Lecture_1_3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Kirovograd Flight academy National aviation university ГЛАУ AIR NAVIGATION for the specialty "Operation of aircraft" Section 1 (3 semester) Basics of Air Navigation Kirovograd 2013
Kirovograd Flight academy National aviation university ГЛАУ AIR NAVIGATION for the specialty "Operation of aircraft" Section 1 (3 semester) Basics of Air Navigation Kirovograd 2013
 List of References Марков В. І. "Воздушная навигация", Кіровоград, КОД, 2003, 2006, 2009, 2011 рр. , «Повітряна навігація» , 2004 р- переклад на українську. Марков В. І. , підручник "Розрахунок безпечних траєкторій польоту в РА", ДЛАУ ГЛАУ 2000 р, 2010 р. Марков В. І. "Навігація ПС з використанням GPS", ДЛАУ, 2001 р. Жалінський О. І. , Мітькін А. В. Методичні рекомендації по виконанню курсової роботи «Навігаційне забезпечення польоту по заданному маршруту» . Кіровоград, ДЛАУ. 2010 р. Чікалов С. О. «Картография с элементами топографии» Уч. пособие. ГЛАУ 2005 г. Марков В. І. , «Навигация на Мн. ВЛ» . Кіровоград, ДЛАУ. 2010 р. Марков В. І. , «Навигация и в трехмерном пространстве» . Кіровоград, ДЛАУ. 2010 р. Additional literature Бєлан В. В. "Авіаційна картографія" Учбовий посібник, 1993 р. Анікін А. М. , Бєлкін А. М. , Ліпін А. В. Повітряна навігація та аеронавігаційне забезпечення польотів. М. : Транспорт , 1992 г. Хівріч І. Г. , Бєлкін А. М. Автоматизоване водіння повітряних суден. М. : Транспорт , 1985 р. Чорний М. А. , Кораблін В. І. Повітряна навігація М. Транспорт 1991 р. Міронов Н. Ф. "Штурманское обеспечение полетов в гражданской авиации" Машиностроение, 1987 р.
List of References Марков В. І. "Воздушная навигация", Кіровоград, КОД, 2003, 2006, 2009, 2011 рр. , «Повітряна навігація» , 2004 р- переклад на українську. Марков В. І. , підручник "Розрахунок безпечних траєкторій польоту в РА", ДЛАУ ГЛАУ 2000 р, 2010 р. Марков В. І. "Навігація ПС з використанням GPS", ДЛАУ, 2001 р. Жалінський О. І. , Мітькін А. В. Методичні рекомендації по виконанню курсової роботи «Навігаційне забезпечення польоту по заданному маршруту» . Кіровоград, ДЛАУ. 2010 р. Чікалов С. О. «Картография с элементами топографии» Уч. пособие. ГЛАУ 2005 г. Марков В. І. , «Навигация на Мн. ВЛ» . Кіровоград, ДЛАУ. 2010 р. Марков В. І. , «Навигация и в трехмерном пространстве» . Кіровоград, ДЛАУ. 2010 р. Additional literature Бєлан В. В. "Авіаційна картографія" Учбовий посібник, 1993 р. Анікін А. М. , Бєлкін А. М. , Ліпін А. В. Повітряна навігація та аеронавігаційне забезпечення польотів. М. : Транспорт , 1992 г. Хівріч І. Г. , Бєлкін А. М. Автоматизоване водіння повітряних суден. М. : Транспорт , 1985 р. Чорний М. А. , Кораблін В. І. Повітряна навігація М. Транспорт 1991 р. Міронов Н. Ф. "Штурманское обеспечение полетов в гражданской авиации" Машиностроение, 1987 р.
 Lecture 1. 3. Topic 1. Cartographic flight support. Total - 18 hours. Lectures - 6 h, Practical work - 6 h, Independent work - 6 h Aeronautical Charts ICAO ГЛАУ A study of the educational material of the subject, students will KNOW: - Classification of the ICAO charts, types of charts; - The appointment, content, scope and accuracy of the different types of charts ICAO. Be able to: - Determine the type of chart ICAO depending on a particular task - Use the chart ICAO - Determine the scale of the map. Plan of the lecture Introduction 1. Type the ICAO aeronautical charts. General requirements for the information published by ICAO chart. 2. Purpose, content, format, scale and accuracy of information on maps ICAO. Explore on their own and take notes on the answers to questions 1 - 19: Output
Lecture 1. 3. Topic 1. Cartographic flight support. Total - 18 hours. Lectures - 6 h, Practical work - 6 h, Independent work - 6 h Aeronautical Charts ICAO ГЛАУ A study of the educational material of the subject, students will KNOW: - Classification of the ICAO charts, types of charts; - The appointment, content, scope and accuracy of the different types of charts ICAO. Be able to: - Determine the type of chart ICAO depending on a particular task - Use the chart ICAO - Determine the scale of the map. Plan of the lecture Introduction 1. Type the ICAO aeronautical charts. General requirements for the information published by ICAO chart. 2. Purpose, content, format, scale and accuracy of information on maps ICAO. Explore on their own and take notes on the answers to questions 1 - 19: Output
 1. 1. Type the ICAO aeronautical charts. General requirements for the information published by ICAO chart ГЛАУ s TYPES OF PROJECTION There are 3 general types of projection surfaces: s > Azimuthal/Plane s > Cylindrical s > Conical.
1. 1. Type the ICAO aeronautical charts. General requirements for the information published by ICAO chart ГЛАУ s TYPES OF PROJECTION There are 3 general types of projection surfaces: s > Azimuthal/Plane s > Cylindrical s > Conical.
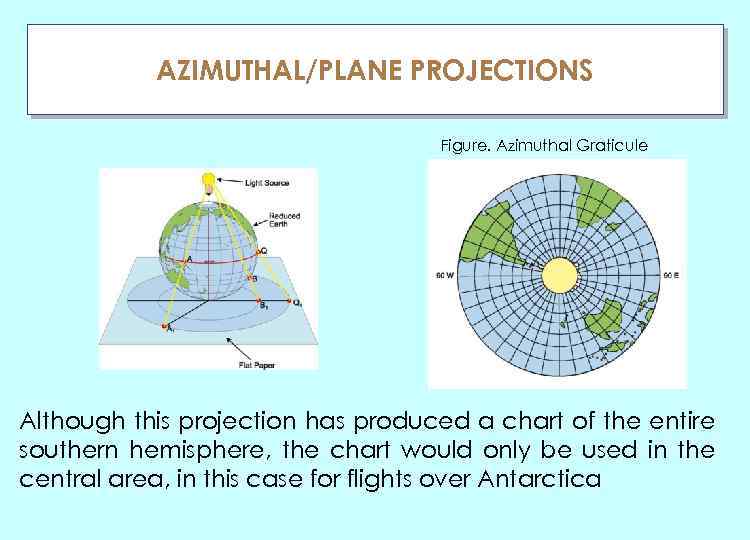 AZIMUTHAL/PLANE PROJECTIONS ГЛАУ Figure. Azimuthal Graticule Although this projection has produced a chart of the entire southern hemisphere, the chart would only be used in the central area, in this case for flights over Antarctica
AZIMUTHAL/PLANE PROJECTIONS ГЛАУ Figure. Azimuthal Graticule Although this projection has produced a chart of the entire southern hemisphere, the chart would only be used in the central area, in this case for flights over Antarctica
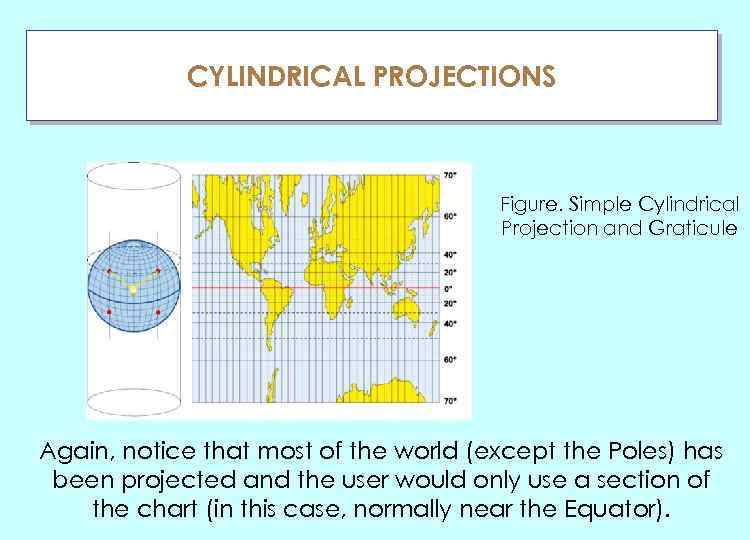 CYLINDRICAL PROJECTIONS ГЛАУ Figure. Simple Cylindrical Projection and Graticule Again, notice that most of the world (except the Poles) has been projected and the user would only use a section of the chart (in this case, normally near the Equator).
CYLINDRICAL PROJECTIONS ГЛАУ Figure. Simple Cylindrical Projection and Graticule Again, notice that most of the world (except the Poles) has been projected and the user would only use a section of the chart (in this case, normally near the Equator).
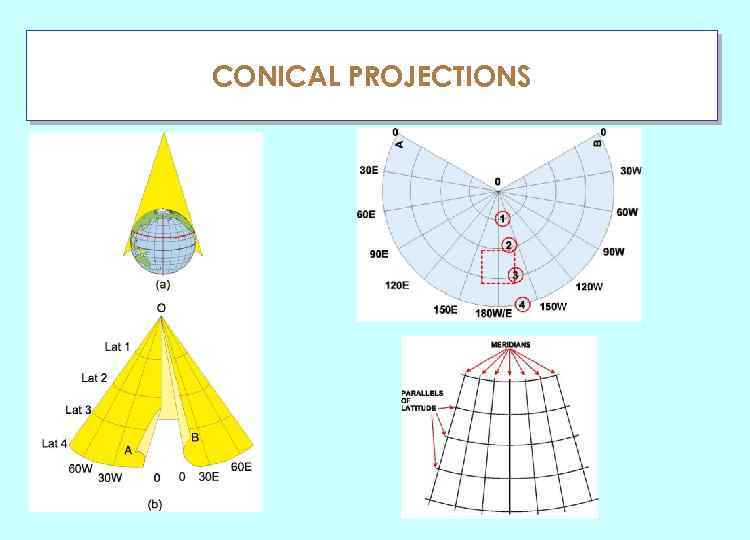 CONICAL PROJECTIONS ГЛАУ
CONICAL PROJECTIONS ГЛАУ
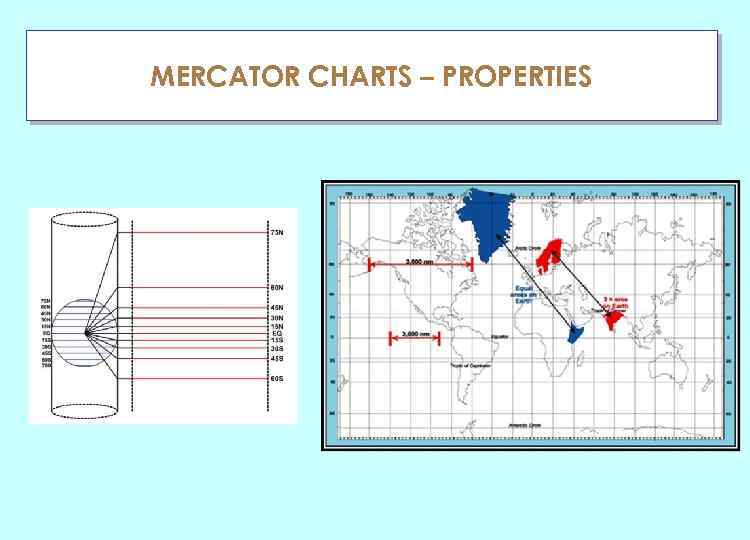 MERCATOR CHARTS – PROPERTIES ГЛАУ
MERCATOR CHARTS – PROPERTIES ГЛАУ
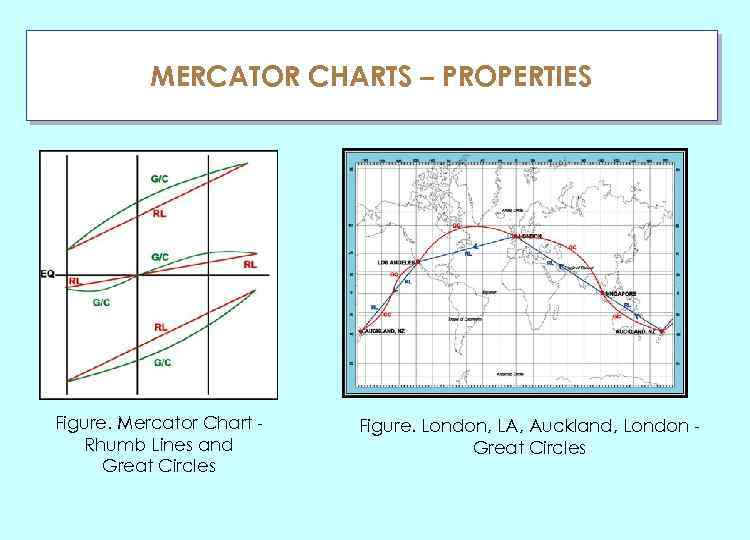 MERCATOR CHARTS – PROPERTIES ГЛАУ Figure. Mercator Chart Rhumb Lines and Great Circles Figure. London, LA, Auckland, London Great Circles
MERCATOR CHARTS – PROPERTIES ГЛАУ Figure. Mercator Chart Rhumb Lines and Great Circles Figure. London, LA, Auckland, London Great Circles
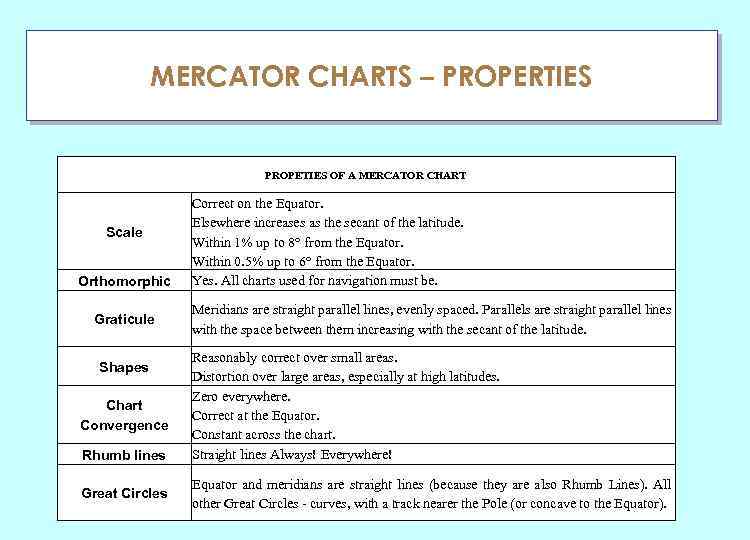 MERCATOR CHARTS – PROPERTIES ГЛАУ PROPETIES OF A MERCATOR CHART Scale Orthomorphic Graticule Shapes Chart Convergence Rhumb lines Great Circles Correct on the Equator. Elsewhere increases as the secant of the latitude. Within 1% up to 8° from the Equator. Within 0. 5% up to 6° from the Equator. Yes. All charts used for navigation must be. Meridians are straight parallel lines, evenly spaced. Parallels are straight parallel lines with the space between them increasing with the secant of the latitude. Reasonably correct over small areas. Distortion over large areas, especially at high latitudes. Zero everywhere. Correct at the Equator. Constant across the chart. Straight lines Always! Everywhere! Equator and meridians are straight lines (because they are also Rhumb Lines). All other Great Circles - curves, with a track nearer the Pole (or concave to the Equator).
MERCATOR CHARTS – PROPERTIES ГЛАУ PROPETIES OF A MERCATOR CHART Scale Orthomorphic Graticule Shapes Chart Convergence Rhumb lines Great Circles Correct on the Equator. Elsewhere increases as the secant of the latitude. Within 1% up to 8° from the Equator. Within 0. 5% up to 6° from the Equator. Yes. All charts used for navigation must be. Meridians are straight parallel lines, evenly spaced. Parallels are straight parallel lines with the space between them increasing with the secant of the latitude. Reasonably correct over small areas. Distortion over large areas, especially at high latitudes. Zero everywhere. Correct at the Equator. Constant across the chart. Straight lines Always! Everywhere! Equator and meridians are straight lines (because they are also Rhumb Lines). All other Great Circles - curves, with a track nearer the Pole (or concave to the Equator).
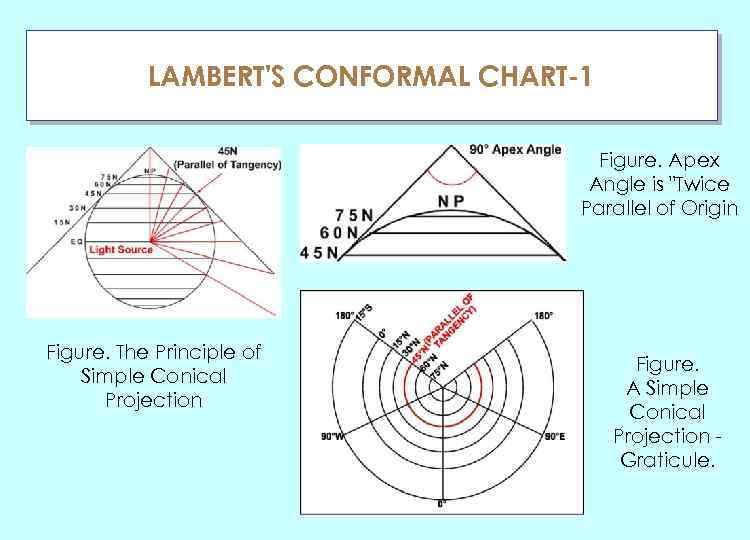 LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-1 ГЛАУ Figure. Apex Angle is "Twice Parallel of Origin Figure. The Principle of Simple Conical Projection Figure. A Simple Conical Projection Graticule.
LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-1 ГЛАУ Figure. Apex Angle is "Twice Parallel of Origin Figure. The Principle of Simple Conical Projection Figure. A Simple Conical Projection Graticule.
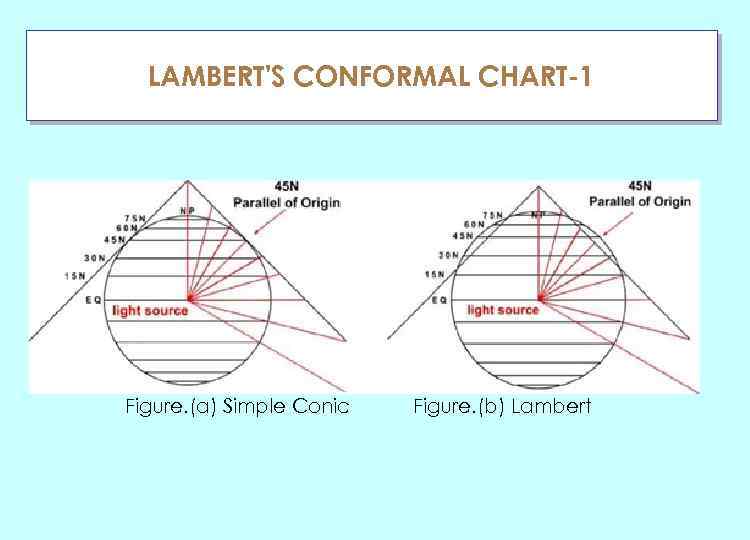 LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-1 ГЛАУ Figure. (a) Simple Conic Figure. (b) Lambert
LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-1 ГЛАУ Figure. (a) Simple Conic Figure. (b) Lambert
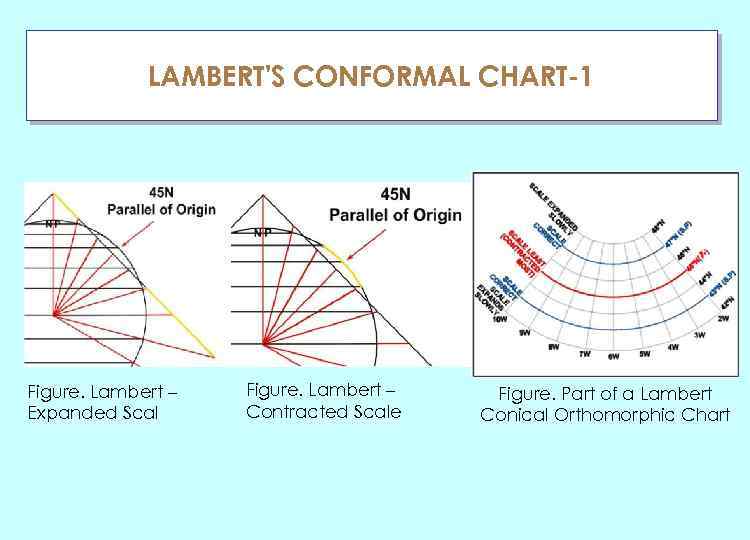 LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-1 ГЛАУ Figure. Lambert – Expanded Scal Figure. Lambert – Contracted Scale Figure. Part of a Lambert Conical Orthomorphic Chart
LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-1 ГЛАУ Figure. Lambert – Expanded Scal Figure. Lambert – Contracted Scale Figure. Part of a Lambert Conical Orthomorphic Chart
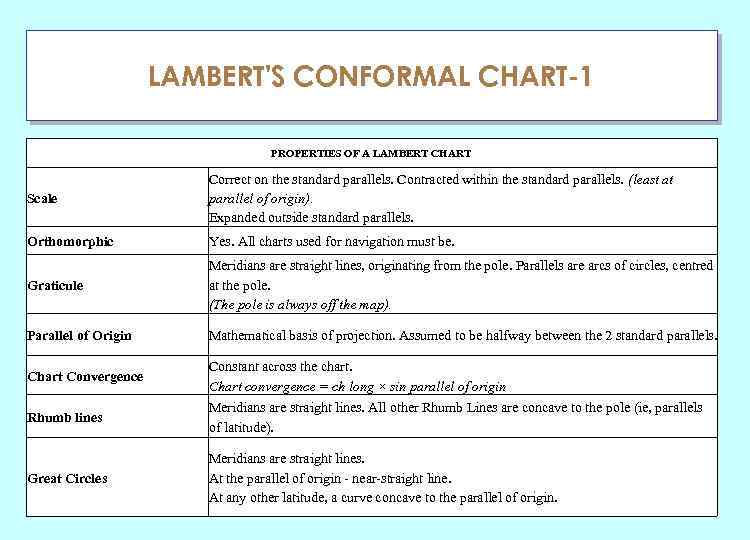 LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-1 ГЛАУ PROPERTIES OF A LAMBERT CHART Scale Correct on the standard parallels. Contracted within the standard parallels. (least at parallel of origin). Expanded outside standard parallels. Orthomorphic Yes. All charts used for navigation must be. Graticule Meridians are straight lines, originating from the pole. Parallels are arcs of circles, centred at the pole. (The pole is always off the map). Parallel of Origin Mathematical basis of projection. Assumed to be halfway between the 2 standard parallels. Chart Convergence Constant across the chart. Chart convergence = ch long × sin parallel of origin Rhumb lines Meridians are straight lines. All other Rhumb Lines are concave to the pole (ie, parallels of latitude). Great Circles Meridians are straight lines. At the parallel of origin - near-straight line. At any other latitude, a curve concave to the parallel of origin.
LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-1 ГЛАУ PROPERTIES OF A LAMBERT CHART Scale Correct on the standard parallels. Contracted within the standard parallels. (least at parallel of origin). Expanded outside standard parallels. Orthomorphic Yes. All charts used for navigation must be. Graticule Meridians are straight lines, originating from the pole. Parallels are arcs of circles, centred at the pole. (The pole is always off the map). Parallel of Origin Mathematical basis of projection. Assumed to be halfway between the 2 standard parallels. Chart Convergence Constant across the chart. Chart convergence = ch long × sin parallel of origin Rhumb lines Meridians are straight lines. All other Rhumb Lines are concave to the pole (ie, parallels of latitude). Great Circles Meridians are straight lines. At the parallel of origin - near-straight line. At any other latitude, a curve concave to the parallel of origin.
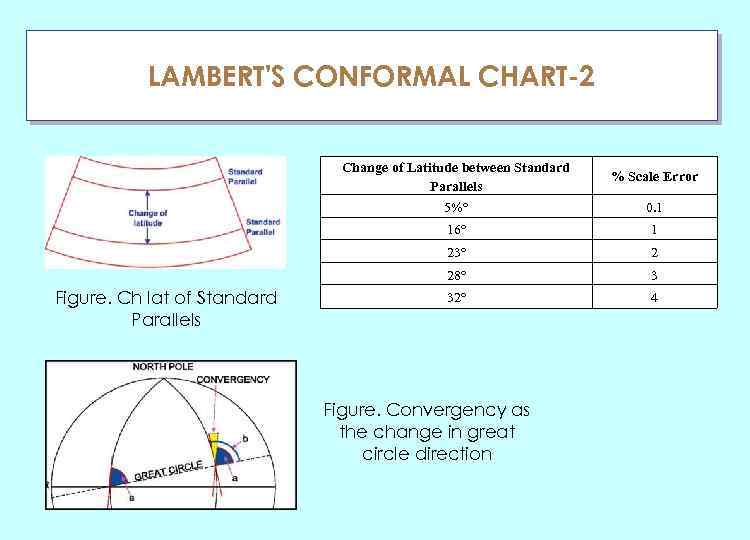 LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-2 ГЛАУ Change of Latitude between Standard Parallels 5%° % Scale Error 0. 1 16° 23° 2 28° Figure. Ch lat of Standard Parallels 1 3 32° 4 Figure. Convergency as the change in great circle direction
LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-2 ГЛАУ Change of Latitude between Standard Parallels 5%° % Scale Error 0. 1 16° 23° 2 28° Figure. Ch lat of Standard Parallels 1 3 32° 4 Figure. Convergency as the change in great circle direction
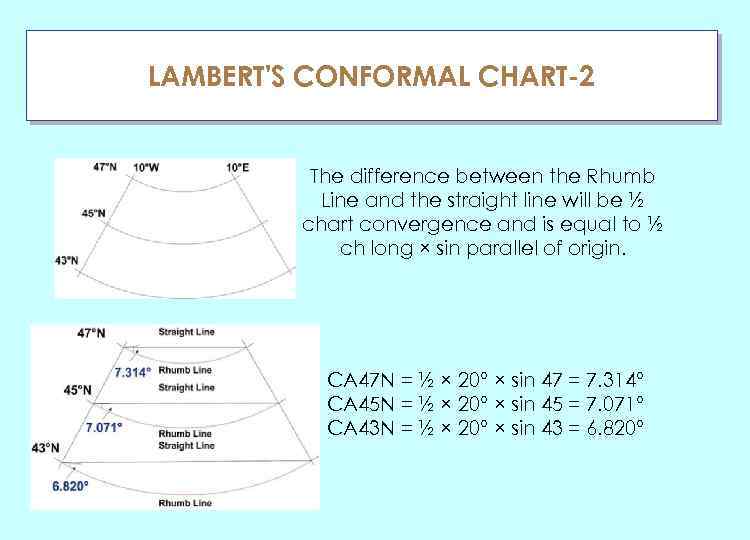 LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-2 ГЛАУ The difference between the Rhumb Line and the straight line will be ½ chart convergence and is equal to ½ ch long × sin parallel of origin. CA 47 N = ½ × 20° × sin 47 = 7. 314° CA 45 N = ½ × 20° × sin 45 = 7. 071° CA 43 N = ½ × 20° × sin 43 = 6. 820°
LAMBERT'S CONFORMAL CHART-2 ГЛАУ The difference between the Rhumb Line and the straight line will be ½ chart convergence and is equal to ½ ch long × sin parallel of origin. CA 47 N = ½ × 20° × sin 47 = 7. 314° CA 45 N = ½ × 20° × sin 45 = 7. 071° CA 43 N = ½ × 20° × sin 43 = 6. 820°
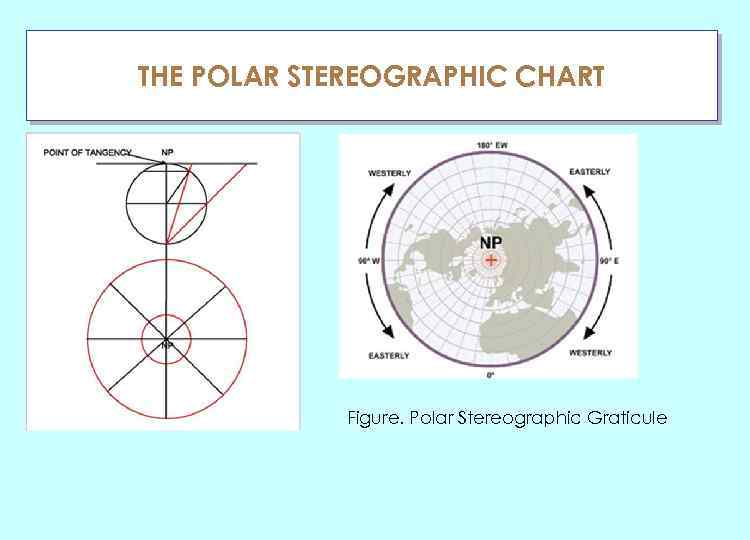 THE POLAR STEREOGRAPHIC CHART ГЛАУ Figure. Polar Stereographic Graticule
THE POLAR STEREOGRAPHIC CHART ГЛАУ Figure. Polar Stereographic Graticule
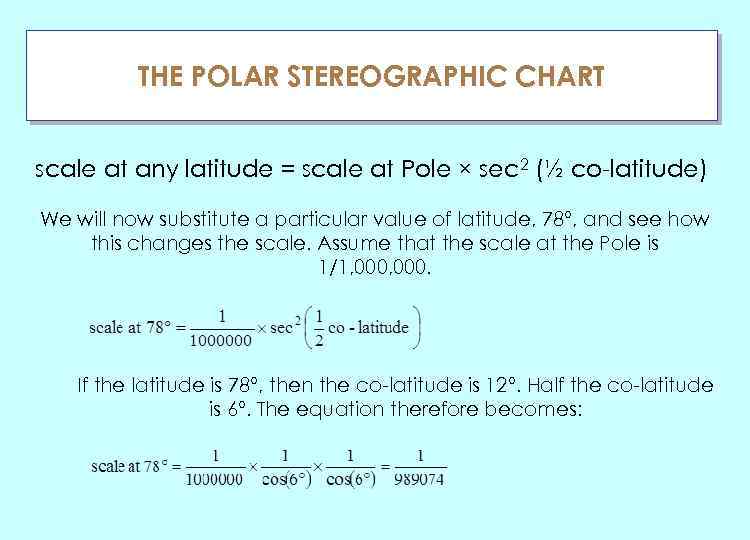 THE POLAR STEREOGRAPHIC CHART ГЛАУ scale at any latitude = scale at Pole × sec 2 (½ co-latitude) We will now substitute a particular value of latitude, 78°, and see how this changes the scale. Assume that the scale at the Pole is 1/1, 000. If the latitude is 78°, then the co-latitude is 12°. Half the co-latitude is 6°. The equation therefore becomes:
THE POLAR STEREOGRAPHIC CHART ГЛАУ scale at any latitude = scale at Pole × sec 2 (½ co-latitude) We will now substitute a particular value of latitude, 78°, and see how this changes the scale. Assume that the scale at the Pole is 1/1, 000. If the latitude is 78°, then the co-latitude is 12°. Half the co-latitude is 6°. The equation therefore becomes:
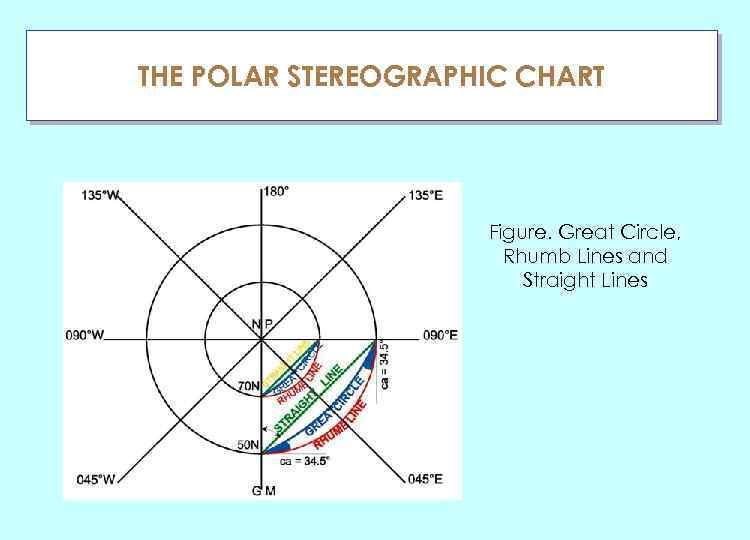 THE POLAR STEREOGRAPHIC CHART ГЛАУ Figure. Great Circle, Rhumb Lines and Straight Lines
THE POLAR STEREOGRAPHIC CHART ГЛАУ Figure. Great Circle, Rhumb Lines and Straight Lines
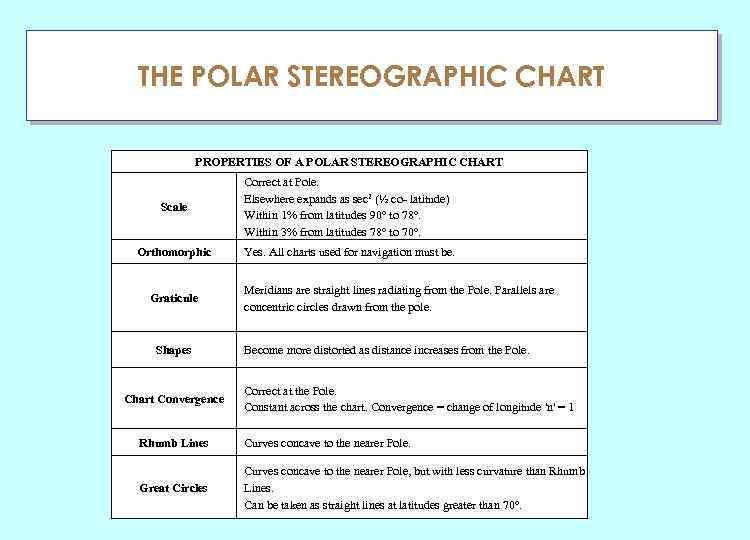 THE POLAR STEREOGRAPHIC CHART ГЛАУ PROPERTIES OF A POLAR STEREOGRAPHIC CHART Scale Correct at Pole. Elsewhere expands as sec 2 (½ co- latitude) Within 1% from latitudes 90° to 78°. Within 3% from latitudes 78° to 70°. Orthomorphic Yes. All charts used for navigation must be. Graticule Shapes Chart Convergence Meridians are straight lines radiating from the Pole. Parallels are concentric circles drawn from the pole. Become more distorted as distance increases from the Pole. Correct at the Pole. Constant across the chart. Convergence = change of longitude 'n' = 1 Rhumb Lines Curves concave to the nearer Pole. Great Circles Curves concave to the nearer Pole, but with less curvature than Rhumb Lines. Can be taken as straight lines at latitudes greater than 70°.
THE POLAR STEREOGRAPHIC CHART ГЛАУ PROPERTIES OF A POLAR STEREOGRAPHIC CHART Scale Correct at Pole. Elsewhere expands as sec 2 (½ co- latitude) Within 1% from latitudes 90° to 78°. Within 3% from latitudes 78° to 70°. Orthomorphic Yes. All charts used for navigation must be. Graticule Shapes Chart Convergence Meridians are straight lines radiating from the Pole. Parallels are concentric circles drawn from the pole. Become more distorted as distance increases from the Pole. Correct at the Pole. Constant across the chart. Convergence = change of longitude 'n' = 1 Rhumb Lines Curves concave to the nearer Pole. Great Circles Curves concave to the nearer Pole, but with less curvature than Rhumb Lines. Can be taken as straight lines at latitudes greater than 70°.
 Map ГЛАУ Map - reduced constructed by mathematical laws, the image of large areas of the earth's surface or the entire earth's surface on a plane. - Marginalia (font) registration card - the title ; - Coordinate (degree) grid - orienteering maps in relation to the cardinal points , scale, - Signs and symbols , and accompanied by a legend. - Elements of the framework (eg , coastlines ). - Special load - depending on the purpose of the map
Map ГЛАУ Map - reduced constructed by mathematical laws, the image of large areas of the earth's surface or the entire earth's surface on a plane. - Marginalia (font) registration card - the title ; - Coordinate (degree) grid - orienteering maps in relation to the cardinal points , scale, - Signs and symbols , and accompanied by a legend. - Elements of the framework (eg , coastlines ). - Special load - depending on the purpose of the map
 Map ГЛАУ Aeronautical charts are meant for planning the preparation and implementation of aviation. Map content (load ) - the degree of the topographic terrain elements on it , and other information necessary for practical purposes ( for the intended purpose of this type of card ) - ANI
Map ГЛАУ Aeronautical charts are meant for planning the preparation and implementation of aviation. Map content (load ) - the degree of the topographic terrain elements on it , and other information necessary for practical purposes ( for the intended purpose of this type of card ) - ANI
 Map ГЛАУ I. Topographic load II. Aeronautical Information ( ANI ) The information published on the maps ICAO: Performance standards for cards 1. Names 2. Marginal notes ( Other information ) 3. Symbols. Abbreviations 4. Units of measurement 5. The scale and projection 6. The dating of the Aeronautical Information 7. Writing place names. Fonts 8. The state borders 9. The relief ( topography) and man-made structures 10. Coloring 11. Prohibited areas, restricted and danger areas 12. Types of ATS airspace 13. Air data 14. Magnetic declination 15. Common frame of reference
Map ГЛАУ I. Topographic load II. Aeronautical Information ( ANI ) The information published on the maps ICAO: Performance standards for cards 1. Names 2. Marginal notes ( Other information ) 3. Symbols. Abbreviations 4. Units of measurement 5. The scale and projection 6. The dating of the Aeronautical Information 7. Writing place names. Fonts 8. The state borders 9. The relief ( topography) and man-made structures 10. Coloring 11. Prohibited areas, restricted and danger areas 12. Types of ATS airspace 13. Air data 14. Magnetic declination 15. Common frame of reference
 Examine yourself questions: ГЛАУ s 3. Purpose, content, format, scale and accuracy of information on maps ICAO. законспектировать ответы на вопросы 1. Какие из 17 типов карт, рекомендованных ICAO являются обязательными? 2. В каком случае издается карта района? 3. В каком случае издается карта SID? 4. В каком случае издается карта STAR? 5. В каком случае издается карта визуального захода на посадку? 6. Для каких целей предназначена карта аэродромных препятствий типа А? 7. В каких случаях карта типа А не публикуется и где об этом публикуется уведомление? 8. Какое буквенное сокращение используется для объявления о том, что ВПП не используется в данном направлении взлета? 9. Какие препятствия в зоне взлета называются существенными? 10. Для каких целей предназначены карты аэродромных препятствий типа В? 11. Какое назначение карт аэродромных препятствий типа С (карта местности и препятствий в РА) в чем их отличие от карт типа А и В? 12. В каких случаях не требуется карта типа С (карта местности и препятствий в РА)? 13. Обязательна ли к изданию карта местности для точного захода на посадку, для каких категорий систем захода и каково ее назначения при определении ВПР? 14. Какая информация в плане и в профиль публикуется на карте местности для точного захода на посадку? 15. Как обозначены движущиеся объекты и при какой их высоте на карте местности для точного захода на посадку? 16. В каких случаях для одного и того же района издаются отдельные маршрутные карты? 17. Какая картографическая проекция применяется при издании маршрутных карт? 18. Как и какая информация о магнитном склонении публикуется на маршрутной карте ICAO? 19. Какой меридиан в качестве опорного, использован для пеленгов, ПУ и радиалов опубликованных на маршрутной карте?
Examine yourself questions: ГЛАУ s 3. Purpose, content, format, scale and accuracy of information on maps ICAO. законспектировать ответы на вопросы 1. Какие из 17 типов карт, рекомендованных ICAO являются обязательными? 2. В каком случае издается карта района? 3. В каком случае издается карта SID? 4. В каком случае издается карта STAR? 5. В каком случае издается карта визуального захода на посадку? 6. Для каких целей предназначена карта аэродромных препятствий типа А? 7. В каких случаях карта типа А не публикуется и где об этом публикуется уведомление? 8. Какое буквенное сокращение используется для объявления о том, что ВПП не используется в данном направлении взлета? 9. Какие препятствия в зоне взлета называются существенными? 10. Для каких целей предназначены карты аэродромных препятствий типа В? 11. Какое назначение карт аэродромных препятствий типа С (карта местности и препятствий в РА) в чем их отличие от карт типа А и В? 12. В каких случаях не требуется карта типа С (карта местности и препятствий в РА)? 13. Обязательна ли к изданию карта местности для точного захода на посадку, для каких категорий систем захода и каково ее назначения при определении ВПР? 14. Какая информация в плане и в профиль публикуется на карте местности для точного захода на посадку? 15. Как обозначены движущиеся объекты и при какой их высоте на карте местности для точного захода на посадку? 16. В каких случаях для одного и того же района издаются отдельные маршрутные карты? 17. Какая картографическая проекция применяется при издании маршрутных карт? 18. Как и какая информация о магнитном склонении публикуется на маршрутной карте ICAO? 19. Какой меридиан в качестве опорного, использован для пеленгов, ПУ и радиалов опубликованных на маршрутной карте?


