20cdd84fafcd117291562f3294f2758d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10

Knowledge Discovery from Data. Bases (KDD) A. K. A. Data Mining & by other names as well Carlo Zaniolo UCLA CS Dept 1

What is Data Mining? z Data mining y. Extraction of interesting (non-trivial, implicit, previously unknown & potentially useful) patterns or knowledge from huge amount of data. z Alternative names y. Knowledge discovery (mining) in databases (KDD), knowledge extraction, data/pattern analysis, data archeology, data dredging, information harvesting, business intelligence, . . . 2

Why Data Mining? z Explosive growth of data available—the Big-Data Revolution x. Business: Web, e-commerce, transactions, stocks, … x. Science: Remote sensing, bioinformatics, scientific simulation, … x. Society and everyone: news, digital cameras, . . . z We are drowning in data -- but starving for knowledge! y Knowledge is the key to improve your business and operations y Data Mining tools and techniques: automate knowledge discovery from large data sets 3

DM Applications E. g. : Marketing products to customers: 1. Find clusters of customers who share the same characteristics: interest, income level, spending habits, etc. , 2. Determine customer purchasing patterns over time 3. Cross-market analysis—Find associations/corelations between product sales (and predict on that basis) 4. Profiling—What types of customers buy what products. 4

DM Applications: Fraud Detection and Security z Approaches: Clustering & outlier detection, looking for unusual patterns. z Applications: Health care, retail, credit card service, telecomm. y Auto insurance: ring of collisions y Money laundering: suspicious monetary transactions y Medical insurance x. Professional patients, ring of doctors, and ring of references x. Unnecessary or correlated screening tests y Telecommunications: phone-call fraud x. Phone call model: destination of the call, duration, time of day or week. Analyze patterns that deviate from an expected norm y Anti-terrorism 5

New Applications z Software Bug Mining z Graph Mining: e. g. finding social networks z Web Mining z Personalization and reccomendations z Mining and Scientific Applications—Biology z Spatio-Temporal and GIS: y. Find geographical clusters. y. Mine for trajectories and travel plans. z Multi Relational Data Mining y. Mining for knowledge and relationship from multiple tables, as in y. Inductive Logic Programming. 6

New Research Topics z Theoretical foundations z Statistical Data Mining z Visual Data Mining z Privacy-Preserving Data Mining 7

A Historical Perspective 1. Machine Learning (AI) 2. Decision Support Environments: Scalability, Integration, Warehousing, OLAP (DB) 3. Statistical foundation and synergism with other disciplines—e. g. , visualization. 4. Mining Streams of sensor & web data 8

Work plan z Introduction Core Techniques: 1. Classification, 2. Association, and 3. Clustering z Process and Systems z New Applications and Research Directions 9
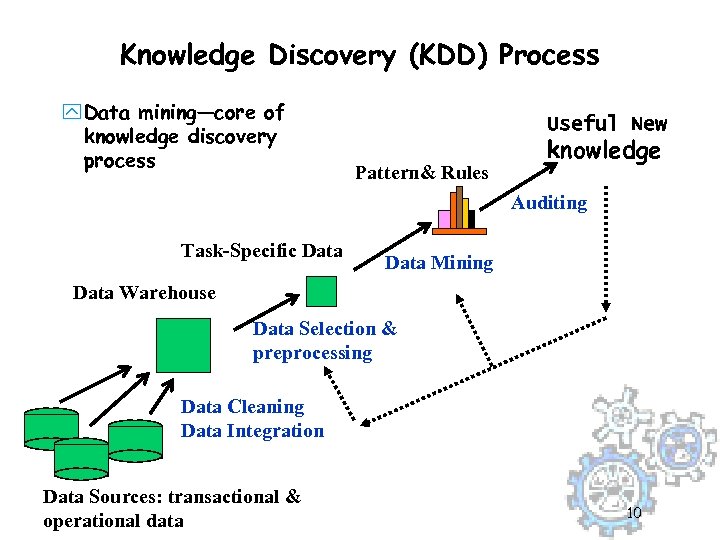
Knowledge Discovery (KDD) Process y Data mining—core of knowledge discovery process Useful New Pattern& Rules knowledge Auditing Task-Specific Data Mining Data Warehouse Data Selection & preprocessing Data Cleaning Data Integration Data Sources: transactional & operational data 10
20cdd84fafcd117291562f3294f2758d.ppt