e75bad0e5992dcffdd84b56c52600b02.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64
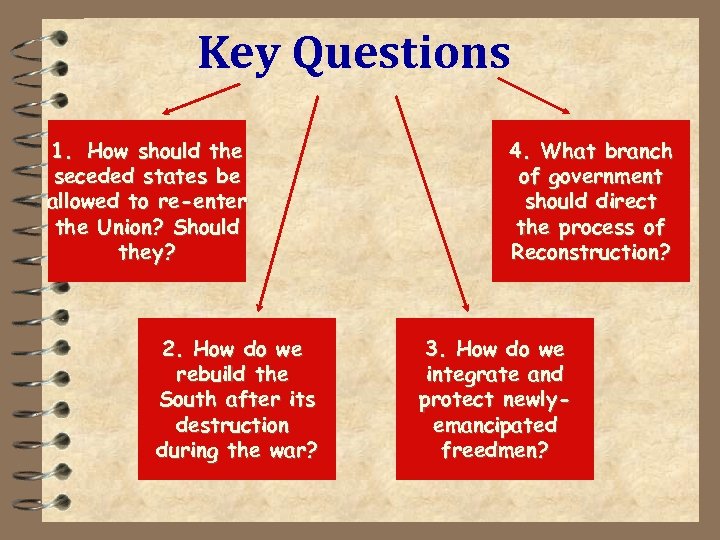 Key Questions 1. How should the seceded states be allowed to re-enter the Union? Should they? 2. How do we rebuild the South after its destruction during the war? 4. What branch of government should direct the process of Reconstruction? 3. How do we integrate and protect newlyemancipated freedmen?
Key Questions 1. How should the seceded states be allowed to re-enter the Union? Should they? 2. How do we rebuild the South after its destruction during the war? 4. What branch of government should direct the process of Reconstruction? 3. How do we integrate and protect newlyemancipated freedmen?
 Phase One: Reconstruction Plans
Phase One: Reconstruction Plans
 Reconstruction Plans 4 A. Lincoln’s Plan – 10% plan – 1860 voters, all ex-Confeds pardoned 4 assassinated b/f issue settled 4 B. Radical Republicans – Thaddeus Stevens, Charles Sumner – dominate Congress 4 want the South punished for the war
Reconstruction Plans 4 A. Lincoln’s Plan – 10% plan – 1860 voters, all ex-Confeds pardoned 4 assassinated b/f issue settled 4 B. Radical Republicans – Thaddeus Stevens, Charles Sumner – dominate Congress 4 want the South punished for the war
 Reconstruction Plans 4 Two Theories “conquered provinces”, “state suicide” 4 RRs – Wade Davis Bill 1864 – a 50% plan – “iron clad” oath – 1860 voters 4 said Congress to direct Recon. 4 pocket vetoed by Lincoln prior to death
Reconstruction Plans 4 Two Theories “conquered provinces”, “state suicide” 4 RRs – Wade Davis Bill 1864 – a 50% plan – “iron clad” oath – 1860 voters 4 said Congress to direct Recon. 4 pocket vetoed by Lincoln prior to death
 Reconstruction Plans 4 C. Andrew Johnson (TN) becomes President 4 Johnson’s Plan – 10% plan 4 S. states admit secession was illegal 4 new state Constitutions – including ratification of the 13 th A.
Reconstruction Plans 4 C. Andrew Johnson (TN) becomes President 4 Johnson’s Plan – 10% plan 4 S. states admit secession was illegal 4 new state Constitutions – including ratification of the 13 th A.
 th 13 Amendment « Ratified in December, 1865 – prior to Southern states returning to Union « Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States or any place subject to their jurisdiction.
th 13 Amendment « Ratified in December, 1865 – prior to Southern states returning to Union « Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States or any place subject to their jurisdiction.
 President Andrew Johnson « 2 nd term Vice-Pres « White Supremacist « Agreed with Lincoln that states had never legally left the Union Nevermind the negroes! I am fighting these traitorous aristocrats, their masters!
President Andrew Johnson « 2 nd term Vice-Pres « White Supremacist « Agreed with Lincoln that states had never legally left the Union Nevermind the negroes! I am fighting these traitorous aristocrats, their masters!
 Reconstruction Plans 4 Responses to Johnson’s Plan 41. Southern States – quick to follow 4*send reps to Congress (Conf) 4*13, 500 ex-Confed’s pardoned by Johnson
Reconstruction Plans 4 Responses to Johnson’s Plan 41. Southern States – quick to follow 4*send reps to Congress (Conf) 4*13, 500 ex-Confed’s pardoned by Johnson
 Reconstruction Plans 42. RRs 4*angry at pardons 4*refuse to admit ex-Confeds to Congress
Reconstruction Plans 42. RRs 4*angry at pardons 4*refuse to admit ex-Confeds to Congress
 Reconstruction Plans 4 Congress – How to protect the former slaves? 4 RR Plan 41. extend the Freedmen’s Bureau 1866, purpose? 4 vetoed by Johnson
Reconstruction Plans 4 Congress – How to protect the former slaves? 4 RR Plan 41. extend the Freedmen’s Bureau 1866, purpose? 4 vetoed by Johnson
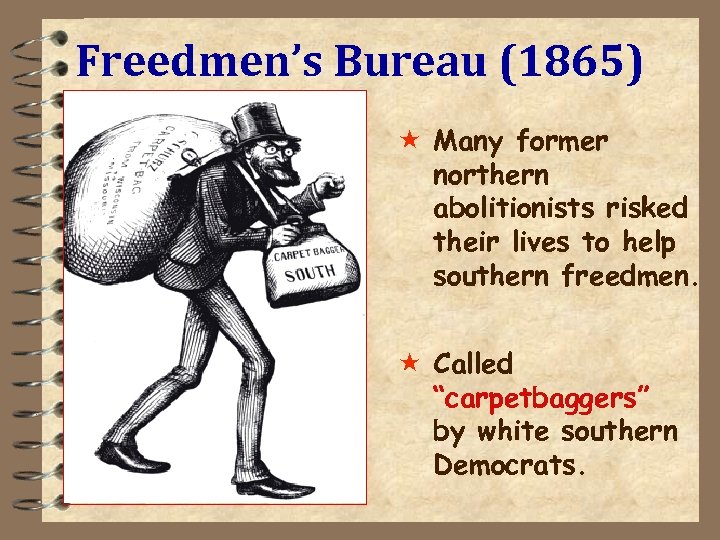 Freedmen’s Bureau (1865) « Many former northern abolitionists risked their lives to help southern freedmen. « Called “carpetbaggers” by white southern Democrats.
Freedmen’s Bureau (1865) « Many former northern abolitionists risked their lives to help southern freedmen. « Called “carpetbaggers” by white southern Democrats.
 Freedmen’s Bureau Through Southern Eyes “Plenty to eat and nothing to do. ”
Freedmen’s Bureau Through Southern Eyes “Plenty to eat and nothing to do. ”
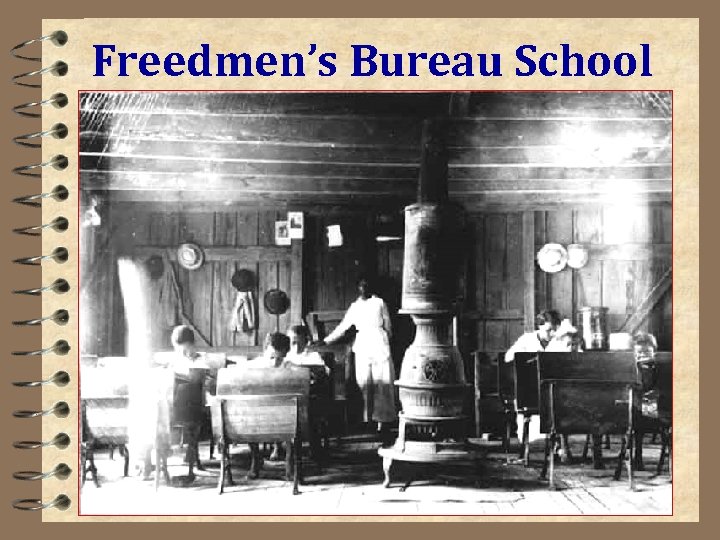 Freedmen’s Bureau School
Freedmen’s Bureau School
 Reconstruction Struggles 4 Springfield Baptist marker
Reconstruction Struggles 4 Springfield Baptist marker
 Reconstruction Plans 42. Civil Rights Act 1866 4*citizenship to former slaves 4*made black codes illegal 4*use of federal troops in S. sts. 4 vetoed by Johnson
Reconstruction Plans 42. Civil Rights Act 1866 4*citizenship to former slaves 4*made black codes illegal 4*use of federal troops in S. sts. 4 vetoed by Johnson
 Phase Two: Reconstruction Struggles
Phase Two: Reconstruction Struggles
 Reconstruction Struggles 4 Why the vetoes by Johnson? 4 believed the Fr. Bureau was a state agency – not federal 4 believed the Civil Rights Act was unconstitutional 4 angers more Republicans
Reconstruction Struggles 4 Why the vetoes by Johnson? 4 believed the Fr. Bureau was a state agency – not federal 4 believed the Civil Rights Act was unconstitutional 4 angers more Republicans
 Reconstruction Struggles 4 RRs Response to Vetoes 4 override both 4 States pass the 14 th amendment 41. Dual citizenship 42. Threat to remove a states’ reps if rights denied
Reconstruction Struggles 4 RRs Response to Vetoes 4 override both 4 States pass the 14 th amendment 41. Dual citizenship 42. Threat to remove a states’ reps if rights denied
 Reconstruction Struggles 43. # of reps based on total pop. 44. Ex-Confeds banned from public office 45. All citizens – equal protection under the law 4 TN – ratifies and is re-admitted
Reconstruction Struggles 43. # of reps based on total pop. 44. Ex-Confeds banned from public office 45. All citizens – equal protection under the law 4 TN – ratifies and is re-admitted
 Reconstruction Struggles 41866 Elections 4 Republican majority elected to House and Senate 4 Johnson’s veto power dead
Reconstruction Struggles 41866 Elections 4 Republican majority elected to House and Senate 4 Johnson’s veto power dead
 Phase Three: Congressional Reconstruction
Phase Three: Congressional Reconstruction
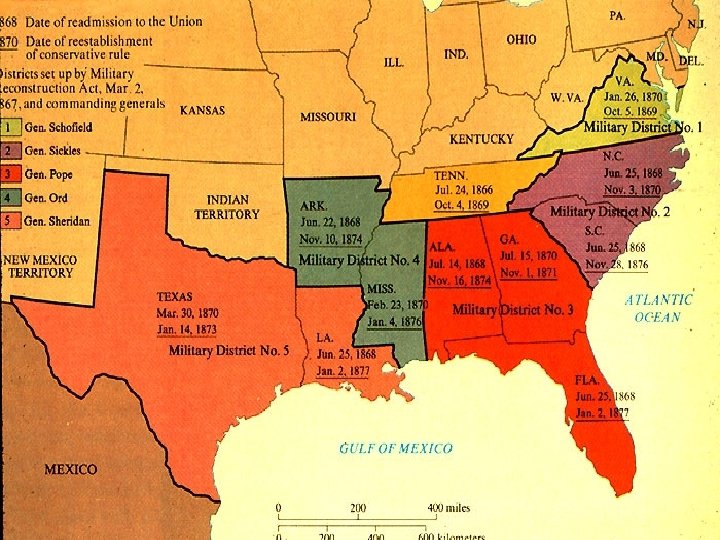
 Congressional Reconstruction 4 First Reconstruction Act 1867 4*divides South into 5 military zones 4*required new state const’s 4*must include all male suffrage 4*required 14 th A. ratified
Congressional Reconstruction 4 First Reconstruction Act 1867 4*divides South into 5 military zones 4*required new state const’s 4*must include all male suffrage 4*required 14 th A. ratified
 Congressional Reconstruction 4 Tenure of Office Act 1867 4 what it did? 4 Johnson’s impeachment for firing Edwin Stanton – Sec. of War 4 trial March 1868 – not guilty
Congressional Reconstruction 4 Tenure of Office Act 1867 4 what it did? 4 Johnson’s impeachment for firing Edwin Stanton – Sec. of War 4 trial March 1868 – not guilty
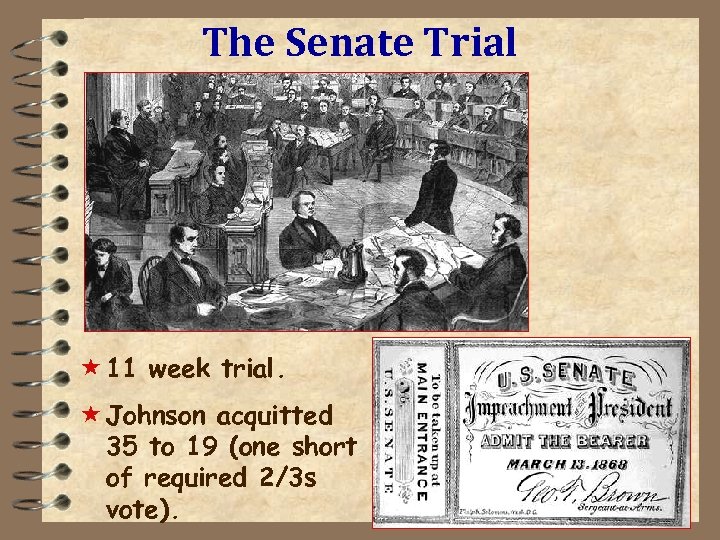 The Senate Trial « 11 week trial. « Johnson acquitted 35 to 19 (one short of required 2/3 s vote).
The Senate Trial « 11 week trial. « Johnson acquitted 35 to 19 (one short of required 2/3 s vote).
 Congressional Reconstruction 4 Election of 1868 – “Waving the Bloody Shirt” 4 Ulysses S. Grant – new Pres. 4500, 000 black men vote 41 st term dominated by economic scandals 4 Repub Party will be split as a result
Congressional Reconstruction 4 Election of 1868 – “Waving the Bloody Shirt” 4 Ulysses S. Grant – new Pres. 4500, 000 black men vote 41 st term dominated by economic scandals 4 Repub Party will be split as a result
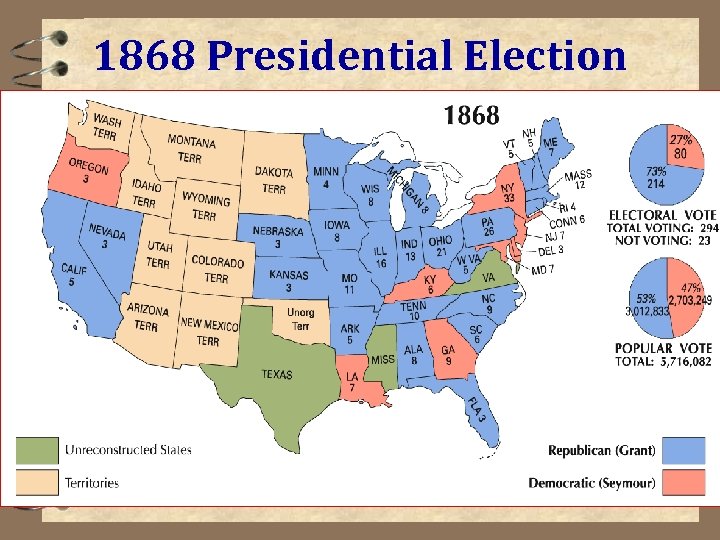 1868 Presidential Election
1868 Presidential Election
 The 1868 Republican Ticket
The 1868 Republican Ticket
 Waving the Bloody Shirt! Republican “Southern Strategy”
Waving the Bloody Shirt! Republican “Southern Strategy”
 Grant Administration Scandals
Grant Administration Scandals
 Grant Scandals 4 Whiskey Ring 4 Attempt to defraud the gov’t of internal tax on whiskey 4 Bribes from whiskey distillers 4 Involved Grant’s Sec of St
Grant Scandals 4 Whiskey Ring 4 Attempt to defraud the gov’t of internal tax on whiskey 4 Bribes from whiskey distillers 4 Involved Grant’s Sec of St
 Grant Scandals 4 Credit Mobilier 4 Stock in Union Pacific RR sold to key congressmen 4 Many owned stock in the RR and the construction company building it 4 Overcharged for building RR
Grant Scandals 4 Credit Mobilier 4 Stock in Union Pacific RR sold to key congressmen 4 Many owned stock in the RR and the construction company building it 4 Overcharged for building RR
 Grant Scandals 4 Belknap Scandal 4 Sec of War 4 Accepted bribes from merchants to keep trading rights in NA territory 4 Charged high prices to supply merchants
Grant Scandals 4 Belknap Scandal 4 Sec of War 4 Accepted bribes from merchants to keep trading rights in NA territory 4 Charged high prices to supply merchants
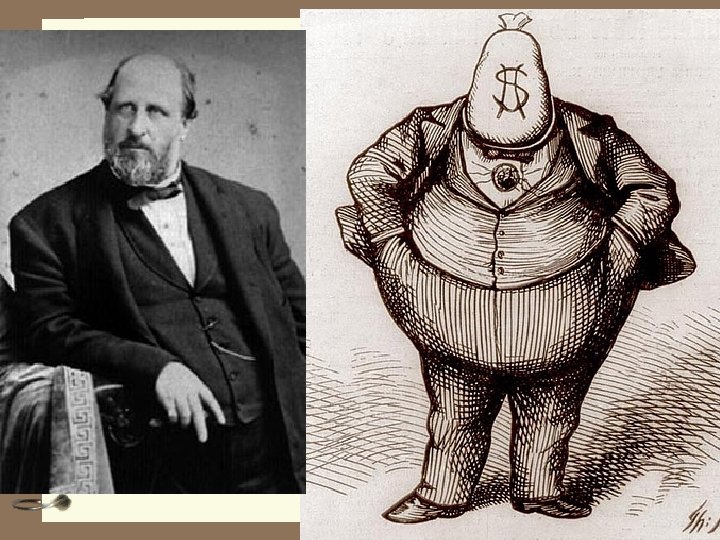
 Municipal Corruption 4 The Tweed Ring 4 William “Boss” Tweed 4 Ran NYC – Tammany Hall 4 Bribery and voting fraud 4 Prosecuted by Samuel Tilden 4 NY Times – Thomas Nast cartoons
Municipal Corruption 4 The Tweed Ring 4 William “Boss” Tweed 4 Ran NYC – Tammany Hall 4 Bribery and voting fraud 4 Prosecuted by Samuel Tilden 4 NY Times – Thomas Nast cartoons



 Congressional Reconstruction 415 th Amendment 1870 4 universal male suffrage placed into the U. S. Const. 4 black men begin to hold office 4 local and state level mostly
Congressional Reconstruction 415 th Amendment 1870 4 universal male suffrage placed into the U. S. Const. 4 black men begin to hold office 4 local and state level mostly
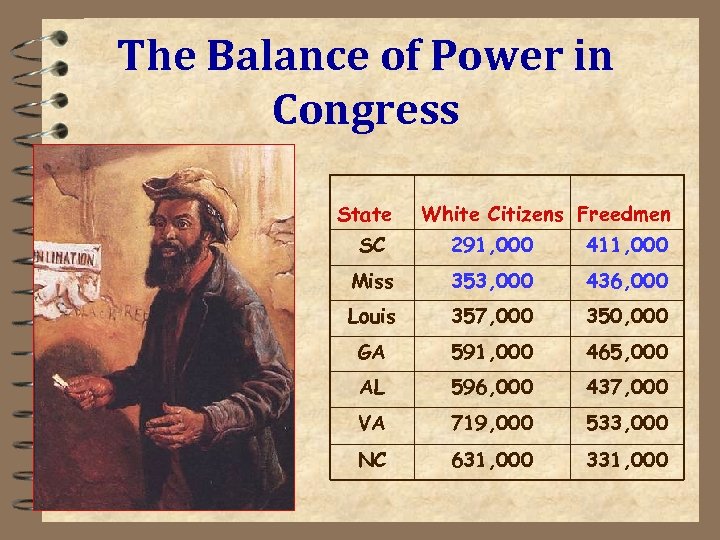 The Balance of Power in Congress State White Citizens Freedmen SC 291, 000 411, 000 Miss 353, 000 436, 000 Louis 357, 000 350, 000 GA 591, 000 465, 000 AL 596, 000 437, 000 VA 719, 000 533, 000 NC 631, 000 331, 000
The Balance of Power in Congress State White Citizens Freedmen SC 291, 000 411, 000 Miss 353, 000 436, 000 Louis 357, 000 350, 000 GA 591, 000 465, 000 AL 596, 000 437, 000 VA 719, 000 533, 000 NC 631, 000 331, 000
 Black Senate & House Delegates
Black Senate & House Delegates
 Colored Rule in a Reconstructed State
Colored Rule in a Reconstructed State
 Changes in the South 4 Invasion of carpetbaggers 4*exploitation of conditions in South OR? 4 Effects of scalawags 4*join Repub. Party 4*betrayal of the Old South OR?
Changes in the South 4 Invasion of carpetbaggers 4*exploitation of conditions in South OR? 4 Effects of scalawags 4*join Repub. Party 4*betrayal of the Old South OR?
 « Many former northern abolitionists risked their lives to help southern freedmen. « Called “carpetbaggers” by white southern Democrats.
« Many former northern abolitionists risked their lives to help southern freedmen. « Called “carpetbaggers” by white southern Democrats.

 Changes in the South 4 Movement of former slaves 4 most became sharecroppers 4 often in the same place 4 how the system worked?
Changes in the South 4 Movement of former slaves 4 most became sharecroppers 4 often in the same place 4 how the system worked?
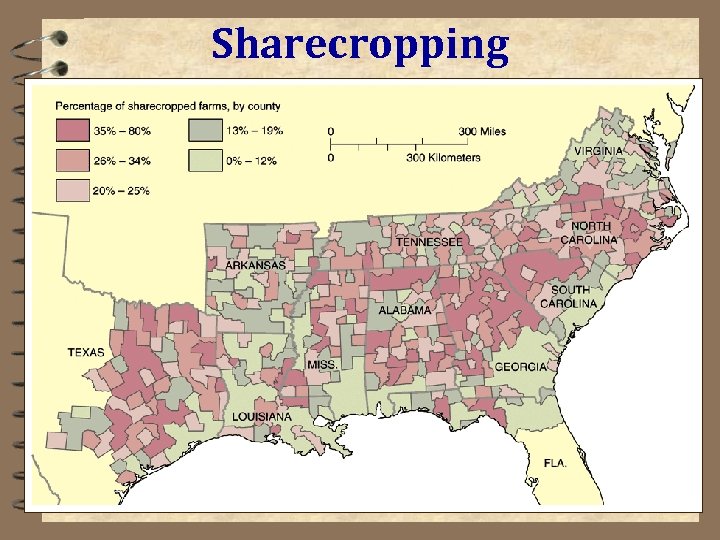 Sharecropping
Sharecropping
 Changes in the South 4 Special Field Order #15 4“ 40 acres and a mule” 4 promised by Sherman 4 denied by Pres. Johnson – restores land to previous owners
Changes in the South 4 Special Field Order #15 4“ 40 acres and a mule” 4 promised by Sherman 4 denied by Pres. Johnson – restores land to previous owners
 Johnson’s Actions – Summary 4 Lenient Recon plan 4 Issues thousands of pardons to ex- Confeds 4 Vetoes Fr Bur renewal and CRts Act 4 Violates Tenure of Office Act and is impeached 4 Denies land granted to GA slaves by Sherman
Johnson’s Actions – Summary 4 Lenient Recon plan 4 Issues thousands of pardons to ex- Confeds 4 Vetoes Fr Bur renewal and CRts Act 4 Violates Tenure of Office Act and is impeached 4 Denies land granted to GA slaves by Sherman
 Phase Four: Reconstruction Collapses
Phase Four: Reconstruction Collapses
 Reconstruction Collapses 41. Rise of Democrats in south 4“Redeemers” 4“ the Solid South” – black codes passed in southern states 4 Examples?
Reconstruction Collapses 41. Rise of Democrats in south 4“Redeemers” 4“ the Solid South” – black codes passed in southern states 4 Examples?
 The “Invisible Empire of the South”
The “Invisible Empire of the South”
 Reconstruction Collapses 42. Rise of the Ku Klux Klan 4 Tenn 1866, vigilante group 4 Goals of KKK 4 A. destroy Repub. Party 4 B. end Cong. Recon
Reconstruction Collapses 42. Rise of the Ku Klux Klan 4 Tenn 1866, vigilante group 4 Goals of KKK 4 A. destroy Repub. Party 4 B. end Cong. Recon
 Reconstruction Collapses 4 C. prevent blacks from exercising political rights 4 D. targets other minorities and whites who assisted them
Reconstruction Collapses 4 C. prevent blacks from exercising political rights 4 D. targets other minorities and whites who assisted them

 Reconstruction Collapses 4 Enforcement Acts 1870 -71 4 to suppress KKK, use of troops 4 to protect elections and courts 43. Amnesty Act 1872 4 returns voting rights and right to hold office to ex-Confeds 4 Southern Democrat Redeemers take advantage – How is this possible?
Reconstruction Collapses 4 Enforcement Acts 1870 -71 4 to suppress KKK, use of troops 4 to protect elections and courts 43. Amnesty Act 1872 4 returns voting rights and right to hold office to ex-Confeds 4 Southern Democrat Redeemers take advantage – How is this possible?
 Reconstruction Collapses 44. 1872 Election 4 Split in Republican party 4 Grant re-elected 4 Liberal Repub’s – nominate Horace Greeley 4 Weakens Repub party 4“Solid” South strengthens 4 Redeemers take advantage
Reconstruction Collapses 44. 1872 Election 4 Split in Republican party 4 Grant re-elected 4 Liberal Repub’s – nominate Horace Greeley 4 Weakens Repub party 4“Solid” South strengthens 4 Redeemers take advantage
 Reconstruction Collapses 45. Election of 1876 4 Rutherford Hayes (R) wins but 4 disputed results – Tilden wins popular vote, short 1 electoral 4 Electoral Commission – with a Repub majority decides election
Reconstruction Collapses 45. Election of 1876 4 Rutherford Hayes (R) wins but 4 disputed results – Tilden wins popular vote, short 1 electoral 4 Electoral Commission – with a Repub majority decides election
 Election of 1876 47 Repub, 7 Democ, 1 neutral 4 neutral – resigns to accept a Senatorial appt 4 Replaced by a Repub judge 4 Hayes declared winner 8 -7
Election of 1876 47 Repub, 7 Democ, 1 neutral 4 neutral – resigns to accept a Senatorial appt 4 Replaced by a Repub judge 4 Hayes declared winner 8 -7
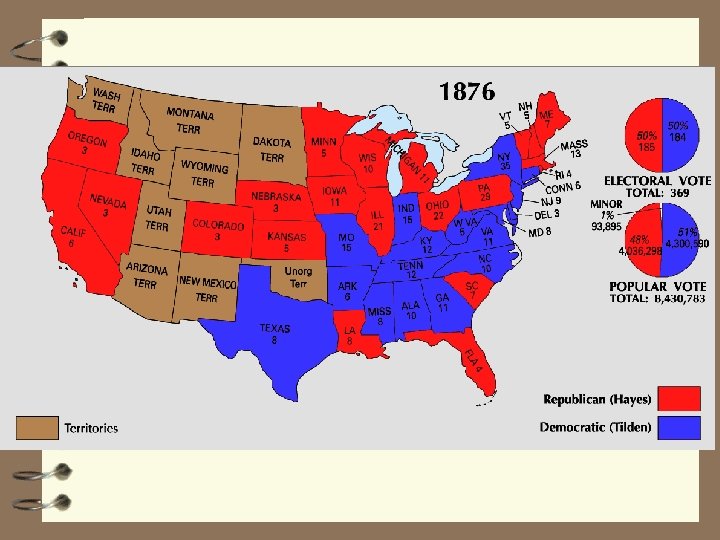
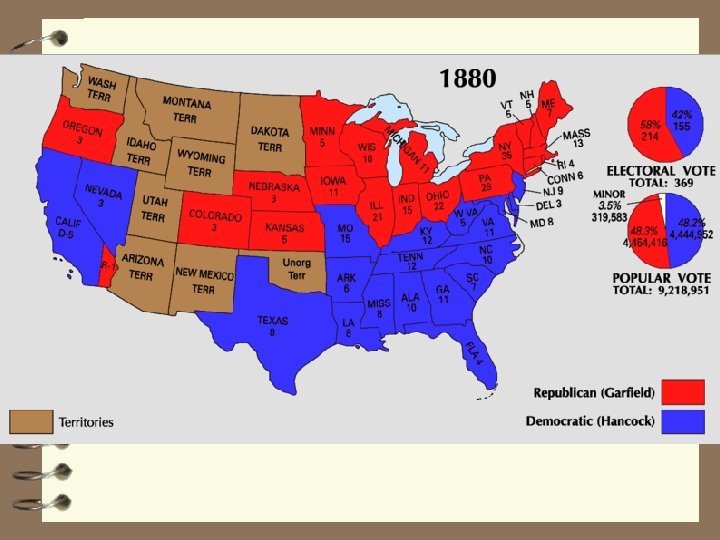
 Compromise of 1877 4 In return for Southern support and promise to guarantee civil rights, Hayes agreed to: 4 A. one term only 4 B. remove troops from SC, LA, FL 4 C. appoint Democrats to cabinet posts and as judges 4 D. spend fed $$ for internal improvements in the south
Compromise of 1877 4 In return for Southern support and promise to guarantee civil rights, Hayes agreed to: 4 A. one term only 4 B. remove troops from SC, LA, FL 4 C. appoint Democrats to cabinet posts and as judges 4 D. spend fed $$ for internal improvements in the south
 Compromise of 1877 4 Results – Southern Democrats control House of Reps 4 home rule estab’d in south 4 ability of southern states to run govt’s w/o fed intervention
Compromise of 1877 4 Results – Southern Democrats control House of Reps 4 home rule estab’d in south 4 ability of southern states to run govt’s w/o fed intervention
 Compromise of 1877 4 new black codes passed limiting rights of freedmen in southern sts. 4 End of Reconstruction – The Great Betrayal 4 Beginning of Jim Crow period in the South and in the nation to the 1960 s
Compromise of 1877 4 new black codes passed limiting rights of freedmen in southern sts. 4 End of Reconstruction – The Great Betrayal 4 Beginning of Jim Crow period in the South and in the nation to the 1960 s


