4aa08156e7df27cf24132b4494b267bc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

Knowledge Assets: Can you measure the intangible? Mary Adams Trek Consulting LLC KM Forum, July 20, 2006

Measuring Knowledge Assets • • Why? What? How? Case studies
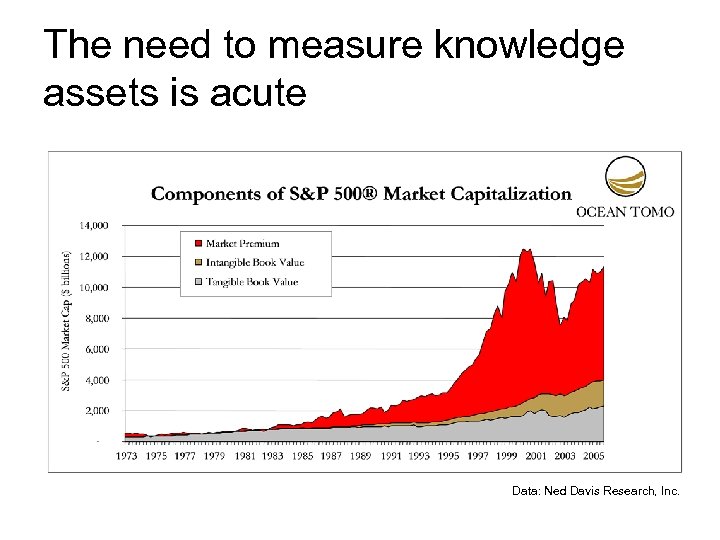
The need to measure knowledge assets is acute Data: Ned Davis Research, Inc.
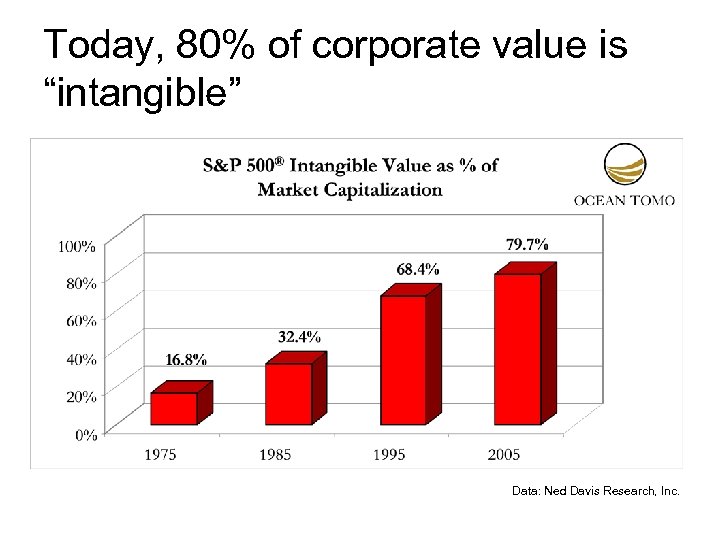
Today, 80% of corporate value is “intangible” Data: Ned Davis Research, Inc.

Our information paradigms are based on an antiquated system

Accounting systems provide several distinct advantages: • • Objective standards Quantitative measures Consistent methodology Consolidated presentation

Pacioli helped us measure value creation based on tangible capital

Today, the value creation process is driven by intellectual capital

Human capital is the creative engine

Relationship capital connects you with the market

Structural capital is the holy grail

Structural capital is an “infinite” resource

The value of structural capital is limited only by its market potential

The last, critical element is the business recipe
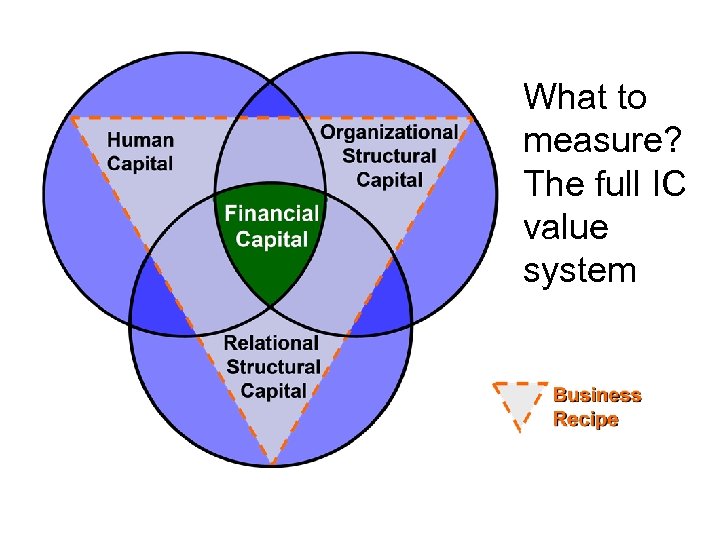
What to measure? The full IC value system

How to measure? Pacioli would advise us to start with an inventory Pacioli’s “Summa” as seen in http: //www. martini-drapelli. it/lucapacioli 1. htm

Today there are three available approaches: • Valuations • Scorecards • Assessments

Valuations
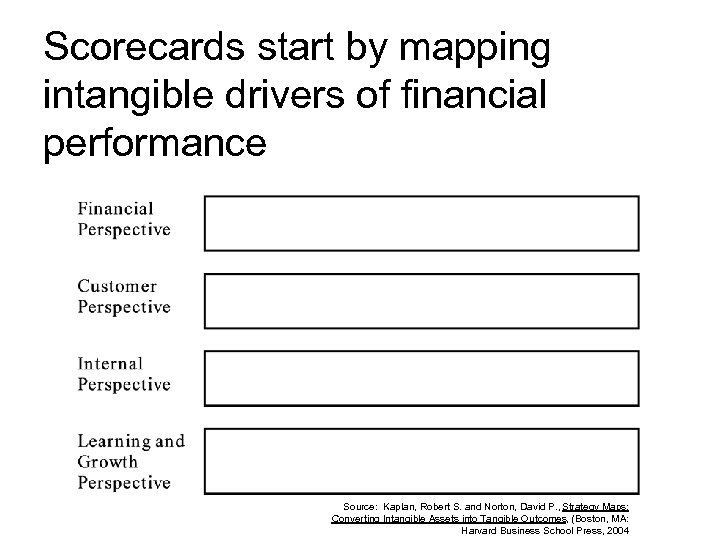
Scorecards start by mapping intangible drivers of financial performance Source: Kaplan, Robert S. and Norton, David P. , Strategy Maps: Converting Intangible Assets into Tangible Outcomes, (Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press, 2004
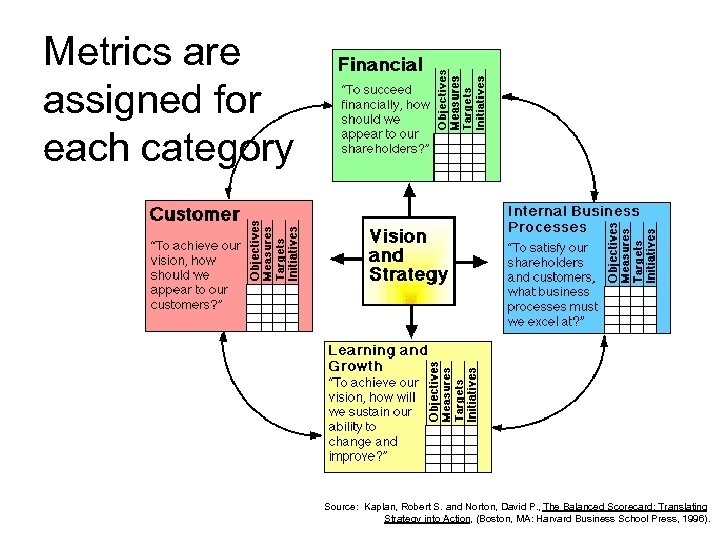
Metrics are assigned for each category Source: Kaplan, Robert S. and Norton, David P. , The Balanced Scorecard: Translating Strategy into Action, (Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press, 1996).
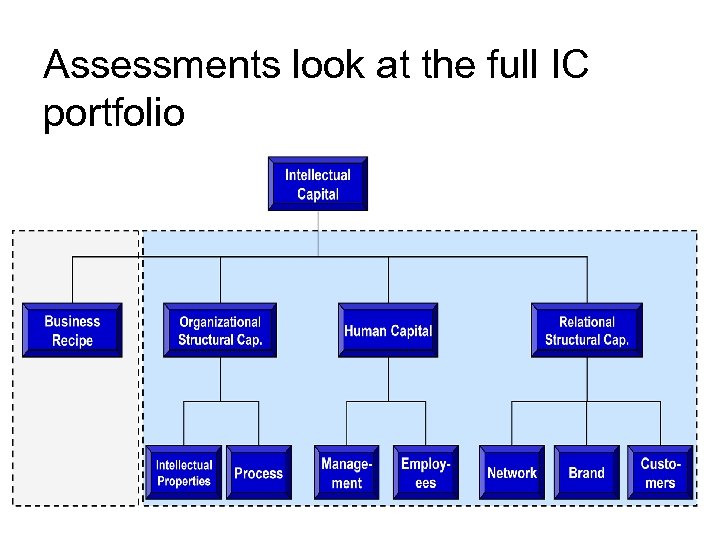
Assessments look at the full IC portfolio
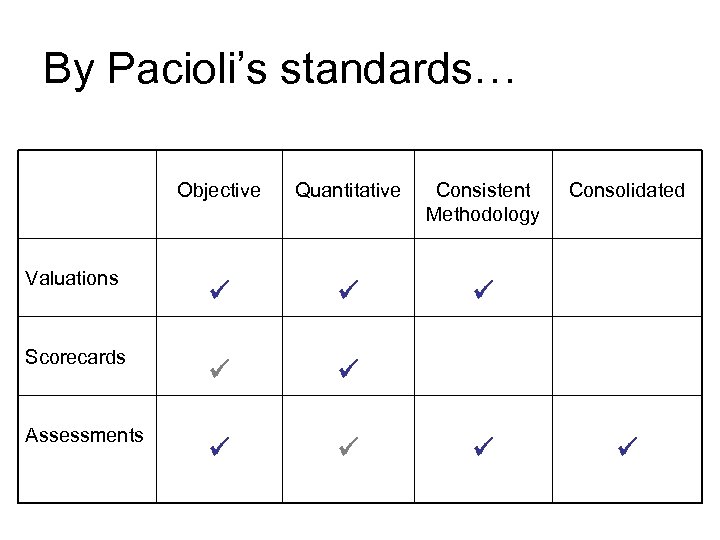
By Pacioli’s standards… Objective Valuations Scorecards Assessments Quantitative Consistent Methodology Consolidated

Quantitative measures are only part of the picture

Case Study: IC Rating™ Events business
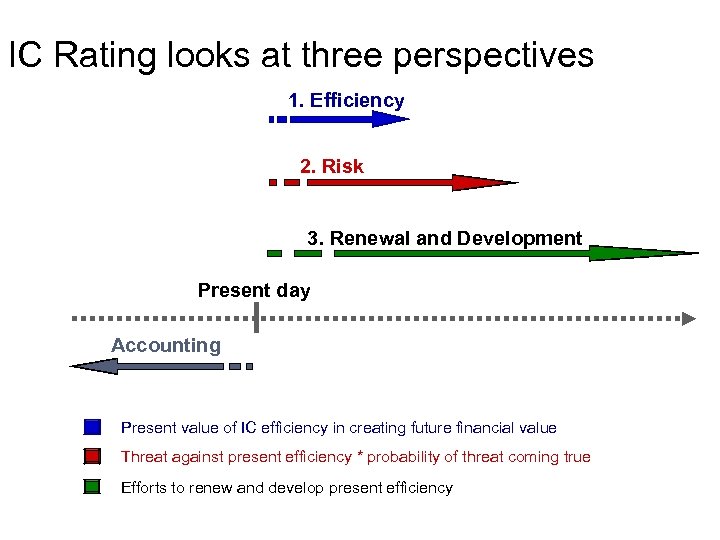
IC Rating looks at three perspectives 1. Efficiency 2. Risk 3. Renewal and Development Present day Accounting Present value of IC efficiency in creating future financial value Threat against present efficiency * probability of threat coming true Efforts to renew and develop present efficiency

Methodology • Interviews with internal (1/3) and external (2/3) stakeholders • Questions include: – Closed questions that lead to a letter rating – Open questions that yield answers that are summarized anonymously in final report
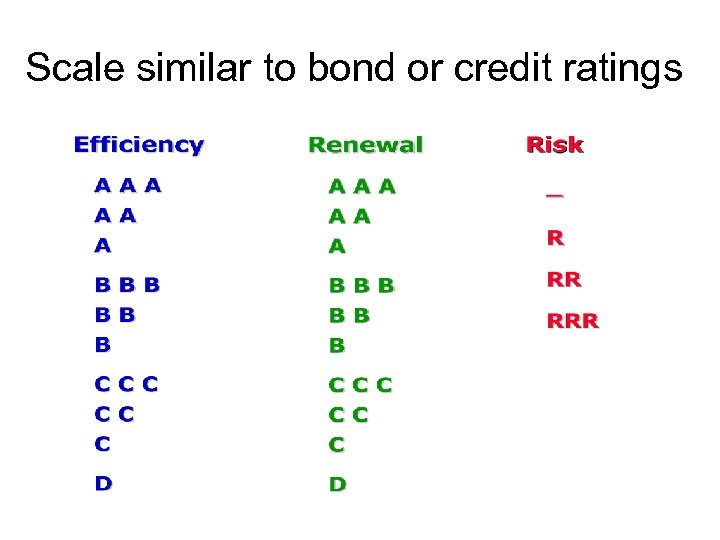
Scale similar to bond or credit ratings
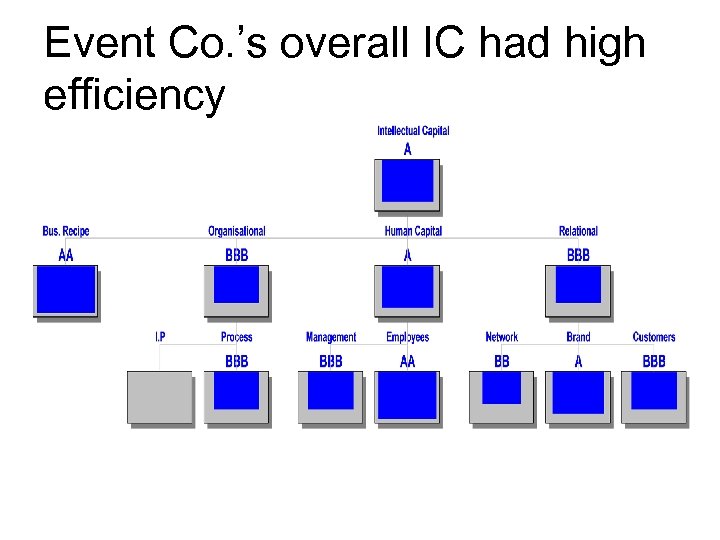
Event Co. ’s overall IC had high efficiency
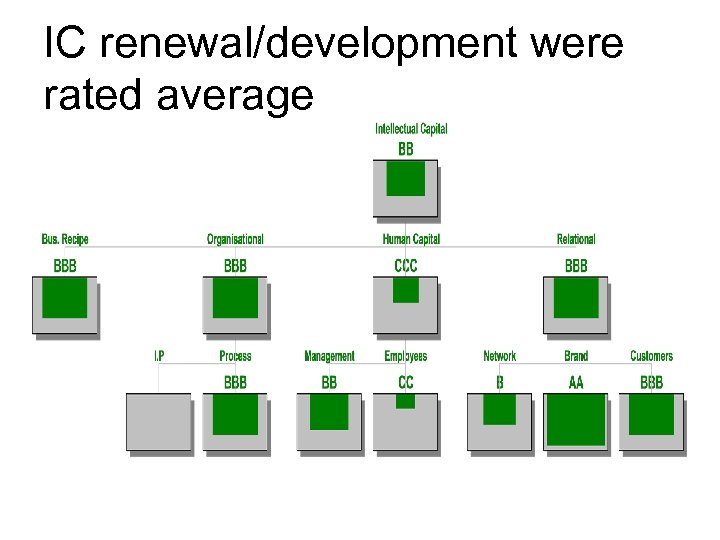
IC renewal/development were rated average
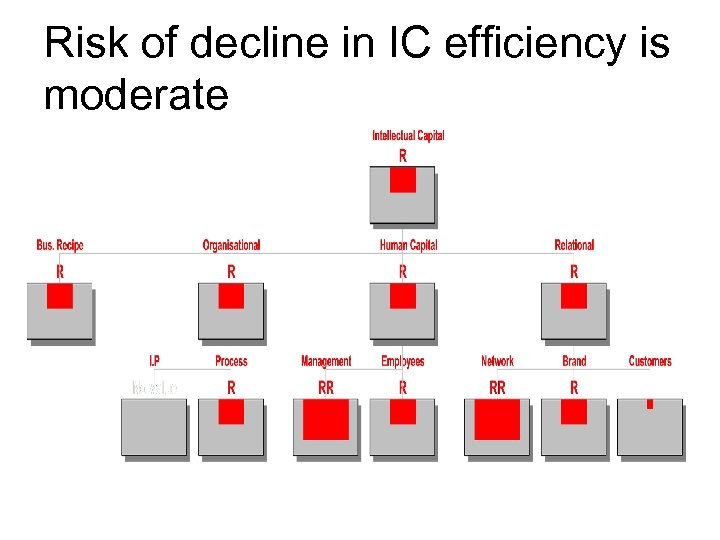
Risk of decline in IC efficiency is moderate
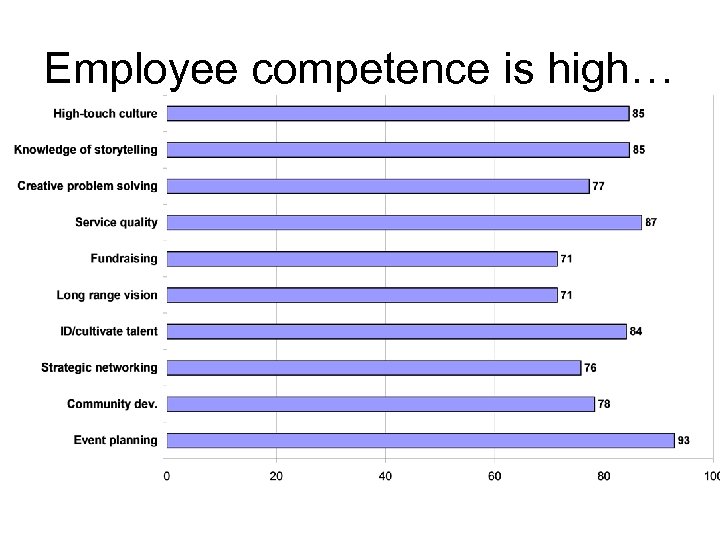
Employee competence is high…
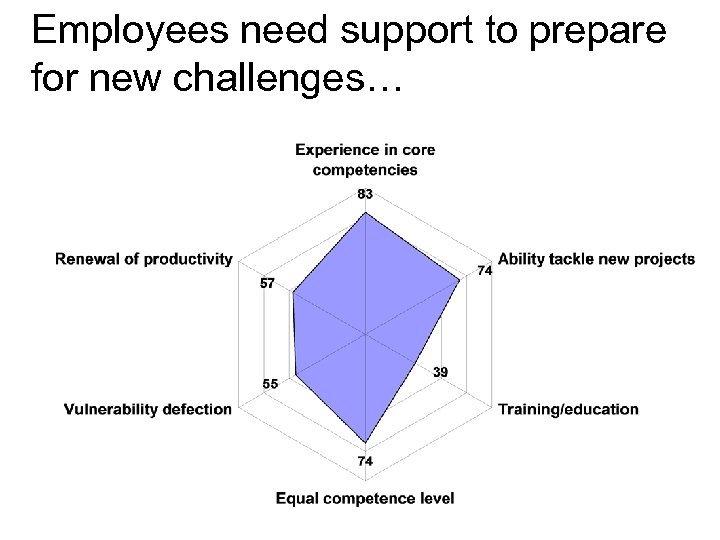
Employees need support to prepare for new challenges…
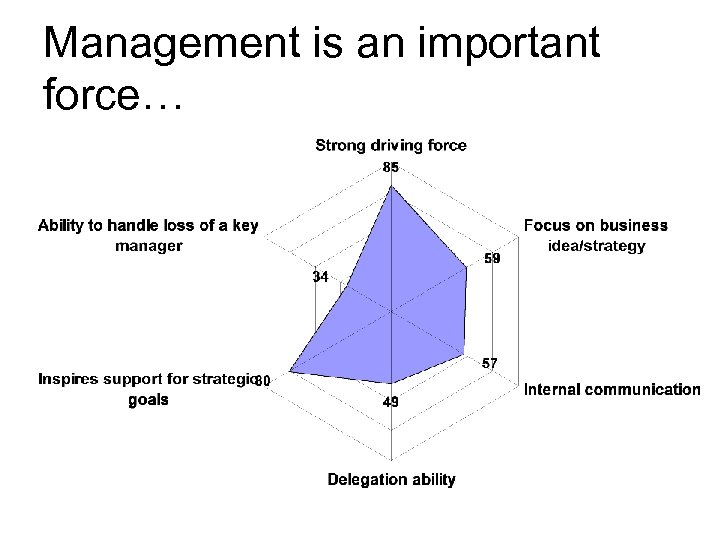
Management is an important force…

Comments from Stakeholders • The sky is the limit in this market. • We could be dead in the water if something happens to our founders. • S. has an intuitive sense for picking talent. • The brand is still not known in the media. • Big issue is the ageing of both the our performers and our audience. • The pricing strategy is brilliant…set in relation to comparable training opportunities. • As long as they are in the business of selling hours they will be susceptible to problems. The biggest opportunity is in information products.

Issues on the table at Event Co. • How to connect with the huge market opportunity • How to profit from latent IP • New business/old business balance • Management succession plan

IC Rating™ Case Studies
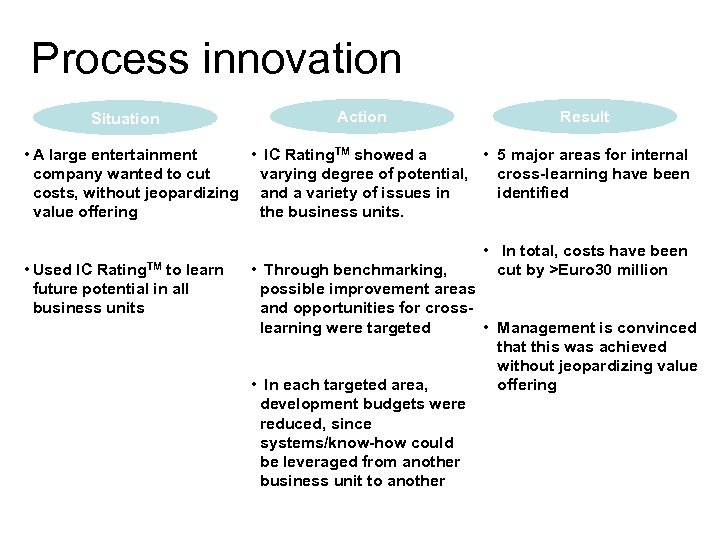
Process innovation Situation Action Result • A large entertainment • IC Rating. TM showed a • 5 major areas for internal company wanted to cut varying degree of potential, cross-learning have been costs, without jeopardizing and a variety of issues in identified value offering the business units. • Used IC Rating. TM to learn future potential in all business units • In total, costs have been cut by >Euro 30 million • Through benchmarking, possible improvement areas and opportunities for crosslearning were targeted • Management is convinced that this was achieved without jeopardizing value • In each targeted area, offering development budgets were reduced, since systems/know-how could be leveraged from another business unit to another

Competitiveness Situation Action • A company was facing new • IC Rating™ displayed competition and felt the severe problems in the need to improve its image corporate culture and the and service levels. management’s internal practices. • The company used IC Rating™ to identify areas of potential improvement in order to become successful in a competitive environment. • On the other hand, the management was rated as strong. The company network and brand also received strong ratings. • With this result at hand the executive team identified and pursued a number of initiatives. Result • By strengthening the internal leadership with new management and training, the employee pride for the organization was enhanced and service improved – in the end increasing productivity by almost 20%.

Strategic Fit Company Profile - Wholesale subsidiary of a large food and low-temperature warehouse and logistics company - Market suffering from low margins and severe competition Situation • Used IC Rating. TM to identify current strengths and weakness as well as its future potential • Wanted to use the results of IC Rating. TM to support merger talks with another large food wholesaler. Action Result • IC Rating. TM showed strength in the sales force and merchandizing abilities, backed by the strong leadership of CEO • The sales organization was changed to solution-based, from the old style ”geographic-based” sales units • Weakness was identified in the process area. Since potential merger partner was famous for its state-of-the-art systems, the rating strengthened the perception of potential synergies. • Also introduced Skandia’s Navigator (and Dolphin system) to become more focused on the vision and strategies • Helped get the merger deal done at favorable terms
Market Valuation Situation Action Result • The number three IT • IC Rating™ divided the IT- • The Group’s overall goal of company on the OM 10% margins was Group into four different Stockholm Stock Exchange categories for potential. individually revised aimed to help the market depending on the potential better understand its shown in IC Rating™. potential as a knowledge • By supplementing this based company. information to the annual report they increased • The day when the result of transparancy: both strong the rating was first shown, • All 35 subsidiary companies and weak sides were the share value of the IT exposed, increasing which comprise the Group company increased by 8%. understanding for potential were rated as well as increasing trust of the Group. • The Group used results to benchmark and navigate the companies into the future.
Buy-side support Situation Action • Major investment fund with • IC Rating. TM showed a very two similar companies in high potential (high rating), the portfolio, Company A in Company A. Company B and Company B had serious issues, particularly in the process capital area. • Only interested in continuing with one of them in a second round • The recommendation was clear: support Company A in second round. Divest • Used IC Rating. TM to Company B. evaluate future potential in both companies Result • The investment fund kept Company A • Company A financially outperformed industry averages after the second round • Company B, despite finding funding elsewhere, underperformed and eventually went bankrupt • The investment fund ROI exceeded 60%

Sell-side support Situation Action • A large communication • IC Rating. TM showed a company needed to sell off varying degree of potential five business units in the business units. • There was no interest from the market so the seller • Seller was very withdrew the companies transparent, presenting and did an IC Rating™ on potential buyers with the each full range of findings TM to identify including strengths and • Used IC Rating weaknesses, opportunities future potential in all five and risks business units Result • All five units were sold • In total, a 20% premium was on the P/E multiple was received, compared to similar deals at the same time • The buyer attributed the premium to the transparency, which reduced buy-side risk.

Measuring knowledge assets helps you find the path to future success

For more information Visit www. icrating. com Visit www. icknowledgecenter. com Contact Mary Adams 781 -729 -9650 adams@trekconsulting. com
4aa08156e7df27cf24132b4494b267bc.ppt