9c5fcda9e30656a2fe769a75586898e0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Key Network Architecture Enablers for Wavelength-on-Demand L 1 VPN Services Chris Liou, Infinera Vijay Vusirikala, Infinera
Outline § Dynamic Wavelength-On-Demand Services & Layer 1 VPN Applications § Key Application Requirements § Architectural Considerations § A Digital Optical Networking Approach Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 2
Outline § Dynamic Wavelength-On-Demand Services & Layer 1 VPN Applications § Key Application Requirements § Architectural Considerations § A Digital Optical Networking Approach Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 3

What is a L 1 VPN? § A Layer 1 network abstraction that presents a secure, dedicated transport network to the end customer § An alternative to a dedicated physical Layer 1 network § May co-exist with other L 1 VPN instances on the same physical carrier network § Provides end-customer with control & visibility over Layer 1 services between Customer Edges (CEs) § Comprised of a set of CEs & the VPN connections provided by the provider (between Provider Edges (PEs)) Varied levels of network management control & visibility § § Standards efforts in progress (IETF, ITU-T) § GMPLS playing a key role in signaling & routing § E. g. , draft-ietf-l 1 vpn-*, ITU-T SG 13 Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 4
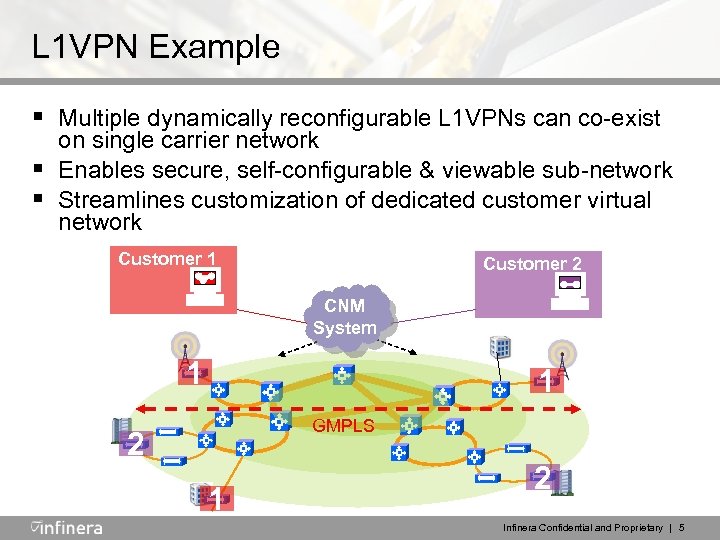
L 1 VPN Example § Multiple dynamically reconfigurable L 1 VPNs can co-exist § § on single carrier network Enables secure, self-configurable & viewable sub-network Streamlines customization of dedicated customer virtual network Customer 1 Customer 2 CNM System 1 1 GMPLS 2 1 2 Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 5
L 1 VPN & Dynamic Wo. D Drivers § Basis for new service offerings for wholesale carriers § An alternative to leased point-to-point waves § Rapid reconfigurability of L 1 services with minimal carrier intervention § Shifts onus of capacity planning away from carrier and into customer’s own hands § Facilitates internal carrier partitioning of common L 1 network § Streamline carrier’s servicing of internal capacity requests § E. g. , wholesale carrier providing IP organization with self-configurable L 1 transport VPN § Dynamic real-time reconfigurability enables many applications § § Dynamic load-sharing based on capacity-on-demand One-time high bandwidth broadcast events Timesharing of network capacity Short-term capacity lease Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 6
Outline § Dynamic Wavelength-On-Demand Services & Layer 1 VPN Applications § Key Application Requirements § Architectural Considerations § A Digital Optical Networking Approach Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 7
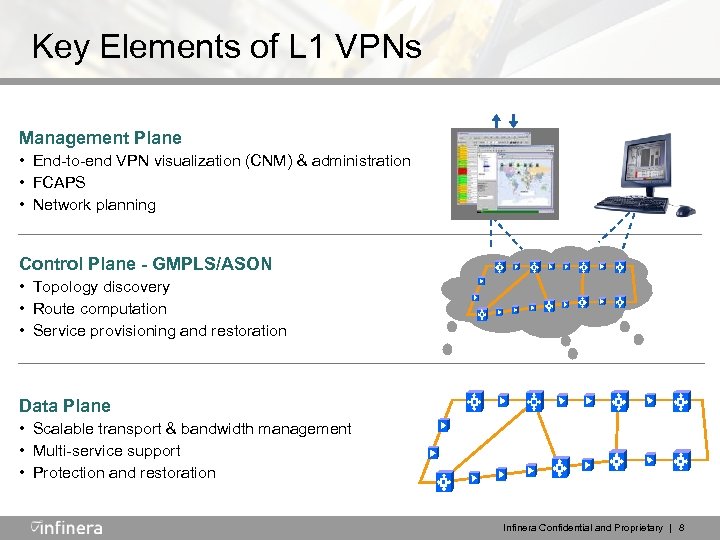
Key Elements of L 1 VPNs Management Plane • End-to-end VPN visualization (CNM) & administration • FCAPS • Network planning Control Plane - GMPLS/ASON • Topology discovery • Route computation • Service provisioning and restoration Data Plane • Scalable transport & bandwidth management • Multi-service support • Protection and restoration Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 8
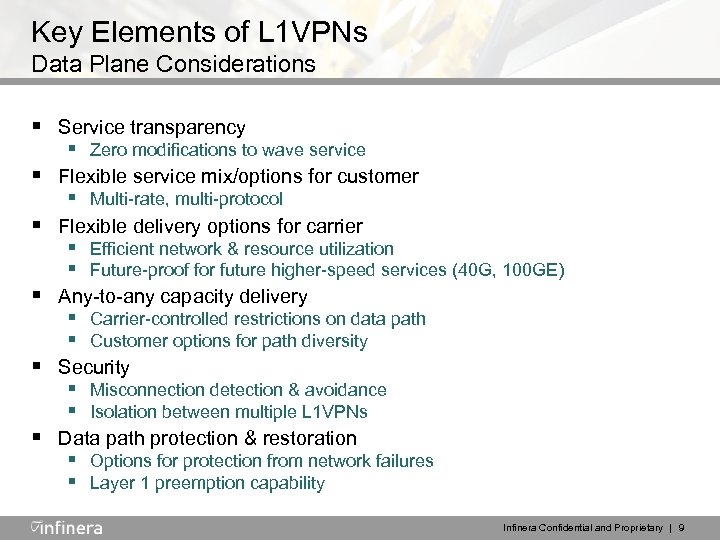
Key Elements of L 1 VPNs Data Plane Considerations § Service transparency § Zero modifications to wave service § Flexible service mix/options for customer § Multi-rate, multi-protocol § Flexible delivery options for carrier § Efficient network & resource utilization § Future-proof for future higher-speed services (40 G, 100 GE) § Any-to-any capacity delivery § Carrier-controlled restrictions on data path § Customer options for path diversity § Security § Misconnection detection & avoidance § Isolation between multiple L 1 VPNs § Data path protection & restoration § Options for protection from network failures § Layer 1 preemption capability Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 9

Key Elements of L 1 VPNs Control Plane Considerations § On-demand “touchless” reconfigurability § Intelligent control plane for streamlined, automated routing & provisioning § Minimal Op. Ex & lead-times Evolution path towards dynamic UNI signaling (CE-PE) § § Secure & isolated control plane functions § Zero interaction between multiple VPNs § Data & Control Plane separation § Data plane unaffected by control plane failures § Customer traffic engineering options for route diversity Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 10
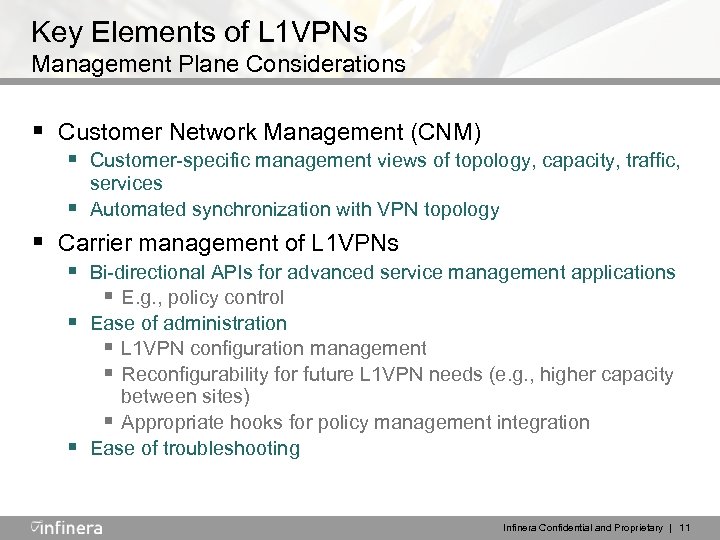
Key Elements of L 1 VPNs Management Plane Considerations § Customer Network Management (CNM) § Customer-specific management views of topology, capacity, traffic, services Automated synchronization with VPN topology § § Carrier management of L 1 VPNs § Bi-directional APIs for advanced service management applications § E. g. , policy control § Ease of administration § L 1 VPN configuration management § Reconfigurability for future L 1 VPN needs (e. g. , higher capacity § between sites) § Appropriate hooks for policy management integration Ease of troubleshooting Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 11
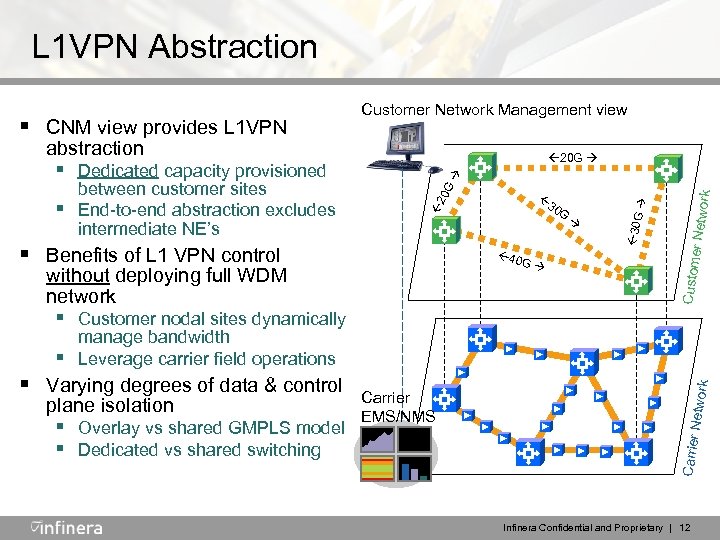
L 1 VPN Abstraction abstraction 20 G G er Netw ork G 40 without deploying full WDM network 30 Custom § Benefits of L 1 VPN control G 2 0 G § between customer sites End-to-end abstraction excludes intermediate NE’s § Dedicated capacity provisioned 30 § CNM view provides L 1 VPN Customer Network Management view § Customer nodal sites dynamically plane isolation § Overlay vs shared GMPLS model § Dedicated vs shared switching Carrier EMS/NMS Network § Varying degrees of data & control Carrier § manage bandwidth Leverage carrier field operations Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 12

Outline § Dynamic Wavelength-On-Demand Services & Layer 1 VPN Applications § Key Application Requirements § Architectural Considerations § A Digital Optical Networking Approach Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 13
L 1 VPN Service Model Options Discussion § Pre-established vs. On-demand PE-PE capacity § PE-PE cross-sectional capacity needs may evolve over § time On-demand link sizing encourages sharing of capacity across multiple customers § Shared vs. dedicated per-VPN switching § L 1 switching function for each VPN can reside “on” or § “off-net” Off-net switching creates natural security partition Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 14
L 1 VPN Service Model Options (contd. ) Discussion § Management vs. Signaling based provisioning § Specifies how dynamic circuit configuration is accomplished § Signaling based model generally more broadly discussed § Overlay vs. Peering signaling model (CE-PE) § Signaling only vs. Signaling + Routing model (aka, Basic vs Enhanced Mode – Routing enables automated membership & TE link information exchange § Virtual Node vs. Virtual Link model § Differing abstraction levels of L 1 VPN capacity § Virtual Link is currently finding favor Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 15

L 1 VPN Service Level Requirements Discussion § Accounting Reporting § Security of provider-customer communication § Data-, control-, and management planes § Data integrity, confidentiality, authentication, and access control § § § Class of Service (e. g. , Availability Class) Performance Reporting Fault Reporting Connectivity Reporting Policy (e. g. , path computation policy, CE-CE signaling pass-through, etc. ) Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 16
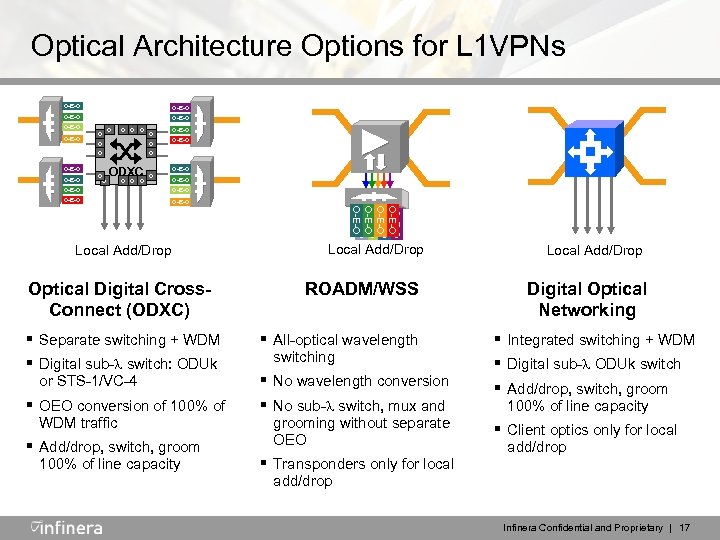
Optical Architecture Options for L 1 VPNs O-E-O O-E-O O O O O-E-O O ODXC O O-E-O O-E-O O-E-O O-E-O Local Add/Drop Optical Digital Cross. Connect (ODXC) § Separate switching + WDM § Digital sub- switch: ODUk or STS-1/VC-4 § OEO conversion of 100% of WDM traffic § Add/drop, switch, groom 100% of line capacity Local Add/Drop ROADM/WSS § All-optical wavelength switching § No wavelength conversion § No sub- switch, mux and grooming without separate OEO § Transponders only for local Local Add/Drop Digital Optical Networking § Integrated switching + WDM § Digital sub- ODUk switch § Add/drop, switch, groom 100% of line capacity § Client optics only for local add/drop Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 17
Outline § Dynamic Wavelength-On-Demand Services & Layer 1 VPN Applications § Key Application Requirements § Architectural Considerations § A Digital Optical Networking Approach Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 18
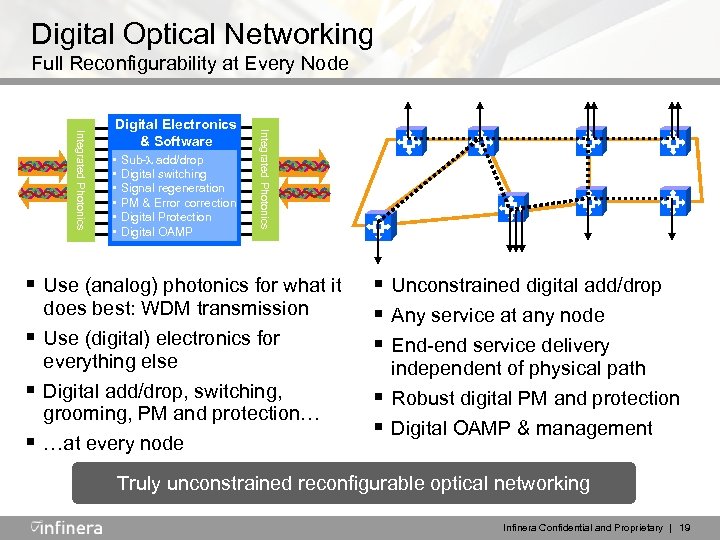
Digital Optical Networking Full Reconfigurability at Every Node • • • Sub- add/drop Digital switching Signal regeneration PM & Error correction Digital Protection Digital OAMP Integrated Photonics Digital Electronics & Software § Use (analog) photonics for what it § § § does best: WDM transmission Use (digital) electronics for everything else Digital add/drop, switching, grooming, PM and protection… …at every node § Unconstrained digital add/drop § Any service at any node § End-end service delivery § § independent of physical path Robust digital PM and protection Digital OAMP & management Truly unconstrained reconfigurable optical networking Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 19
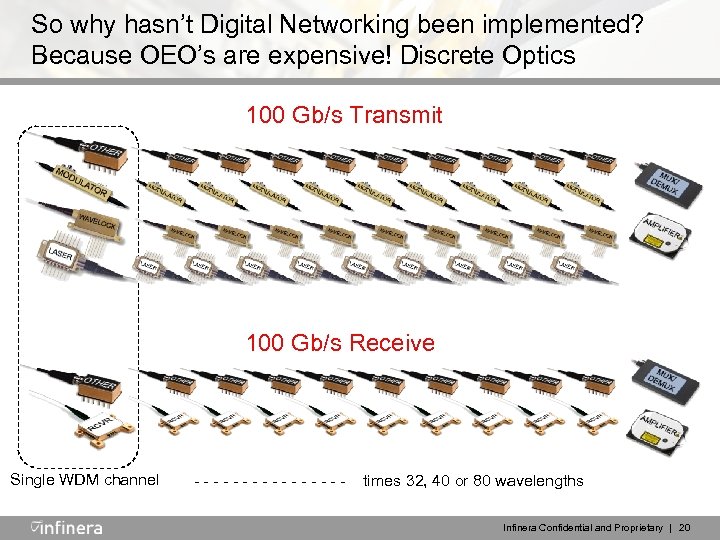
So why hasn’t Digital Networking been implemented? Because OEO’s are expensive! Discrete Optics 100 Gb/s Transmit 100 Gb/s Receive Single WDM channel -------- times 32, 40 or 80 wavelengths Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 20
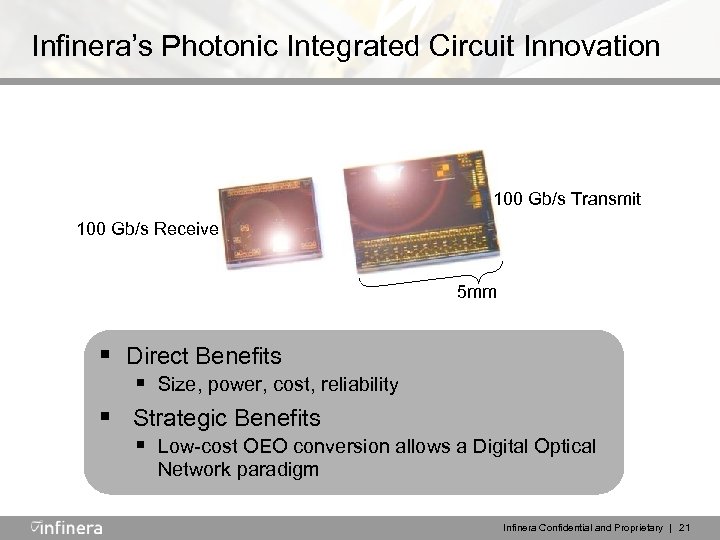
Infinera’s Photonic Integrated Circuit Innovation 100 Gb/s Transmit 100 Gb/s Receive 5 mm 100 § Direct Benefits Gb/s Receive § Size, power, cost, reliability § Strategic Benefits § Low-cost OEO conversion allows a Digital Optical Network paradigm Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 21
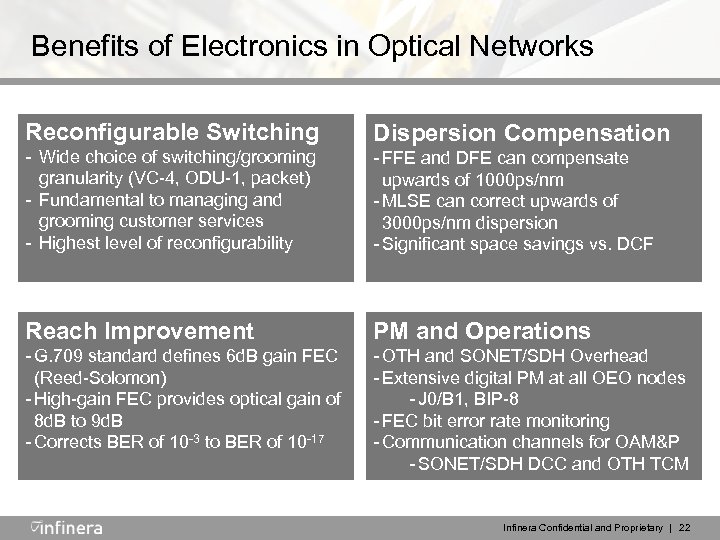
Benefits of Electronics in Optical Networks Reconfigurable Switching - Wide choice of switching/grooming granularity (VC-4, ODU-1, packet) - Fundamental to managing and grooming customer services - Highest level of reconfigurability Dispersion Compensation - FFE and DFE can compensate upwards of 1000 ps/nm - MLSE can correct upwards of 3000 ps/nm dispersion - Significant space savings vs. DCF Reach Improvement PM and Operations - G. 709 standard defines 6 d. B gain FEC (Reed-Solomon) - High-gain FEC provides optical gain of 8 d. B to 9 d. B - Corrects BER of 10 -3 to BER of 10 -17 - OTH and SONET/SDH Overhead - Extensive digital PM at all OEO nodes - J 0/B 1, BIP-8 - FEC bit error rate monitoring - Communication channels for OAM&P - SONET/SDH DCC and OTH TCM Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 22
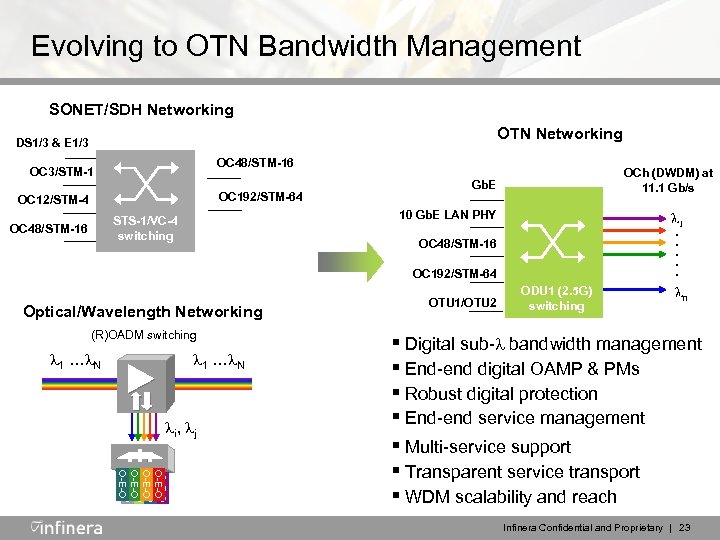
Evolving to OTN Bandwidth Management SONET/SDH Networking DS 1/3 & E 1/3 OC 48/STM-16 OC 3/STM-1 OC 192/STM-64 OC 12/STM-4 STS-1/VC-4 switching 1 . . . OC 48/STM-16 OTN management § Digital sub- bandwidth. Networking § End-end digital OAMP & PMs OCh (DWDM) at Gb. E § Robust digital protection 11. 1 Gb/s § End-end. Gb. E LAN PHY 10 service management OC 48/STM-16 OC 192/STM-64 Optical/Wavelength Networking (R)OADM switching 1 … N i , j OTU 1/OTU 2 ODU 1 (2. 5 G) switching n O-E-O O-E-O § Digital sub- bandwidth management § End-end digital § Multi-service support OAMP & PMs § Robust digital protection § Transparent service transport End-end and reach § WDM§scalabilityservice management § Multi-service support § Transparent service transport § WDM scalability and reach Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 23
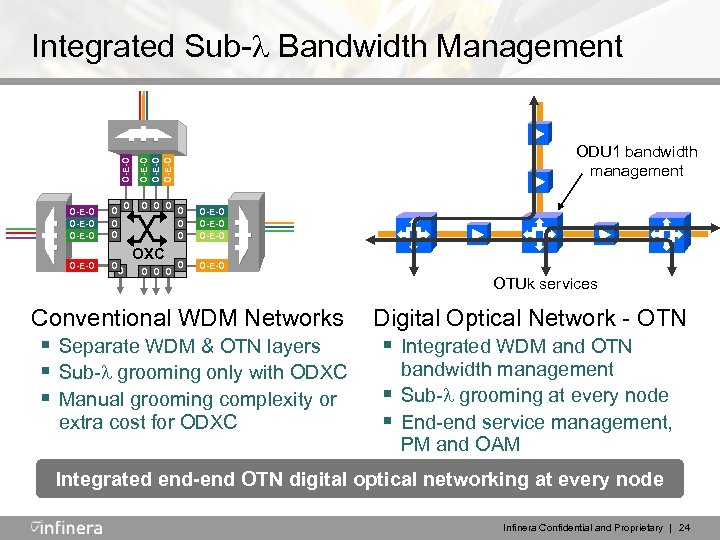
O-E-O Integrated Sub- Bandwidth Management O-E-O O O ODU 1 bandwidth management O-E-O O O OXC O O O O-E-O O O-E-O Conventional WDM Networks § Separate WDM & OTN layers § Sub- grooming only with ODXC § Manual grooming complexity or extra cost for ODXC OTUk services Digital Optical Network - OTN § Integrated WDM and OTN § § bandwidth management Sub- grooming at every node End-end service management, PM and OAM Integrated end-end OTN digital optical networking at every node Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 24
Digital Optical Network - Characteristics § 100 G digital bandwidth increments § Readily deployable capacity usable by any service § Rapid service deployment § Service activation is decoupled from transmission layer design and constraints Enables efficient protection and restoration schemes Integrated sub-wavelength bandwidth management Automated GMPLS end-to-end service activation Built-in PRBS testing for service readiness § § § Digital Optical Networking approach provides futureproofing for 40 G & 100 Gb. E § Ease of reconfigurability at data plane, control plane and management plane Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 25
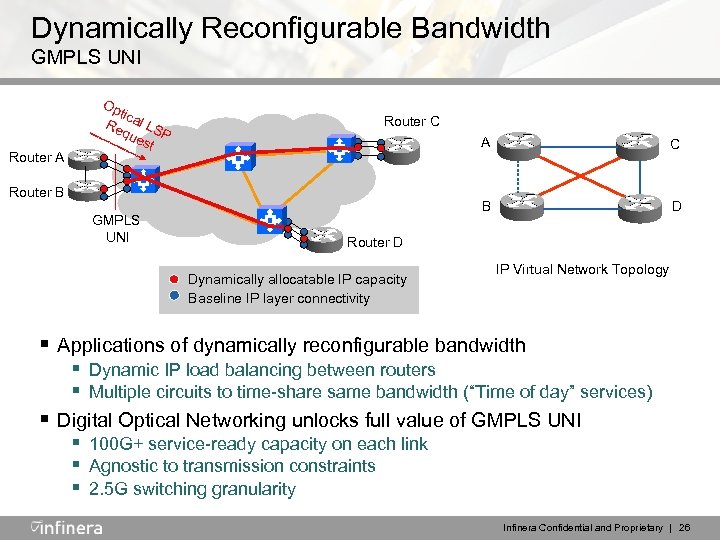
Dynamically Reconfigurable Bandwidth GMPLS UNI Router A Op tic Re al LS que P st Router C A B Router B GMPLS UNI C D Router D Dynamically allocatable IP capacity Baseline IP layer connectivity IP Virtual Network Topology § Applications of dynamically reconfigurable bandwidth § Dynamic IP load balancing between routers § Multiple circuits to time-share same bandwidth (“Time of day” services) § Digital Optical Networking unlocks full value of GMPLS UNI § 100 G+ service-ready capacity on each link § Agnostic to transmission constraints § 2. 5 G switching granularity Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 26
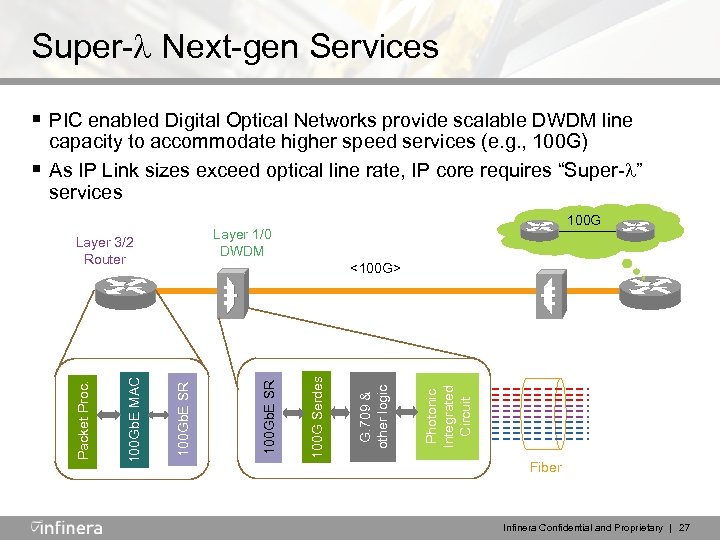
Super- Next-gen Services § PIC enabled Digital Optical Networks provide scalable DWDM line Photonic Integrated Circuit G. 709 & other logic 100 G Serdes 100 Gb. E SR <100 G> 100 Gb. E SR 100 Gb. E MAC 100 G Layer 1/0 DWDM Layer 3/2 Router Packet Proc. § capacity to accommodate higher speed services (e. g. , 100 G) As IP Link sizes exceed optical line rate, IP core requires “Super- ” services Fiber Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 27
L 1 VPN Evolution § L 1 VPNs should scale in two dimensions to accommodate future evolution § L 1 VPN Size and Traffic growth § Control plane and management plane to scale § accordingly § Ease of reconfigurability of both logical circuits & cross-connect capacity needs to be maintained New Services § Today most L 1 VPN designs want 1 G-10 G § … with path to 40 G & 100 Gb. E services Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 28
Summary § L 1 VPN architecture involves data plane, control plane and management plane § Key Characteristics of L 1 VPNs § Scalability § Ease of reconfigurability § Customized control § Digital Optical Networking Architecture provides key benefits for L 1 VPNs § Service layer decoupled from transmission layer § Integrated sub-lambda bandwidth management § End-to-end GMPLS intelligence Infinera Confidential and Proprietary | 29
9c5fcda9e30656a2fe769a75586898e0.ppt