a4e278e22683fe48ff23746cff499fe6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64

KNC

Rebus CL 1. 1 CS 2. 3 CR 3. 4 CW 4. 2

Rebus CL 1. 1 CS 2. 3 CR 3. 4 CW 4. 2

Rebus

Task Crafting a curriculum is like………………….

“Designing a curriculum is like designing a house; an architect consults his client to find out what the functions of the rooms are to be, how the space is to be used. He will also consider the money available, the character of the site, the climate, and from this a model and design will be drawn up. ” Curriculum Studies in Post-compulsory and Adult Education By Mary Neary “A curriculum is like a road map; it helps you get where you want to go. It includes goals and objectives for children's learning in all areas of development: social/emotional, physical, cognitive, and language” “Crafting a curriculum is like writing a lesson plan. It is like making something with the different components and putting them together in a very creative way. ”

Task Structure ribe the Desc urrent of the C n Kuwait riculum i Cur

1 The Teaching Plan consists of twelve subjects at the primary, thirteen at the intermediate and eleven at the secondary stages. 2 The number of weekly periods is one of the highest in the world at all levels. 3 The structure of the current “National Curriculum Documents” varies from subject to subject. 4 5 6 Basically, the curriculum process in schools is led by the textbooks. Teachers have a relatively reduced space for personal initiative and creativity as the concrete lesson planning is “the same for all”. The approach in the classroom is heavily textbookcentered and doesn’t depend on the learning needs of the students or the competences supposed to be developed in them.

ll as sly as we viou ical, tated pre ic, polit facts s nom All the ges cial, eco al challen ew so ation the n nd n, intern needs a l, huma ing cultura ol w learn ne rds scho owa and the tudents t s than ations of r, better ne expect of that soo how erations s gen and life d future m – n curriculu current a new later, nt a brand ed st rece e mo Kuwait n to the rld. d the Wo adapted n an fully the Natio s of challenge

National Curriculum Framework is: • the leading, core document of the Kuwait National Curriculum. • the guide for policy makers, curriculum and textbook writers. • the guide for schools and education administrators in the process of designing, organizing, managing and evaluating school activities and their effectiveness.

National Curriculum Framework is: the main reference document for: - the development of the Teaching Plan (TP) - the development of the subject curricula - the development of the teaching and learning resources for students and their teachers. - other types of support materials for the school principals and the teachers for implementing the new curriculum as well as for improving their continuous professional development.

National Curriculum Framework Covers: • the concrete ways in which the learning is organized and offered to children and students of Kuwait throughout various education stages, from grades 1 to 12. • the curriculum organizers; external, internal, and connecting organizers. • the conceptual foundations of the new Kuwait National Curriculum

Curriculum Organizers External and internal factors and mechanism according to which the Kuwait National Curriculum Framework structures the curriculum substance (material). Concretely determine what, (why, how, based on what rationale, in which order and – last but not least – with which kind of benefits for children and students) is learned in the Kuwait education system. Are “umbrellas” that regulate and support the selection of the learning process and its underlying content
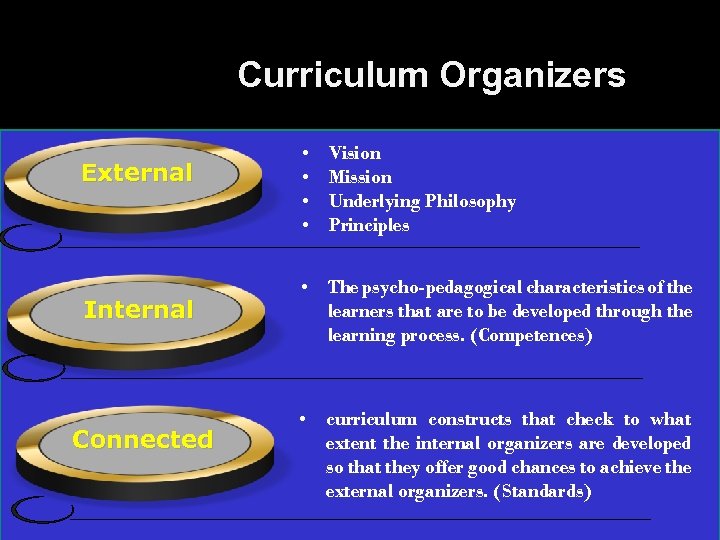
Curriculum Organizers External Internal Connected • • Vision Mission Underlying Philosophy Principles • The psycho-pedagogical characteristics of the learners that are to be developed through the learning process. (Competences) • curriculum constructs that check to what extent the internal organizers are developed so that they offer good chances to achieve the external organizers. (Standards)
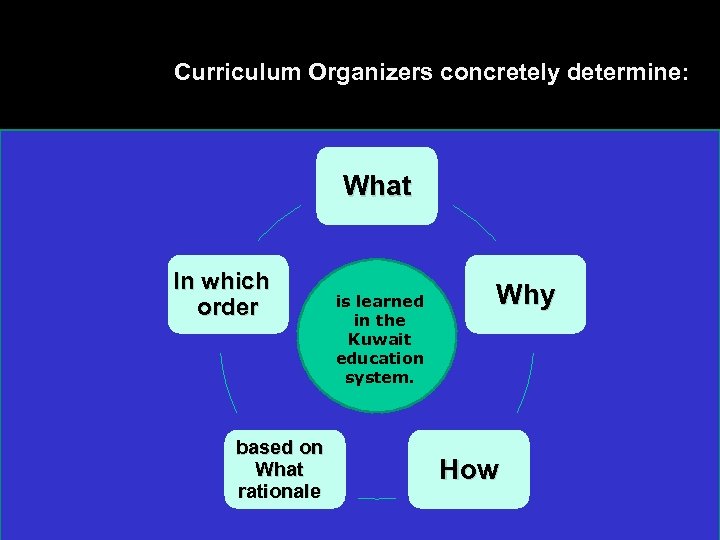
Curriculum Organizers concretely determine: What In which order based on What rationale is learned in the Kuwait education system. Why How

External Organizers Vision • The Vision of the new Kuwait National Curriculum is built on the Vision on the future of the Nation as expressed by His Highness the Amir of the State of Kuwait needs to prepare citizens who – as Highness the Amir mentioned recently - are working hard to achieve the national vision by fully acquiring the competences required for the 21 st Century as well as for successfully facing the challenges of globalization, a knowledge economy and the digital age while preserving the Islamic and Arabic values cherished by all citizens of Kuwait.

VISION " … we have to invest in human and innovative promising powers of our youth , enhance their gifts and urge them to participate in building the country. This shall not be realized but through the assessment and development of our educational entities and their curricula, and updating our educational system to be up to the contemporary requirements. Building the future of our country should be accompanied by the process of building and qualifying the Kuwaiti national. Our students should utilize their gifts and devote their powers and time for academic achievement, studying contemporary sciences, and not to give attention to any calls that might keep them from their academic achievement…".

VISION Responsible citizens, Confident in their Islamic, national and global identity Connected to other people and the environment VISION Contributors to the wellbeing of Kuwait socially, culturally, and environmentally Lifelong learners Effective in using digital communication tools Critical and creative thinkers Active seekers, users and producers of knowledge
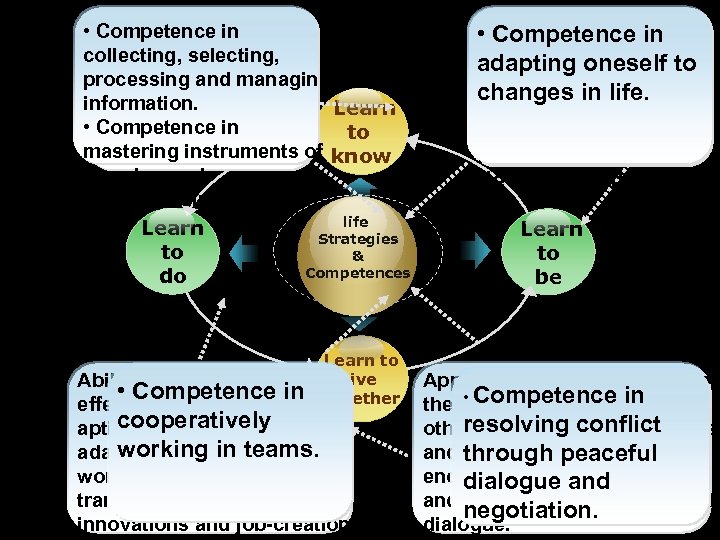
• Developing the faculties Competence in collecting, selecting, of memory, imagination, processing and managing reasoning, probleminformation. the ability Learn solving, and • to think critically Competence in to mastering instruments of knowing and understanding. life Learn Strategies to & Competences do Learn to Live together Ability to communicate • Competence in effectively with others; cooperatively aptitude toward team work; working change in adaptability to in teams. the world of work; competence in transforming knowledge into innovations and job-creation • Competence in Learning to be human adapting oneself to acquiring universally changes in life. values shared human beneficial to personality development Learn to be Appreciation of the diversity of • Competence in the human race; respect of resolving conflict other people and their cultures and through peaceful values; capability of encountering others dialogue and resolving conflicts through negotiation. dialogue.

External Organizers Mission In the light of the vision Kuwait has for its future, the mission of the new Kuwait National Curriculum is to contribute to the education of a new generation fully assuming the supreme Islamic Values and displaying the key competencies for the 21 st Century, needed for making the country a financial and commercial power of the current world. On the ground of preserving Islamic, Arabic and National Kuwait values, schools should educate citizens that love and respect their country, their traditions and national identity being at the same time open towards acquiring multiple identities as citizens of Kuwait, the Gulf, the larger Arab World and the World at large.

External Organizers Philosophy Education for All and Inclusiveness are the key pillars of any National Curriculum (‘Quality education cannot be but inclusive’) Philosophy of Globalization, Knowledge and Learning Economy, Digital Age and Sustainable Development while preserving National Values and Traditions should be conducive for a quality National Curriculum

External Organizers Principles A. Principles related to Curriculum as an overall System B. Principles related to the Learning Process C. Principles related to the Teaching Process D. Principles related to the Assessment of Students’ Achievements
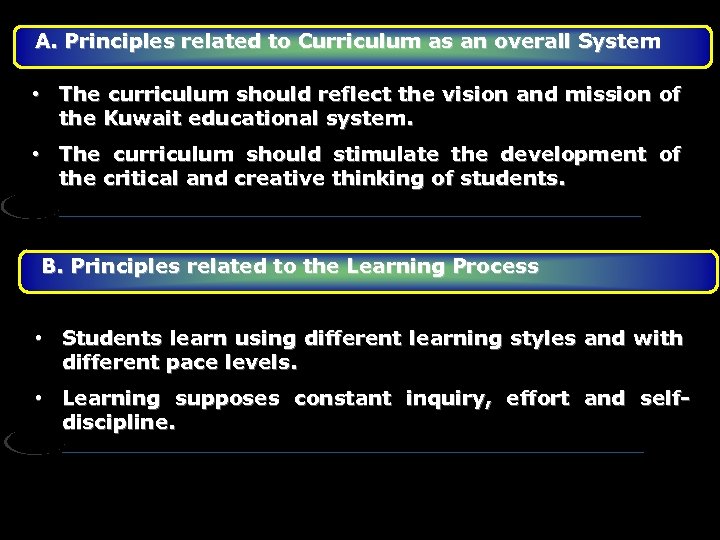
A. Principles related to Curriculum as an overall System • The curriculum should reflect the vision and mission of the Kuwait educational system. • The curriculum should stimulate the development of the critical and creative thinking of students. B. Principles related to the Learning Process • Students learn using different learning styles and with different pace levels. • Learning supposes constant inquiry, effort and selfdiscipline.

C. Principles related to the Teaching Process • Teaching does not only mean a transfer of knowledge, it also includes a transfer of behaviors and attitudes. • Teaching must be carried out in contexts which will connect the school activity with real, everyday life. D. Principles related to the Assessment of Students’ Achievements • Assessment should involve the use of a wide variety of methods. • Assessment should lead students to an appropriate self -appraisal and to a continuous improvement of their performances. • Assessment is based on the student curriculum standards defined by the curriculum and showing what students are expected to achieve at the end of their various educational levels.
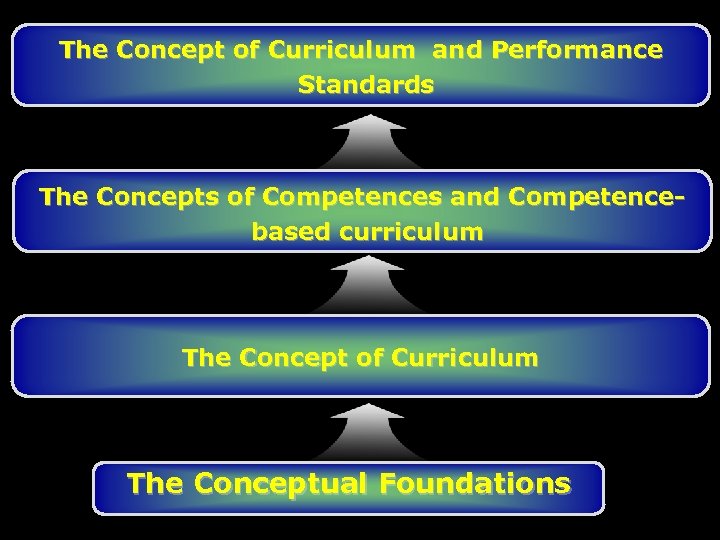
The Concept of Curriculum and Performance Standards The Concepts of Competences and Competencebased curriculum The Concept of Curriculum The Conceptual Foundations

What Type of Curriculum? CBC

WHAT IS CBE? Competence-based education (CBE) emerged in the 1970 s in the US. It referred to an educational movement that advocated defining educational goals in terms of precise measurable description of the knowledge, skills, and behaviours students should possess at the end of a course of study. (Guskey, 2005).

WHAT IS CBLT? • Docking (1994) summarized what CBLT is: “it is designed not around the notion of subject knowledge but around the notion of competence. The focus moves from what students know about language to what they can do with it. ”

WHAT IS CBLT? • Focuses on the outcomes of language learning. • Emphasises what learners are expected to achieve with the target language. • Starts with a clear picture of what is important for students to be able to do, then organising curriculum, instruction, and assessment to make sure this learning ultimately happens.

The curriculum is a system of learning experiences and opportunities that are planned for children and young people through their education. A curriculum represents a highly organized system of knowledge, skills and attitudes/values that all individuals are offered by a given education system. curriculum Curriculum is the reality of learning in the classroom. Curriculum is NOT the textbook
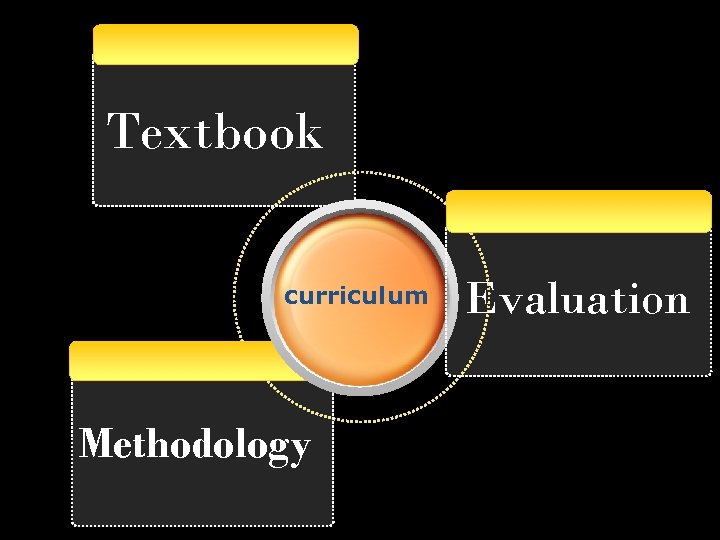
Textbook curriculum Methodology Evaluation
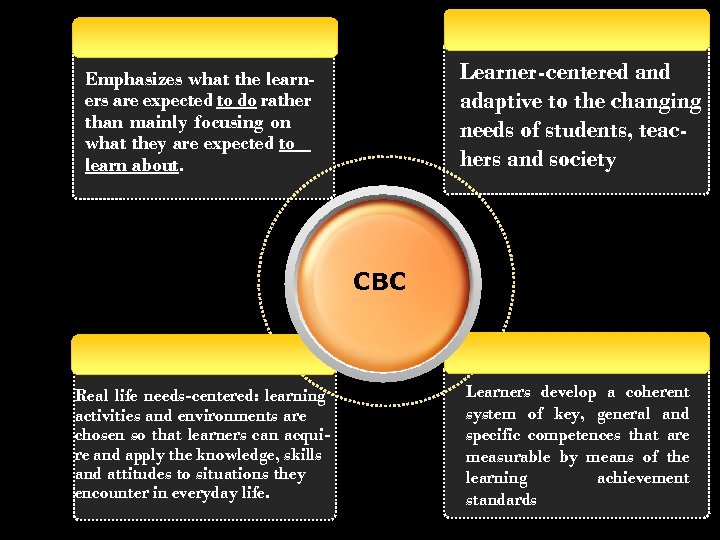
Learner-centered and adaptive to the changing needs of students, teachers and society Emphasizes what the learners are expected to do rather than mainly focusing on what they are expected to learn about. CBC Real life needs-centered: learning activities and environments are chosen so that learners can acquire and apply the knowledge, skills and attitudes to situations they encounter in everyday life. Learners develop a coherent system of key, general and specific competences that are measurable by means of the learning achievement standards
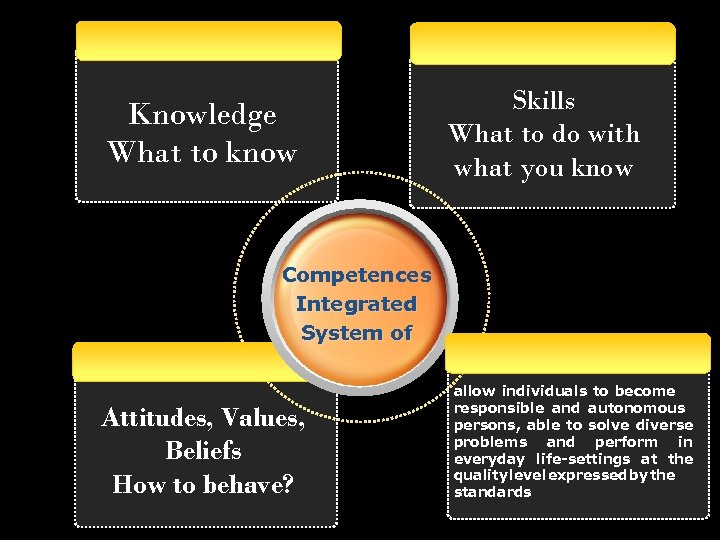
Knowledge What to know Skills What to do with what you know Competences Integrated System of Attitudes, Values, Beliefs How to behave? allow individuals to become responsible and autonomous persons, able to solve diverse problems and perform in everyday life-settings at the quality level expressed by the standards
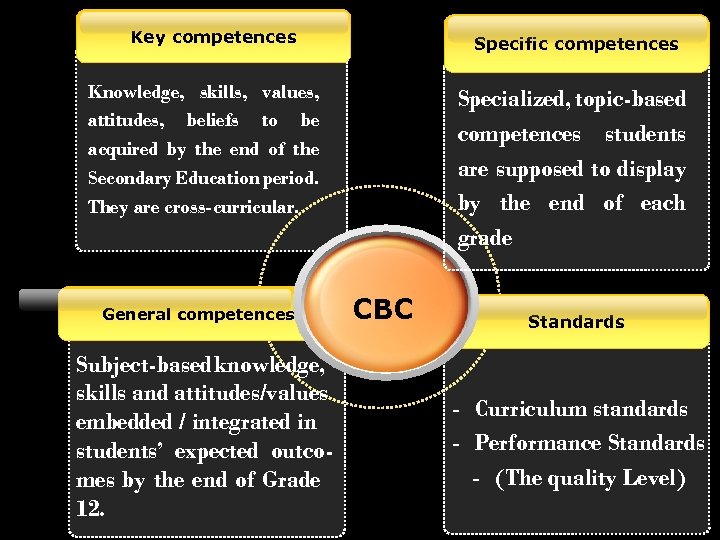
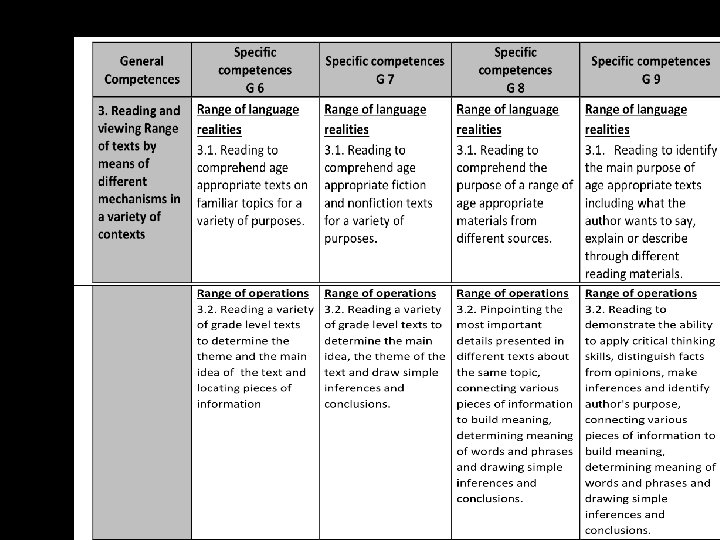
Key competences Specific competences Knowledge, skills, values, attitudes, beliefs to be acquired by the end of the Secondary Education period. They are cross-curricular. General competences Subject-based knowledge, skills and attitudes/values embedded / integrated in students’ expected outcomes by the end of Grade 12. Specialized, topic-based competences students are supposed to display by the end of each grade CBC Standards - Curriculum standards - Performance Standards - (The quality Level)

Ranges or Dimensions The Key Competences students should master by the end of Grade 12 are: 1. A range of realities specific to the subject (knowledge, i. e. to know what, when, where etc. ) 2. A range of operations (skills and strategies) specific to the subject (i. e. to do; to know how) 3. A range of personal and social responses (attitudes, values, beliefs) mobilized by the knowledge and skills acquired in a certain subject (i. e. to ex-press a value; to behave in a certain way; to take a stand; to have a point of view etc. ) • A range of connections with other subjects and domains.

Even though they are described one after the other, in reality they function simultaneously in the human mind, as competences are – in fact – integrated systems and processes that put into work knowledge – skills – values/attitudes, and connections.

Curriculum Standards They describe to what extent the specific competences should be achieved by the end of each grade. As they are relevant for the students’ progress in learning, they are a matter of school- and class-based formative and summative assessment.

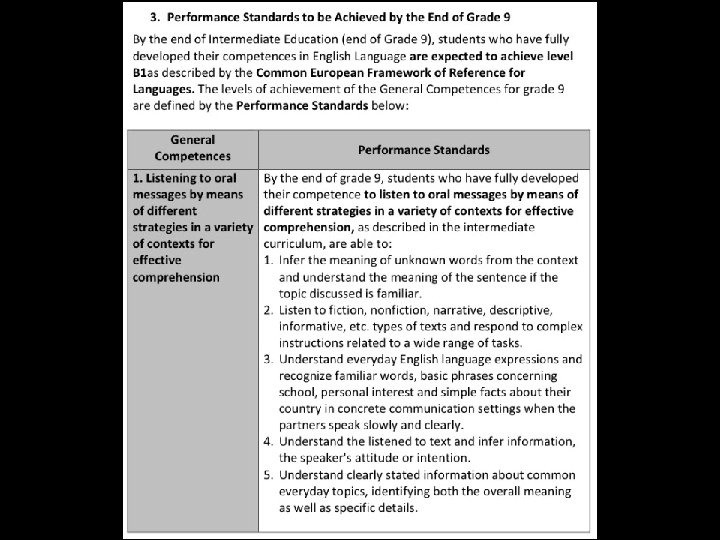
Performance Standards The quality level to be achieved by students in performing their general competences by the end of each of the school stages. The measurement of the performance standards is a matter of different forms of national summative assessments or examinations. They will only be used for the national assessment carried out for four subjects – Mathematics, English, Science and Arabic – by Center for Educational Development under the National acronym MESA.


Key Competences The Key Competences students should master by the end of Grade 12 are: 1. Islamic Religious and Ethical Competences 2. Communicative Competences in Arabic Language 3. Communicative Competences in English and other Foreign Languages 3. Mathematical Competences 4. Social and Civic Competences 5. Scientific, Technological and Digital Competences 6. Personal Development and Learning to Learn Competences 7. Life and Work, Economic and Financial Competences
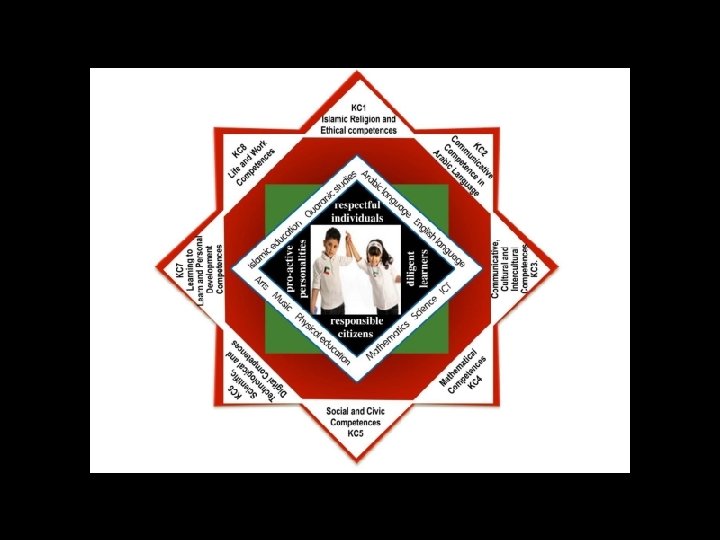

Key Competences The Key Competences are achieved gradually step by step, year by means of all that students learn in school. The levels achieved by the Key Competences by the end of grades 5 – 9 – 12 are developed in the Kuwait National Curriculum in order to let teachers, students, parents and society to know what they can expect from their students/children when they graduate a certain stage of the education system. (for an example, see Annex 9 – that presents the Key Competences as expected to be achieved by the end of grade 5).
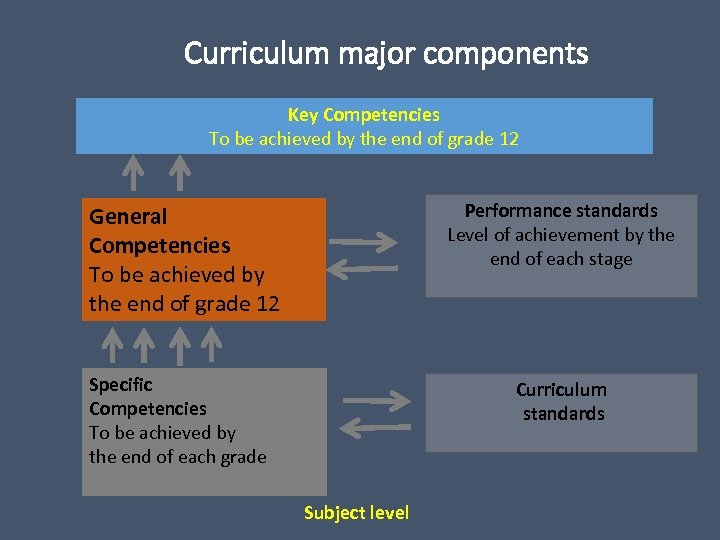
Curriculum major components Key Competencies To be achieved by the end of grade 12 Performance standards Level of achievement by the end of each stage General Competencies To be achieved by the end of grade 12 Specific Competencies To be achieved by the end of each grade Curriculum standards Subject level

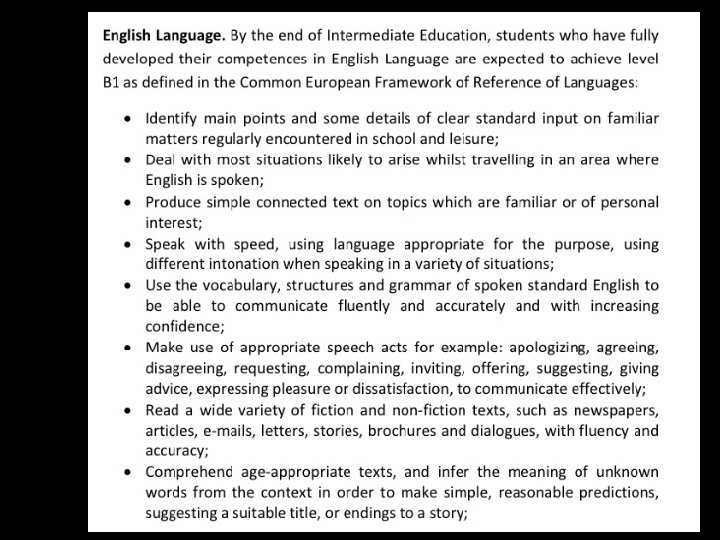
Kuwait National Curriculum and Standards English Language (Intermediate Stage) The document is addressed to teachers, students and parents, supervisors, school principals and Heads of departments, as well as to education policy makers, leaders and managers, working at different levels of the educational system. The Curriculum and Standards document is based on, and starts from the basic curriculum statements (vision, mission, philosophy, and principles) of the Kuwait National Curriculum Framework.
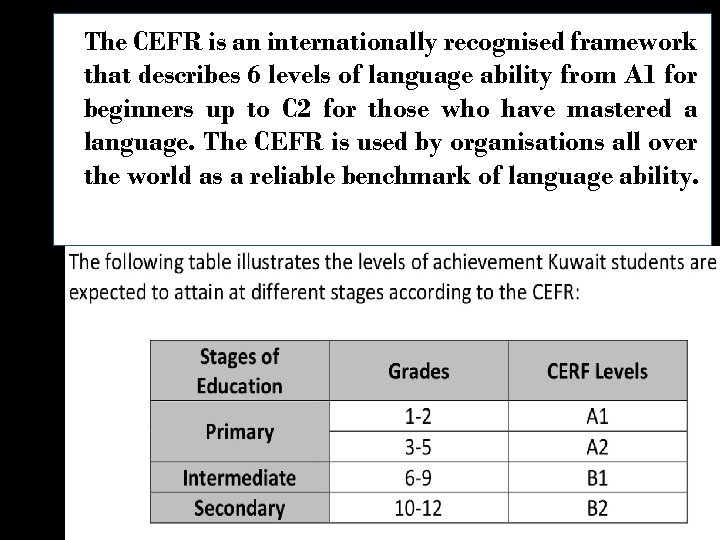
The CEFR is an internationally recognised framework that describes 6 levels of language ability from A 1 for beginners up to C 2 for those who have mastered a language. The CEFR is used by organisations all over the world as a reliable benchmark of language ability. www. themegaller y. com
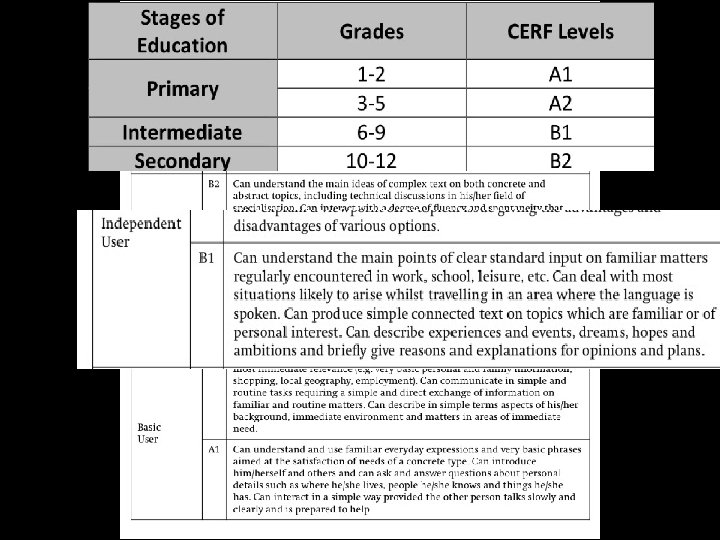
www. themegaller y. com

www. themegaller y. com


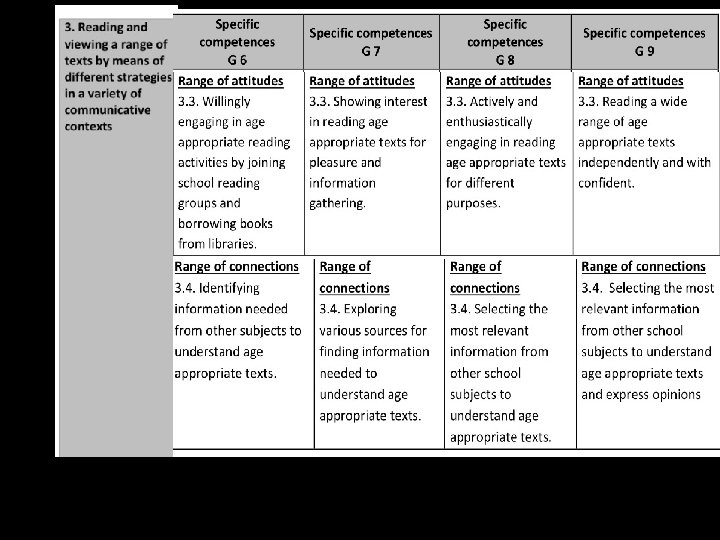
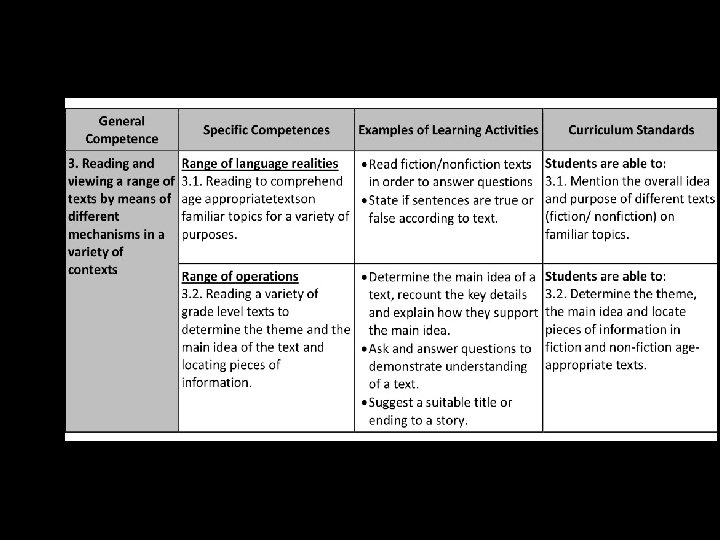
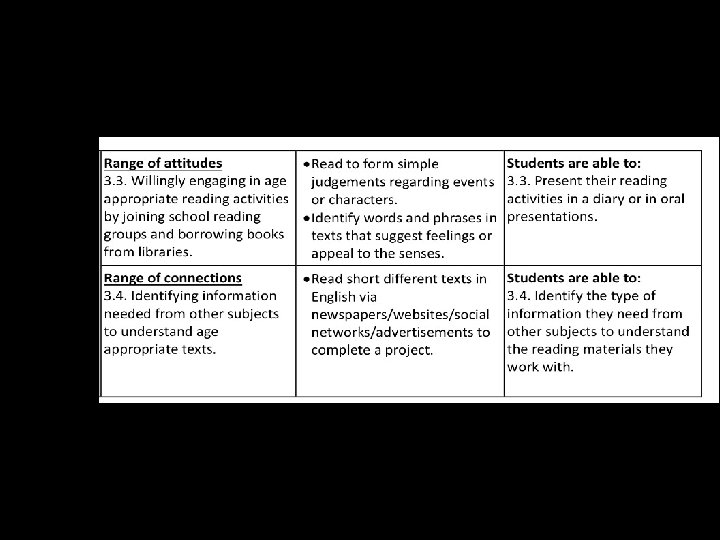
General Competences General competencies developed through the study of English • 1. Listening to oral messages by means of different strategies in a variety of contexts for effective comprehension • 2. Speaking by using strategies of individual and interactive speech in a variety of communicative contexts • 3. Reading and viewing a range of texts by means of different strategies in a variety of contexts • 4. Writing a range of texts adapted to a variety of communicative purposes



www. themegaller y. com
www. themegaller y. com

Preparing Teachers How should we prepare teachers? Continuous high quality professional development is critical to developing and maintaining high quality teachers. Ensure that all teachers novice or experienced have the chance to improve their classroom instruction by receiving ongoing training aimed at professional growth and better student outcomes. Placing greater emphasis on observing and evaluating teachers’ teaching skills and content knowledge in their actual classrooms throughout their careers.

Our expectations How should we prepare teachers? Developing teachers’ different teaching strategies to help them cope with curriculum changes. Predicting and overcoming difficulties following the implementation of the new curriculum. With experience, practice, assistance and training, teachers can learn and improve to become better teachers.

How should we prepare teachers? Teachers who are aware of the fact that first and foremost, quality teaching is evidenced by producing high levels of student learning. Teachers with skills that are much larger in scope than those necessary to simply transmit knowledge. Teachers showing a qualitative improvement towards: “professionalization”, having a better balance between theory and practice, broadening their pedagogical and didactic skills, creating links to research and utilizing new technologies.
How should we prepare teachers? Teachers who value each student as a unique person with individual needs who engage students in the learning process with inspiring energy. Teachers who are creative in teaching technique and willing to explore new approaches. Teachers who are good listeners to students and to their parents. Teachers who are continuous learners who are organized in presenting lessons, displaying efficient and effective classroom management and enjoying students and the learning environment.
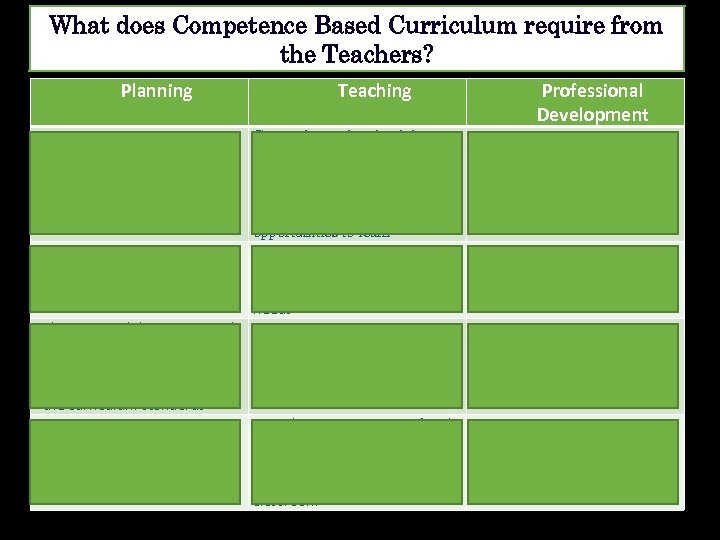
What does Competence Based Curriculum require from the Teachers? Planning Teaching Generating and maintaining students' motivation by Participating actively in supporting each student to planning the learning units discover his/her potentials and the annual plan providing sufficient opportunities to learn Choosing interactive methods Adapting the teaching style, of teaching on a daily basis to methodology and selected achieve the desired outcomes activities to cater for learners' needs Choosing and designing a wide Promoting student-centred range of activities that learning by facilitating shared, represent best the curricular cooperative and active learning contents and help to achieve and problem solving skills the curriculum standards Providing opportunities of real Planning the teaching-learning- life interaction and authentic assessment process within a communicative situations larger period of time inside and outside the classroom Professional Development Being actively involved in CPD programs to foster his/her teaching competencies in order to operate with the new curriculum Reflecting on his/her performance as a teacher frequently Accessing the experience of other teachers to exchange ideas Collaborating with other teachers of different subjects, school management and community

THANK YOU
a4e278e22683fe48ff23746cff499fe6.ppt