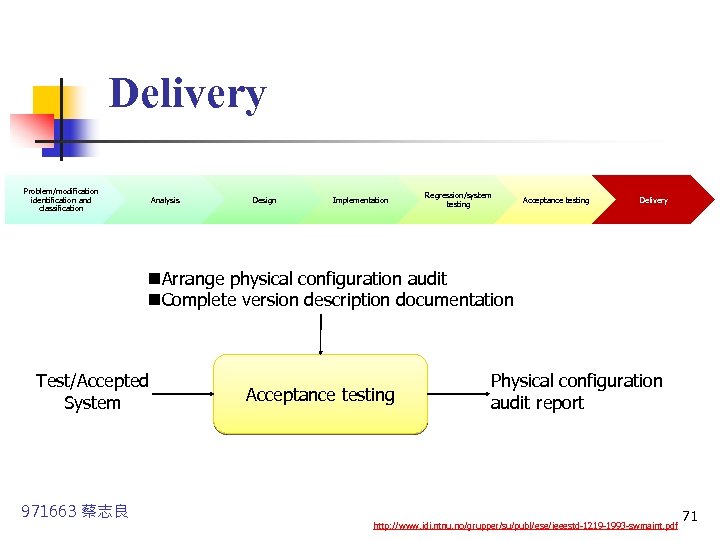 Delivery Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery n. Arrange physical configuration audit n. Complete version description documentation Test/Accepted System 971663 蔡志良 Acceptance testing Physical configuration audit report http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 71
Delivery Problem/modification identification and classification Analysis Design Implementation Regression/system testing Acceptance testing Delivery n. Arrange physical configuration audit n. Complete version description documentation Test/Accepted System 971663 蔡志良 Acceptance testing Physical configuration audit report http: //www. idi. ntnu. no/grupper/su/publ/ese/ieeestd-1219 -1993 -swmaint. pdf 71
 Q&A Thanks 971663 蔡志良 72
Q&A Thanks 971663 蔡志良 72
 Software process improvement CMMI Capability Maturity Model Integration Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971626 劉建旻 73
Software process improvement CMMI Capability Maturity Model Integration Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971626 劉建旻 73
 Introduction to CMMI n n A process improvement approach whose goal is to help organizations improve their performance. CMMI can be used to guide process improvement across a project, a division, or an entire organization. 971626 劉建旻 http: //zh. wikipedia. org/wiki/Wikipedia 74
Introduction to CMMI n n A process improvement approach whose goal is to help organizations improve their performance. CMMI can be used to guide process improvement across a project, a division, or an entire organization. 971626 劉建旻 http: //zh. wikipedia. org/wiki/Wikipedia 74
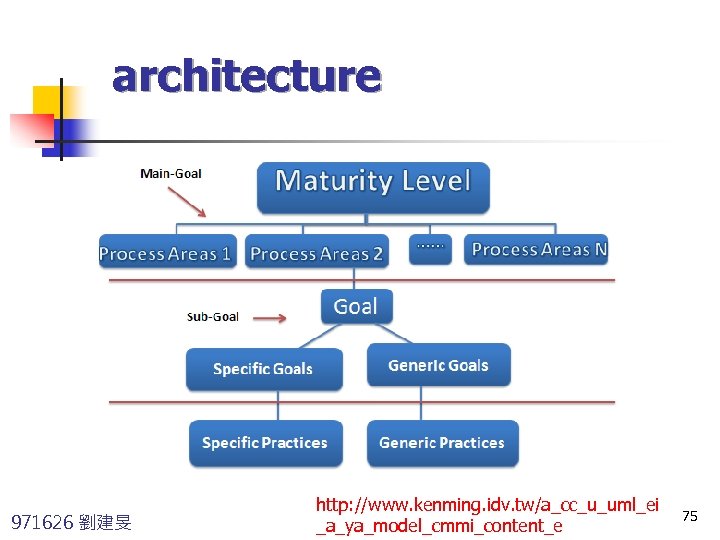 architecture 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. kenming. idv. tw/a_cc_u_uml_ei _a_ya_model_cmmi_content_e 75
architecture 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. kenming. idv. tw/a_cc_u_uml_ei _a_ya_model_cmmi_content_e 75
 Maturity levels 971626 劉建旻 http: //zh. wikipedia. org/wiki/Wikipedia
Maturity levels 971626 劉建旻 http: //zh. wikipedia. org/wiki/Wikipedia
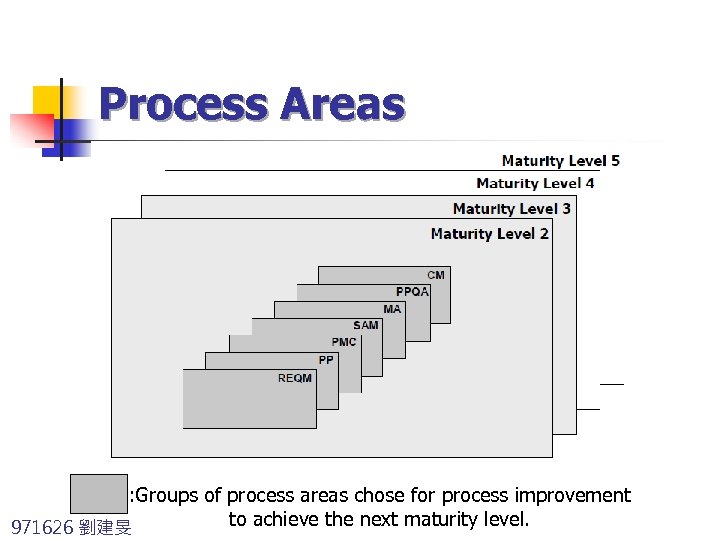 Process Areas : Groups of process areas chose for process improvement to achieve the next maturity level. 971626 劉建旻
Process Areas : Groups of process areas chose for process improvement to achieve the next maturity level. 971626 劉建旻
 Level 1 1. 2. 3. 971626 劉建旻 Processes are usually ad hoc and chaotic. Do not provide a stable environment. Produce products and services, but frequently exceed the budget and schedule of their projects. http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
Level 1 1. 2. 3. 971626 劉建旻 Processes are usually ad hoc and chaotic. Do not provide a stable environment. Produce products and services, but frequently exceed the budget and schedule of their projects. http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
 Level 2 Process Areas n Requirements Management(REQM): n n n Project Planning(PP): n n Build and Maintain the project plan. Project Monitoring and Control(PMC): n n 1. Manages products and product components of the project requirements 2. Define project plans, work products and demand Provide understanding of the progress of the project Supplier Agreement Management (SAM): n Manage the procurement of the suppliers’ products and services. 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
Level 2 Process Areas n Requirements Management(REQM): n n n Project Planning(PP): n n Build and Maintain the project plan. Project Monitoring and Control(PMC): n n 1. Manages products and product components of the project requirements 2. Define project plans, work products and demand Provide understanding of the progress of the project Supplier Agreement Management (SAM): n Manage the procurement of the suppliers’ products and services. 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
 Level 2 Process Areas(Cont) n Measurement and Analysis(MA): n n Process and Product Quality Assurance(PPQA): n n Develop and support the capacity of measure of management information. Provide staff and management echelon with the objective observation of process. Configuration Management(CM): n Establish and maintain management through constructing identification, building control, building records and construction of the state audit. 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
Level 2 Process Areas(Cont) n Measurement and Analysis(MA): n n Process and Product Quality Assurance(PPQA): n n Develop and support the capacity of measure of management information. Provide staff and management echelon with the objective observation of process. Configuration Management(CM): n Establish and maintain management through constructing identification, building control, building records and construction of the state audit. 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
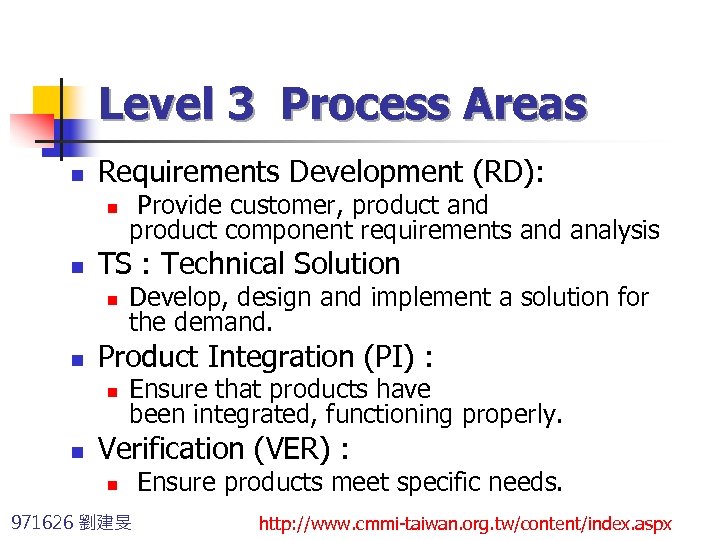 Level 3 Process Areas n Requirements Development (RD): n n TS : Technical Solution n n Develop, design and implement a solution for the demand. Product Integration (PI) : n n Provide customer, product and product component requirements and analysis Ensure that products have been integrated, functioning properly. Verification (VER) : n Ensure products meet specific needs. 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
Level 3 Process Areas n Requirements Development (RD): n n TS : Technical Solution n n Develop, design and implement a solution for the demand. Product Integration (PI) : n n Provide customer, product and product component requirements and analysis Ensure that products have been integrated, functioning properly. Verification (VER) : n Ensure products meet specific needs. 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
 Level 3 Process Areas(Cont) n Validation (VAL) : n n Organizational Process Focus (OPF): n n n Prove the products or product components, can indeed play a specific function. 1. Establish and maintain the process of organization and understanding of process assets 2. Define, plan and implement improvement activities of organization process Organizational Process Definition(OPD): n Build and maintain assets of the organization process. 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
Level 3 Process Areas(Cont) n Validation (VAL) : n n Organizational Process Focus (OPF): n n n Prove the products or product components, can indeed play a specific function. 1. Establish and maintain the process of organization and understanding of process assets 2. Define, plan and implement improvement activities of organization process Organizational Process Definition(OPD): n Build and maintain assets of the organization process. 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
 Level 3 Process Areas(Cont) n Organizational Training (OT) : n n Integrated Project Management (IPM): n n Develop staff’s skills and knowledge 1. Build and manage the project and its key personnel. 2. Establish project common prospect 3. integrat project team structure Risk Management (RSKM): n n 1. Define the risk of potential problems 2. plan risk management to reduce the negative impact. 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
Level 3 Process Areas(Cont) n Organizational Training (OT) : n n Integrated Project Management (IPM): n n Develop staff’s skills and knowledge 1. Build and manage the project and its key personnel. 2. Establish project common prospect 3. integrat project team structure Risk Management (RSKM): n n 1. Define the risk of potential problems 2. plan risk management to reduce the negative impact. 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
 Level 3 Process Areas(Cont) n Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR): n n Organizational Environment for Integration : n n n Use structured methods, in according to established criteria, to evaluate the alternatives. 1. Provides the basis for an integrated project environment 2. Manage staff. Integrated Teaming: n 971626 劉建旻 Form and maintain integrated team. http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
Level 3 Process Areas(Cont) n Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR): n n Organizational Environment for Integration : n n n Use structured methods, in according to established criteria, to evaluate the alternatives. 1. Provides the basis for an integrated project environment 2. Manage staff. Integrated Teaming: n 971626 劉建旻 Form and maintain integrated team. http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
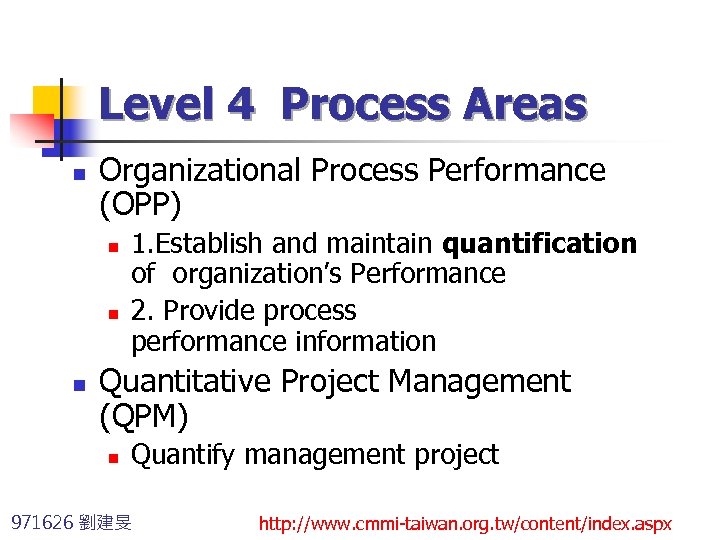 Level 4 Process Areas n Organizational Process Performance (OPP) n n n 1. Establish and maintain quantification of organization’s Performance 2. Provide process performance information Quantitative Project Management (QPM) n Quantify management project 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
Level 4 Process Areas n Organizational Process Performance (OPP) n n n 1. Establish and maintain quantification of organization’s Performance 2. Provide process performance information Quantitative Project Management (QPM) n Quantify management project 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
 Level 5 Process Areas n Organizational Innovation and Deployment(OID) n n n 1. Select and promote gradual improvement 2. Improve organizational processes and technology measurably. Causal Analysis and Resolution (CAR) n n 1. Define Loss and other problems 2. Take preventive measures 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
Level 5 Process Areas n Organizational Innovation and Deployment(OID) n n n 1. Select and promote gradual improvement 2. Improve organizational processes and technology measurably. Causal Analysis and Resolution (CAR) n n 1. Define Loss and other problems 2. Take preventive measures 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
 Others Specific Goals: 1. Only for specific target areas in a single process 2. stressed the unique characteristics Specific Practices: 1. achieve a specific goal 2. Corresponding to specific goals Generic Goals: General objectives applicable to all process areas. Generic Practices: 1. implement any process area 2. Improve the performance and control of any process 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
Others Specific Goals: 1. Only for specific target areas in a single process 2. stressed the unique characteristics Specific Practices: 1. achieve a specific goal 2. Corresponding to specific goals Generic Goals: General objectives applicable to all process areas. Generic Practices: 1. implement any process area 2. Improve the performance and control of any process 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. cmmi-taiwan. org. tw/content/index. aspx
 Evaluation 1. Evaluation Unit : SEI(Software Engineering Institute). 2. Use SCAMPI for appraising organizations using CMMI. 3. SCAMPI ( Standard CMMI Appraisal Method for Process Improvement) 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. sei. cmu. edu/ 88
Evaluation 1. Evaluation Unit : SEI(Software Engineering Institute). 2. Use SCAMPI for appraising organizations using CMMI. 3. SCAMPI ( Standard CMMI Appraisal Method for Process Improvement) 971626 劉建旻 http: //www. sei. cmu. edu/ 88
 Q&A Thanks 971626 劉建旻 89
Q&A Thanks 971626 劉建旻 89
 Software process improvement ISO/IEC TR 15504 (Information technology — Software process assessment ) Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 90
Software process improvement ISO/IEC TR 15504 (Information technology — Software process assessment ) Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 90
 ISO/IEC TR 15504(Information technology — Software process assessment ) n Ø Ø ISO/IEC TR 15504 consists of the following parts : Part 1: Concepts and introductory guide Part 2: A reference model for processes and process capability Part 3: Performing an assessment Part 4: Guide to performing assessments 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 91
ISO/IEC TR 15504(Information technology — Software process assessment ) n Ø Ø ISO/IEC TR 15504 consists of the following parts : Part 1: Concepts and introductory guide Part 2: A reference model for processes and process capability Part 3: Performing an assessment Part 4: Guide to performing assessments 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 91
 ISO/IEC TR 15504(Information technology — Software process assessment ) Ø Ø Ø Part 5: An assessment model and indicator guidance Part 6: Guide to competency of assessors Part 7: Guide for use in process improvement Part 8: Guide for use in determining supplier process capability Part 9: Vocabulary 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 92
ISO/IEC TR 15504(Information technology — Software process assessment ) Ø Ø Ø Part 5: An assessment model and indicator guidance Part 6: Guide to competency of assessors Part 7: Guide for use in process improvement Part 8: Guide for use in determining supplier process capability Part 9: Vocabulary 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 92
 ISO/IEC TR 15504 -7 - Scope Ø Ø invoking a software process assessment using the results of a software process assessment measuring software process effectiveness and improvement effectiveness identifying improvement actions aligned to business goals 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 93
ISO/IEC TR 15504 -7 - Scope Ø Ø invoking a software process assessment using the results of a software process assessment measuring software process effectiveness and improvement effectiveness identifying improvement actions aligned to business goals 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 93
 ISO/IEC TR 15504 -7 - Scope Ø Ø Ø using a process model compatible with the reference model defined in ISO/IEC TR 15504 -2 as a framework for improvement issues related to organizational culture in the context of software process improvement dealing with management issues for software process improvement 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 94
ISO/IEC TR 15504 -7 - Scope Ø Ø Ø using a process model compatible with the reference model defined in ISO/IEC TR 15504 -2 as a framework for improvement issues related to organizational culture in the context of software process improvement dealing with management issues for software process improvement 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 94
 Process improvement basics Ø Ø Ø software process improvement demands investment, planning, dedicated people, management time and capital investment software process improvement is a team effort effective change requires an understanding of the current process and clear goals for improvement 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 95
Process improvement basics Ø Ø Ø software process improvement demands investment, planning, dedicated people, management time and capital investment software process improvement is a team effort effective change requires an understanding of the current process and clear goals for improvement 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 95
 Process improvement basics Ø Ø software process improvement is continuous – it involves continual learning and evolution software process changes will not be sustained without conscious effort and periodic reinforcement 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 96
Process improvement basics Ø Ø software process improvement is continuous – it involves continual learning and evolution software process changes will not be sustained without conscious effort and periodic reinforcement 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 96
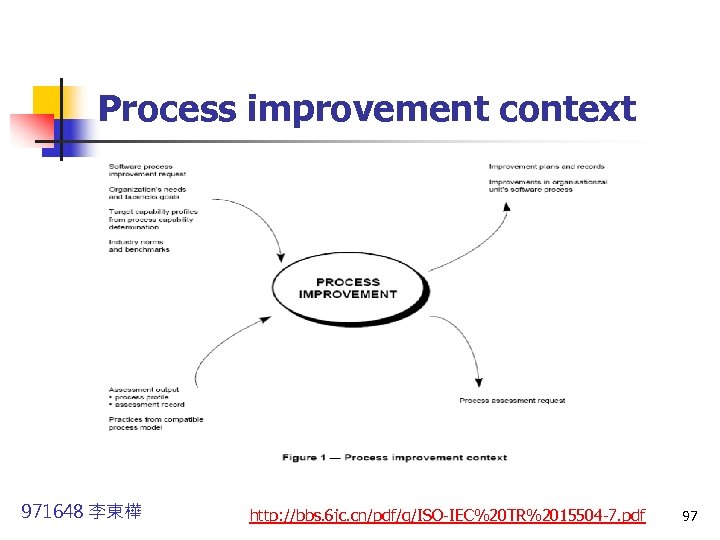 Process improvement context 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 97
Process improvement context 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 97
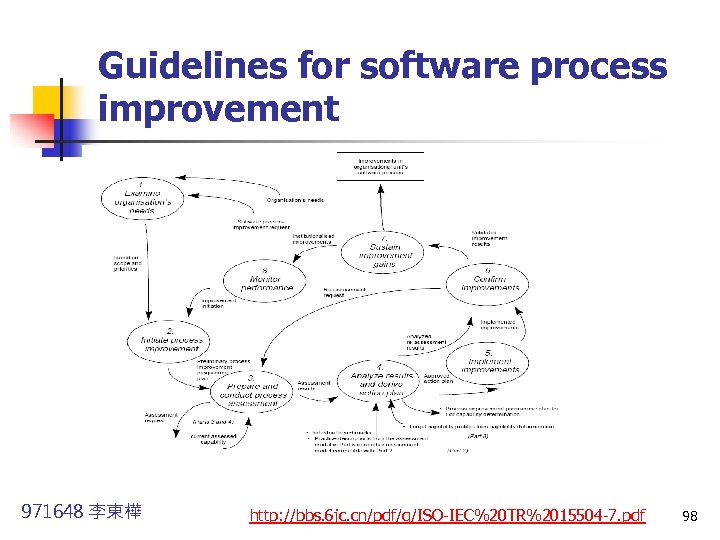 Guidelines for software process improvement 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 98
Guidelines for software process improvement 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf 98
 STEP 2 - Initiate process improvement Ø Ø (1)Set a project (2)Find the needs and goals 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
STEP 2 - Initiate process improvement Ø Ø (1)Set a project (2)Find the needs and goals 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
 STEP 3 - Prepare for and conduct a process assessment Ø Ø Ø Ø (1)Prepare assessment input (2)Find a Sponsor (3)Competent assessor (4)Assessment purpose (5)Assessment scope (6)Assessment Constraints (7)Conduct a process assessment 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
STEP 3 - Prepare for and conduct a process assessment Ø Ø Ø Ø (1)Prepare assessment input (2)Find a Sponsor (3)Competent assessor (4)Assessment purpose (5)Assessment scope (6)Assessment Constraints (7)Conduct a process assessment 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
 STEP 4 - Analyze assessment output and derive action plan Ø Ø Ø Ø (1)Identify improvement areas (2)Analyze assessment results (3)Analyze needs and goals (4)Analyze effectiveness measurements (5)Analyze risks (6)List improvement areas (7)Define specific improvement goals and set targets (8)Derive action plan 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
STEP 4 - Analyze assessment output and derive action plan Ø Ø Ø Ø (1)Identify improvement areas (2)Analyze assessment results (3)Analyze needs and goals (4)Analyze effectiveness measurements (5)Analyze risks (6)List improvement areas (7)Define specific improvement goals and set targets (8)Derive action plan 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
 STEP 5 - Implement improvements Ø Ø (1)Operate approach to implementation (2)Detailed implementation planning (3)Implement improvement actions (4)Monitor the process improvement project 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
STEP 5 - Implement improvements Ø Ø (1)Operate approach to implementation (2)Detailed implementation planning (3)Implement improvement actions (4)Monitor the process improvement project 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
 STEP 6 – Confirm improvements Ø Ø (1)Improve targets (2)Organize culture (3)Re-evaluate risks (4)Re-evaluate cost-benefit 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
STEP 6 – Confirm improvements Ø Ø (1)Improve targets (2)Organize culture (3)Re-evaluate risks (4)Re-evaluate cost-benefit 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
 STEP 7 - Sustain improvement gains Ø Institutionalized improvements 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
STEP 7 - Sustain improvement gains Ø Institutionalized improvements 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
 STEP 8 - Monitor performance Ø Ø (1)Monitor performance of the software process (2)Review the process improvement programme 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
STEP 8 - Monitor performance Ø Ø (1)Monitor performance of the software process (2)Review the process improvement programme 971648 李東樺 http: //bbs. 6 jc. cn/pdf/g/ISO-IEC%20 TR%2015504 -7. pdf
 Q&A Thanks 971648 李東樺 106
Q&A Thanks 971648 李東樺 106
 IT governance COBIT Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971635 王政欽 107
IT governance COBIT Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971635 王政欽 107
 COBIT n In 1996, the first edition of COBIT was released. n In 1998, the second edition added "Management Guidelines". n In 2000, the third edition was released. n In 2003, an on-line version became available. n In December 2005, the fourth edition was initially released. n In May 2007, the current 4. 1 revision was released. 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 108
COBIT n In 1996, the first edition of COBIT was released. n In 1998, the second edition added "Management Guidelines". n In 2000, the third edition was released. n In 2003, an on-line version became available. n In December 2005, the fourth edition was initially released. n In May 2007, the current 4. 1 revision was released. 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 108
 What does COBIT do? n n n Improves IT efficiency and effectiveness. Helps IT understand the needs of the business. Puts practices in place to meet the business needs as efficiently as possible. Ensures alignment of business and IT. Helps executives understand manage IT investments throughout their life cycle. 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 109
What does COBIT do? n n n Improves IT efficiency and effectiveness. Helps IT understand the needs of the business. Puts practices in place to meet the business needs as efficiently as possible. Ensures alignment of business and IT. Helps executives understand manage IT investments throughout their life cycle. 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 109
 How does COBIT support the governance of IT? COBIT supports IT governance by providing a framework to ensure that: n n IT is aligned with the business IT enables the business and maximizes benefits IT resources are used responsibly IT risks are managed appropriately 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 110
How does COBIT support the governance of IT? COBIT supports IT governance by providing a framework to ensure that: n n IT is aligned with the business IT enables the business and maximizes benefits IT resources are used responsibly IT risks are managed appropriately 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 110
 ® COBIT Business Benefits COBIT® provides guidance for executive management to govern IT within the enterprise n More effective tools for IT to support business goals n More transparent and predictable full life-cycle IT costs n More timely and reliable information from IT n Higher quality IT services and more successful projects n More effective management of IT-related risks 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 111
® COBIT Business Benefits COBIT® provides guidance for executive management to govern IT within the enterprise n More effective tools for IT to support business goals n More transparent and predictable full life-cycle IT costs n More timely and reliable information from IT n Higher quality IT services and more successful projects n More effective management of IT-related risks 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 111
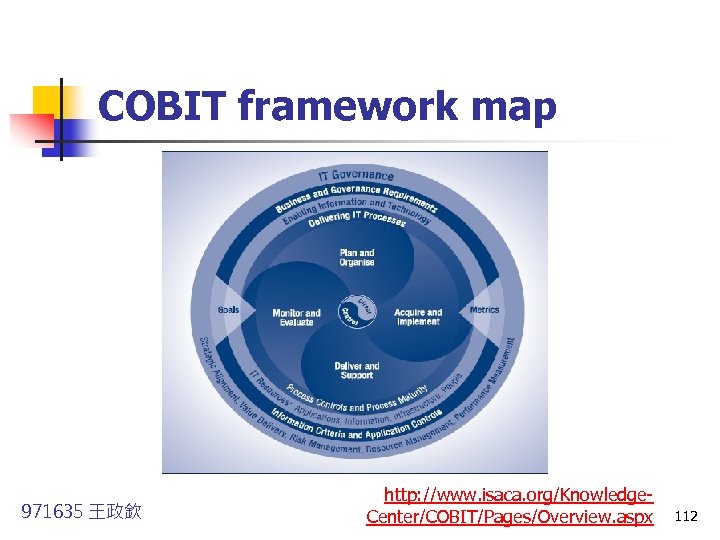 COBIT framework map 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 112
COBIT framework map 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 112
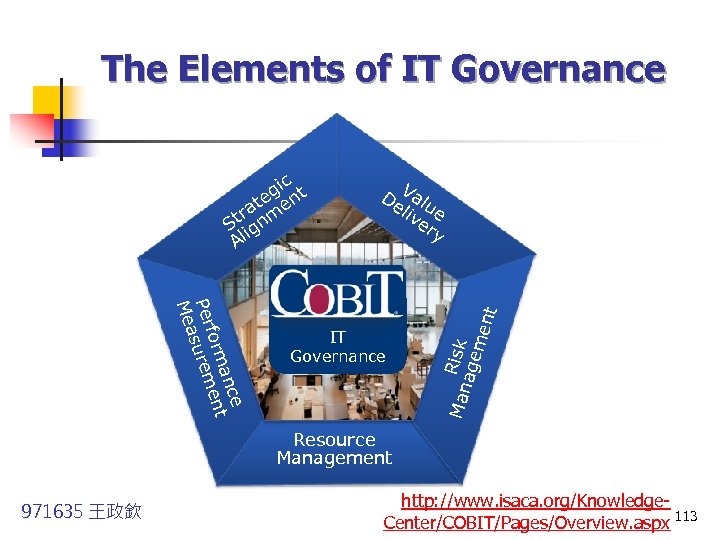 The Elements of IT Governance De Valu liv e er y IT Governance Man Risk age men e anc t form en Per surem Mea t c gi nt e at me r St ign Al Resource Management 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 113
The Elements of IT Governance De Valu liv e er y IT Governance Man Risk age men e anc t form en Per surem Mea t c gi nt e at me r St ign Al Resource Management 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 113
 IT Governance Focus Areas Strategic alignment Ensuring the linkage of business and IT plans; and aligning IT operations with enterprise operations. n n n Value delivery Executing the value proposition throughout the delivery cycle, ensuring that IT delivers the promised benefits against the strategy. Performance measurement tracks and monitors strategy implementation, project 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 114
IT Governance Focus Areas Strategic alignment Ensuring the linkage of business and IT plans; and aligning IT operations with enterprise operations. n n n Value delivery Executing the value proposition throughout the delivery cycle, ensuring that IT delivers the promised benefits against the strategy. Performance measurement tracks and monitors strategy implementation, project 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 114
 IT Governance Focus Areas n n Risk management It’s appetite for risk, understanding of compliance requirements, transparency. Resource management is about the optimal investment in, and the proper management of, critical IT resources. 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 115
IT Governance Focus Areas n n Risk management It’s appetite for risk, understanding of compliance requirements, transparency. Resource management is about the optimal investment in, and the proper management of, critical IT resources. 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 115
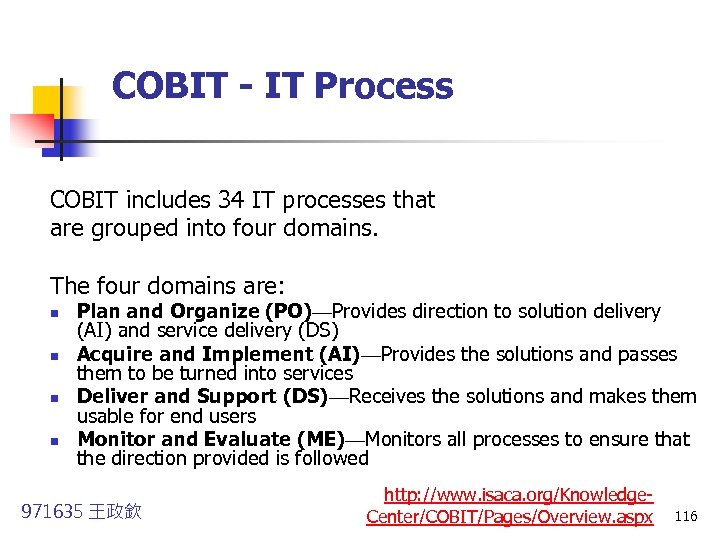 COBIT - IT Process COBIT includes 34 IT processes that are grouped into four domains. The four domains are: n n Plan and Organize (PO)—Provides direction to solution delivery (AI) and service delivery (DS) Acquire and Implement (AI)—Provides the solutions and passes them to be turned into services Deliver and Support (DS)—Receives the solutions and makes them usable for end users Monitor and Evaluate (ME)—Monitors all processes to ensure that the direction provided is followed 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 116
COBIT - IT Process COBIT includes 34 IT processes that are grouped into four domains. The four domains are: n n Plan and Organize (PO)—Provides direction to solution delivery (AI) and service delivery (DS) Acquire and Implement (AI)—Provides the solutions and passes them to be turned into services Deliver and Support (DS)—Receives the solutions and makes them usable for end users Monitor and Evaluate (ME)—Monitors all processes to ensure that the direction provided is followed 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 116
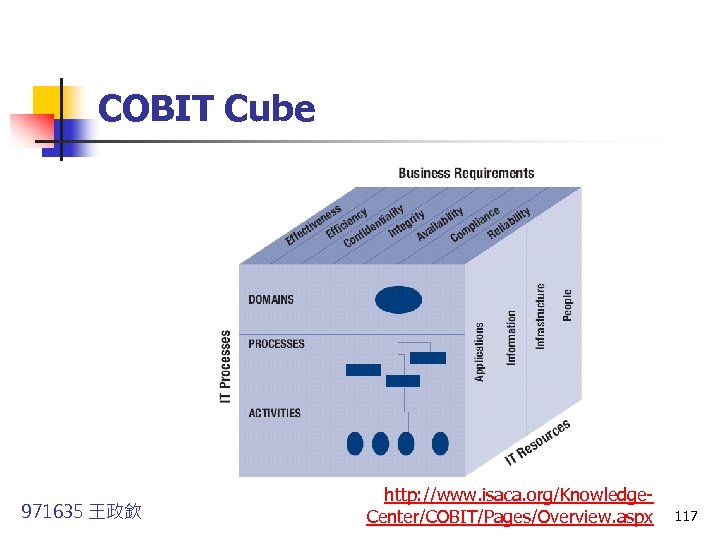 COBIT Cube 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 117
COBIT Cube 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 117
 Business requirements n To satisfy business objectives, information needs to conform to certain control 7 criteria. 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 118
Business requirements n To satisfy business objectives, information needs to conform to certain control 7 criteria. 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 118
 COBIT’S INFORMATION CRITERIA n n n n Effectiveness Efficiency Confidentiality. Integrity Availability Compliance Reliability 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 119
COBIT’S INFORMATION CRITERIA n n n n Effectiveness Efficiency Confidentiality. Integrity Availability Compliance Reliability 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 119
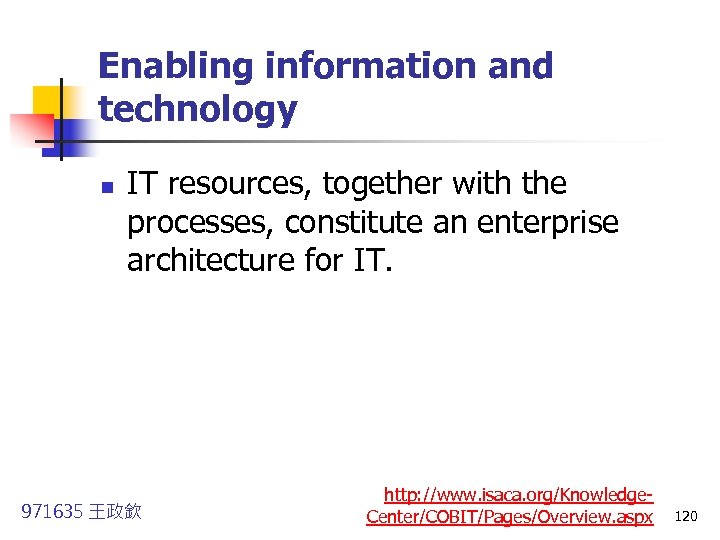 Enabling information and technology n IT resources, together with the processes, constitute an enterprise architecture for IT. 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 120
Enabling information and technology n IT resources, together with the processes, constitute an enterprise architecture for IT. 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 120
 IT RESOURCES n n Applications Information Infrastructure People 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 121
IT RESOURCES n n Applications Information Infrastructure People 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 121
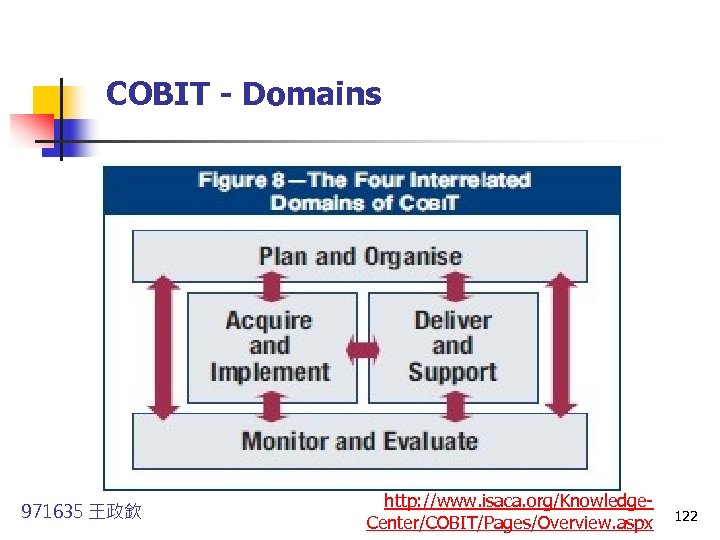 COBIT - Domains 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 122
COBIT - Domains 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 122
 Plan and Organize (PO) n n n n n PO 1 Define a Strategic IT Plan PO 2 Define the Information Architecture PO 3 Determine Technological Direction PO 4 Define the IT Processes, Organization and Relationships PO 5 Manage the IT Investment PO 6 Communicate Management Aims and Direction PO 7 Manage IT Human Resources PO 8 Manage Quality PO 9 Assess and Manage IT Risks PO 10 Manage Projects 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 123
Plan and Organize (PO) n n n n n PO 1 Define a Strategic IT Plan PO 2 Define the Information Architecture PO 3 Determine Technological Direction PO 4 Define the IT Processes, Organization and Relationships PO 5 Manage the IT Investment PO 6 Communicate Management Aims and Direction PO 7 Manage IT Human Resources PO 8 Manage Quality PO 9 Assess and Manage IT Risks PO 10 Manage Projects 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 123
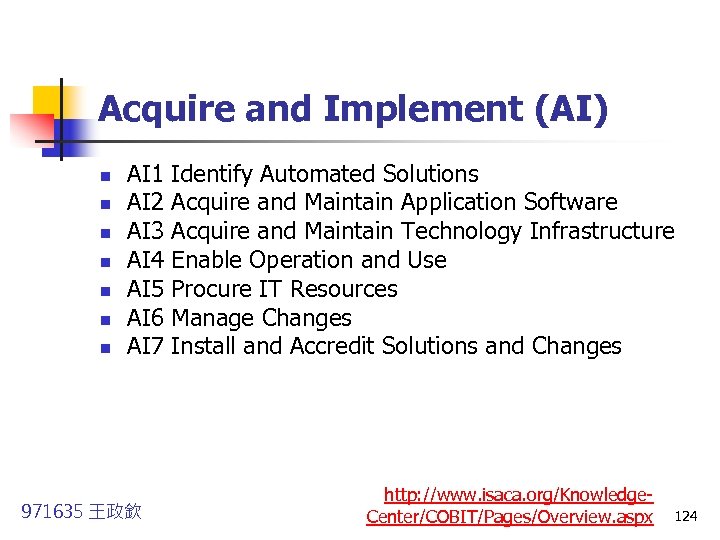 Acquire and Implement (AI) n n n n AI 1 Identify Automated Solutions AI 2 Acquire and Maintain Application Software AI 3 Acquire and Maintain Technology Infrastructure AI 4 Enable Operation and Use AI 5 Procure IT Resources AI 6 Manage Changes AI 7 Install and Accredit Solutions and Changes 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 124
Acquire and Implement (AI) n n n n AI 1 Identify Automated Solutions AI 2 Acquire and Maintain Application Software AI 3 Acquire and Maintain Technology Infrastructure AI 4 Enable Operation and Use AI 5 Procure IT Resources AI 6 Manage Changes AI 7 Install and Accredit Solutions and Changes 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 124
 Deliver and Support (DS) n n n n DS 1 Define and Manage Service Levels DS 2 Manage Third-party Services DS 3 Manage Performance and Capacity DS 4 Ensure Continuous Service DS 5 Ensure Systems Security DS 6 Identify and Allocate Costs DS 7 Educate and Train Users DS 8 Manage Service Desk and Incidents DS 9 Manage the Configuration DS 10 Manage Problems DS 11 Manage Data DS 12 Manage the Physical Environment DS 13 Manage Operations 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 125
Deliver and Support (DS) n n n n DS 1 Define and Manage Service Levels DS 2 Manage Third-party Services DS 3 Manage Performance and Capacity DS 4 Ensure Continuous Service DS 5 Ensure Systems Security DS 6 Identify and Allocate Costs DS 7 Educate and Train Users DS 8 Manage Service Desk and Incidents DS 9 Manage the Configuration DS 10 Manage Problems DS 11 Manage Data DS 12 Manage the Physical Environment DS 13 Manage Operations 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 125
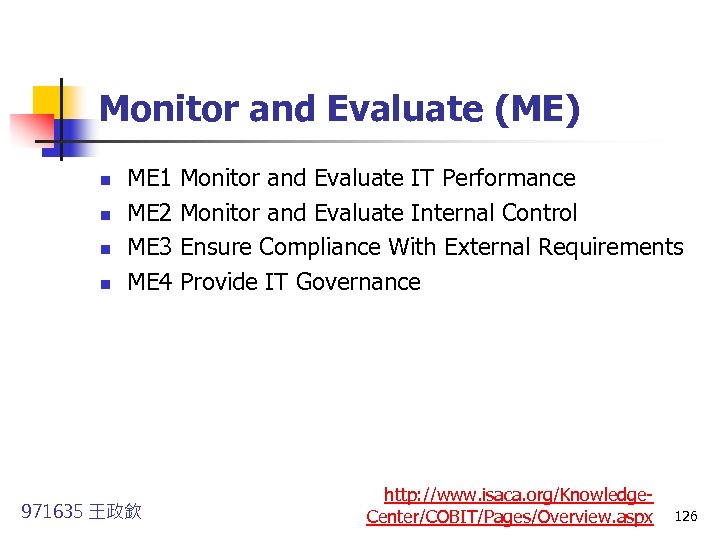 Monitor and Evaluate (ME) n n ME 1 Monitor and Evaluate IT Performance ME 2 Monitor and Evaluate Internal Control ME 3 Ensure Compliance With External Requirements ME 4 Provide IT Governance 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 126
Monitor and Evaluate (ME) n n ME 1 Monitor and Evaluate IT Performance ME 2 Monitor and Evaluate Internal Control ME 3 Ensure Compliance With External Requirements ME 4 Provide IT Governance 971635 王政欽 http: //www. isaca. org/Knowledge. Center/COBIT/Pages/Overview. aspx 126
 Q&A Thanks 971635 王政欽 127
Q&A Thanks 971635 王政欽 127
 ITIL System Life Cycle Process standard (International Standards Organization / International Electrotechnical Commission) Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971654 林建順
ITIL System Life Cycle Process standard (International Standards Organization / International Electrotechnical Commission) Advisor:Dr. Celeste Ng Reporter: 971654 林建順
 Introduction of ITIL(Information Technical Infrastructure Library) Is a development of information management practices of 20 years. Quickly adopted as the standard method used to manage increasingly complex IT environment. 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Side. Main. asp x? Volume=42&TNo=33
Introduction of ITIL(Information Technical Infrastructure Library) Is a development of information management practices of 20 years. Quickly adopted as the standard method used to manage increasingly complex IT environment. 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Side. Main. asp x? Volume=42&TNo=33
 IT Service Support n n Configuration Management Incident Management Problem Management Change Management 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Side. Main. aspx? Volu me=42&TNo=33
IT Service Support n n Configuration Management Incident Management Problem Management Change Management 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Side. Main. aspx? Volu me=42&TNo=33
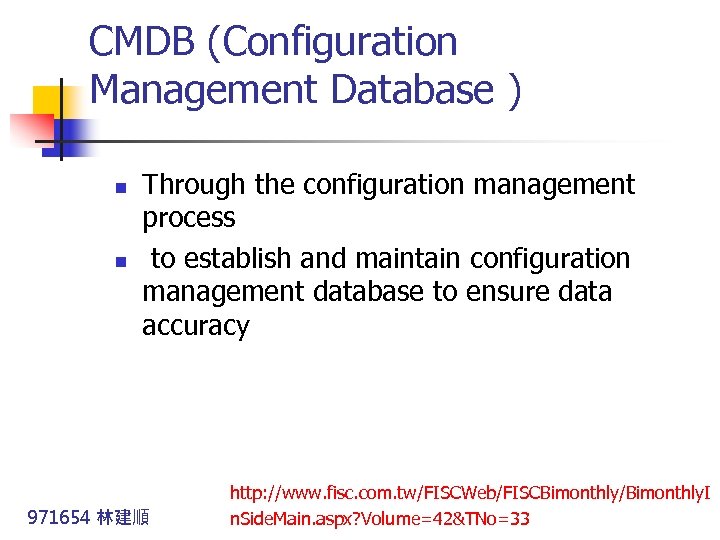 CMDB (Configuration Management Database ) n n Through the configuration management process to establish and maintain configuration management database to ensure data accuracy 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. I n. Side. Main. aspx? Volume=42&TNo=33
CMDB (Configuration Management Database ) n n Through the configuration management process to establish and maintain configuration management database to ensure data accuracy 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. I n. Side. Main. aspx? Volume=42&TNo=33
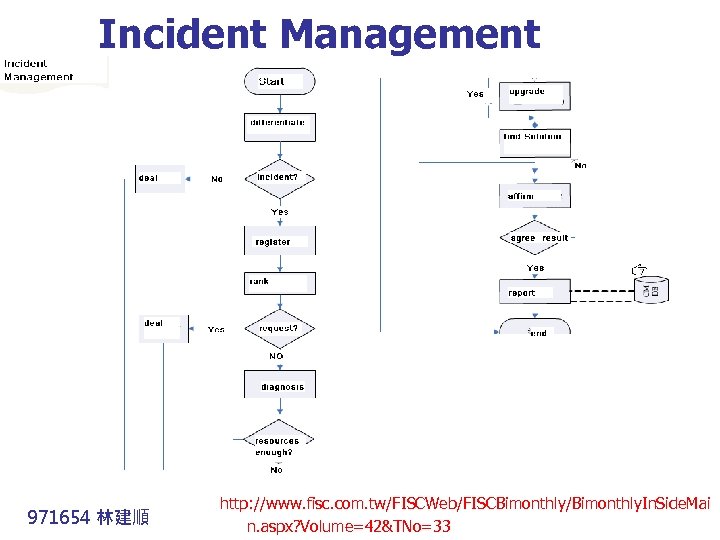 Incident Management 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Side. Mai n. aspx? Volume=42&TNo=33
Incident Management 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Side. Mai n. aspx? Volume=42&TNo=33
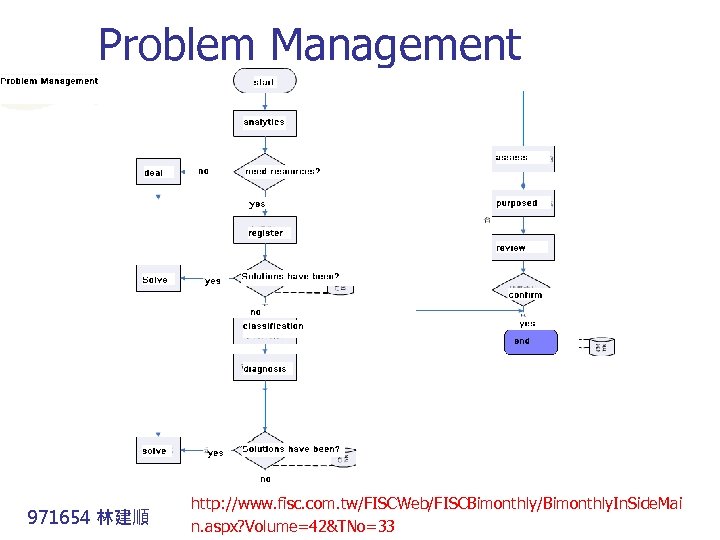 Problem Management 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Side. Mai n. aspx? Volume=42&TNo=33
Problem Management 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Side. Mai n. aspx? Volume=42&TNo=33
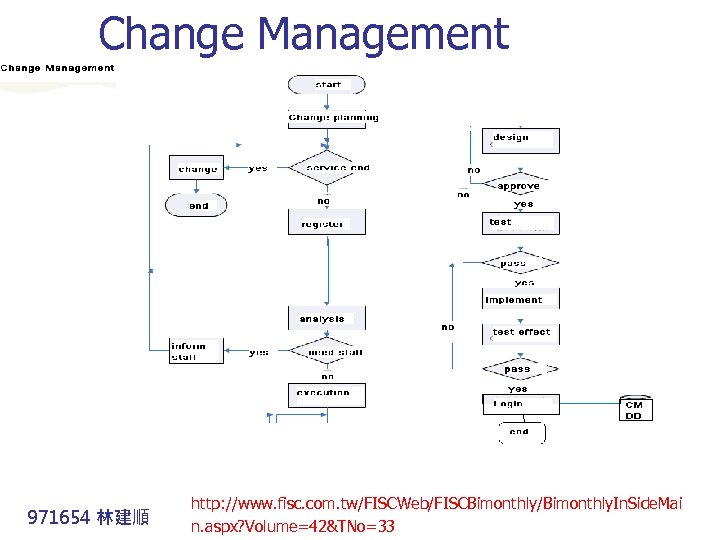 Change Management 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Side. Mai n. aspx? Volume=42&TNo=33
Change Management 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Side. Mai n. aspx? Volume=42&TNo=33
 Configuration Management Lifecycle 971654 林建順 http: //www. docin. com/p-7413521. html
Configuration Management Lifecycle 971654 林建順 http: //www. docin. com/p-7413521. html
 Basic process of ITIL Help Desk n Monitoring information infrastructure systems. n The system provides users with relevant information. n Communicate with vendors or system to solve the users problem. 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Si de. Main. aspx? Volume=42&TNo=33
Basic process of ITIL Help Desk n Monitoring information infrastructure systems. n The system provides users with relevant information. n Communicate with vendors or system to solve the users problem. 971654 林建順 http: //www. fisc. com. tw/FISCWeb/FISCBimonthly/Bimonthly. In. Si de. Main. aspx? Volume=42&TNo=33
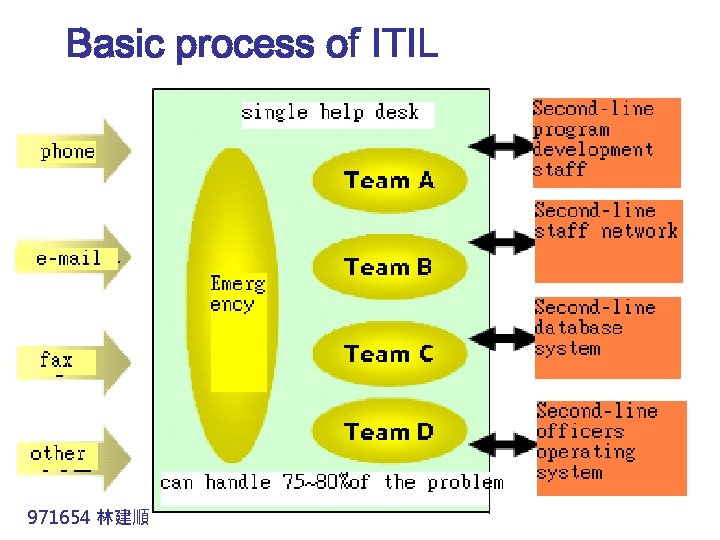 Basic process of ITIL 971654 林建順
Basic process of ITIL 971654 林建順
 ITIL For IT Governance n n n Establishment of a central information room To solve the problem with the professional division of labor Innovation to create competitive 971654 林建順 http: //www. kpmg. com. tw/ATTACH/News/234_9609. pdf
ITIL For IT Governance n n n Establishment of a central information room To solve the problem with the professional division of labor Innovation to create competitive 971654 林建順 http: //www. kpmg. com. tw/ATTACH/News/234_9609. pdf
 ITIL for corporation n n Hospital Bank Enterprise Business 971654 林建順 http: //www. kpmg. com. tw/ATTACH/News/234_9609. pdf
ITIL for corporation n n Hospital Bank Enterprise Business 971654 林建順 http: //www. kpmg. com. tw/ATTACH/News/234_9609. pdf
 Conclusion n n The role of IT departments in the company, from technical support, and then converted into information service provider. The practical experience of the industry worldwide has been the validation of large companies. 971654 林建順 http: //www. kpmg. com. tw/ATTACH/News/234_9609. pdf
Conclusion n n The role of IT departments in the company, from technical support, and then converted into information service provider. The practical experience of the industry worldwide has been the validation of large companies. 971654 林建順 http: //www. kpmg. com. tw/ATTACH/News/234_9609. pdf
 Q&A Thanks 971654 林建順
Q&A Thanks 971654 林建順


