
Kingdom of Cambodia Nation Religion King Ministry of Labour and Vocational Training Directorate General of TVET Current Status & Future TVET Policy Direction 02 November 2011 Mr. TEP OEUN, Deputy Director General Directorate General for Technical and Vocational Education and Training Ministry of Labour and Vocational Training

Contents 1. Introductions 2. Challenges/Issues 3. Policy & Planning for TVET Development 4. Cambodia TVET outcomes

1. Introduction 1. 1 Goal: Poverty Reduction • Providing skills training, • Creating jobs, • Improving productivity, Increasing Incomes

1. 2 Government policy in TVET Track 1: Poverty Reduction-basic skills for the rural poor to improve family income. Track 2: Supporting Industrial Development-higher level skills as requested by industry or required in the future to attract industry.

1. 3 Type of Skills Training Formal Training Courses • Certificate Level I, II, & III • Diploma Degree • Bachelor Degree Non-formal Training Courses • • Samdech Techo’s Special Fund • National Training Fund Voucher Skill Training Program • Post-harvest Technology Skills Bridging Program • Apprenticeship Training Special Training Needs Source: TVET programs for 2010 -2011, Department of TVETM
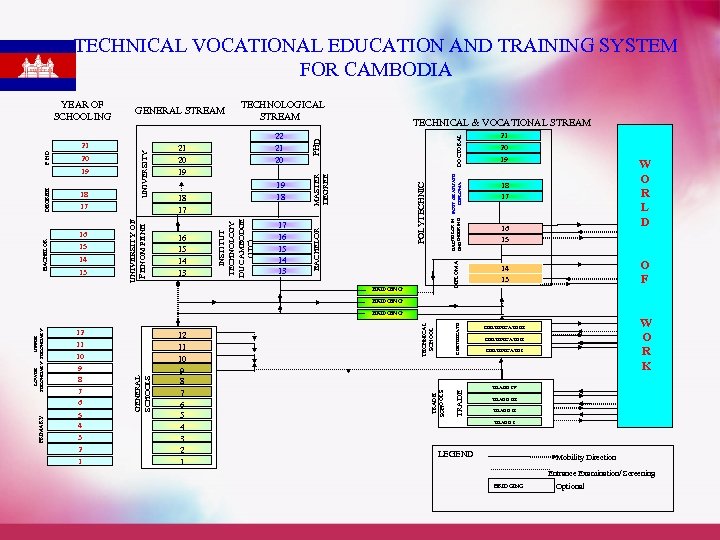
TECHNICAL VOCATIONAL EDUCATION AND TRAINING SYSTEM FOR CAMBODIA 14 13 DOCTORAL BACHELOR IN POST GRATUATE ENGINEERING DIPLOMA 15 16 15 14 13 17 16 15 14 13 DIPLOMA BACHELOR 16 18 17 POLYTECHNIC 17 19 18 21 20 19 TECHNICAL & VOCATIONAL STREAM PHD 18 22 21 20 BACHELOR DEGREE 19 UNIVERSITY 20 UNIVERSITY OF PHNOM PENH PHD 21 TECHNOLOGICAL STREAM MASTER DEGREE GENERAL STREAM INSTITUT TECHNOLOGY DU CAMBODGE (ITC) YEAR OF SCHOOLING BRIDGING 21 20 19 W O R L D 18 17 16 15 O F 14 13 BRIDGING 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 CERTIFICATE TECHNICAL SCHOOL 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 W O R K CERTIFICATE III CERTIFICATE I TRADE IV TRADE 9 8 GENERAL SCHOOLS 12 11 10 TRADE SCHOOLS PRIMARY LOWER UPPER SECONDARY BRIDGING TRADE III TRADE I LEGEND Mobility Direction Entrance Examination/ Screening BRIDGING Optional
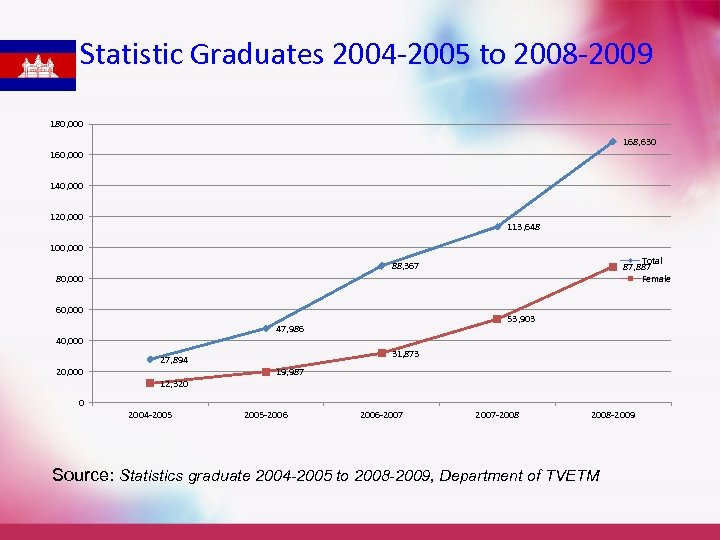
Statistic Graduates 2004 -2005 to 2008 -2009 180, 000 168, 630 160, 000 140, 000 120, 000 113, 648 100, 000 Total 87, 887 Female 88, 367 80, 000 60, 000 53, 903 47, 986 40, 000 31, 873 27, 894 20, 000 12, 320 19, 987 0 2004 -2005 -2006 -2007 -2008 -2009 Source: Statistics graduate 2004 -2005 to 2008 -2009, Department of TVETM
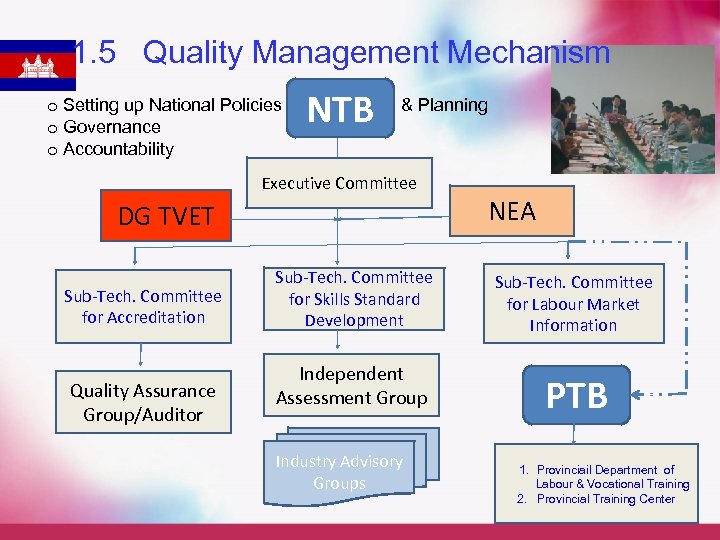
1. 5 Quality Management Mechanism o Setting up National Policies o Governance o Accountability NTB & Planning Executive Committee NEA DG TVET Sub-Tech. Committee for Accreditation Quality Assurance Group/Auditor Sub-Tech. Committee for Skills Standard Development Independent Assessment Group Industry Advisory Groups Sub-Tech. Committee for Labour Market Information PTB 1. Provinciail Department of Labour & Vocational Training 2. Provincial Training Center
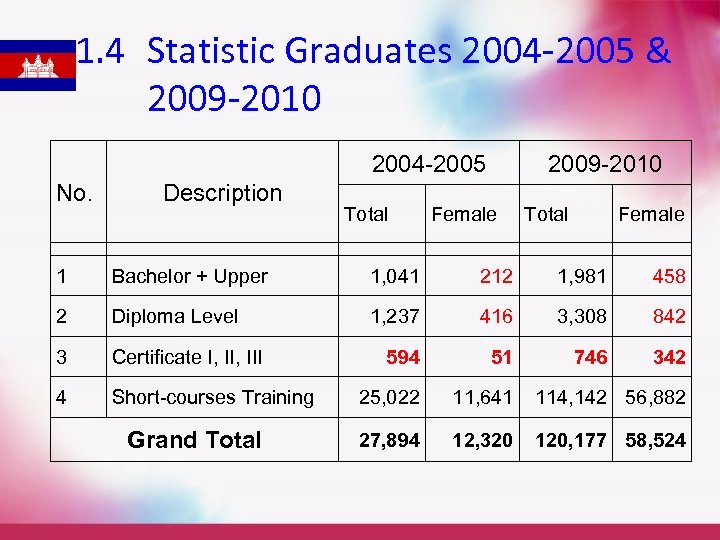
1. 4 Statistic Graduates 2004 -2005 & 2009 -2010 2004 -2005 No. Description Total 2009 -2010 Female Total Female 1 Bachelor + Upper 1, 041 212 1, 981 458 2 Diploma Level 1, 237 416 3, 308 842 3 Certificate I, III 594 51 746 342 4 Short-courses Training 25, 022 11, 641 114, 142 56, 882 27, 894 12, 320 120, 177 58, 524 Grand Total

1. 6 TVET Projects 1. STVET/ADB Grant No. 0178 CAM (2010 -2015) - Formal training program that are more relevant to industry Expanding and better quality non-formal training program Strengthening institutional capacity to plan & manage TVET 2. JFPR/ADB No. 9133 CAM (2010 -2012) - Post-harvest technology, food processing, and marketing, Skills Bridging Program for Poor Rural Area - Strengthening capacity building of TVET - ILO (Job Centers, Gender Mainstreaming) Connecting School, ITE (2011 -2013) 3. JICA (2010 -2012) 4. Bilateral Cooperation Projects 5. Others

2. Challenges How to 1. Make TVET Responsive, Relevant, Effective, Efficient, Flexible & Sustainable, 2. Make TVET system attractive to society, 3. Meet the aspirations of students, 4. Build capacity to keep pace with new developments and standards (especially amongst teachers /instructors, etc), 5. Improve management as well as financial management , 6. Clarify and elaborate TVET regulations (e. g. Dual system) 7. Formulate performance reward system.

2. 1 External Issues 1. Social Factor o population growth, o social perception of TVET, o job market & employment trends, o natural calamities/disasters. 2. Economic Growth, 3. Legal & Regulatory Framework, 4. Rapid Technological Development, 5. Globalization.
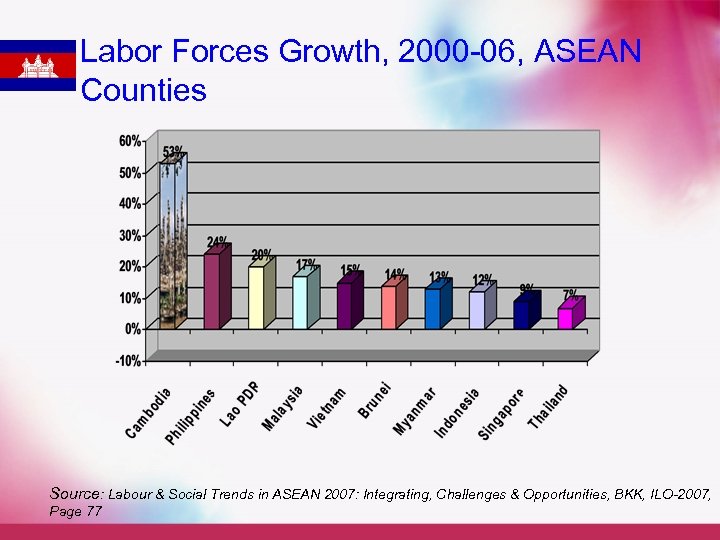
Labor Forces Growth, 2000 -06, ASEAN Counties Source: Labour & Social Trends in ASEAN 2007: Integrating, Challenges & Opportunities, BKK, ILO-2007, Page 77
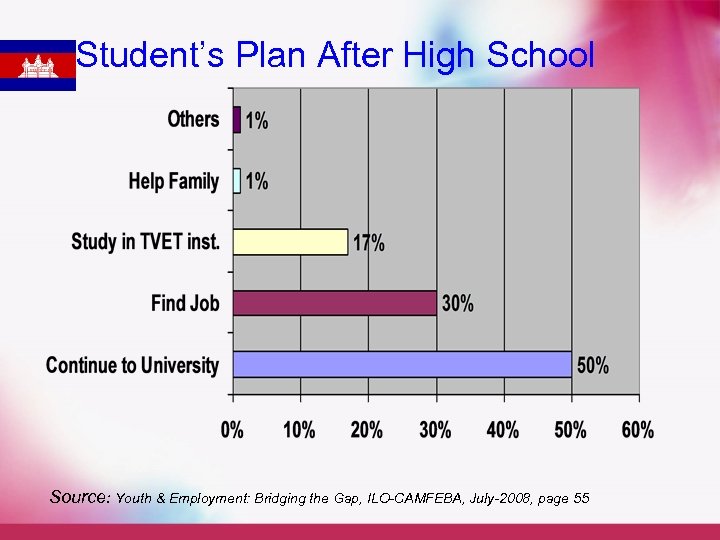
Student’s Plan After High School Source: Youth & Employment: Bridging the Gap, ILO-CAMFEBA, July-2008, page 55

2. 2 Internal Issues 1. NQF, SCS and ST not in place 2. Inability to attract in sufficient numbers those who need skills training the most-unemployed, under-employed, disadvantaged and drop-outs 3. Inadequate Qualified TVET Personnel, 4. Weak Leadership & Management, 5. Poor Communication & Marketing, 6. Inadequate & Inappropriate Teaching/Learning Materials, Equipment & Environment, 7. Inequitable Access, 8. Limited Public Private Partnership.
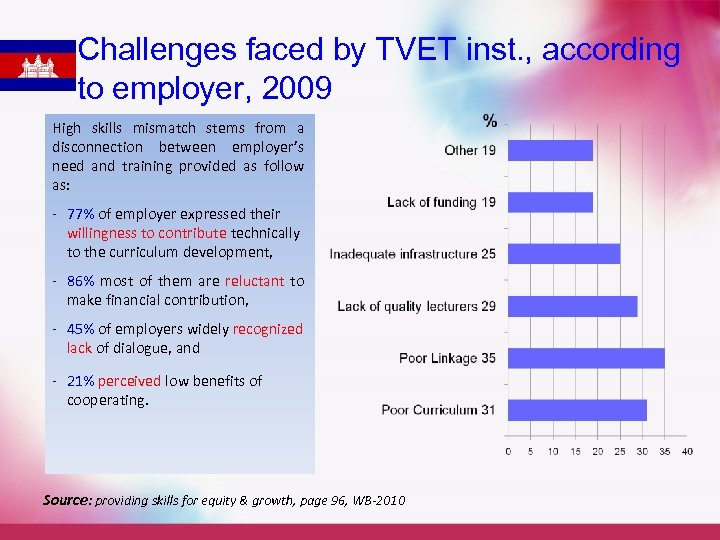
Challenges faced by TVET inst. , according to employer, 2009 High skills mismatch stems from a disconnection between employer’s need and training provided as follow as: - 77% of employer expressed their willingness to contribute technically to the curriculum development, - 86% most of them are reluctant to make financial contribution, - 45% of employers widely recognized lack of dialogue, and - 21% perceived low benefits of cooperating. Source: providing skills for equity & growth, page 96, WB-2010

3. TVET Policies & Planning
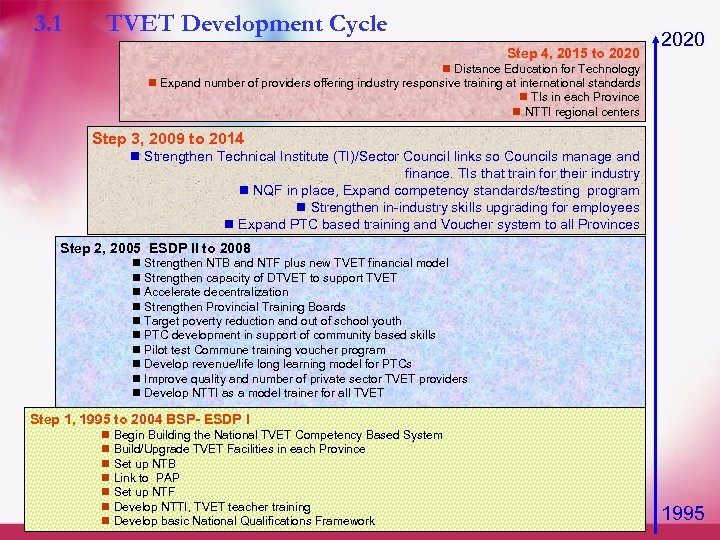
3. 1 TVET Development Cycle Step 4, 2015 to 2020 Distance Education for Technology Expand number of providers offering industry responsive training at international standards TIs in each Province NTTI regional centers Step 3, 2009 to 2014 Strengthen Technical Institute (TI)/Sector Council links so Councils manage and finance. TIs that train for their industry NQF in place, Expand competency standards/testing program Strengthen in-industry skills upgrading for employees Expand PTC based training and Voucher system to all Provinces Step 2, 2005 ESDP II to 2008 Strengthen NTB and NTF plus new TVET financial model Strengthen capacity of DTVET to support TVET Accelerate decentralization Strengthen Provincial Training Boards Target poverty reduction and out of school youth PTC development in support of community based skills Pilot test Commune training voucher program Develop revenue/life long learning model for PTCs Improve quality and number of private sector TVET providers Develop NTTI as a model trainer for all TVET Step 1, 1995 to 2004 BSP- ESDP I Begin Building the National TVET Competency Based System Build/Upgrade TVET Facilities in each Province Set up NTB Link to PAP Set up NTF Develop NTTI, TVET teacher training Develop basic National Qualifications Framework 1995

3. 2 National TVET Development Plan 1. Macro Policy 1 : Poverty Reduction Policy 2 : Decentralization Policy 3 : Supporting Enterprise Growth with a Skilled Workforce

National TVET Development Plan(cont. ) 2. Development Policy to Support the Macro Policy 4 : Out of School Youth Policy 5 : Self-employment Policy 6 : Micro Credit Access Policy 7 : Small Enterprise Support Policy 8 : Community & Enterprise Based Training (outreach)

National TVET Development Plan (cont) 3. Enabling Policy to sustain the demand driven TVET system Policy 9 : PPP-Beneficiary Financing TVET Policy 10 : PPP-Enterprise Involvement in TVET Policy 11 : PPP-Expanding the provision of TVET Policy 12 : Assuring Quality of TVET provision Policy 13 : Quality of TVET Leadership, Management & Coordination, Policy 14 : Labor Market Information, Policy 15 : Skills Competency Standard.
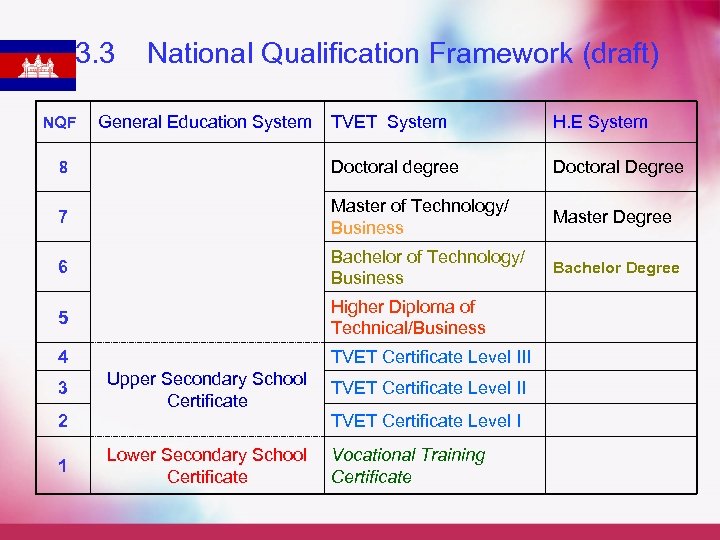
3. 3 National Qualification Framework (draft) TVET System H. E System 8 Doctoral degree Doctoral Degree 7 Master of Technology/ Business Master Degree 6 Bachelor of Technology/ Business Bachelor Degree 5 Higher Diploma of Technical/Business 4 TVET Certificate Level III NQF 3 2 1 General Education System Upper Secondary School Certificate TVET Certificate Level II Lower Secondary School Certificate Vocational Training Certificate TVET Certificate Level I
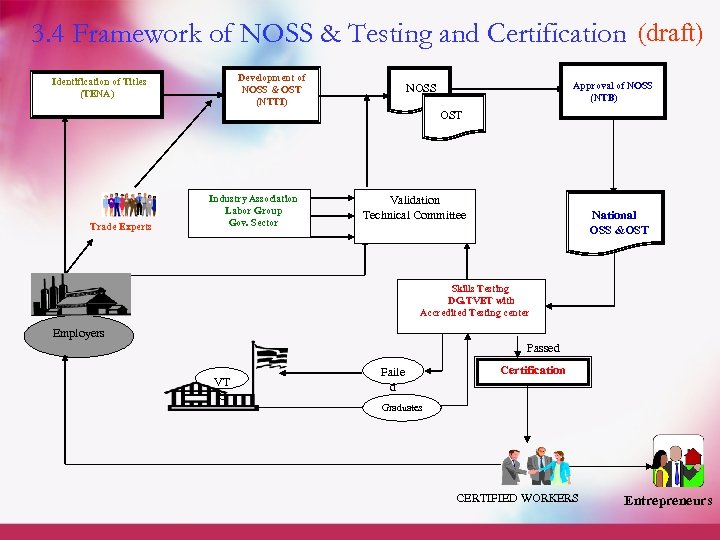
3. 4 Framework of NOSS & Testing and Certification (draft) Development of NOSS & OST (NTTI) Identification of Titles (TENA) Approval of NOSS (NTB) NOSS OST Trade Experts Industry Association Labor Group Gov. Sector Validation Technical Committee National OSS &OST Skills Testing DG. TVET with Accredited Testing center Employers Passed VT C Faile d Certification Graduates CERTIFIED WORKERS Entrepreneurs

3. 5 Target Groups 1. Vulnerable groups, 2. Students drop out in General Education, 3. Unemployment, under employment, and re-employment, 4. 9 -year & 12 -year Graduates,
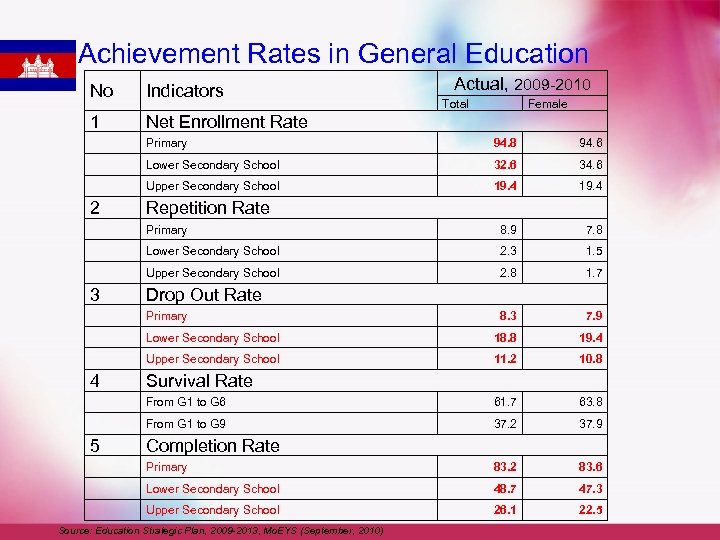
Achievement Rates in General Education No Indicators 1 Actual, 2009 -2010 Net Enrollment Rate Total Female Primary 32. 6 34. 6 Upper Secondary School 19. 4 Primary 8. 9 7. 8 Lower Secondary School 2. 3 1. 5 Upper Secondary School 2. 8 1. 7 8. 3 7. 9 Lower Secondary School 18. 8 19. 4 Upper Secondary School 11. 2 10. 8 From G 1 to G 6 61. 7 63. 8 From G 1 to G 9 37. 2 37. 9 Primary 83. 2 83. 6 Lower Secondary School 48. 7 47. 3 Upper Secondary School 3 94. 6 Lower Secondary School 2 94. 8 26. 1 22. 5 Repetition Rate Drop Out Rate Primary 4 5 Survival Rate Completion Rate Source: Education Strategic Plan, 2009 -2013, Mo. EYS (September, 2010)
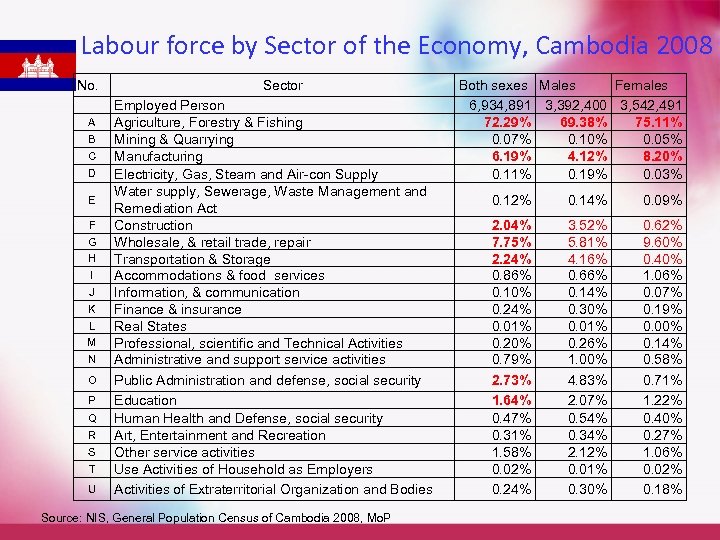
Labour force by Sector of the Economy, Cambodia 2008 No. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U Sector Employed Person Agriculture, Forestry & Fishing Mining & Quarrying Manufacturing Electricity, Gas, Steam and Air-con Supply Water supply, Sewerage, Waste Management and Remediation Act Construction Wholesale, & retail trade, repair Transportation & Storage Accommodations & food services Information, & communication Finance & insurance Real States Professional, scientific and Technical Activities Administrative and support service activities Public Administration and defense, social security Education Human Health and Defense, social security Art, Entertainment and Recreation Other service activities Use Activities of Household as Employers Activities of Extraterritorial Organization and Bodies Source: NIS, General Population Census of Cambodia 2008, Mo. P Both sexes Males Females 6, 934, 891 3, 392, 400 3, 542, 491 72. 29% 69. 38% 75. 11% 0. 07% 0. 10% 0. 05% 6. 19% 4. 12% 8. 20% 0. 11% 0. 19% 0. 03% 0. 12% 0. 14% 0. 09% 2. 04% 7. 75% 2. 24% 0. 86% 0. 10% 0. 24% 0. 01% 0. 20% 0. 79% 2. 73% 1. 64% 0. 47% 0. 31% 1. 58% 0. 02% 0. 24% 3. 52% 5. 81% 4. 16% 0. 66% 0. 14% 0. 30% 0. 01% 0. 26% 1. 00% 4. 83% 2. 07% 0. 54% 0. 34% 2. 12% 0. 01% 0. 30% 0. 62% 9. 60% 0. 40% 1. 06% 0. 07% 0. 19% 0. 00% 0. 14% 0. 58% 0. 71% 1. 22% 0. 40% 0. 27% 1. 06% 0. 02% 0. 18%
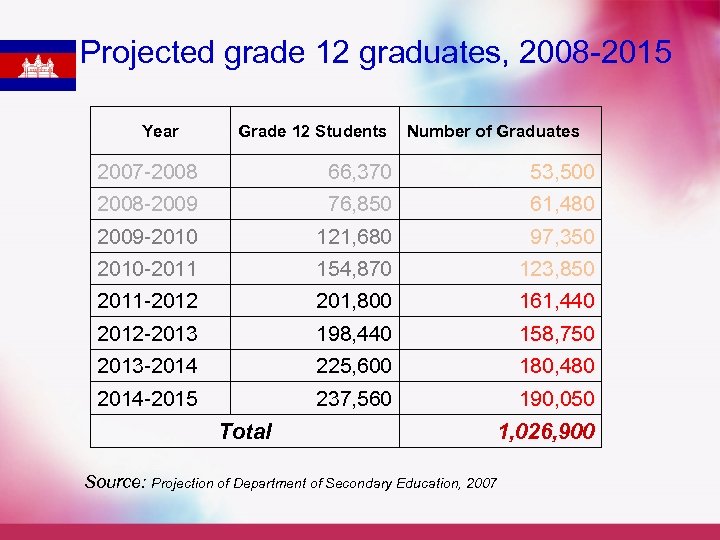
Projected grade 12 graduates, 2008 -2015 Year Grade 12 Students Number of Graduates 2007 -2008 66, 370 53, 500 2008 -2009 76, 850 61, 480 2009 -2010 121, 680 97, 350 2010 -2011 154, 870 123, 850 2011 -2012 201, 800 161, 440 2012 -2013 198, 440 158, 750 2013 -2014 225, 600 180, 480 2014 -2015 237, 560 190, 050 Total 1, 026, 900 Source: Projection of Department of Secondary Education, 2007

4. Cambodia TVET Outcome • Formulating comprehensive TVET Policy and Regulatory Framework • Equitable access, and Improving skills competencies • Improving Quality Assurance and Accreditation • Creating jobs in rural areas to increase agricultural productivity

Cambodia TVET Outcome • Creating jobs in formal and nonformal sectors • Ensuring continued improvement in national productivity • Increasing family generating income.

Or Kun Thank You