4b811b25077e94d016e089eb66f75065.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Knowledge and Quality of Life with Particular Reference to the Ageing Population George K Radda University Laboratory of Physiology and Cardiac Science University of Oxford UK
Knowledge and Quality of Life with Particular Reference to the Ageing Population George K Radda University Laboratory of Physiology and Cardiac Science University of Oxford UK
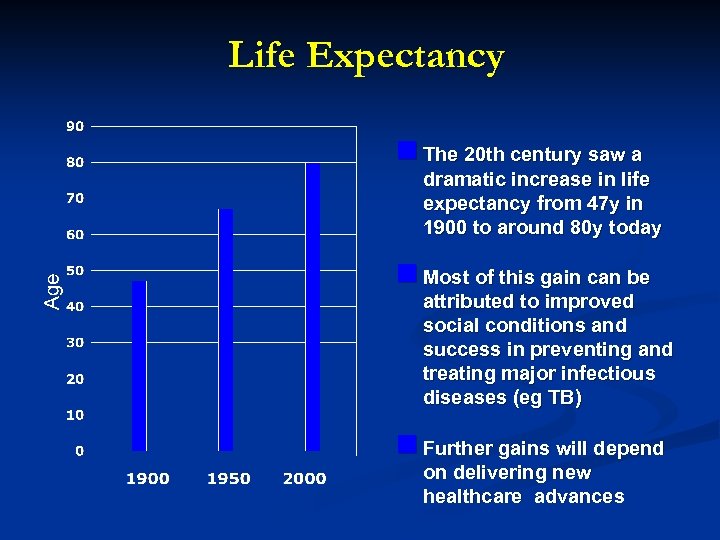 Life Expectancy n The 20 th century saw a dramatic increase in life expectancy from 47 y in 1900 to around 80 y today n Most of this gain can be attributed to improved social conditions and success in preventing and treating major infectious diseases (eg TB) n Further gains will depend on delivering new healthcare advances
Life Expectancy n The 20 th century saw a dramatic increase in life expectancy from 47 y in 1900 to around 80 y today n Most of this gain can be attributed to improved social conditions and success in preventing and treating major infectious diseases (eg TB) n Further gains will depend on delivering new healthcare advances
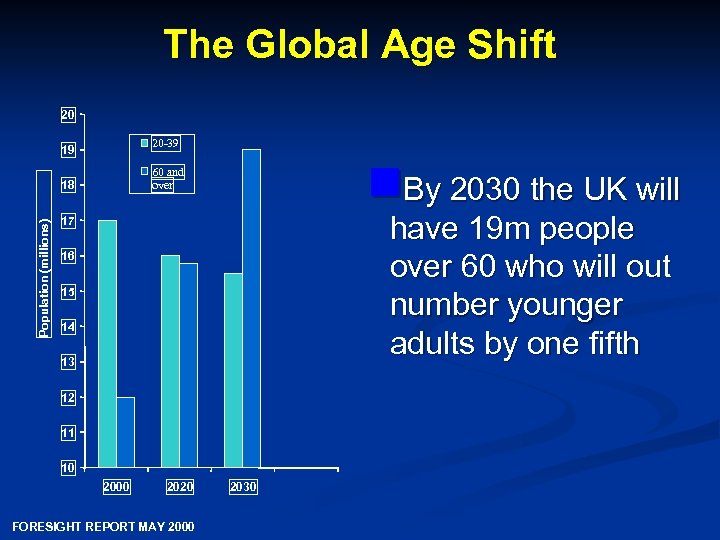 The Global Age Shift 20 20 -39 19 18 Population (millions) n. By 2030 the UK will 60 and over have 19 m people over 60 who will out number younger adults by one fifth 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 2000 2020 FORESIGHT REPORT MAY 2000 2030
The Global Age Shift 20 20 -39 19 18 Population (millions) n. By 2030 the UK will 60 and over have 19 m people over 60 who will out number younger adults by one fifth 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 2000 2020 FORESIGHT REPORT MAY 2000 2030
 Improve Quality of Life in Ageing Challenges • to promote healthy ageing • to improve the management of age-related illnesses • to encourage leading edge, multidisciplinary research that will inform these aims
Improve Quality of Life in Ageing Challenges • to promote healthy ageing • to improve the management of age-related illnesses • to encourage leading edge, multidisciplinary research that will inform these aims
 Genes, Brain and Ageing - Mouse to Man • What are the key genes in ageing? • How do they relate to ageing effects on brain and cognitive function? • Can we use the information from functional genomics to delay or reverse the effects of ageing? Babraham Institute - Laboratory of Cognitive & Developmental Neuroscience
Genes, Brain and Ageing - Mouse to Man • What are the key genes in ageing? • How do they relate to ageing effects on brain and cognitive function? • Can we use the information from functional genomics to delay or reverse the effects of ageing? Babraham Institute - Laboratory of Cognitive & Developmental Neuroscience
 Major Health Challenges n Ageing n Mental health n Infectious diseases n Obesity/Nutrition n Heart disease n Cancer
Major Health Challenges n Ageing n Mental health n Infectious diseases n Obesity/Nutrition n Heart disease n Cancer
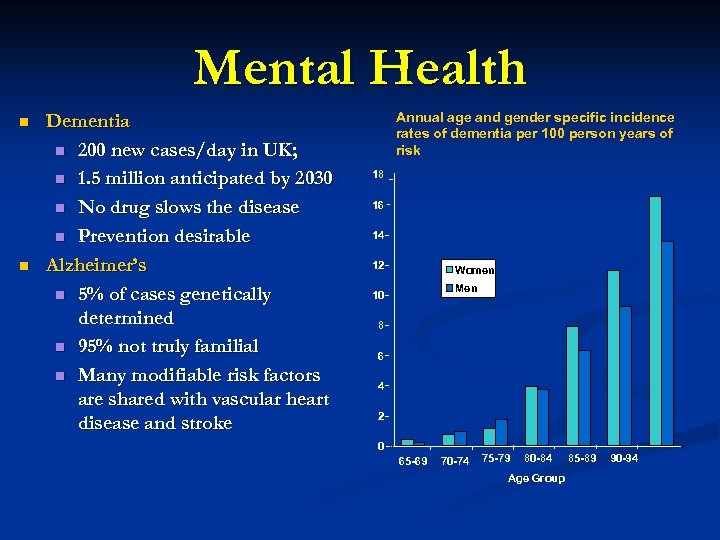 Mental Health n Dementia n 200 new cases/day in UK; n 1. 5 million anticipated by 2030 n No drug slows the disease n Prevention desirable Alzheimer’s n 5% of cases genetically determined n 95% not truly familial n Many modifiable risk factors are shared with vascular heart disease and stroke Annual age and gender specific incidence rates of dementia per 100 person years of risk 18 16 14 12 Incidence rate n Women Men 10 8 6 4 2 0 65 -69 70 -74 75 -79 80 -84 Age Group 85 -89 90 -94 95+
Mental Health n Dementia n 200 new cases/day in UK; n 1. 5 million anticipated by 2030 n No drug slows the disease n Prevention desirable Alzheimer’s n 5% of cases genetically determined n 95% not truly familial n Many modifiable risk factors are shared with vascular heart disease and stroke Annual age and gender specific incidence rates of dementia per 100 person years of risk 18 16 14 12 Incidence rate n Women Men 10 8 6 4 2 0 65 -69 70 -74 75 -79 80 -84 Age Group 85 -89 90 -94 95+
 Multidisciplinary Research and Neurodegenerative Disease • Mental ill health and neurodegenerative diseases cost the UK economy £ 6. 3 bn each year • Costs will increase still further as the population ages • Current treatments contain symptoms, but do not effect cure
Multidisciplinary Research and Neurodegenerative Disease • Mental ill health and neurodegenerative diseases cost the UK economy £ 6. 3 bn each year • Costs will increase still further as the population ages • Current treatments contain symptoms, but do not effect cure
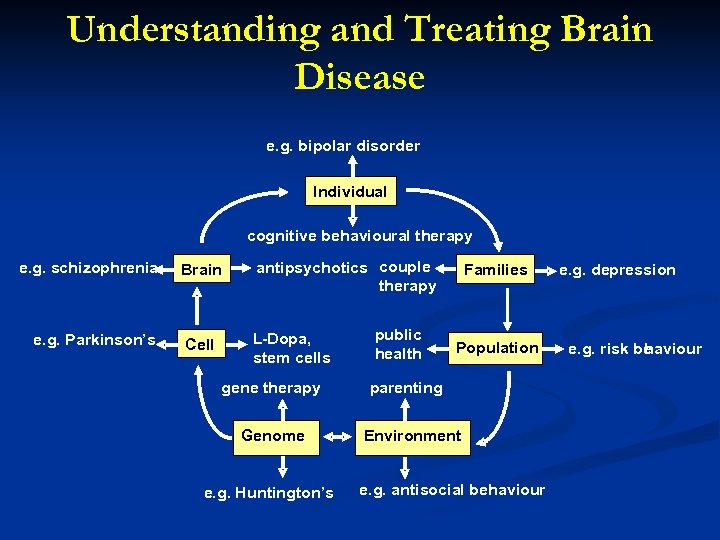 Understanding and Treating Brain Disease e. g. bipolar disorder Individual cognitive behavioural therapy e. g. schizophrenia e. g. Parkinson’s Brain antipsychotics couple therapy Cell L-Dopa, stem cells gene therapy Genome e. g. Huntington’s public health Families Population parenting Environment e. g. antisocial behaviour e. g. depression e. g. risk be aviour h
Understanding and Treating Brain Disease e. g. bipolar disorder Individual cognitive behavioural therapy e. g. schizophrenia e. g. Parkinson’s Brain antipsychotics couple therapy Cell L-Dopa, stem cells gene therapy Genome e. g. Huntington’s public health Families Population parenting Environment e. g. antisocial behaviour e. g. depression e. g. risk be aviour h
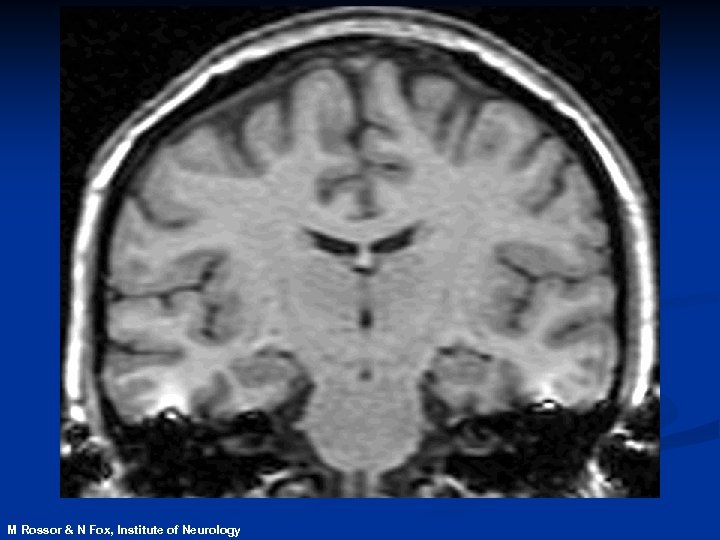
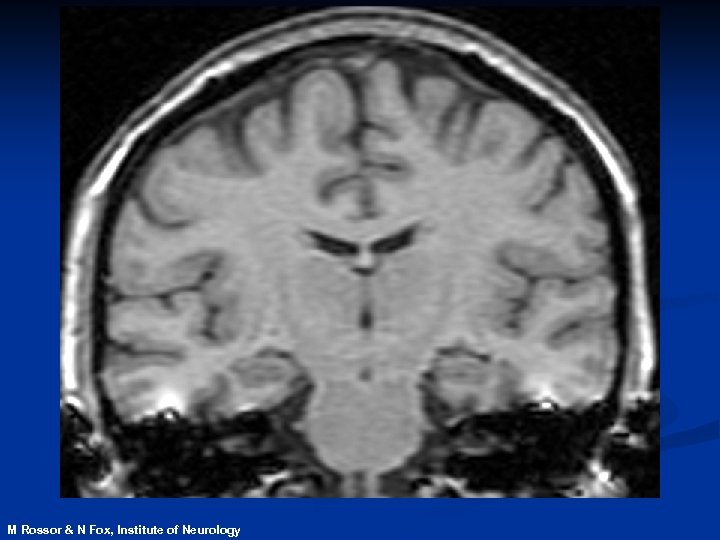
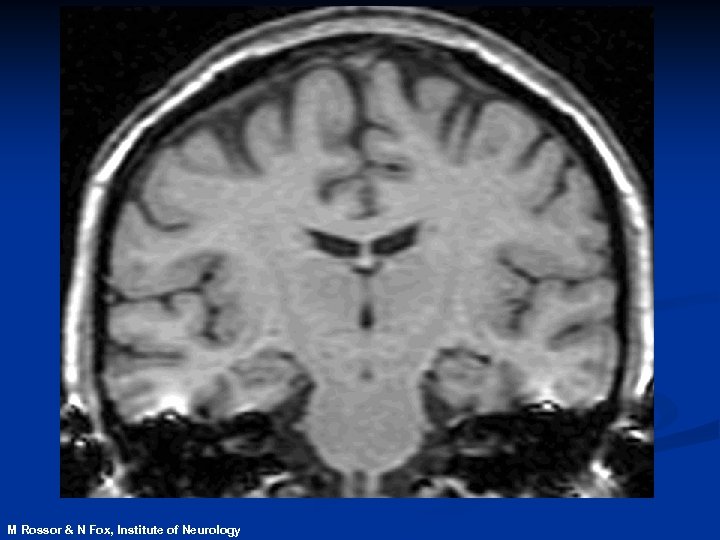
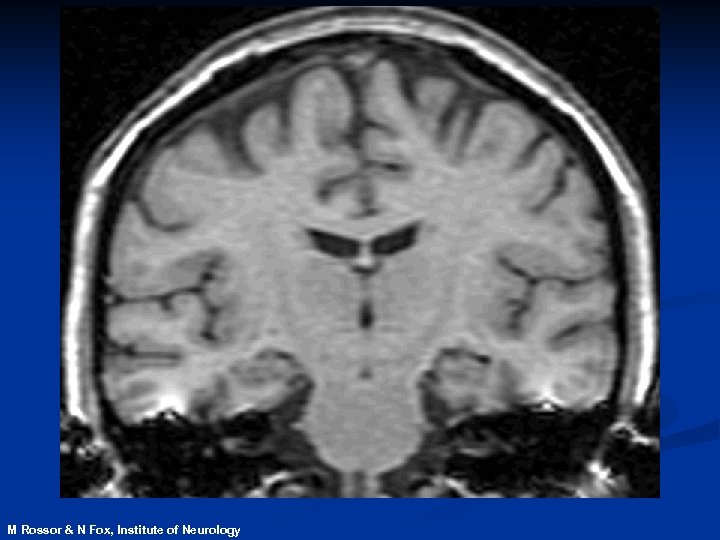
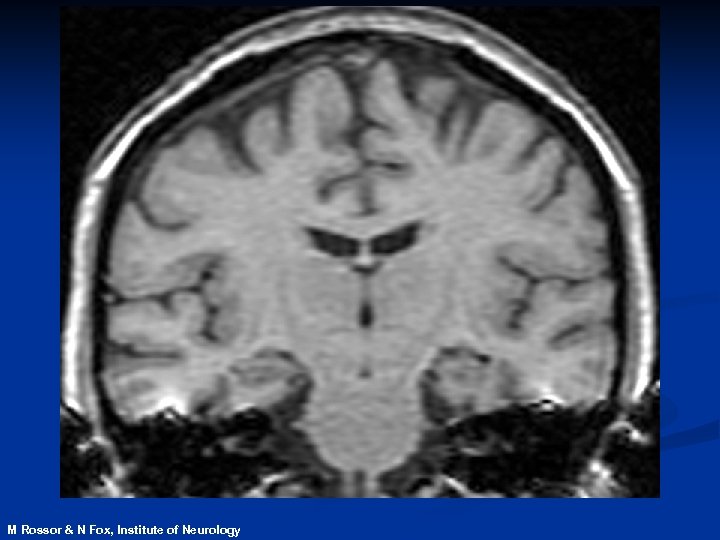
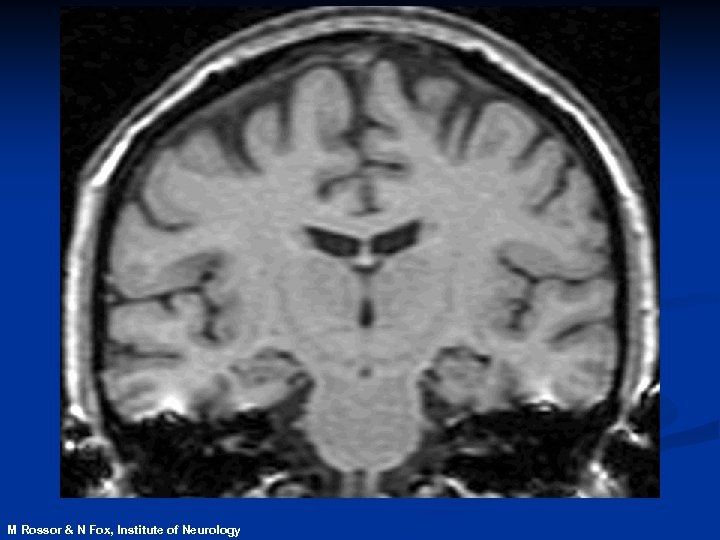
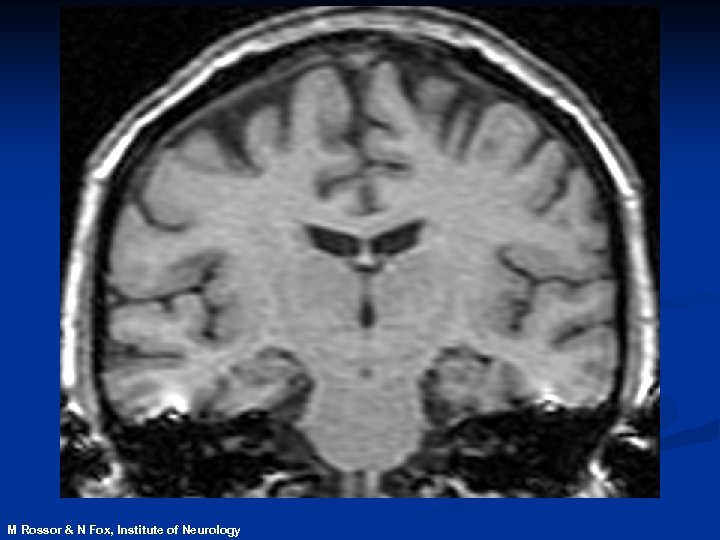
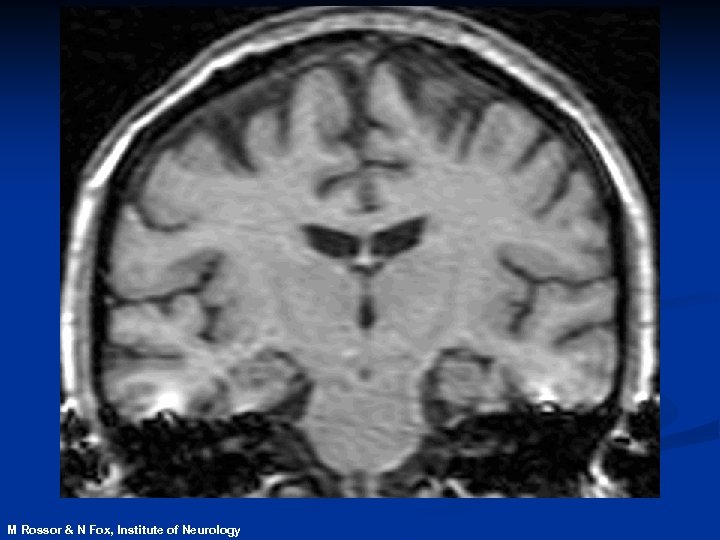
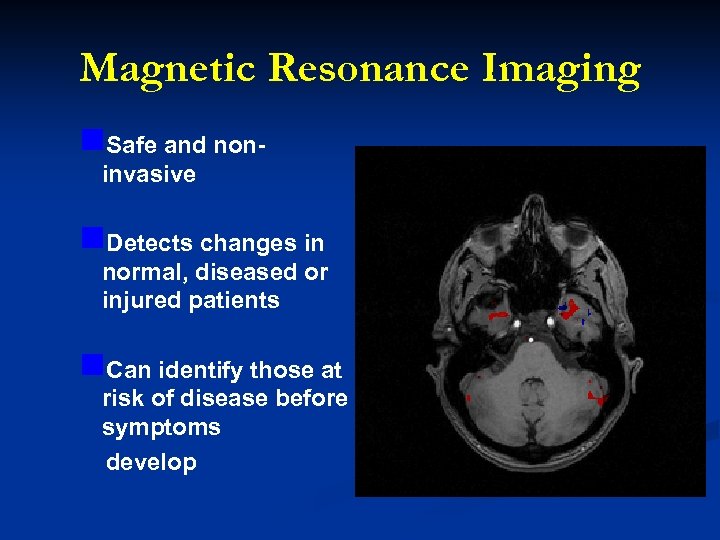 Magnetic Resonance Imaging n. Safe and noninvasive n. Detects changes in normal, diseased or injured patients n. Can identify those at risk of disease before symptoms develop
Magnetic Resonance Imaging n. Safe and noninvasive n. Detects changes in normal, diseased or injured patients n. Can identify those at risk of disease before symptoms develop
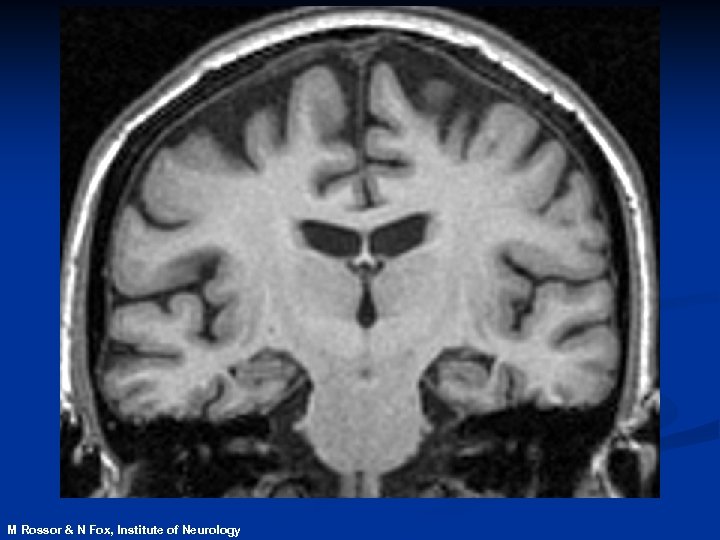
 M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
 M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
 M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
 M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
 M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
 M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
 M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
 M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
 M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
 M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
 M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology
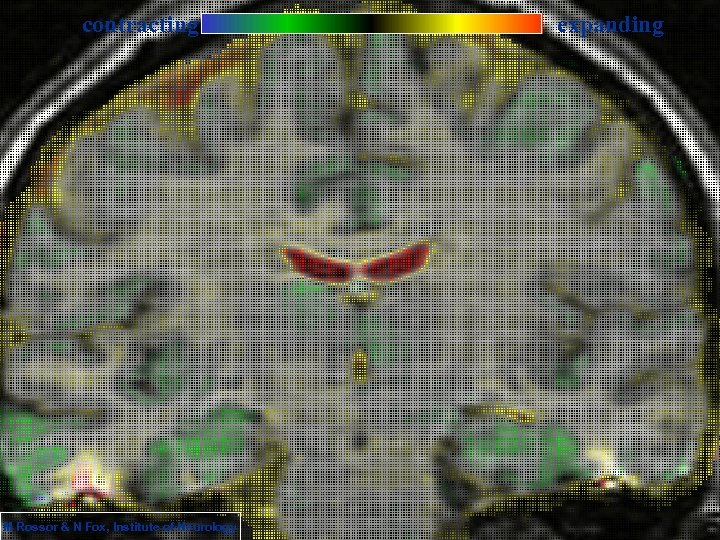 contracting M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology expanding
contracting M Rossor & N Fox, Institute of Neurology expanding
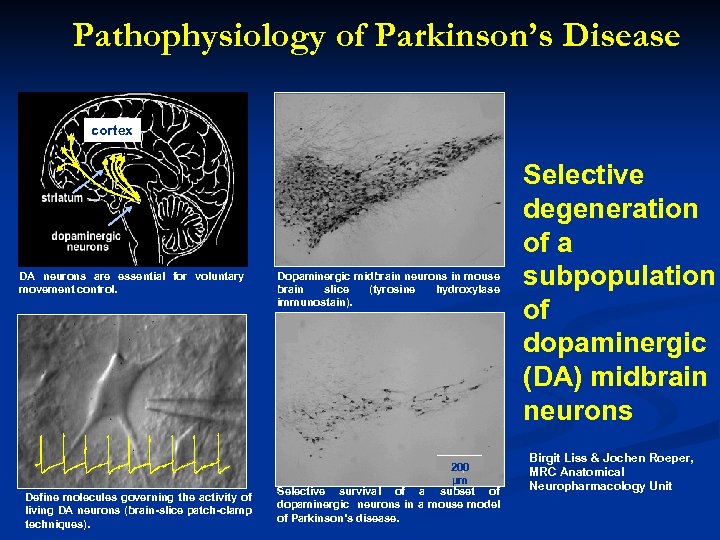 Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease cortex DA neurons are essential for voluntary movement control. Define molecules governing the activity of living DA neurons (brain-slice patch-clamp techniques). Dopaminergic midbrain neurons in mouse brain slice (tyrosine hydroxylase immunostain). 200 µm Selective survival of a subset of dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Selective degeneration of a subpopulation of dopaminergic (DA) midbrain neurons Birgit Liss & Jochen Roeper, MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology Unit
Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease cortex DA neurons are essential for voluntary movement control. Define molecules governing the activity of living DA neurons (brain-slice patch-clamp techniques). Dopaminergic midbrain neurons in mouse brain slice (tyrosine hydroxylase immunostain). 200 µm Selective survival of a subset of dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Selective degeneration of a subpopulation of dopaminergic (DA) midbrain neurons Birgit Liss & Jochen Roeper, MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology Unit
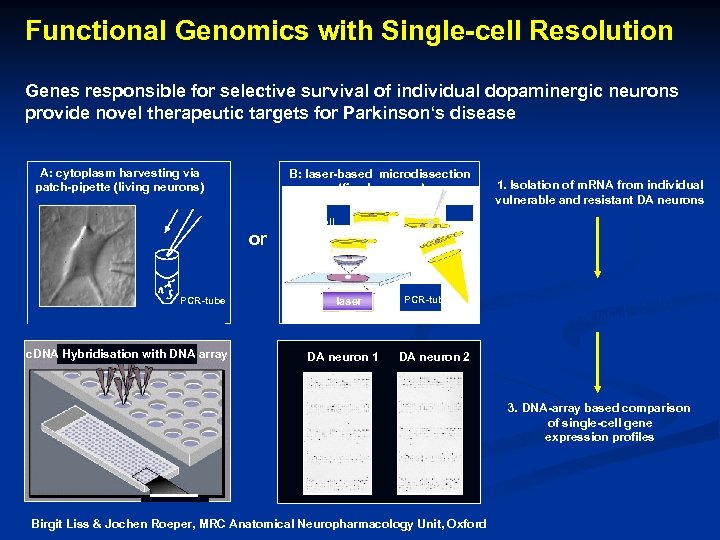 Functional Genomics with Single-cell Resolution Genes responsible for selective survival of individual dopaminergic neurons provide novel therapeutic targets for Parkinson‘s disease A: cytoplasm harvesting via patch-pipette (living neurons) B: laser-based microdissection (fixed neurons) 1. Isolation of m. RNA from individual vulnerable and resistant DA neurons single cell or PCR-tube c. DNA Hybridisation with DNA array laser DA neuron 1 PCR-tube 2. Linear m. RNA amplification, synthesis of labelled c. DNA DA neuron 2 3. DNA-array based comparison of single-cell gene expression profiles Birgit Liss & Jochen Roeper, MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology Unit, Oxford
Functional Genomics with Single-cell Resolution Genes responsible for selective survival of individual dopaminergic neurons provide novel therapeutic targets for Parkinson‘s disease A: cytoplasm harvesting via patch-pipette (living neurons) B: laser-based microdissection (fixed neurons) 1. Isolation of m. RNA from individual vulnerable and resistant DA neurons single cell or PCR-tube c. DNA Hybridisation with DNA array laser DA neuron 1 PCR-tube 2. Linear m. RNA amplification, synthesis of labelled c. DNA DA neuron 2 3. DNA-array based comparison of single-cell gene expression profiles Birgit Liss & Jochen Roeper, MRC Anatomical Neuropharmacology Unit, Oxford
 Treating Parkinson’s Disease The MRC and Parkinson’s Disease Society have recently funded a £ 1. 25 m trial to test the long-term effectiveness of surgery versus drug treatment for Parkinson’s Disease • Parkinson’s Disease is controlled by drugs but these become less effective over time and the period of relief they offer also decreases • Surgery provides longer periods of quality living as opposed to the 1 -2 h that drugs offer, but the long term effects on quality of life of the patient and carer need to be evaluated • The trial is being led from the QE hospital in Birmingham
Treating Parkinson’s Disease The MRC and Parkinson’s Disease Society have recently funded a £ 1. 25 m trial to test the long-term effectiveness of surgery versus drug treatment for Parkinson’s Disease • Parkinson’s Disease is controlled by drugs but these become less effective over time and the period of relief they offer also decreases • Surgery provides longer periods of quality living as opposed to the 1 -2 h that drugs offer, but the long term effects on quality of life of the patient and carer need to be evaluated • The trial is being led from the QE hospital in Birmingham
 Embryonic Stem Cells UK NICHE n Pioneering UK research by Martin Evans n The UK recently became the first country in the world to approve properly conducted research on the use of embryonic stem cells n This provides a window of opportunity and indeed an obligation to grasp the potential of stem cell based therapies
Embryonic Stem Cells UK NICHE n Pioneering UK research by Martin Evans n The UK recently became the first country in the world to approve properly conducted research on the use of embryonic stem cells n This provides a window of opportunity and indeed an obligation to grasp the potential of stem cell based therapies
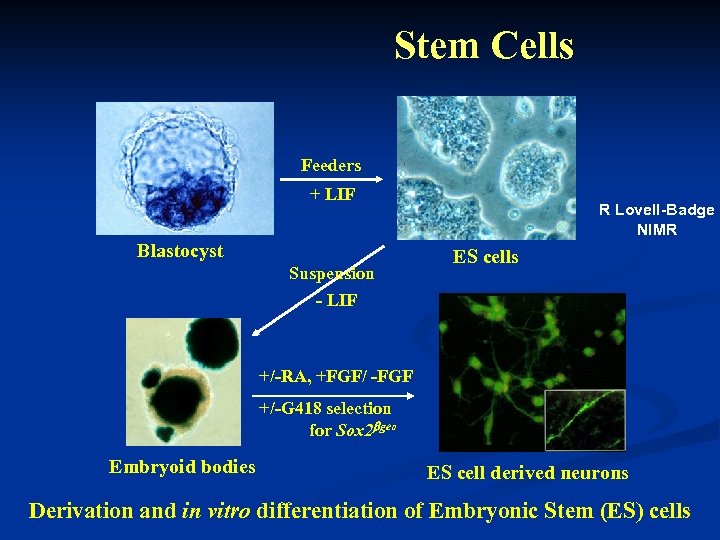 Stem Cells Feeders + LIF Blastocyst Suspension R Lovell-Badge NIMR ES cells - LIF +/-RA, +FGF/ -FGF +/-G 418 selection for Sox 2 bgeo Embryoid bodies ES cell derived neurons Derivation and in vitro differentiation of Embryonic Stem (ES) cells
Stem Cells Feeders + LIF Blastocyst Suspension R Lovell-Badge NIMR ES cells - LIF +/-RA, +FGF/ -FGF +/-G 418 selection for Sox 2 bgeo Embryoid bodies ES cell derived neurons Derivation and in vitro differentiation of Embryonic Stem (ES) cells
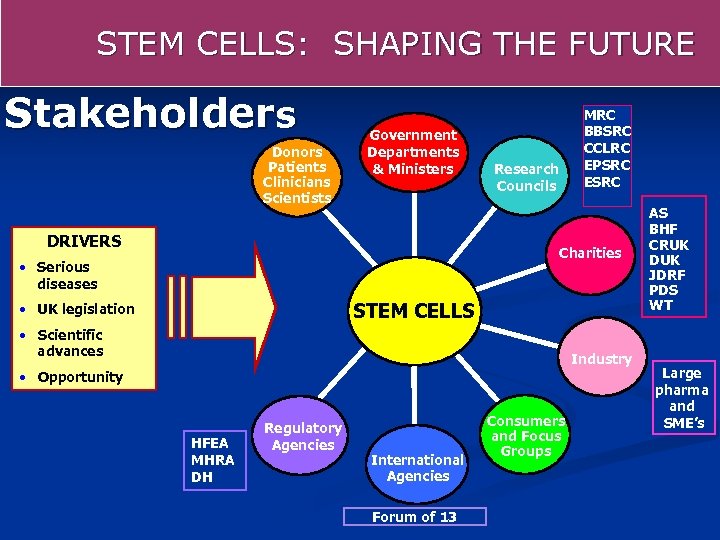 STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE Stakeholders Donors Patients Clinicians Scientists Government Departments Government & Ministers DRIVERS MRC BBSRC CCLRC EPSRC ESRC Research Councils Charities • Serious diseases STEM CELLS • UK legislation • Scientific advances Industry • Opportunity HFEA MHRA DH Regulatory Agencies International Agencies Forum of 13 Consumers and Focus Groups AS BHF CRUK DUK JDRF PDS WT Large pharma and SME’s
STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE Stakeholders Donors Patients Clinicians Scientists Government Departments Government & Ministers DRIVERS MRC BBSRC CCLRC EPSRC ESRC Research Councils Charities • Serious diseases STEM CELLS • UK legislation • Scientific advances Industry • Opportunity HFEA MHRA DH Regulatory Agencies International Agencies Forum of 13 Consumers and Focus Groups AS BHF CRUK DUK JDRF PDS WT Large pharma and SME’s
 STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE Funders Co-ordinating Committee n 15 Agencies n Communications Coalition n Annual Conference n Career Development Fellowships n Training Course n Research Funding (JDRF/MRC Mo. U) Res. Councils: BBSRC, CCLRC, EPSRC, ESRC, MRC Res. Charities: AS, BHF, CRUK, DUK, JDRF, PDS, WT Reg. Agencies: DH, HFEA, MHRA
STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE Funders Co-ordinating Committee n 15 Agencies n Communications Coalition n Annual Conference n Career Development Fellowships n Training Course n Research Funding (JDRF/MRC Mo. U) Res. Councils: BBSRC, CCLRC, EPSRC, ESRC, MRC Res. Charities: AS, BHF, CRUK, DUK, JDRF, PDS, WT Reg. Agencies: DH, HFEA, MHRA
 STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE National Facilities n UK Stem Cell Bank - established at NIBSC with funding from MRC & BBSRC local management committee established one year devoted to recruitment/refurbishment clinical grade facilities installed; MHRA accreditation required research grade facilities completed ready to accession research grade lines applications to bank research grade lines currently under review by Steering Committee
STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE National Facilities n UK Stem Cell Bank - established at NIBSC with funding from MRC & BBSRC local management committee established one year devoted to recruitment/refurbishment clinical grade facilities installed; MHRA accreditation required research grade facilities completed ready to accession research grade lines applications to bank research grade lines currently under review by Steering Committee
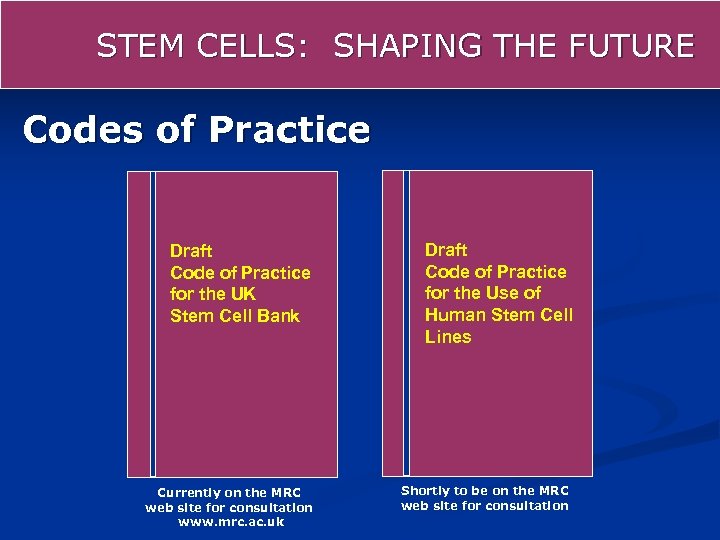 STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE Codes of Practice Draft Code of Practice for the UK Stem Cell Bank Currently on the MRC web site for consultation www. mrc. ac. uk Draft Code of Practice for the Use of Human Stem Cell Lines Shortly to be on the MRC web site for consultation
STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE Codes of Practice Draft Code of Practice for the UK Stem Cell Bank Currently on the MRC web site for consultation www. mrc. ac. uk Draft Code of Practice for the Use of Human Stem Cell Lines Shortly to be on the MRC web site for consultation
 STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE Communications n UK Funders Communications Coalition - briefing pack on stem cells - MORI poll of public attitudes n Corporate Communication Activities - UK and EU parliamentary briefings - MRC attitudinal survey of IVF and other donors n Consumers - Consumer Liaison Groups review guidance documents - Steering Committee includes two lay members
STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE Communications n UK Funders Communications Coalition - briefing pack on stem cells - MORI poll of public attitudes n Corporate Communication Activities - UK and EU parliamentary briefings - MRC attitudinal survey of IVF and other donors n Consumers - Consumer Liaison Groups review guidance documents - Steering Committee includes two lay members
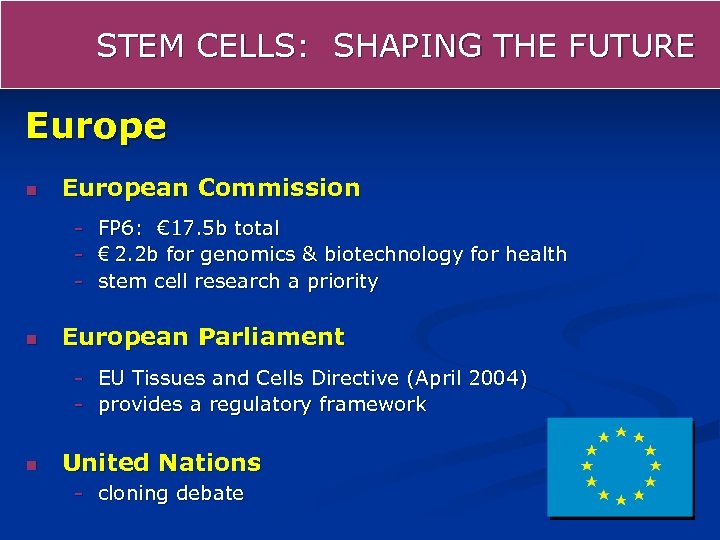 STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE Europe n European Commission - n FP 6: € 17. 5 b total € 2. 2 b for genomics & biotechnology for health stem cell research a priority European Parliament - EU Tissues and Cells Directive (April 2004) - provides a regulatory framework n United Nations - cloning debate
STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE Europe n European Commission - n FP 6: € 17. 5 b total € 2. 2 b for genomics & biotechnology for health stem cell research a priority European Parliament - EU Tissues and Cells Directive (April 2004) - provides a regulatory framework n United Nations - cloning debate
 STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE International Stem Cell Forum n 13 agencies from 12 countries - meets twice per year - portfolio sharing - policy discussions - joint funding initiatives - collaborative agreement AUSTRALIA, CANADA, FINLAND, FRANCE, GERMANY, ISRAEL, JDRF, JAPAN, SINGAPORE, SWEDEN, THE NETHERLANDS, UK, USA
STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE International Stem Cell Forum n 13 agencies from 12 countries - meets twice per year - portfolio sharing - policy discussions - joint funding initiatives - collaborative agreement AUSTRALIA, CANADA, FINLAND, FRANCE, GERMANY, ISRAEL, JDRF, JAPAN, SINGAPORE, SWEDEN, THE NETHERLANDS, UK, USA
 STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE International Stem Cell Forum n Joint Initiatives - characterisation of stem cell lines (UK lead) - ethics landscape (Canada lead) - IPR Landscape (Australia lead) - web database of international research and training opportunities (UK lead)
STEM CELLS: SHAPING THE FUTURE International Stem Cell Forum n Joint Initiatives - characterisation of stem cell lines (UK lead) - ethics landscape (Canada lead) - IPR Landscape (Australia lead) - web database of international research and training opportunities (UK lead)
 Dementia & Quality of Life How to extend the active participation of older people with dementia in society • Investigate cognition of the external environment by people with dementia · Identify design factors which influence the ability of older people with dementia to negotiate their external environment · Offer guidance to designers on the criteria to consider in developing urban areas that are accessible to those with dementia · Find ways to promote communication for elderly people with dementia using multimedia techniques
Dementia & Quality of Life How to extend the active participation of older people with dementia in society • Investigate cognition of the external environment by people with dementia · Identify design factors which influence the ability of older people with dementia to negotiate their external environment · Offer guidance to designers on the criteria to consider in developing urban areas that are accessible to those with dementia · Find ways to promote communication for elderly people with dementia using multimedia techniques
 Gloucester Smart House
Gloucester Smart House
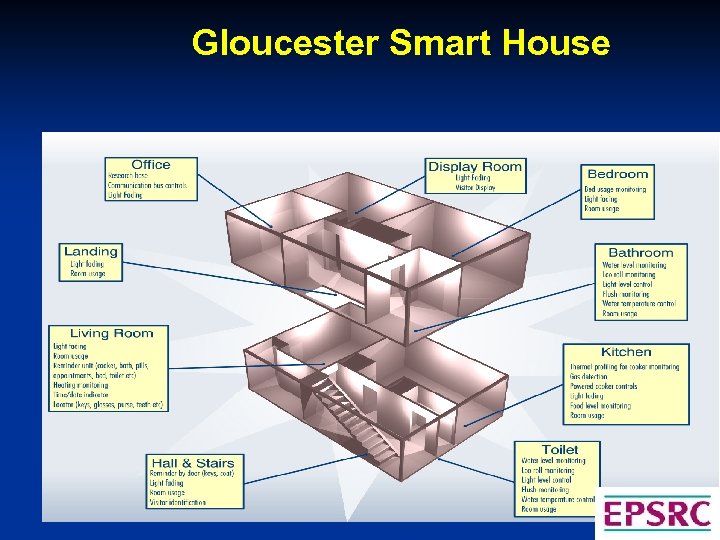
 Gloucester Smart House Locator – A device to help people locate lost items e. g. purse, glasses Bath monitor – A monitor to help stop people filling the bath to overflowing whilst still allowing full control of the taps Cooker monitor – A device that monitors the cooker and acts to prevent dangerous situation occurring Night-time guidance – Guides the resident of a house to the toilet with gentle lighting Communications – Research into reliable and accurate means of communication with people with dementia
Gloucester Smart House Locator – A device to help people locate lost items e. g. purse, glasses Bath monitor – A monitor to help stop people filling the bath to overflowing whilst still allowing full control of the taps Cooker monitor – A device that monitors the cooker and acts to prevent dangerous situation occurring Night-time guidance – Guides the resident of a house to the toilet with gentle lighting Communications – Research into reliable and accurate means of communication with people with dementia
 Major Health Challenges n Ageing n Mental health n Infectious diseases n Obesity/Diabetes n Heart disease n Cancer
Major Health Challenges n Ageing n Mental health n Infectious diseases n Obesity/Diabetes n Heart disease n Cancer
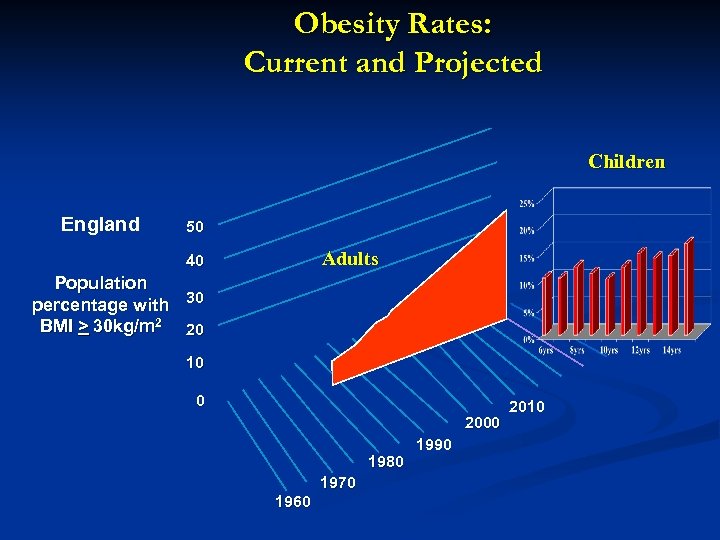 Obesity Rates: Current and Projected Children England 50 Adults 40 Population percentage with 30 BMI > 30 kg/m 2 20 10 0 2000 1980 1970 1960 1990 2010
Obesity Rates: Current and Projected Children England 50 Adults 40 Population percentage with 30 BMI > 30 kg/m 2 20 10 0 2000 1980 1970 1960 1990 2010
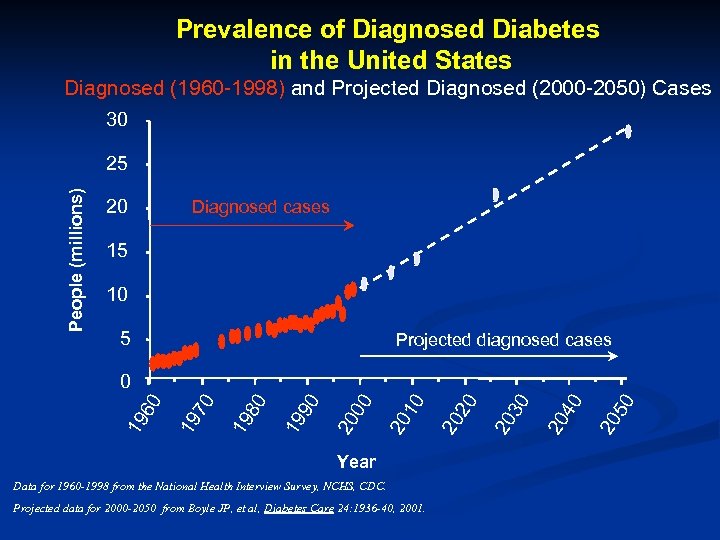 Prevalence of Diagnosed Diabetes in the United States Diagnosed (1960 -1998) and Projected Diagnosed (2000 -2050) Cases 30 People (millions) 25 20 Diagnosed cases 15 10 5 Projected diagnosed cases Year Data for 1960 -1998 from the National Health Interview Survey, NCHS, CDC. Projected data for 2000 -2050 from Boyle JP, et al, Diabetes Care 24: 1936 -40, 2001. 50 20 40 20 30 20 20 20 10 20 00 20 90 19 80 19 70 19 19 60 0
Prevalence of Diagnosed Diabetes in the United States Diagnosed (1960 -1998) and Projected Diagnosed (2000 -2050) Cases 30 People (millions) 25 20 Diagnosed cases 15 10 5 Projected diagnosed cases Year Data for 1960 -1998 from the National Health Interview Survey, NCHS, CDC. Projected data for 2000 -2050 from Boyle JP, et al, Diabetes Care 24: 1936 -40, 2001. 50 20 40 20 30 20 20 20 10 20 00 20 90 19 80 19 70 19 19 60 0
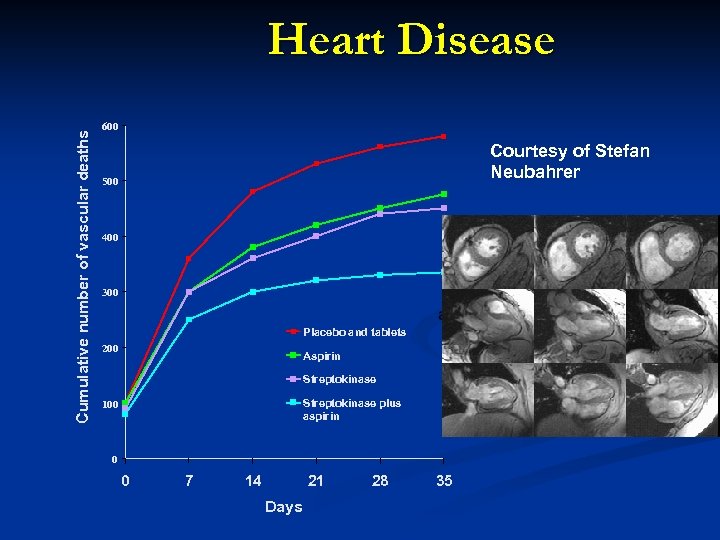 Cumulative number of vascular deaths Heart Disease 600 Courtesy of Stefan Neubahrer 500 400 300 Placebo and tablets 200 Aspirin Streptokinase plus aspirin 100 0 0 7 14 21 Days 28 35
Cumulative number of vascular deaths Heart Disease 600 Courtesy of Stefan Neubahrer 500 400 300 Placebo and tablets 200 Aspirin Streptokinase plus aspirin 100 0 0 7 14 21 Days 28 35
 Heart Protection Study Clinical Trials Service Unit, Oxford (R Collins) Supported by MRC, BHF & Merck & Roche Vitamins n n n n After allowance for non-compliance, 40 mg daily simvastatin safely reduces the risk of heart attack, of stroke, and of revascularisation by at least one-third 5 years of statin treatment typically prevents these “major vascular events” in about: 100 of every 1000 with previous MI 80 " " other CHD 70 " " diabetes (age 40+) 70 " " previous stroke 70 " " other PVD irrespective of cholesterol level (or age, or sex, or other treatments)
Heart Protection Study Clinical Trials Service Unit, Oxford (R Collins) Supported by MRC, BHF & Merck & Roche Vitamins n n n n After allowance for non-compliance, 40 mg daily simvastatin safely reduces the risk of heart attack, of stroke, and of revascularisation by at least one-third 5 years of statin treatment typically prevents these “major vascular events” in about: 100 of every 1000 with previous MI 80 " " other CHD 70 " " diabetes (age 40+) 70 " " previous stroke 70 " " other PVD irrespective of cholesterol level (or age, or sex, or other treatments)

 Genetic Diversity n n The current world population of 6 billion descends from a few tens of thousands of progenitors who inhabited Africa some 200, 000 years ago Small, isolated populations (eg in remote parts of Sardinia) interbreed and maintain only a limited degree of genetic variation In contrast, large populations (eg in the UK) show much greater variation This offers 2 routes into studying genetic diversity and mapping common diseases like heart disease and dementia
Genetic Diversity n n The current world population of 6 billion descends from a few tens of thousands of progenitors who inhabited Africa some 200, 000 years ago Small, isolated populations (eg in remote parts of Sardinia) interbreed and maintain only a limited degree of genetic variation In contrast, large populations (eg in the UK) show much greater variation This offers 2 routes into studying genetic diversity and mapping common diseases like heart disease and dementia
 The UK Biobank Medical Research Council Wellcome. Trust Department of Health
The UK Biobank Medical Research Council Wellcome. Trust Department of Health
 Bio. Bank UK n n n Long term prospective research framework Relative contributions of genotype, environmental exposure and chance to risk of common diseases n Cohort of 500, 000 adults (aged 45 – 69) n Nested case control studies n Monitoring for incident disease Central repository of biological samples and linked database n Genotype n Other biological assays n Exposure data
Bio. Bank UK n n n Long term prospective research framework Relative contributions of genotype, environmental exposure and chance to risk of common diseases n Cohort of 500, 000 adults (aged 45 – 69) n Nested case control studies n Monitoring for incident disease Central repository of biological samples and linked database n Genotype n Other biological assays n Exposure data
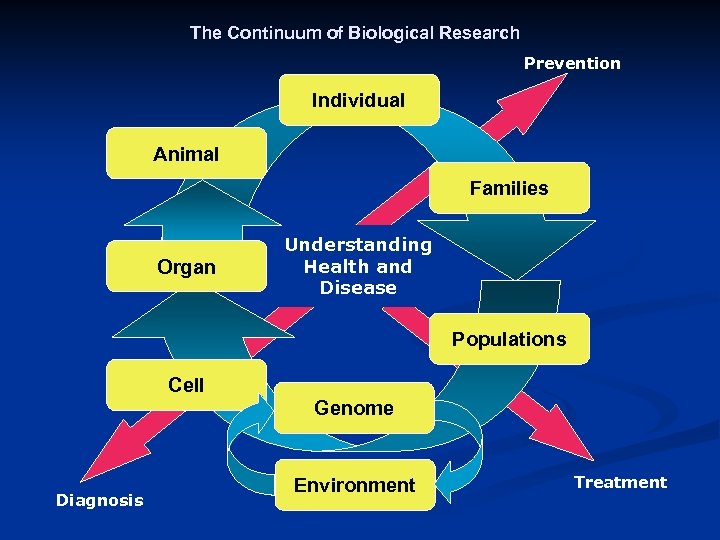 The Continuum of Biological Research Prevention Individual Animal Families Organ Understanding Health and Disease Populations Cell Genome Diagnosis Environment Treatment
The Continuum of Biological Research Prevention Individual Animal Families Organ Understanding Health and Disease Populations Cell Genome Diagnosis Environment Treatment


