c077876c51f5fde30cb9cd11d9bc64b3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Keys & Key Management Chapters 7, 8 Keys – Symmetric Length – Public Key Length Key Management – Generating, Using, Storing Keys – Backup Keys – Destroying Keys
Keys & Key Management Chapters 7, 8 Keys – Symmetric Length – Public Key Length Key Management – Generating, Using, Storing Keys – Backup Keys – Destroying Keys
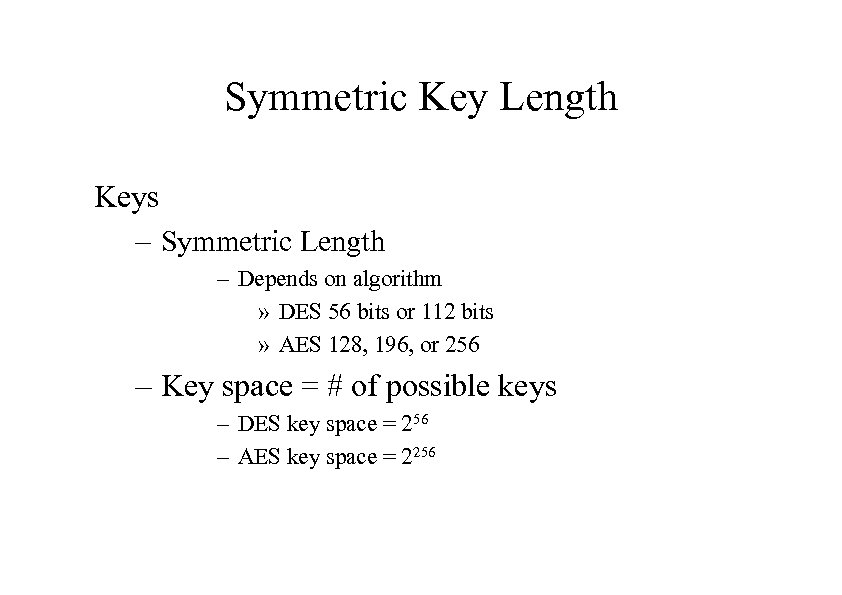 Symmetric Key Length Keys – Symmetric Length – Depends on algorithm » DES 56 bits or 112 bits » AES 128, 196, or 256 – Key space = # of possible keys – DES key space = 256 – AES key space = 2256
Symmetric Key Length Keys – Symmetric Length – Depends on algorithm » DES 56 bits or 112 bits » AES 128, 196, or 256 – Key space = # of possible keys – DES key space = 256 – AES key space = 2256
 Public Key Length Keys – Depend on the product of two very large primes » Easy to multiply » Hard to factor – Cracking Public key crypto depends on factoring very large numbers
Public Key Length Keys – Depend on the product of two very large primes » Easy to multiply » Hard to factor – Cracking Public key crypto depends on factoring very large numbers
 Current Recommendations • For confidentiality beyond 2030 use 3072 bit keys for both RSA and D-H. • 3072 bit keys for RSA is equivalent to 128 bit AES keys • For more secure asymmetric encryption you have to use Elliptic Curve Cryptography ECC Keys should be twice the length of the AES key length
Current Recommendations • For confidentiality beyond 2030 use 3072 bit keys for both RSA and D-H. • 3072 bit keys for RSA is equivalent to 128 bit AES keys • For more secure asymmetric encryption you have to use Elliptic Curve Cryptography ECC Keys should be twice the length of the AES key length
 Factoring Methods General number sieve – 2048 bit numbers = 3*1020 mip-years Special number field sieve – 2048 bit numbers = 4*1014 mip-years
Factoring Methods General number sieve – 2048 bit numbers = 3*1020 mip-years Special number field sieve – 2048 bit numbers = 4*1014 mip-years
 Generating Keys Bad/weak keys – Some keys are very weak, some are poor choices – Some are prone to dictionary attacks Random symmetric keys – Must test for know weak keys for an algorithm
Generating Keys Bad/weak keys – Some keys are very weak, some are poor choices – Some are prone to dictionary attacks Random symmetric keys – Must test for know weak keys for an algorithm
 Generating Keys Key generation – Hash of passwords – Hash of pass phrases Information theory – English 1. 3 bits of info per 8 bit character – 10 words = 49 characters = 64 bit key
Generating Keys Key generation – Hash of passwords – Hash of pass phrases Information theory – English 1. 3 bits of info per 8 bit character – 10 words = 49 characters = 64 bit key
 Distributing Keys Large networks have large problems • 6 person networks require 15 key exchanges • 1000 person networks require 500, 000 key exchanges • A very good random number generator is required
Distributing Keys Large networks have large problems • 6 person networks require 15 key exchanges • 1000 person networks require 500, 000 key exchanges • A very good random number generator is required
 Using Keys Key storage Sits on disk subject to forensic exam, nosey co-worker, etc. Who uses the key
Using Keys Key storage Sits on disk subject to forensic exam, nosey co-worker, etc. Who uses the key
 Storing Keys Magnetic card stripes Smart cards RFIDs Some key host Key escrow server
Storing Keys Magnetic card stripes Smart cards RFIDs Some key host Key escrow server
 Backup Keys What if • The key owner forgets • The key owner quits • The key owner dies • The computer is stolen/destroyed
Backup Keys What if • The key owner forgets • The key owner quits • The key owner dies • The computer is stolen/destroyed
 Destroying Keys have a limited lifetime Validation that the key is destroyed Ket storage medium must be completely destroyed
Destroying Keys have a limited lifetime Validation that the key is destroyed Ket storage medium must be completely destroyed
 Key Management • PKI – Public Key Infrastructure • X. 509 is the generally accepted standard for PKI held by ITU • IETF X. 509 working group pkix • MIL uses it.
Key Management • PKI – Public Key Infrastructure • X. 509 is the generally accepted standard for PKI held by ITU • IETF X. 509 working group pkix • MIL uses it.
 Certificate: Data: Version: 1 (0 x 0) Serial Number: 7829 (0 x 1 e 95) Signature Algorithm: md 5 With. RSAEncryption Issuer: C=ZA, ST=Western Cape, L=Cape Town, O=Thawte Consulting cc, OU=Certification Services Division, CN=Thawte Server CA/email. Address=server-certs@thawte. com Validity Not Before: Jul 9 16: 04: 02 1998 GMT Not After : Jul 9 16: 04: 02 1999 GMT Subject: C=US, ST=Maryland, L=Pasadena, O=Brent Baccala, OU=Free. Soft, CN=www. freesoft. org/email. Address=baccala@freesoft. org Subject Public Key Info: Public Key Algorithm: rsa. Encryption RSA Public Key: (1024 bit) Modulus (1024 bit): 00: b 4: 31: 98: 0 a: c 4: bc: 62: c 1: 88: aa: dc: b 0: c 8: bb: 33: 35: 19: d 5: 0 c: 64: b 9: 3 d: 41: b 2: 96: fc: f 3: 31: e 1: 66: 36: d 0: 8 e: 56: 12: 44: ba: 75: eb: e 8: 1 c: 9 c: 5 b: 66: 70: 33: 52: 14: c 9: ec: 4 f: 91: 51: 70: 39: de: 53: 85: 17: 16: 94: 6 e: ee: f 4: d 5: 6 f: d 5: ca: b 3: 47: 5 e: 1 b: 0 c: 7 b: c 5: cc: 2 b: 6 b: c 1: 90: c 3: 16: 31: 0 d: bf: 7 a: c 7: 47: 77: 8 f: a 0: 21: c 7: 4 c: d 0: 16: 65: 00: c 1: 0 f: d 7: b 8: 80: e 3: d 2: 75: 6 b: c 1: ea: 9 e: 5 c: ea: 7 d: c 1: a 1: 10: bc: b 8: e 8: 35: 1 c: 9 e: 27: 52: 7 e: 41: 8 f Exponent: 65537 (0 x 10001) Signature Algorithm: md 5 With. RSAEncryption 93: 5 f: 8 f: 5 f: c 5: af: bf: 0 a: ab: a 5: 6 d: fb: 24: 5 f: b 6: 59: 5 d: 92: 2 e: 4 a: 1 b: 8 b: ac: 7 d: 99: 17: 5 d: cd: 19: f 6: ad: ef: 63: 2 f: 92: ab: 2 f: 4 b: cf: 0 a: 13: 90: ee: 2 c: 0 e: 43: 03: be: f 6: ea: 8 e: 9 c: 67: d 0: a 2: 40: 03: f 7: ef: 6 a: 15: 09: 79: a 9: 46: ed: b 7: 16: 1 b: 41: 72: 0 d: 19: aa: ad: dd: 9 a: df: ab: 97: 50: 65: f 5: 5 e: 85: a 6: ef: 19: d 1: 5 a: de: 9 d: ea: 63: cd: cb: cc: 6 d: 5 d: 01: 85: b 5: 6 d: c 8: f 3: d 9: f 7: 8 f: 0 e: fc: ba: 1 f: 34: e 9: 96: 6 e: 6 c: cf: f 2: ef: 9 b: bf: de: b 5: 22: 68: 9 f To
Certificate: Data: Version: 1 (0 x 0) Serial Number: 7829 (0 x 1 e 95) Signature Algorithm: md 5 With. RSAEncryption Issuer: C=ZA, ST=Western Cape, L=Cape Town, O=Thawte Consulting cc, OU=Certification Services Division, CN=Thawte Server CA/email. Address=server-certs@thawte. com Validity Not Before: Jul 9 16: 04: 02 1998 GMT Not After : Jul 9 16: 04: 02 1999 GMT Subject: C=US, ST=Maryland, L=Pasadena, O=Brent Baccala, OU=Free. Soft, CN=www. freesoft. org/email. Address=baccala@freesoft. org Subject Public Key Info: Public Key Algorithm: rsa. Encryption RSA Public Key: (1024 bit) Modulus (1024 bit): 00: b 4: 31: 98: 0 a: c 4: bc: 62: c 1: 88: aa: dc: b 0: c 8: bb: 33: 35: 19: d 5: 0 c: 64: b 9: 3 d: 41: b 2: 96: fc: f 3: 31: e 1: 66: 36: d 0: 8 e: 56: 12: 44: ba: 75: eb: e 8: 1 c: 9 c: 5 b: 66: 70: 33: 52: 14: c 9: ec: 4 f: 91: 51: 70: 39: de: 53: 85: 17: 16: 94: 6 e: ee: f 4: d 5: 6 f: d 5: ca: b 3: 47: 5 e: 1 b: 0 c: 7 b: c 5: cc: 2 b: 6 b: c 1: 90: c 3: 16: 31: 0 d: bf: 7 a: c 7: 47: 77: 8 f: a 0: 21: c 7: 4 c: d 0: 16: 65: 00: c 1: 0 f: d 7: b 8: 80: e 3: d 2: 75: 6 b: c 1: ea: 9 e: 5 c: ea: 7 d: c 1: a 1: 10: bc: b 8: e 8: 35: 1 c: 9 e: 27: 52: 7 e: 41: 8 f Exponent: 65537 (0 x 10001) Signature Algorithm: md 5 With. RSAEncryption 93: 5 f: 8 f: 5 f: c 5: af: bf: 0 a: ab: a 5: 6 d: fb: 24: 5 f: b 6: 59: 5 d: 92: 2 e: 4 a: 1 b: 8 b: ac: 7 d: 99: 17: 5 d: cd: 19: f 6: ad: ef: 63: 2 f: 92: ab: 2 f: 4 b: cf: 0 a: 13: 90: ee: 2 c: 0 e: 43: 03: be: f 6: ea: 8 e: 9 c: 67: d 0: a 2: 40: 03: f 7: ef: 6 a: 15: 09: 79: a 9: 46: ed: b 7: 16: 1 b: 41: 72: 0 d: 19: aa: ad: dd: 9 a: df: ab: 97: 50: 65: f 5: 5 e: 85: a 6: ef: 19: d 1: 5 a: de: 9 d: ea: 63: cd: cb: cc: 6 d: 5 d: 01: 85: b 5: 6 d: c 8: f 3: d 9: f 7: 8 f: 0 e: fc: ba: 1 f: 34: e 9: 96: 6 e: 6 c: cf: f 2: ef: 9 b: bf: de: b 5: 22: 68: 9 f To


