d83266d0179c9bc3c382e6d89e8e881c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57

Knowing Your Computer b Software b Files b Data Storage b Internet 1

Understanding Computer Software Basics b Software Determines do. what a computer can b Software can transform a computer from one kind of machine to another 2

Understanding Computer Software Basics Software can transform a computer to: b Drafting station b Filing system b Flight simulator b Calculator b Music studio 3

Understanding Computer Software Basics Computer Program: b Is a set of detail, step-by-step instructions that tell a computer how to solve a problem or carry out a task. b The steps in a computer program are written in a language that the computer can interpret or “understand”. 4

Understanding Computer Software Basics Data: b Are the words, numbers, and graphics that describe • • People Events things Ideas 5

Understanding Computer Software Basics Software: • Computer programs • Data used by the programs 6

Understanding Computer Software Basics Software: • Software may include more than one computer program, if those programs work together to carry out a task 7

Understanding Computer Software Basics Software: • Software can include data, but data alone is not software. 8

Understanding Computer Software Basics Software: • For Example: – Word Processing software might include the data for a dictionary. – Data you create using a word processor is not referred to as software. 9

Understanding Computer Software Basics There are two major categories of software. 10

Understanding Computer Software Basics Software Categories: • System Software Helps the computer carry out its basic operating tasks • Application Software Helps the human user carry out a task 11
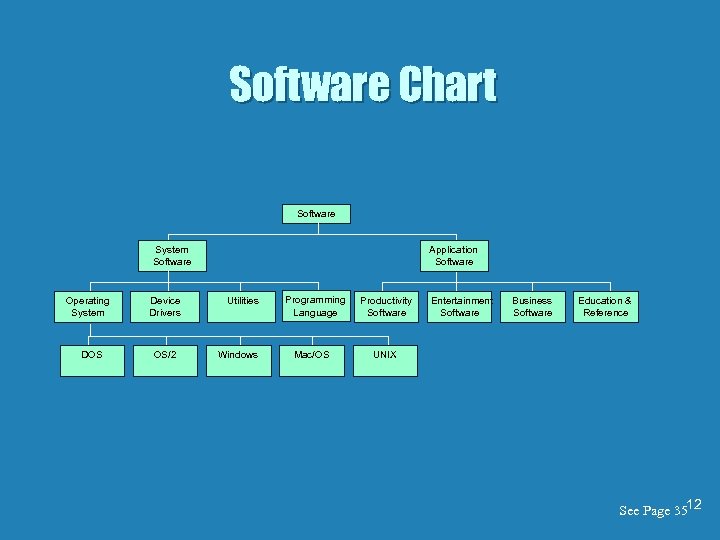
Software Chart Software System Software Operating System DOS Device Drivers OS/2 Application Software Utilities Windows Programming Language Mac/OS Productivity Software Entertainment Software Business Software Education & Reference UNIX See Page 3512

Defining and recognizing operating systems The Operating System: • The operating system works between the computer hardware and applications software. • An operating system helps you start an application, then it works behind the scenes 13

Defining and recognizing operating systems Operating Systems: • • • CP/M - Control Program for Microcomputers DOS - Disk Operating system Window 3. 1, Window 3. 11 Windows 95, Windows 98 Windows NT, Windows 2000 Windows XP OS/2 Mac OS UNIX 14 See Page 39

DOS 6. 5 C: > | 15
Windows 3. 1, 3. 11 16

Defining and recognizing operating systems Windows 95 and 98 – Provides some basic networking capabilities, making them suitable operating systems for homes and businesses – They are classified as desktop operating systems and would not be found on a minicomputer, mainframe, or supercomputer 17 See Page 39

Defining and recognizing operating systems Windows NT, Windows 2000 – Are workstation versions of the Windows operating system. – Designed for the desktop but does support small networks. – – – Increased security, Greater reliability Ability to support specialized software applications 18 See Page 39
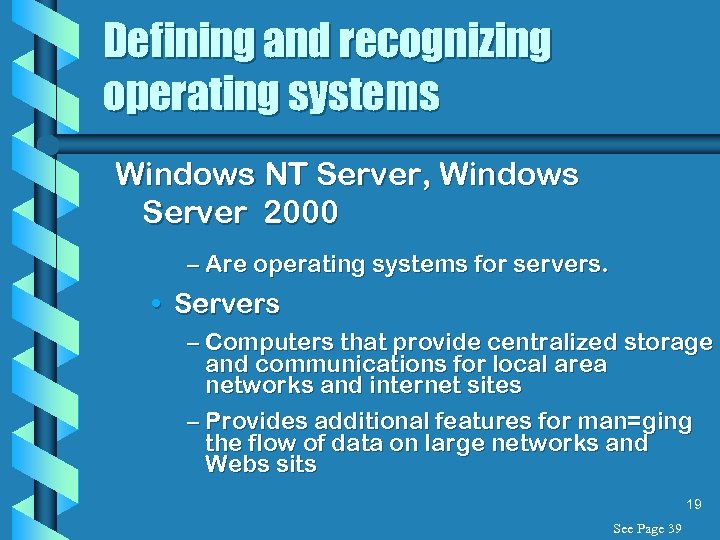
Defining and recognizing operating systems Windows NT Server, Windows Server 2000 – Are operating systems for servers. • Servers – Computers that provide centralized storage and communications for local area networks and internet sites – Provides additional features for man=ging the flow of data on large networks and Webs sits 19 See Page 39

20

21

Defining and recognizing operating systems What does the Operating System do: • • • Control basic input and output Ensure adequate space Allocate system resources Manage storage space Detect equipment failure Maintain security See Page 3622

Defining Storage Technology 23 See Page 43

Defining Storage Technology b Storage Technology - Refers to a storage device and the media it uses. b Storage medium - is the disk, tape, paper, or other substance that contains data 24 See Page 43
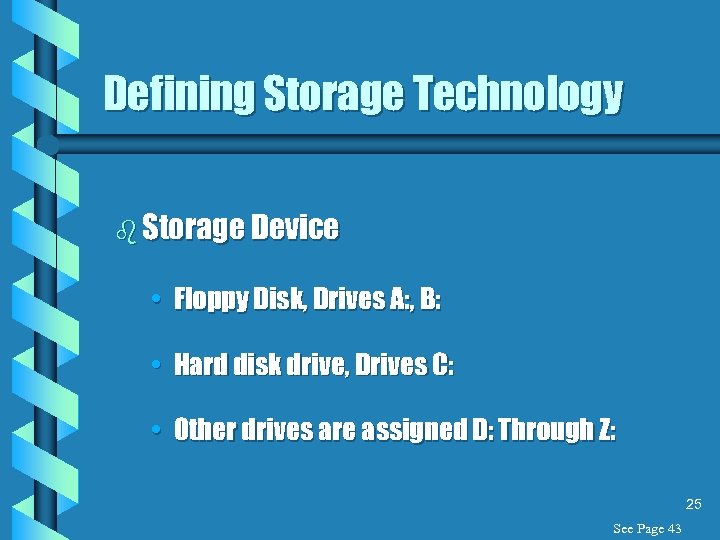
Defining Storage Technology b Storage Device • Floppy Disk, Drives A: , B: • Hard disk drive, Drives C: • Other drives are assigned D: Through Z: 25 See Page 43

Defining Storage Technology b Computer terms to know. • Writing data or saving a file The process of storing data. • Reading data, loading data or opening a file The process of retrieving data. 26
Defining Storage Technology b Storage Specifications: • Storage technology comparisons are often based on storage capacity and speed. • Knowing the characteristics of a storage devise or storage medium helps you determine which one is best for a particular task. 27

Defining Storage Technology b Storage Capacity: • The maximum amount of data that can be stored on a storage medium 28
Defining Storage Technology b Storage Capacity: • Data is stored as bytes. – Each byte usually represents one character 29
Defining Storage Technology b Storage Capacity: The Bit ! • Short for Binary Digit; – either 1 or 0 in the binary number system • A BIT is the smallest unit of information handled by a computer 30
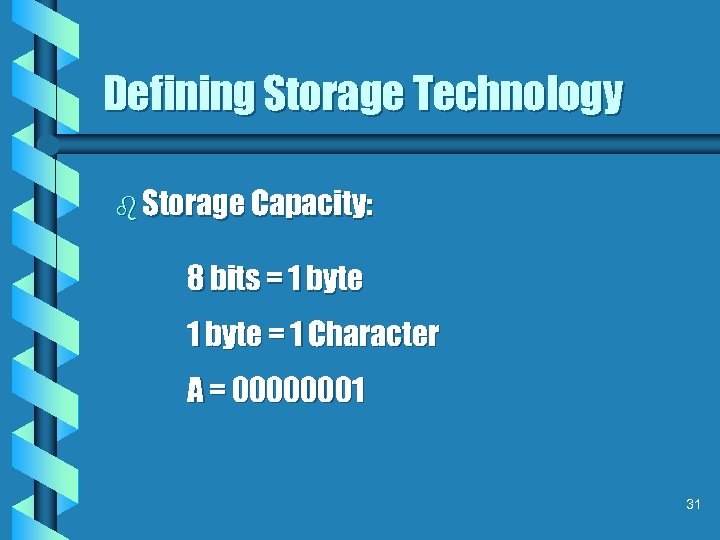
Defining Storage Technology b Storage Capacity: 8 bits = 1 byte = 1 Character A = 00000001 31
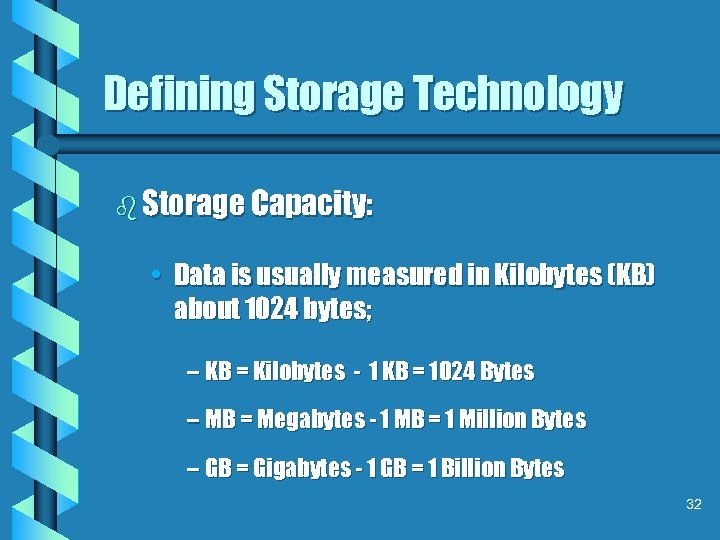
Defining Storage Technology b Storage Capacity: • Data is usually measured in Kilobytes (KB) about 1024 bytes; – KB = Kilobytes - 1 KB = 1024 Bytes – MB = Megabytes - 1 MB = 1 Million Bytes – GB = Gigabytes - 1 GB = 1 Billion Bytes 32

Defining Storage Technology b Storage Capacity: • When you read that the storage capacity of a computer is 850 MB, • It means the hard disk on that computer can store up to 850 million bytes of information • That is equivalent to approximately 225, 000 single-spaced pages of text 33
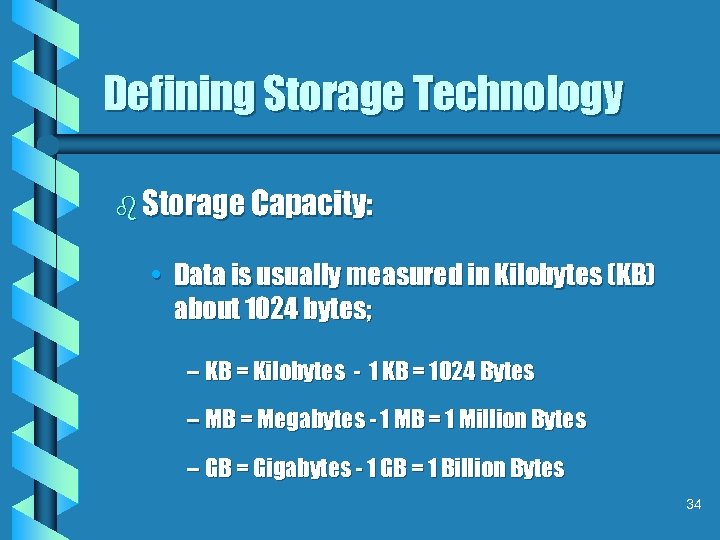
Defining Storage Technology b Storage Capacity: • Data is usually measured in Kilobytes (KB) about 1024 bytes; – KB = Kilobytes - 1 KB = 1024 Bytes – MB = Megabytes - 1 MB = 1 Million Bytes – GB = Gigabytes - 1 GB = 1 Billion Bytes 34

Defining Storage Technology b Computer terms to know. • Access time • The average time it takes a computer to locate data on the storage medium and read it. • Millisecond (ms) - Access time measured in millisecond, a thousandth of a second. 35

Defining Storage Technology Data Storage 36
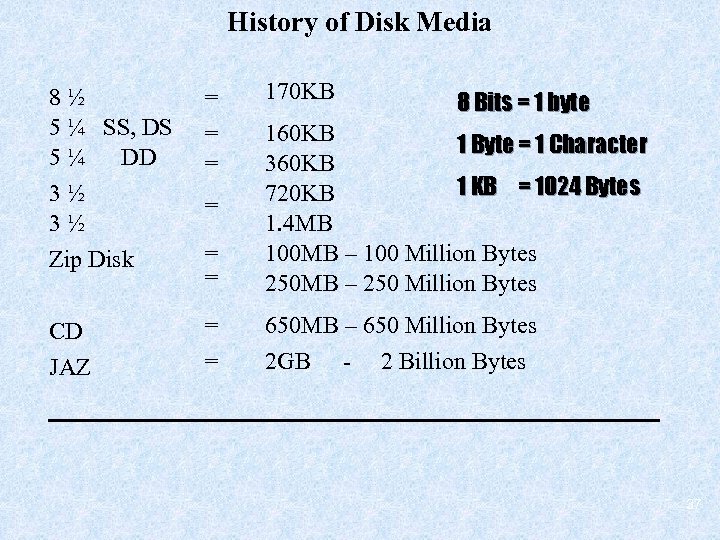
History of Disk Media 170 KB 8½ 5 ¼ SS, DS 5¼ DD 3½ 3½ Zip Disk = = = 160 KB 1 Byte = 1 Character 360 KB 1 KB = 1024 Bytes 720 KB 1. 4 MB 100 MB – 100 Million Bytes 250 MB – 250 Million Bytes CD JAZ = = 650 MB – 650 Million Bytes 2 GB - 2 Billion Bytes = 8 Bits = 1 byte 37
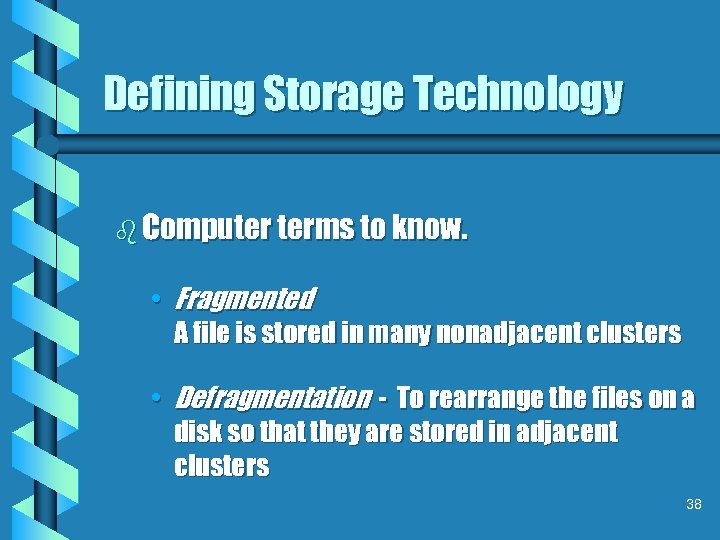
Defining Storage Technology b Computer terms to know. • Fragmented A file is stored in many nonadjacent clusters • Defragmentation - To rearrange the files on a disk so that they are stored in adjacent clusters 38
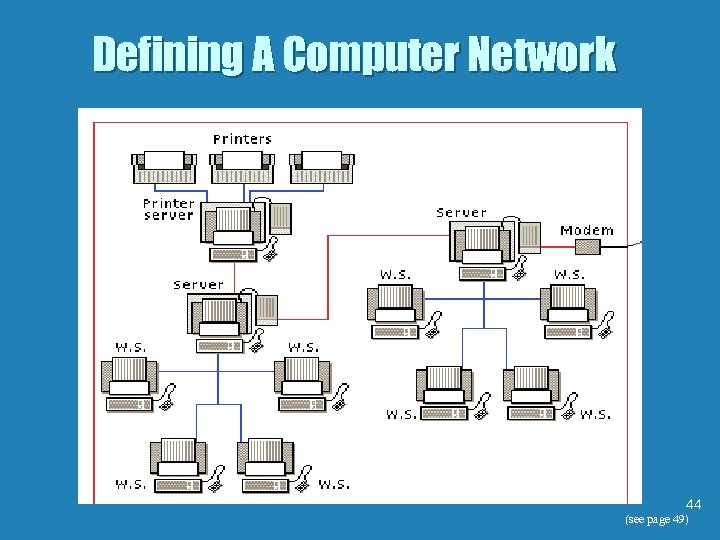
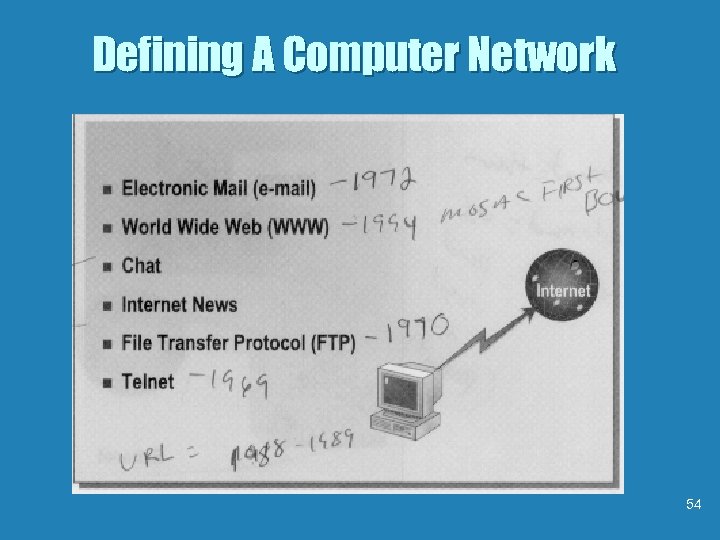
Defining Computer Networks 39 (see page 49)

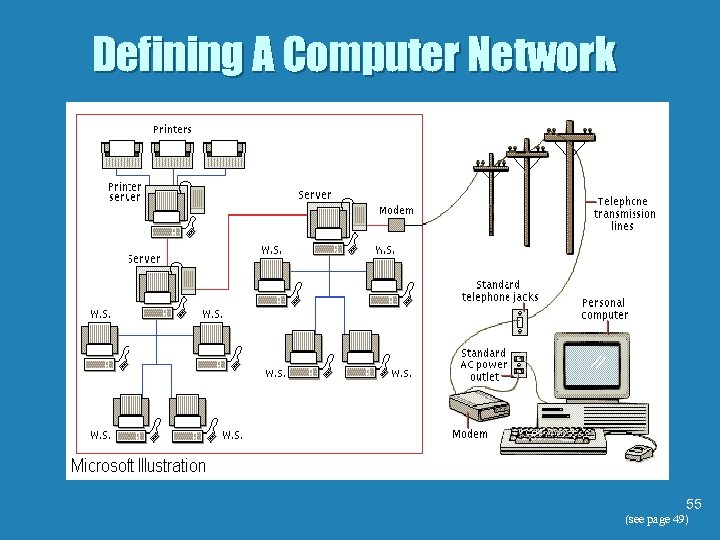
Defining Computer Networks b Computer terms to know. • Stand-alone computer - A computer that is not connected to a network. • Workstation - A computer that is connected to a network using cable or other communications 40 (see page 49)
Defining Computer Networks b Computer terms to know. • Network Server - A computer that is connected to a network and that “serves” or distributes resources to network users. • Network Printer - Provides output capabilities to all the network users. • Node - Each device on a network, including 41 workstations, servers, and printers (see page 49)
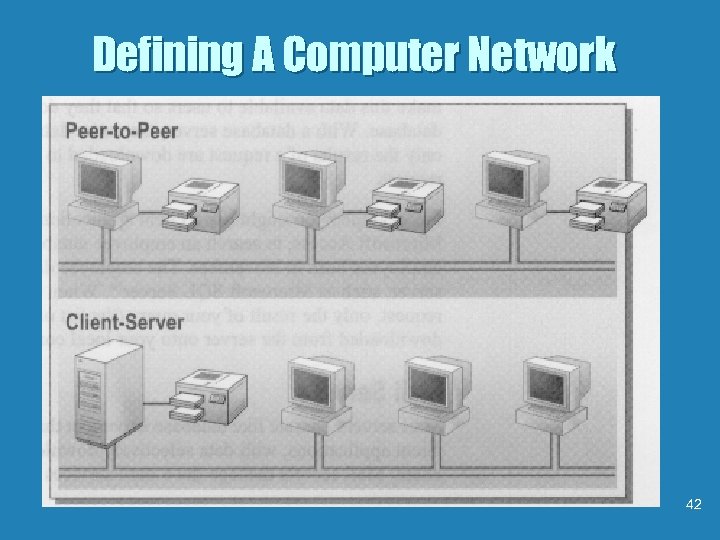
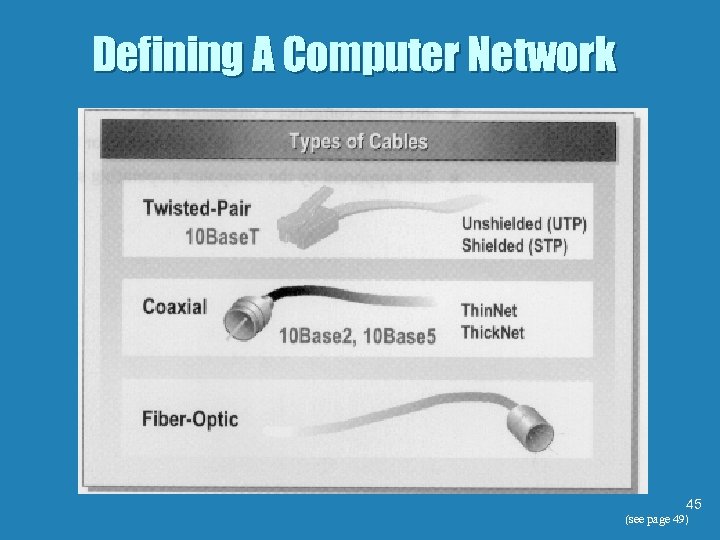
Defining A Computer Network 42
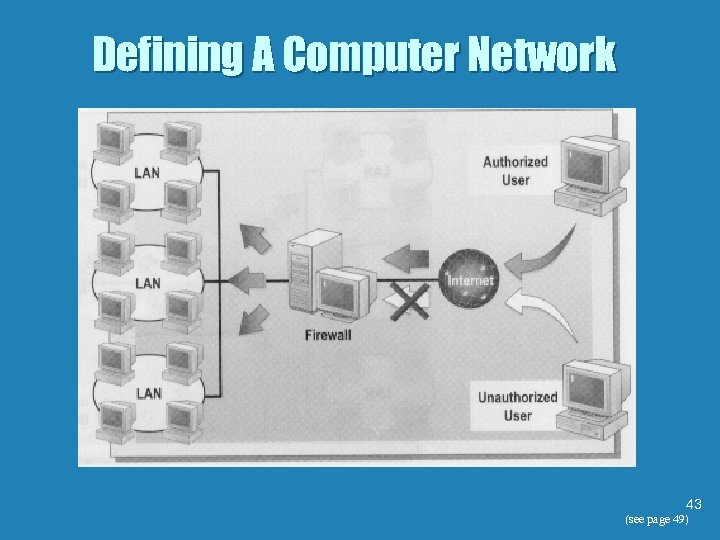
Defining A Computer Network 43 (see page 49)
Defining A Computer Network 44 (see page 49)
Defining A Computer Network 45 (see page 49)

Understanding how the Internet Works b There are three kinds of computer networks • Local area networks (LAN) • Private branch exchange (PBX) networks • Wide-area networks (WAN) or [WWW] World Wide Web 46

Understanding Multimedia Computing 47

Understanding Multimedia Computing b Computer terms to know. • Multimedia An integrated collection of computer-based text, graphics, sound, animation, photo images, and video. (see page 47) 48 (see page 47)

Understanding Multimedia Computing b Computer terms to know. • Hypertext - Documents that could be linked to each other, Linked documents make it possible for a reader to jump from a passage in one document to a related passage in another document. 49 (see page 47)

Understanding Multimedia Computing b Computer terms to know. • Hypermedia - The links in today’s applications often involve graphics, sound, and video, as well as text. 50 (see page 47)
51
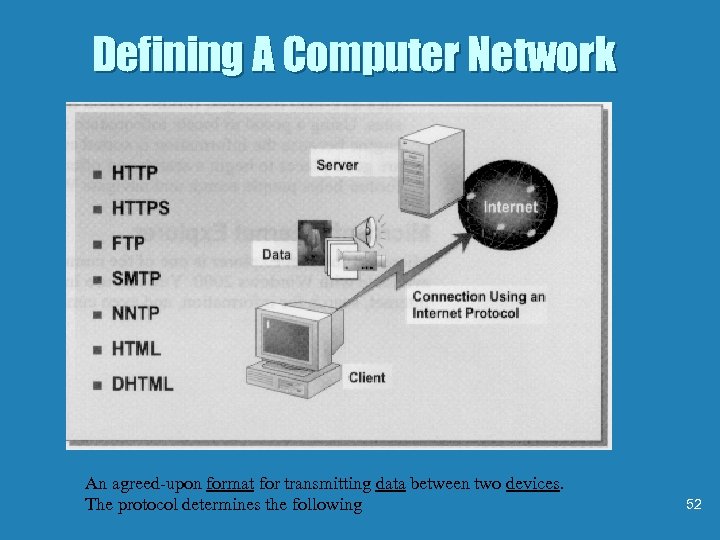
Defining A Computer Network An agreed-upon format for transmitting data between two devices. The protocol determines the following 52

Defining A Computer Network HTTP – Hyper. Text Transfer Protocol. Is a convention for sending messages from a server to a client by using TCP/IP HTTP communications are in plain text and not Encrypted. HTTPS – Secure. Enables you to make a secure Web server connection by using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) SSL is an encryption technology. FTP – File Transfer Protocol. Enables you to transfer files between two computers on a network. SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. Enables you to send e-mail over the Internet NNTP – Network News Transfer Protocol. Enables you to post, distribute, and retrieve messages on Internet and intranet news Groups. HTML – Hypertext Markup Language. Is the standard language for creating and formatting Web pages. Defines how text appears when viewed in a Web browser. DHTML – Dynamic. Refers to HTML extensions that support animations and enable you to create interactive Web pages 53
Defining A Computer Network 54
Defining A Computer Network 55 (see page 49)

Understanding how the Internet Works Computer terms to know. • WWW - World Wide Web • Web Page - World Wide Web consists of pages which contains information on a particular topic • Web Browser - Software to access World Wide Web information • Links - Pointers to other web pages • HTML - Hypertext Markup Language • URL - Uniform Resource Locator 56

4 Types of Printers to Remember 1. 2. 3. 4. Laser. Jet Inkjet Bubble Jet Dot Matrix 57
d83266d0179c9bc3c382e6d89e8e881c.ppt