b036e70716ad7c82b5bb84ed0c3c32e4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Kelemen Zádor Dániel kelemen. daniel@sqi. hu The comparison of ISO 9001: 2000 and CMMI-DEV v 1. 2
Kelemen Zádor Dániel kelemen. daniel@sqi. hu The comparison of ISO 9001: 2000 and CMMI-DEV v 1. 2
 Content About ISO 9001: 2000 About CMMI v 1. 2 Main differences Differences in terminology Similarities ISO 9001: 2000 and CMMI in the Hungarian market Rate of return How could we develop a CMMI-conform system having ISO 9001: 2000 as a basis? 2
Content About ISO 9001: 2000 About CMMI v 1. 2 Main differences Differences in terminology Similarities ISO 9001: 2000 and CMMI in the Hungarian market Rate of return How could we develop a CMMI-conform system having ISO 9001: 2000 as a basis? 2
 The ISO 9000 standard family ISO 9000: 2005 Fundamentals and Vocabulary ISO 9001: 2000 Requirements ISO 9004: 2000 Guidelines for performance improvements ISO 90003: 2005 Guidelines for the application of ISO 9001: 2000 to computer software 3
The ISO 9000 standard family ISO 9000: 2005 Fundamentals and Vocabulary ISO 9001: 2000 Requirements ISO 9004: 2000 Guidelines for performance improvements ISO 90003: 2005 Guidelines for the application of ISO 9001: 2000 to computer software 3
 The ISO 9001: 2000 Minőségirányítási rendszerek. Követelmények 0. Introduction 1. Scope 2. Normative reference 3. Terms and definitions 4. Quality management system 5. Management responsibility 6. Resource management 7. Product realization 8. Measurement, analysis and improvement Annexes 4
The ISO 9001: 2000 Minőségirányítási rendszerek. Követelmények 0. Introduction 1. Scope 2. Normative reference 3. Terms and definitions 4. Quality management system 5. Management responsibility 6. Resource management 7. Product realization 8. Measurement, analysis and improvement Annexes 4
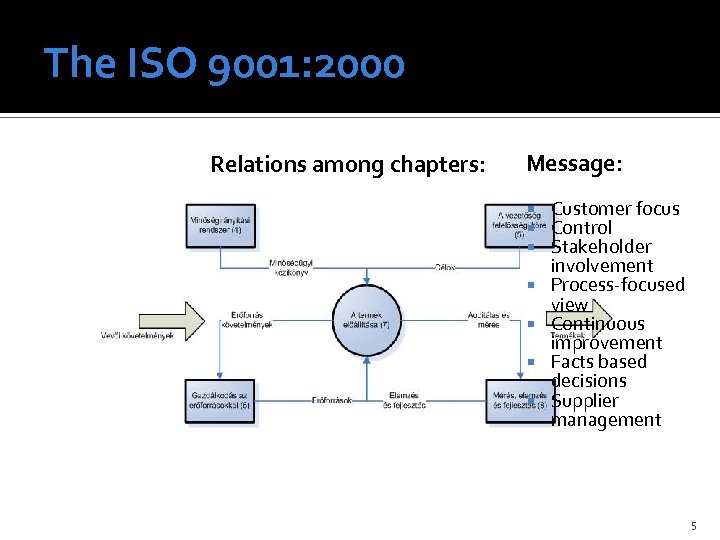 The ISO 9001: 2000 Relations among chapters: Message: Customer focus Control Stakeholder involvement Process-focused view Continuous improvement Facts based decisions Supplier management 5
The ISO 9001: 2000 Relations among chapters: Message: Customer focus Control Stakeholder involvement Process-focused view Continuous improvement Facts based decisions Supplier management 5
 The CMMI For software developers Process based approach Defines process areas (22) Process area categories: Process management Project management Technical Support Multi-level (ML 1 -5 /CL 0 -5) Focus on software- and system development 6
The CMMI For software developers Process based approach Defines process areas (22) Process area categories: Process management Project management Technical Support Multi-level (ML 1 -5 /CL 0 -5) Focus on software- and system development 6
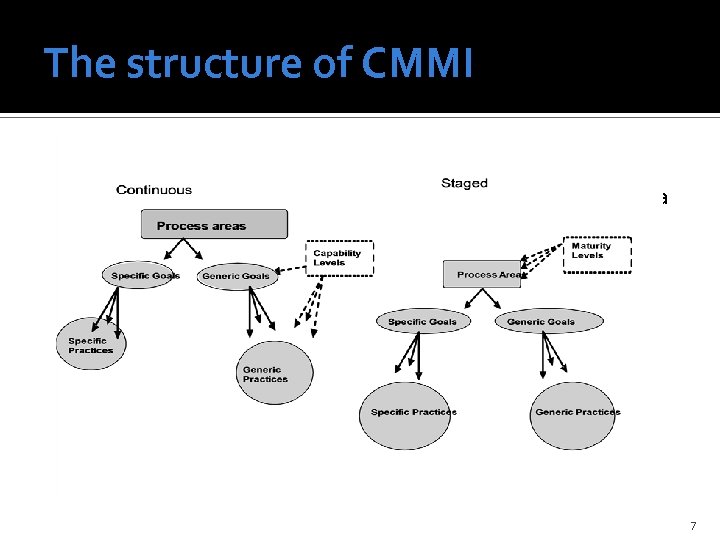 The structure of CMMI Folyamat alapú megközelítés Folyamatcsoportokat definál (a v 1. 2 22 -t) Folyamat(csoport) kategóriák: Folyamatmenedzsment Projektmenedzsment Műszaki Támogató Többszintű (ML 1 -5 /CL 0 -5) Kiemeli a szoftver- és rendszerfejlesztést 7
The structure of CMMI Folyamat alapú megközelítés Folyamatcsoportokat definál (a v 1. 2 22 -t) Folyamat(csoport) kategóriák: Folyamatmenedzsment Projektmenedzsment Műszaki Támogató Többszintű (ML 1 -5 /CL 0 -5) Kiemeli a szoftver- és rendszerfejlesztést 7
 (Previous) comparison of approaches Boris Mutafelija, Harvey Stromberg (2001 -2004), ISO->CMMI v 1. 0, CMMI v 1. 0 ->ISO Based on the results of Mutafelija: Angela Tuffley, Terrence P. Rout (2005) ISO->CMMI v 1. 0 They analyzed the same requirements, they got similar results. Concentrating only on the content. Comparison of CMMI v 1. 2 and MSZ EN ISO 9001: 2000: ISO->CMMI v 1. 2 ISO and CMMI in the Hungarian Market ROI of these approaches 8
(Previous) comparison of approaches Boris Mutafelija, Harvey Stromberg (2001 -2004), ISO->CMMI v 1. 0, CMMI v 1. 0 ->ISO Based on the results of Mutafelija: Angela Tuffley, Terrence P. Rout (2005) ISO->CMMI v 1. 0 They analyzed the same requirements, they got similar results. Concentrating only on the content. Comparison of CMMI v 1. 2 and MSZ EN ISO 9001: 2000: ISO->CMMI v 1. 2 ISO and CMMI in the Hungarian Market ROI of these approaches 8
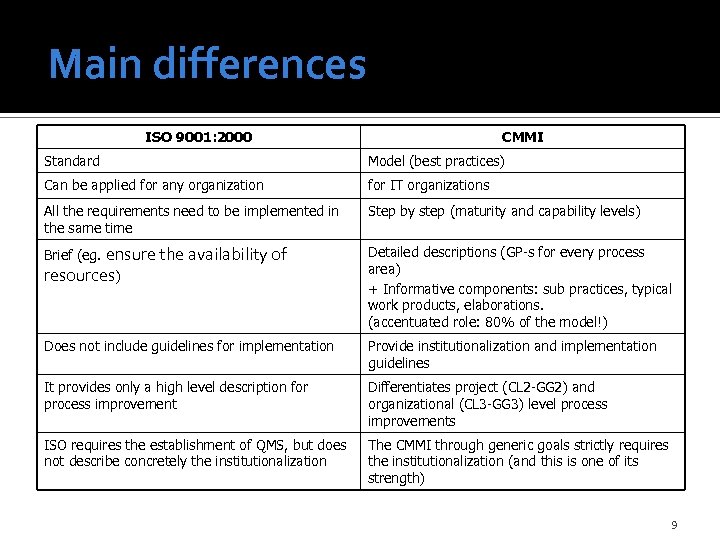 Main differences ISO 9001: 2000 CMMI Standard Model (best practices) Can be applied for any organization for IT organizations All the requirements need to be implemented in the same time Step by step (maturity and capability levels) Brief (eg. ensure the availability of resources) Detailed descriptions (GP-s for every process area) + Informative components: sub practices, typical work products, elaborations. (accentuated role: 80% of the model!) Does not include guidelines for implementation Provide institutionalization and implementation guidelines It provides only a high level description for process improvement Differentiates project (CL 2 -GG 2) and organizational (CL 3 -GG 3) level process improvements ISO requires the establishment of QMS, but does not describe concretely the institutionalization The CMMI through generic goals strictly requires the institutionalization (and this is one of its strength) 9
Main differences ISO 9001: 2000 CMMI Standard Model (best practices) Can be applied for any organization for IT organizations All the requirements need to be implemented in the same time Step by step (maturity and capability levels) Brief (eg. ensure the availability of resources) Detailed descriptions (GP-s for every process area) + Informative components: sub practices, typical work products, elaborations. (accentuated role: 80% of the model!) Does not include guidelines for implementation Provide institutionalization and implementation guidelines It provides only a high level description for process improvement Differentiates project (CL 2 -GG 2) and organizational (CL 3 -GG 3) level process improvements ISO requires the establishment of QMS, but does not describe concretely the institutionalization The CMMI through generic goals strictly requires the institutionalization (and this is one of its strength) 9
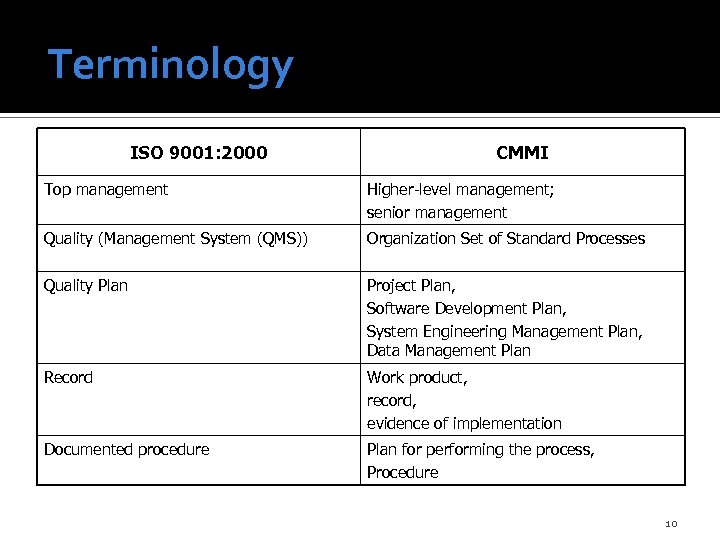 Terminology ISO 9001: 2000 CMMI Top management Higher-level management; senior management Quality (Management System (QMS)) Organization Set of Standard Processes Quality Plan Project Plan, Software Development Plan, System Engineering Management Plan, Data Management Plan Record Work product, record, evidence of implementation Documented procedure Plan for performing the process, Procedure 10
Terminology ISO 9001: 2000 CMMI Top management Higher-level management; senior management Quality (Management System (QMS)) Organization Set of Standard Processes Quality Plan Project Plan, Software Development Plan, System Engineering Management Plan, Data Management Plan Record Work product, record, evidence of implementation Documented procedure Plan for performing the process, Procedure 10
 ISO 9001: 2000 principles in CMMI Customer focus GP 2. 7 Identify and Involve Relevant Stakeholders PP, IPM Plan Stakeholder Involvement RD, TS A CMMI is weaker than ISO GP 2. 1 Establish an Organizational Policy GP 2. 4 Assign Responsability GP 2. 10, Review Status with Higher Level Management OPF Control Stakeholder involvement GP 2. 3 Provide Resources GP 2. 5 Train People GP 2. 7 Identify and Involve Relevant Stakeholders 11
ISO 9001: 2000 principles in CMMI Customer focus GP 2. 7 Identify and Involve Relevant Stakeholders PP, IPM Plan Stakeholder Involvement RD, TS A CMMI is weaker than ISO GP 2. 1 Establish an Organizational Policy GP 2. 4 Assign Responsability GP 2. 10, Review Status with Higher Level Management OPF Control Stakeholder involvement GP 2. 3 Provide Resources GP 2. 5 Train People GP 2. 7 Identify and Involve Relevant Stakeholders 11
 ISO 9001: 2000 principles in CMMI Process-focus For every process must be applied: ▪ GP 2. 2 Plan the process ▪ GP 3. 1 Establish a defined process Continuous improvement Capability and maturity levels Facts based decisions DAR – Decision analysis and resolution GP 2. 8 Monitor and Controll the process PMC, IPM, MA Supplier management SAM – Supplier agreement management ▪ (can be excluded in certain cases) CMMI is weaker in cooperation CMMI mainly focuses on control 12
ISO 9001: 2000 principles in CMMI Process-focus For every process must be applied: ▪ GP 2. 2 Plan the process ▪ GP 3. 1 Establish a defined process Continuous improvement Capability and maturity levels Facts based decisions DAR – Decision analysis and resolution GP 2. 8 Monitor and Controll the process PMC, IPM, MA Supplier management SAM – Supplier agreement management ▪ (can be excluded in certain cases) CMMI is weaker in cooperation CMMI mainly focuses on control 12
 Uncovered IS 0 9001: 2000 requirements in CMMI Assign management representative Internal communication the effectiveness of QMS Validation required before product delivery and implementation Onsite control of suppliers Handling customer property Calibration of measurement devices Establish a method for measuring and using customer satisfaction Elaboration of Criteria, scope, frequency, method of internal audits Independency of auditors (not in every case) 13
Uncovered IS 0 9001: 2000 requirements in CMMI Assign management representative Internal communication the effectiveness of QMS Validation required before product delivery and implementation Onsite control of suppliers Handling customer property Calibration of measurement devices Establish a method for measuring and using customer satisfaction Elaboration of Criteria, scope, frequency, method of internal audits Independency of auditors (not in every case) 13
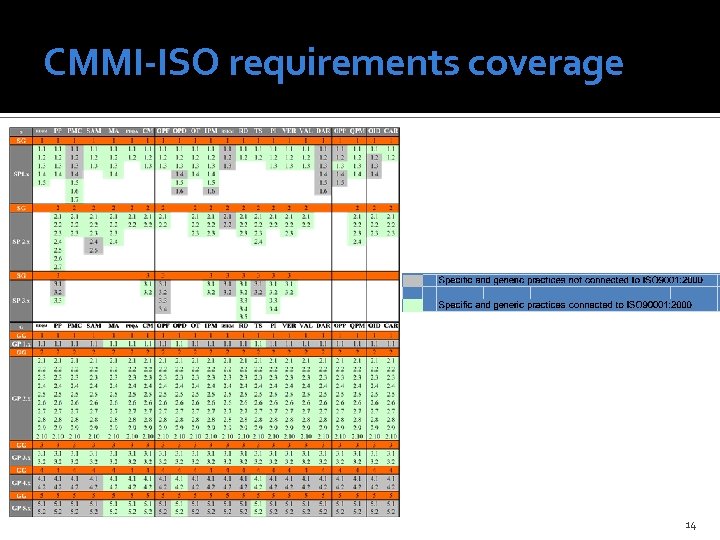 CMMI-ISO requirements coverage 14
CMMI-ISO requirements coverage 14
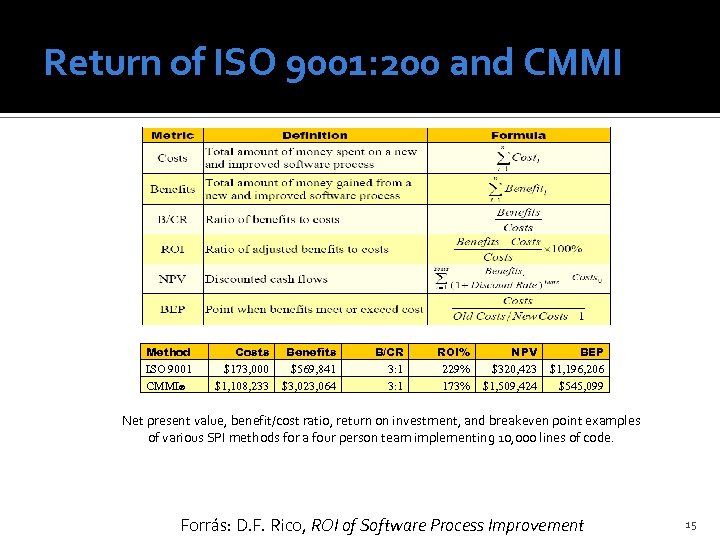 Return of ISO 9001: 200 and CMMI Method Costs Benefits B/CR ROI% NPV BEP ISO 9001 CMMI® $173, 000 $1, 108, 233 $569, 841 $3, 023, 064 3: 1 229% 173% $320, 423 $1, 509, 424 $1, 196, 206 $545, 099 Net present value, benefit/cost ratio, return on investment, and breakeven point examples of various SPI methods for a four person team implementing 10, 000 lines of code. Forrás: D. F. Rico, ROI of Software Process Improvement 15
Return of ISO 9001: 200 and CMMI Method Costs Benefits B/CR ROI% NPV BEP ISO 9001 CMMI® $173, 000 $1, 108, 233 $569, 841 $3, 023, 064 3: 1 229% 173% $320, 423 $1, 509, 424 $1, 196, 206 $545, 099 Net present value, benefit/cost ratio, return on investment, and breakeven point examples of various SPI methods for a four person team implementing 10, 000 lines of code. Forrás: D. F. Rico, ROI of Software Process Improvement 15
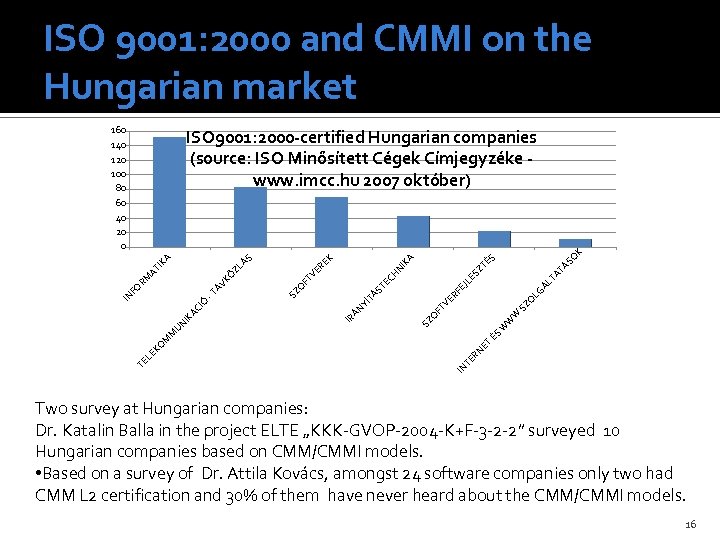 ISO 9001: 2000 and CMMI on the Hungarian market 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 LG ÁL T ES FE SZ O ER W FT V ÉS W W SZ O YÍ ÁN IR JL TÁ ST EC SZ O AT ÁS O ZT É S KA EK ER FT V HN I T NE TE R IN TE LE KO M M UN IK ÁC I Ó IN -T FO ÁV K RM Ö AT ZL ÁS IK A K ISO 9001: 2000 -certified Hungarian companies (source: ISO Minősített Cégek Címjegyzéke www. imcc. hu 2007 október) Two survey at Hungarian companies: Dr. Katalin Balla in the project ELTE „KKK-GVOP-2004 -K+F-3 -2 -2” surveyed 10 Hungarian companies based on CMM/CMMI models. • Based on a survey of Dr. Attila Kovács, amongst 24 software companies only two had CMM L 2 certification and 30% of them have never heard about the CMM/CMMI models. 16
ISO 9001: 2000 and CMMI on the Hungarian market 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 LG ÁL T ES FE SZ O ER W FT V ÉS W W SZ O YÍ ÁN IR JL TÁ ST EC SZ O AT ÁS O ZT É S KA EK ER FT V HN I T NE TE R IN TE LE KO M M UN IK ÁC I Ó IN -T FO ÁV K RM Ö AT ZL ÁS IK A K ISO 9001: 2000 -certified Hungarian companies (source: ISO Minősített Cégek Címjegyzéke www. imcc. hu 2007 október) Two survey at Hungarian companies: Dr. Katalin Balla in the project ELTE „KKK-GVOP-2004 -K+F-3 -2 -2” surveyed 10 Hungarian companies based on CMM/CMMI models. • Based on a survey of Dr. Attila Kovács, amongst 24 software companies only two had CMM L 2 certification and 30% of them have never heard about the CMM/CMMI models. 16
 How could we develop a CMMI-conform system having ISO 9001: 2000 as a basis? Some essential requirements: Transforming the quality assurance ▪ Quality assurance assigned to projects (starting from CL/ML 2) ▪ Product quality assurance (CMMI recommends ISO 9126) Introducing measurements ▪ CMMI recommends GQM (Goal-Question-Metric) ▪ Continuous measurement and improvement of products, processes and resources Establishing configuration audits, baselines Estimates, risk management in projects Planning, monitoring and measuring every process Requirements bidirectional traceability ML/CL 3: ▪ Defining and introducing technical processes ▪ Organizational procedures and tailoring guidelines for every process 17
How could we develop a CMMI-conform system having ISO 9001: 2000 as a basis? Some essential requirements: Transforming the quality assurance ▪ Quality assurance assigned to projects (starting from CL/ML 2) ▪ Product quality assurance (CMMI recommends ISO 9126) Introducing measurements ▪ CMMI recommends GQM (Goal-Question-Metric) ▪ Continuous measurement and improvement of products, processes and resources Establishing configuration audits, baselines Estimates, risk management in projects Planning, monitoring and measuring every process Requirements bidirectional traceability ML/CL 3: ▪ Defining and introducing technical processes ▪ Organizational procedures and tailoring guidelines for every process 17
 Thank you for attention! kelemen. daniel@sqi. hu www. cmmi. hu 18
Thank you for attention! kelemen. daniel@sqi. hu www. cmmi. hu 18


