Клетки, ткани, органы иммунной системы.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Клетки, ткани, органы иммунной системы
Клетки, ткани, органы иммунной системы








 22. 2 MEGAKARYOCYTE Megakaryocytes are the precursor cells from which blood platelets derive. These gigantic cells undergo an elaborate fragmentation process that pinches off portions of the cell’s cytoplasm. These fragments are the platelets, which are then swept away in the blood stream. Platelets are important for blood coagulation at sites of injury.
22. 2 MEGAKARYOCYTE Megakaryocytes are the precursor cells from which blood platelets derive. These gigantic cells undergo an elaborate fragmentation process that pinches off portions of the cell’s cytoplasm. These fragments are the platelets, which are then swept away in the blood stream. Platelets are important for blood coagulation at sites of injury.
 15. 2 CHEMOTAXIS OF NEUTROPHILS These human neutrophils, taken from the blood of a graduate student, are mobile cells that will quickly migrate to sites of injury to help fight infection. They are attracted there by chemical signals that are released by other cells of the immune system or by invading microbes. In this experiment tiny amounts of chemoattractant are released from a micropipette. When neutrophils sense these compounds they polarize and move towards the source. When the source of the chemoattractant is moved, the neutrophil immediately sends out a new protrusion, and its cell body reorients towards the new location.
15. 2 CHEMOTAXIS OF NEUTROPHILS These human neutrophils, taken from the blood of a graduate student, are mobile cells that will quickly migrate to sites of injury to help fight infection. They are attracted there by chemical signals that are released by other cells of the immune system or by invading microbes. In this experiment tiny amounts of chemoattractant are released from a micropipette. When neutrophils sense these compounds they polarize and move towards the source. When the source of the chemoattractant is moved, the neutrophil immediately sends out a new protrusion, and its cell body reorients towards the new location.
 15. 3 NEUTROPHIL CHASE Neutrophils are white blood cells that hunt and kill bacteria. In this spread a neutrophil is seen in the midst of red blood cells. A Staphylococcus aureus bacterium has been added. The bacterium releases a chemoattractant that is sensed by the neutrophil. The neutrophil becomes polarized, and starts chasing the bacterium which, powered by its flagella, swims in a random path, seemingly avoiding its predator. Eventually, the neutrophil catches up with the bacterium and engulfs it by phagocytosis.
15. 3 NEUTROPHIL CHASE Neutrophils are white blood cells that hunt and kill bacteria. In this spread a neutrophil is seen in the midst of red blood cells. A Staphylococcus aureus bacterium has been added. The bacterium releases a chemoattractant that is sensed by the neutrophil. The neutrophil becomes polarized, and starts chasing the bacterium which, powered by its flagella, swims in a random path, seemingly avoiding its predator. Eventually, the neutrophil catches up with the bacterium and engulfs it by phagocytosis.
 24. 5 KILLER T-CELL Cytotoxic lymphocytes, also called killer T-cells, bind tightly to their target cells and then release toxic compounds by exocytosis into the cleft between the two cells. Here, a killer T-cell has attached to a fibroblast and proceeds to attack it. The fibroblast quickly retracts and rounds up. The movie is too short to tell whether it has actually been killed or will recover.
24. 5 KILLER T-CELL Cytotoxic lymphocytes, also called killer T-cells, bind tightly to their target cells and then release toxic compounds by exocytosis into the cleft between the two cells. Here, a killer T-cell has attached to a fibroblast and proceeds to attack it. The fibroblast quickly retracts and rounds up. The movie is too short to tell whether it has actually been killed or will recover.
 Кислородзависимый механизм бактерицидности 2/11/2018 16
Кислородзависимый механизм бактерицидности 2/11/2018 16









 Активация комплемента по классическому пути u Фермент С 1 состоит из 1 молекулы C 1 q (3 субъединицы), 2 молекул С 1 r, 2 молекул C 1 s
Активация комплемента по классическому пути u Фермент С 1 состоит из 1 молекулы C 1 q (3 субъединицы), 2 молекул С 1 r, 2 молекул C 1 s
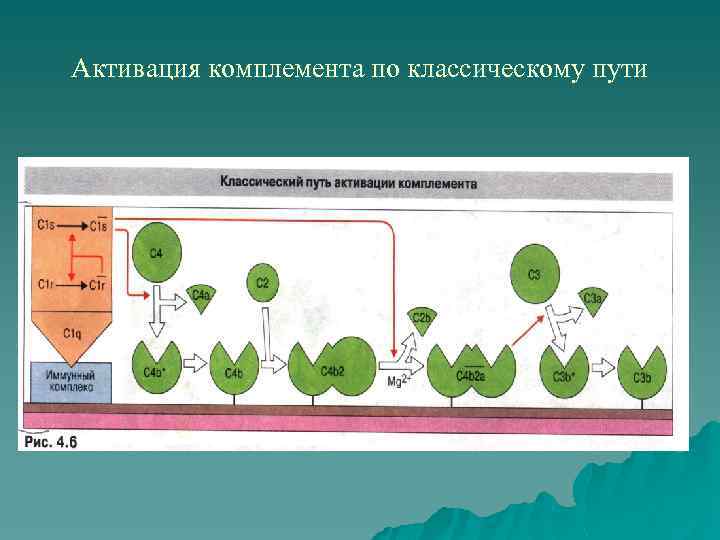 Активация комплемента по классическому пути
Активация комплемента по классическому пути
 Защита клеток хозяина u ФУД (усиливает диссоциацию с4 b 2 a, подавляет связывание с4 b с с2 ) u CD 59 (связывается с с8, препятствует присоединению с9)
Защита клеток хозяина u ФУД (усиливает диссоциацию с4 b 2 a, подавляет связывание с4 b с с2 ) u CD 59 (связывается с с8, препятствует присоединению с9)
 Интерфероны
Интерфероны

 ОСНОВНОЙ ЭФФЕКТ NS 5 A РЕЗИСТЕНТНОСТЬ ВГС К IFNa РЕАЛИЗУЕТСЯ ПОСРЕДСТВОМ РЕПРЕССИИ ПРОТЕИНКИНАЗЫ PKR ПОД ДЕЙСТВИЕМ NS 5 A ds. RNA NS 5 A P PKR e. IF 2 a P X PKR NS 5 A e. IF 2 a e. IF 2 b Трансляция e. IF 2 a P e. IF 2 b Нет трансляции
ОСНОВНОЙ ЭФФЕКТ NS 5 A РЕЗИСТЕНТНОСТЬ ВГС К IFNa РЕАЛИЗУЕТСЯ ПОСРЕДСТВОМ РЕПРЕССИИ ПРОТЕИНКИНАЗЫ PKR ПОД ДЕЙСТВИЕМ NS 5 A ds. RNA NS 5 A P PKR e. IF 2 a P X PKR NS 5 A e. IF 2 a e. IF 2 b Трансляция e. IF 2 a P e. IF 2 b Нет трансляции
 Воспаление u Реакция организма, обеспечивающая привлечение лейкоцитов и растворимых факторов плазмы (комплемент, антитела) в очаг инфекции или повреждения тканей. Проявление – кровенаполнения капиляров, увеличение проницаемости для макромолекул, усиленная миграция лейкоцитов. Обеспечивается медиаторами воспаления.
Воспаление u Реакция организма, обеспечивающая привлечение лейкоцитов и растворимых факторов плазмы (комплемент, антитела) в очаг инфекции или повреждения тканей. Проявление – кровенаполнения капиляров, увеличение проницаемости для макромолекул, усиленная миграция лейкоцитов. Обеспечивается медиаторами воспаления.



