24bd9a0f6dab1ce67691547e74f04fee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Knowledge Creation Tools for DAML Grit Denker, Jerry R. Hobbs, David Martin Srini Narayanan, Richard Waldinger SRI International
Knowledge Creation Tools for DAML Grit Denker, Jerry R. Hobbs, David Martin Srini Narayanan, Richard Waldinger SRI International
 Outline q DAML-S q Process A Service Markup Language. Models for Web-services Ø Core theories and markup for transactions, processes, time, interactions Ø Execution Semantics, monitoring, and simulation-- DEMO q Other Work-in-progress Ø Theories & inference for the Semantic Web Ø Models of Security and Trust Ø Resource Site Construction Tool m DAML+OIL plugin to Protégé – DEMO Ø Frame. Net in DAML
Outline q DAML-S q Process A Service Markup Language. Models for Web-services Ø Core theories and markup for transactions, processes, time, interactions Ø Execution Semantics, monitoring, and simulation-- DEMO q Other Work-in-progress Ø Theories & inference for the Semantic Web Ø Models of Security and Trust Ø Resource Site Construction Tool m DAML+OIL plugin to Protégé – DEMO Ø Frame. Net in DAML
 DAML-S: Goals q Full automation of service use Ø DAML markups provide enough info for an agent to find, select, enact and use a service never before encountered q Service queries requests handled seamlessly with information Ø Allow for composition of both Ø Many components & tools can work for both m Search q Support & selection, ontology translation, … inference in selecting and using services Joint work with Stanford-KSL, CMU, BBN, Nokia
DAML-S: Goals q Full automation of service use Ø DAML markups provide enough info for an agent to find, select, enact and use a service never before encountered q Service queries requests handled seamlessly with information Ø Allow for composition of both Ø Many components & tools can work for both m Search q Support & selection, ontology translation, … inference in selecting and using services Joint work with Stanford-KSL, CMU, BBN, Nokia
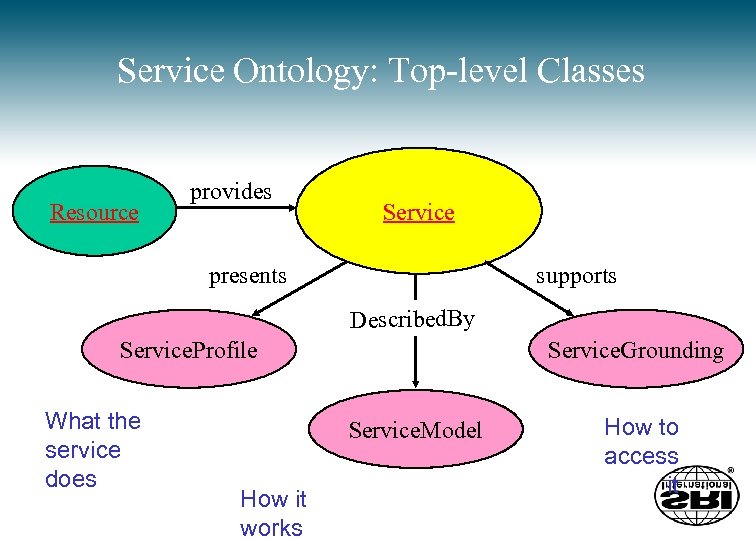 Service Ontology: Top-level Classes Resource provides Service presents supports Described. By Service. Profile What the service does Service. Grounding Service. Model How it works How to access it
Service Ontology: Top-level Classes Resource provides Service presents supports Described. By Service. Profile What the service does Service. Grounding Service. Model How it works How to access it
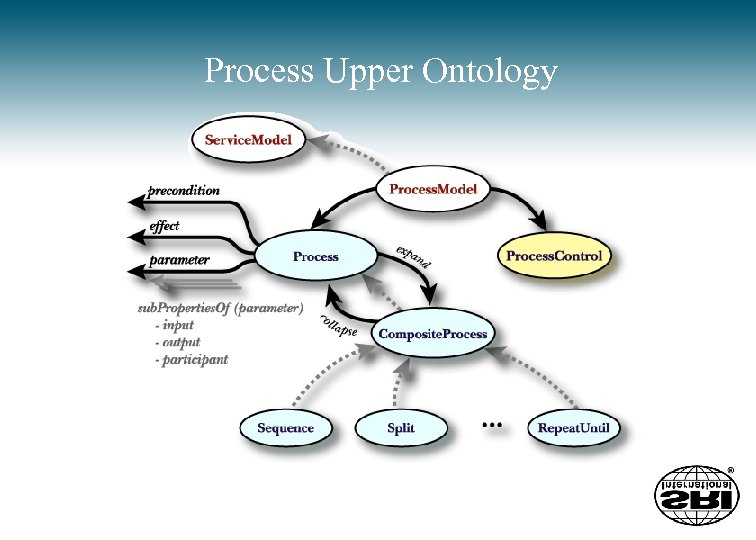 Process Upper Ontology
Process Upper Ontology
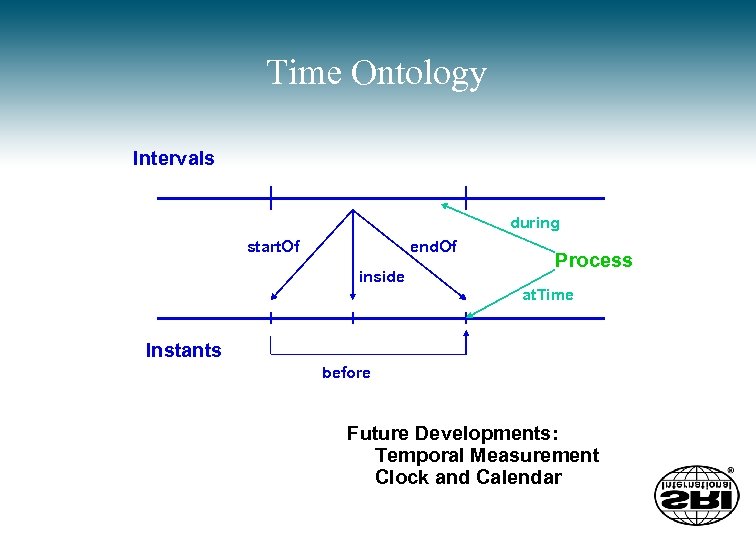 Time Ontology Intervals during start. Of end. Of inside Process at. Time Instants before Future Developments: Temporal Measurement Clock and Calendar
Time Ontology Intervals during start. Of end. Of inside Process at. Time Instants before Future Developments: Temporal Measurement Clock and Calendar
 (Simple) Process “What does it do? ” q Requirements for use; results of use Ø “Black box” view: Information needed to execute an atomic service Ø Inputs, outputs, preconditions, effects, … Ø “Binding rules” for inputs, outputs Ø “Roles” involved q May vary for different service classes q Can employ logical rules, conditional I/0, effects. q Atomic Transaction
(Simple) Process “What does it do? ” q Requirements for use; results of use Ø “Black box” view: Information needed to execute an atomic service Ø Inputs, outputs, preconditions, effects, … Ø “Binding rules” for inputs, outputs Ø “Roles” involved q May vary for different service classes q Can employ logical rules, conditional I/0, effects. q Atomic Transaction
 Service Model “How does it work? ” q Semantic description of a service Ø“Glass box” view ØDetailed characterization of what it does q May vary for different service classes q Analogous to procedure body (but abstract)
Service Model “How does it work? ” q Semantic description of a service Ø“Glass box” view ØDetailed characterization of what it does q May vary for different service classes q Analogous to procedure body (but abstract)
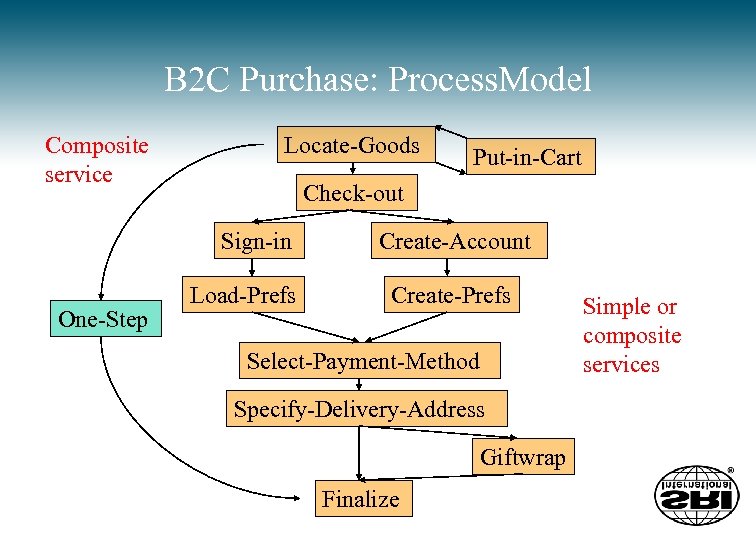 B 2 C Purchase: Process. Model Composite service Locate-Goods Check-out Sign-in One-Step Put-in-Cart Load-Prefs Create-Account Create-Prefs Select-Payment-Method Specify-Delivery-Address Giftwrap Finalize Simple or composite services
B 2 C Purchase: Process. Model Composite service Locate-Goods Check-out Sign-in One-Step Put-in-Cart Load-Prefs Create-Account Create-Prefs Select-Payment-Method Specify-Delivery-Address Giftwrap Finalize Simple or composite services
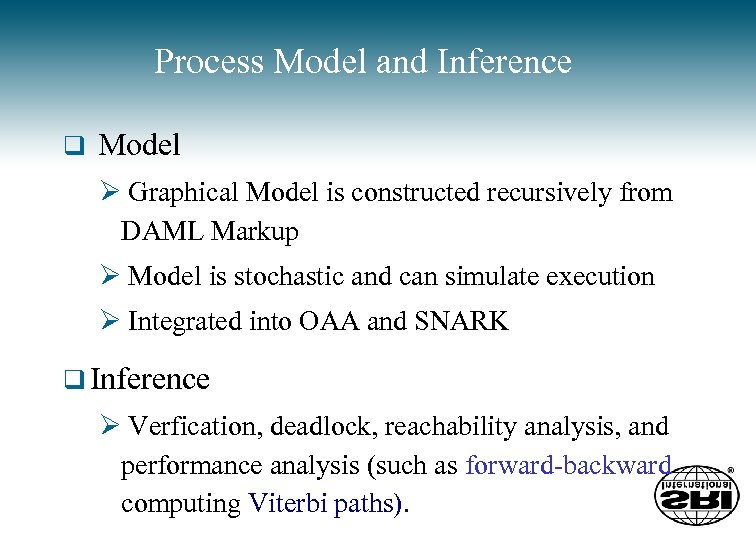 Process Model and Inference q Model Ø Graphical Model is constructed recursively from DAML Markup Ø Model is stochastic and can simulate execution Ø Integrated into OAA and SNARK q Inference Ø Verfication, deadlock, reachability analysis, and performance analysis (such as forward-backward computing Viterbi paths).
Process Model and Inference q Model Ø Graphical Model is constructed recursively from DAML Markup Ø Model is stochastic and can simulate execution Ø Integrated into OAA and SNARK q Inference Ø Verfication, deadlock, reachability analysis, and performance analysis (such as forward-backward computing Viterbi paths).
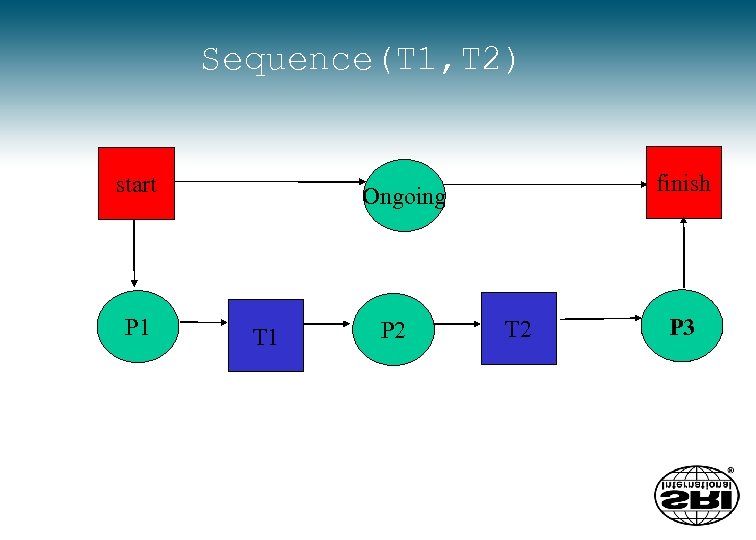 Sequence(T 1, T 2) start P 1 finish Ongoing T 1 P 2 T 2 P 3
Sequence(T 1, T 2) start P 1 finish Ongoing T 1 P 2 T 2 P 3
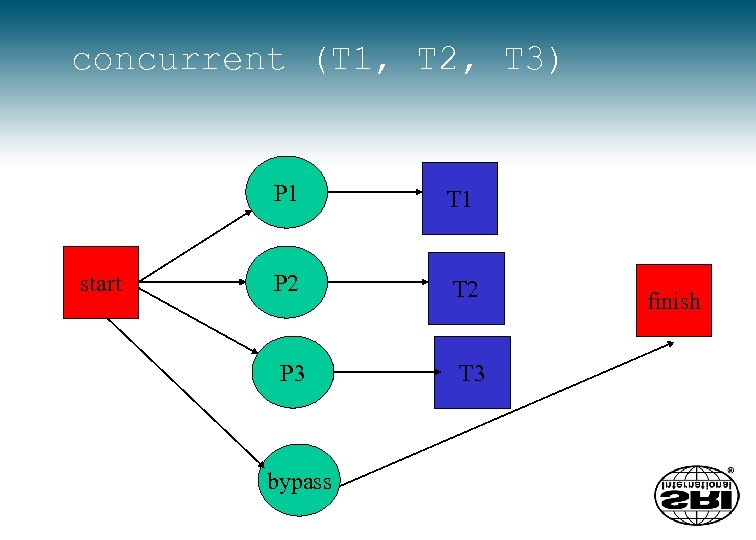 concurrent (T 1, T 2, T 3) P 1 start T 1 P 2 T 2 P 3 T 3 bypass finish
concurrent (T 1, T 2, T 3) P 1 start T 1 P 2 T 2 P 3 T 3 bypass finish
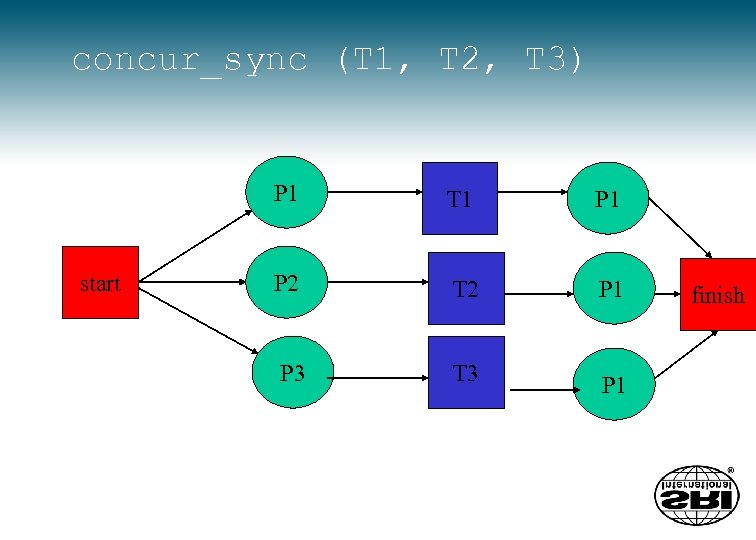 concur_sync (T 1, T 2, T 3) P 1 start T 1 P 2 T 2 P 1 P 3 T 3 P 1 finish
concur_sync (T 1, T 2, T 3) P 1 start T 1 P 2 T 2 P 1 P 3 T 3 P 1 finish
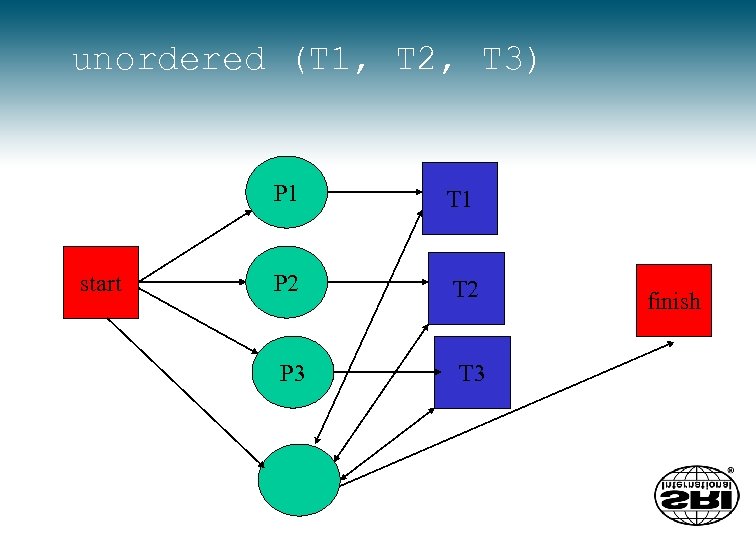 unordered (T 1, T 2, T 3) P 1 start T 1 P 2 T 2 P 3 T 3 finish
unordered (T 1, T 2, T 3) P 1 start T 1 P 2 T 2 P 3 T 3 finish
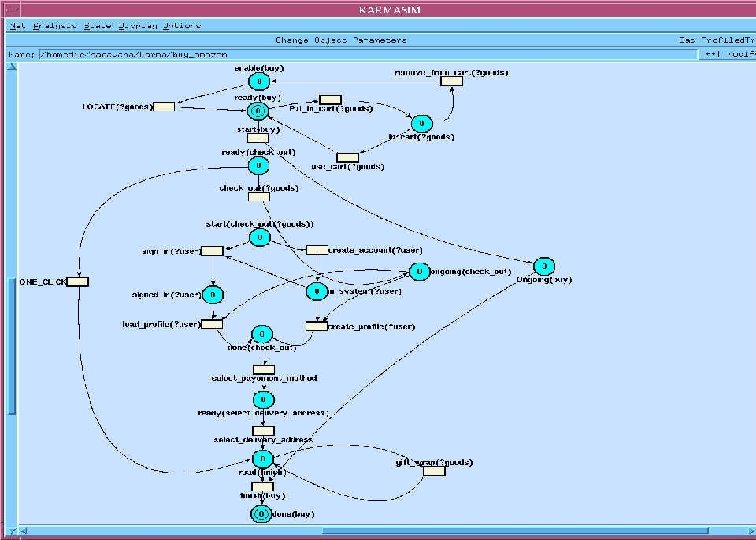
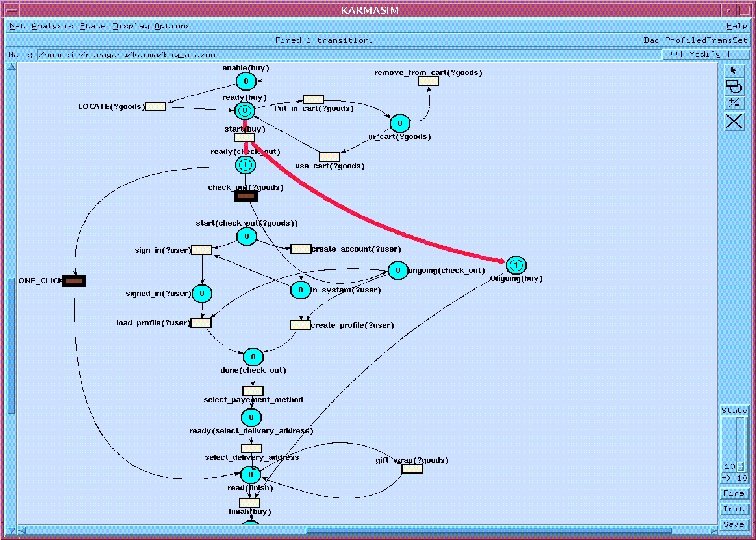
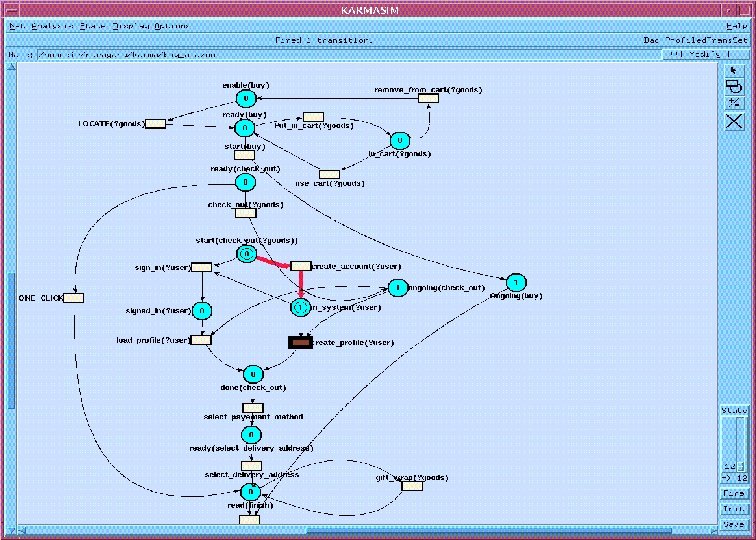
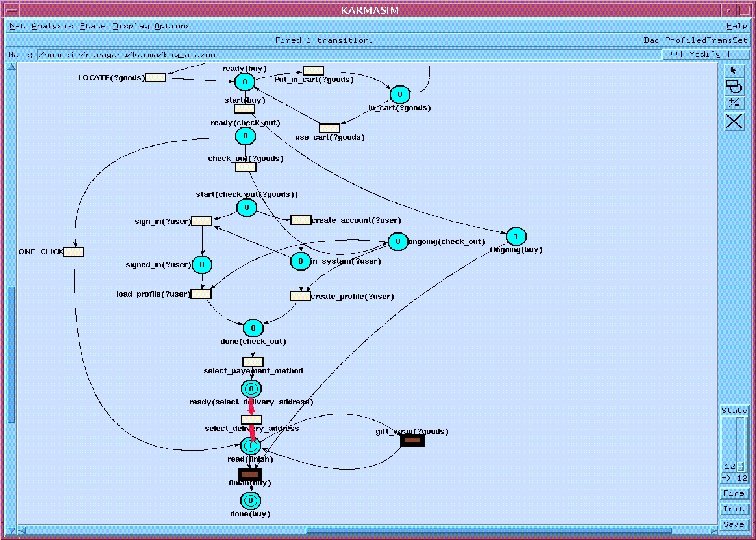
 Execution Semantics q Model is a high level Stochastic Petri Net and has a well specified execution semantics. q Being extended to the more expressive Rewriting Logic (joint with Jose Meseguer) Ø Rewriting Logic is a logic of distributed systems. Ø There is a widely used rewriting logic tool, Maude. More at http: //maude. csl. sri. com
Execution Semantics q Model is a high level Stochastic Petri Net and has a well specified execution semantics. q Being extended to the more expressive Rewriting Logic (joint with Jose Meseguer) Ø Rewriting Logic is a logic of distributed systems. Ø There is a widely used rewriting logic tool, Maude. More at http: //maude. csl. sri. com
 Status q Process Tool ready for release , pending stable DAML-S. q DAML-S 0. 5 at http: //www. daml. org/services/ ØJoint work with Stanford KSL, CMU, BBN, Yale, Nokia q SRI’s DAML work is described at http: //www. ai. sri. com/daml
Status q Process Tool ready for release , pending stable DAML-S. q DAML-S 0. 5 at http: //www. daml. org/services/ ØJoint work with Stanford KSL, CMU, BBN, Yale, Nokia q SRI’s DAML work is described at http: //www. ai. sri. com/daml
 What’s Hot q DAML-S is a serious attempt to use DAML+OIL. q Process Modeling Tool for DAML-S descriptions Ø Execution Semantics Ø Resources, Ø Execution monitoring Ø Simulation Ø Inference
What’s Hot q DAML-S is a serious attempt to use DAML+OIL. q Process Modeling Tool for DAML-S descriptions Ø Execution Semantics Ø Resources, Ø Execution monitoring Ø Simulation Ø Inference
 What’s hard q DAML-S expressivity/naturalness issues Ø How to define scripts Ø How to define unification constraints, etc. . Ø Services are like verbs, ontologies are more natural to represent nouns. q Achieving and maintaining consensus q Coordinating with industry standards Ø With existing industry proposals m ex. XLANG
What’s hard q DAML-S expressivity/naturalness issues Ø How to define scripts Ø How to define unification constraints, etc. . Ø Services are like verbs, ontologies are more natural to represent nouns. q Achieving and maintaining consensus q Coordinating with industry standards Ø With existing industry proposals m ex. XLANG


