efe5f189113d192a84e3ac73aa57662c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Kehittyneen terapian lääkevalmisteiden (ATMP) myyntilupaprosessi ja CAT Fimea GLP-keskustelupäivä 2. 9. 2015 Paula Salmikangas CAT Chair An agency of the European Union
Kehittyneen terapian lääkevalmisteiden (ATMP) myyntilupaprosessi ja CAT Fimea GLP-keskustelupäivä 2. 9. 2015 Paula Salmikangas CAT Chair An agency of the European Union
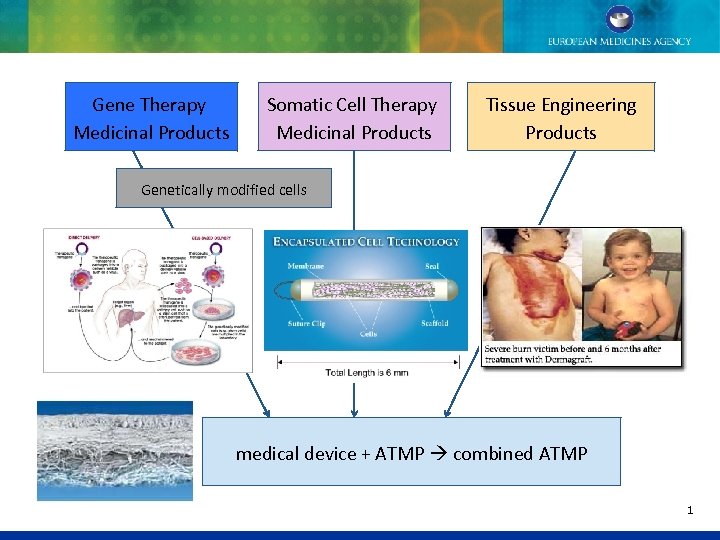 Gene Therapy Medicinal Products Somatic Cell Therapy Medicinal Products Tissue Engineering Products Genetically modified cells medical device + ATMP combined ATMP 1
Gene Therapy Medicinal Products Somatic Cell Therapy Medicinal Products Tissue Engineering Products Genetically modified cells medical device + ATMP combined ATMP 1
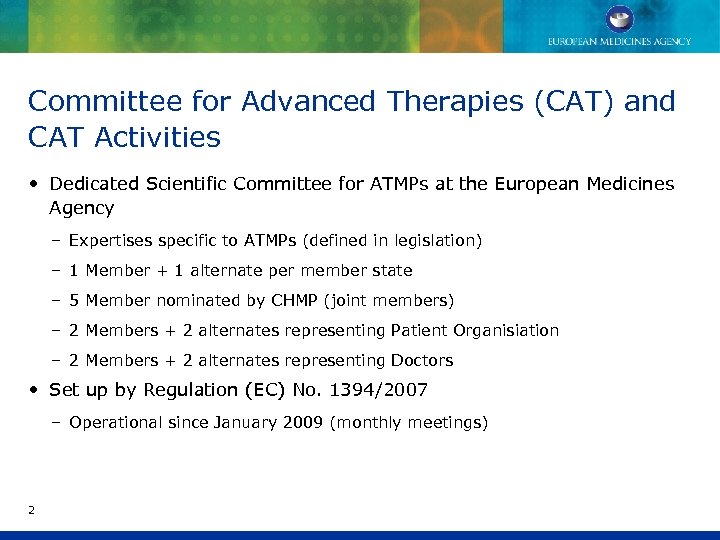 Committee for Advanced Therapies (CAT) and CAT Activities • Dedicated Scientific Committee for ATMPs at the European Medicines Agency – Expertises specific to ATMPs (defined in legislation) – 1 Member + 1 alternate per member state – 5 Member nominated by CHMP (joint members) – 2 Members + 2 alternates representing Patient Organisiation – 2 Members + 2 alternates representing Doctors • Set up by Regulation (EC) No. 1394/2007 – Operational since January 2009 (monthly meetings) 2
Committee for Advanced Therapies (CAT) and CAT Activities • Dedicated Scientific Committee for ATMPs at the European Medicines Agency – Expertises specific to ATMPs (defined in legislation) – 1 Member + 1 alternate per member state – 5 Member nominated by CHMP (joint members) – 2 Members + 2 alternates representing Patient Organisiation – 2 Members + 2 alternates representing Doctors • Set up by Regulation (EC) No. 1394/2007 – Operational since January 2009 (monthly meetings) 2
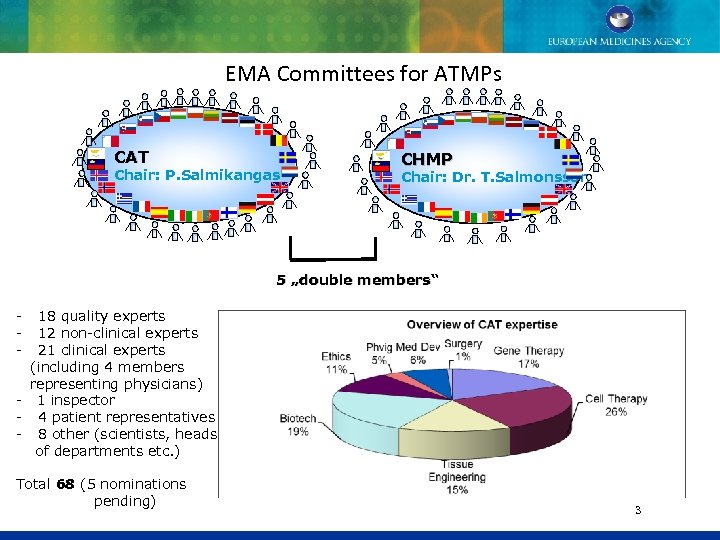 EMA Committees for ATMPs CAT Chair: P. Salmikangas CHMP Chair: Dr. T. Salmonsson 5 „double members“ - 18 quality experts - 12 non-clinical experts - 21 clinical experts (including 4 members representing physicians) - 1 inspector - 4 patient representatives - 8 other (scientists, heads of departments etc. ) Total 68 (5 nominations pending) 3
EMA Committees for ATMPs CAT Chair: P. Salmikangas CHMP Chair: Dr. T. Salmonsson 5 „double members“ - 18 quality experts - 12 non-clinical experts - 21 clinical experts (including 4 members representing physicians) - 1 inspector - 4 patient representatives - 8 other (scientists, heads of departments etc. ) Total 68 (5 nominations pending) 3
 Tasks of the CAT Tasks of the Committee for Advanced Therapies (CAT) EVALUATION Scientific Advice Support to PDCO Support to CHMP / COMP CERTIFICATION Interaction with stakeholders CLASSIFICATION Publications, Guidelines 4
Tasks of the CAT Tasks of the Committee for Advanced Therapies (CAT) EVALUATION Scientific Advice Support to PDCO Support to CHMP / COMP CERTIFICATION Interaction with stakeholders CLASSIFICATION Publications, Guidelines 4
 ATMP Evaluation procedure ATMPs will follow the Centralised procedure (mandatory scope) single MA (marketing authorisation) for entire EU: • 210 Day procedure • Evaluation by two independent (Rapp/Co. Rapp) teams from CAT, includes CHMP-co-ordinators to ensure transparency between the two Committees • All scientific discussion and adoption of key documents at CAT, followed by CHMP discussion CAT/CHMP opinion goes to the European Commission, which grants or refuses the MA 5
ATMP Evaluation procedure ATMPs will follow the Centralised procedure (mandatory scope) single MA (marketing authorisation) for entire EU: • 210 Day procedure • Evaluation by two independent (Rapp/Co. Rapp) teams from CAT, includes CHMP-co-ordinators to ensure transparency between the two Committees • All scientific discussion and adoption of key documents at CAT, followed by CHMP discussion CAT/CHMP opinion goes to the European Commission, which grants or refuses the MA 5
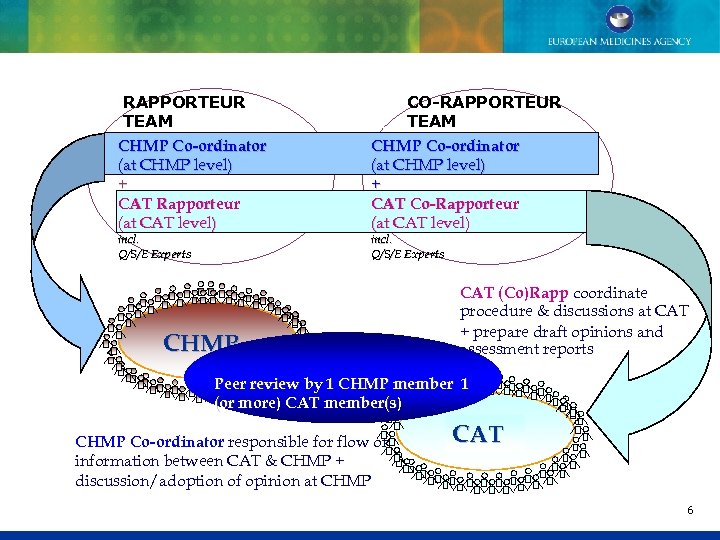 RAPPORTEUR TEAM CHMP Co-ordinator (at CHMP level) + CAT Rapporteur (at CAT level) incl. Q/S/E Experts CO-RAPPORTEUR TEAM CHMP Co-ordinator (at CHMP level) + CAT Co-Rapporteur (at CAT level) incl. Q/S/E Experts CHMP CAT (Co)Rapp coordinate procedure & discussions at CAT + prepare draft opinions and assessment reports Peer review by 1 CHMP member 1 (or more) CAT member(s) CHMP Co-ordinator responsible for flow of information between CAT & CHMP + discussion/adoption of opinion at CHMP CAT 6
RAPPORTEUR TEAM CHMP Co-ordinator (at CHMP level) + CAT Rapporteur (at CAT level) incl. Q/S/E Experts CO-RAPPORTEUR TEAM CHMP Co-ordinator (at CHMP level) + CAT Co-Rapporteur (at CAT level) incl. Q/S/E Experts CHMP CAT (Co)Rapp coordinate procedure & discussions at CAT + prepare draft opinions and assessment reports Peer review by 1 CHMP member 1 (or more) CAT member(s) CHMP Co-ordinator responsible for flow of information between CAT & CHMP + discussion/adoption of opinion at CHMP CAT 6
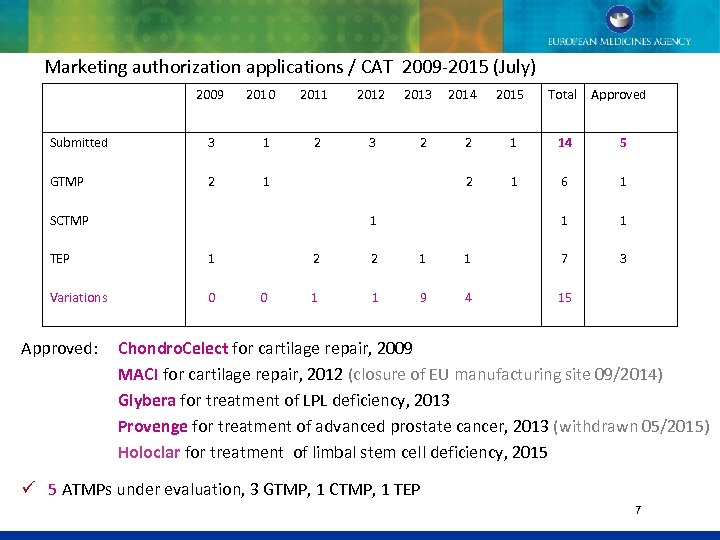 Marketing authorization applications / CAT 2009 -2015 (July) 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 Total Approved Submitted GTMP SCTMP TEP 3 1 2 3 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 14 6 1 7 Variations 0 1 9 4 15 5 1 1 3 Approved: Chondro. Celect for cartilage repair, 2009 MACI for cartilage repair, 2012 (closure of EU manufacturing site 09/2014) Glybera for treatment of LPL deficiency, 2013 Provenge for treatment of advanced prostate cancer, 2013 (withdrawn 05/2015) Holoclar for treatment of limbal stem cell deficiency, 2015 ü 5 ATMPs under evaluation, 3 GTMP, 1 CTMP, 1 TEP 7
Marketing authorization applications / CAT 2009 -2015 (July) 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 Total Approved Submitted GTMP SCTMP TEP 3 1 2 3 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 14 6 1 7 Variations 0 1 9 4 15 5 1 1 3 Approved: Chondro. Celect for cartilage repair, 2009 MACI for cartilage repair, 2012 (closure of EU manufacturing site 09/2014) Glybera for treatment of LPL deficiency, 2013 Provenge for treatment of advanced prostate cancer, 2013 (withdrawn 05/2015) Holoclar for treatment of limbal stem cell deficiency, 2015 ü 5 ATMPs under evaluation, 3 GTMP, 1 CTMP, 1 TEP 7
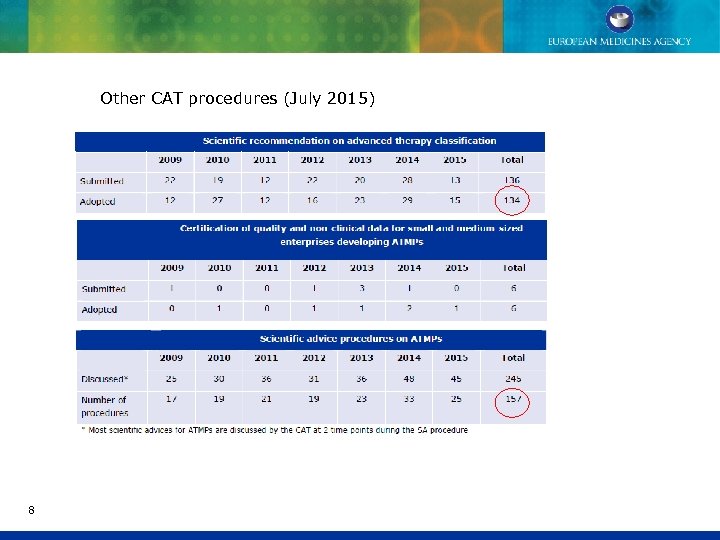 Other CAT procedures (July 2015) 8
Other CAT procedures (July 2015) 8
 Certification procedure • Only for SMEs • Scientific evaluation by CAT of – (early) quality / development data (Module 3) – (early) non-clinical data (Module 4) • 90 day procedure • Evaluation to the scientific standards of a marketing autorisation application – The SME applicant will always received the evaluation report (and List of issue for future consideration) – If positive evaluation: Certificate by EMA • 6 Certification procedures finalised (July 2015) – Bone marrow derived progenitor cells for cardiac repair 9 Presentation C Schneider (13 February 2012)
Certification procedure • Only for SMEs • Scientific evaluation by CAT of – (early) quality / development data (Module 3) – (early) non-clinical data (Module 4) • 90 day procedure • Evaluation to the scientific standards of a marketing autorisation application – The SME applicant will always received the evaluation report (and List of issue for future consideration) – If positive evaluation: Certificate by EMA • 6 Certification procedures finalised (July 2015) – Bone marrow derived progenitor cells for cardiac repair 9 Presentation C Schneider (13 February 2012)
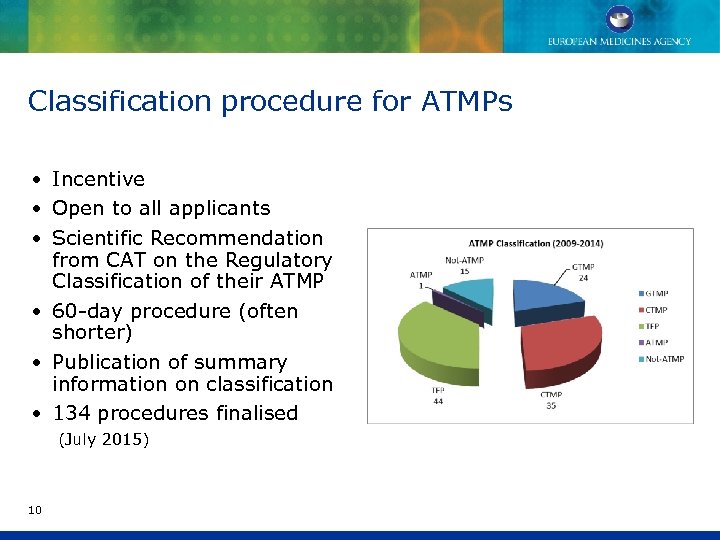 Classification procedure for ATMPs • Incentive • Open to all applicants • Scientific Recommendation from CAT on the Regulatory Classification of their ATMP • 60 -day procedure (often shorter) • Publication of summary information on classification • 134 procedures finalised (July 2015) 10
Classification procedure for ATMPs • Incentive • Open to all applicants • Scientific Recommendation from CAT on the Regulatory Classification of their ATMP • 60 -day procedure (often shorter) • Publication of summary information on classification • 134 procedures finalised (July 2015) 10
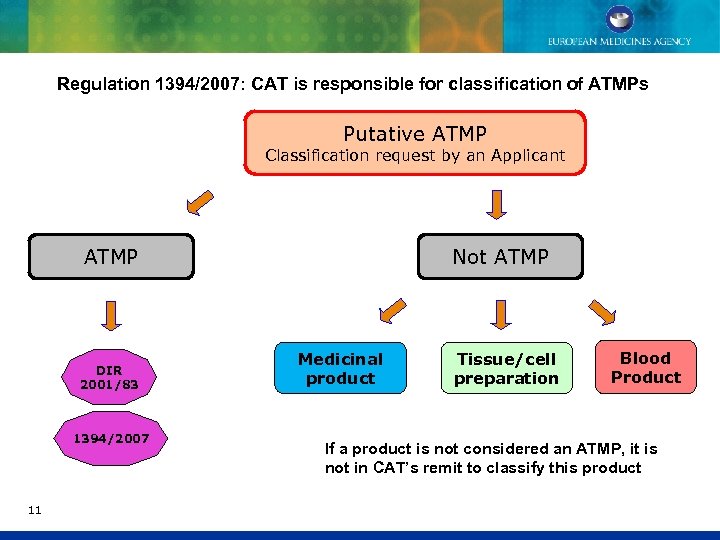 Regulation 1394/2007: CAT is responsible for classification of ATMPs Putative ATMP Classification request by an Applicant ATMP DIR 2001/83 1394/2007 11 Not ATMP Medicinal product Tissue/cell preparation Blood Product If a product is not considered an ATMP, it is not in CAT’s remit to classify this product
Regulation 1394/2007: CAT is responsible for classification of ATMPs Putative ATMP Classification request by an Applicant ATMP DIR 2001/83 1394/2007 11 Not ATMP Medicinal product Tissue/cell preparation Blood Product If a product is not considered an ATMP, it is not in CAT’s remit to classify this product
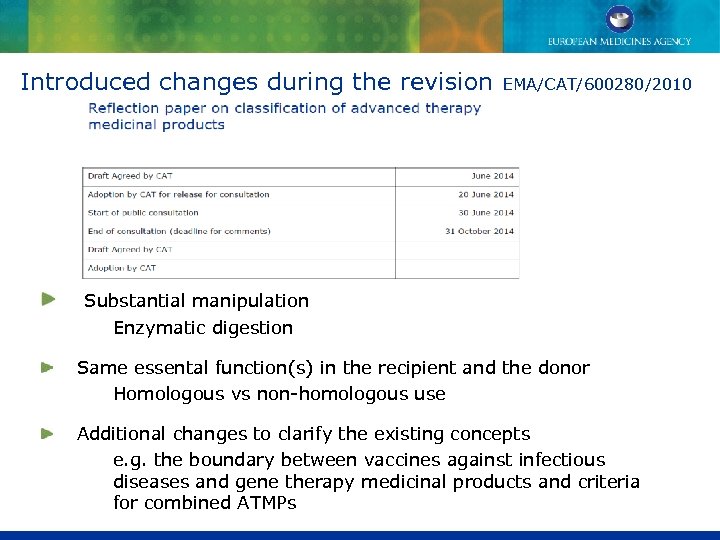 Introduced changes during the revision EMA/CAT/600280/2010 Substantial manipulation Enzymatic digestion Same essental function(s) in the recipient and the donor Homologous vs non-homologous use Additional changes to clarify the existing concepts e. g. the boundary between vaccines against infectious diseases and gene therapy medicinal products and criteria for combined ATMPs
Introduced changes during the revision EMA/CAT/600280/2010 Substantial manipulation Enzymatic digestion Same essental function(s) in the recipient and the donor Homologous vs non-homologous use Additional changes to clarify the existing concepts e. g. the boundary between vaccines against infectious diseases and gene therapy medicinal products and criteria for combined ATMPs
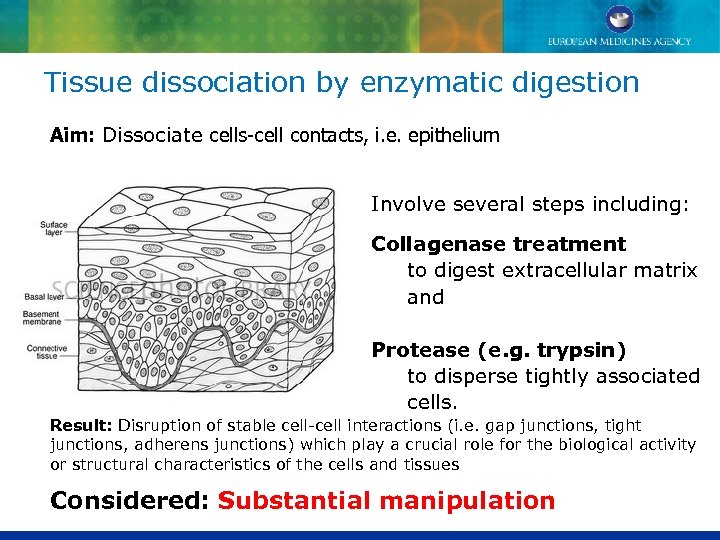 Tissue dissociation by enzymatic digestion Aim: Dissociate cells-cell contacts, i. e. epithelium Involve several steps including: Collagenase treatment to digest extracellular matrix and Protease (e. g. trypsin) to disperse tightly associated cells. Result: Disruption of stable cell-cell interactions (i. e. gap junctions, tight junctions, adherens junctions) which play a crucial role for the biological activity or structural characteristics of the cells and tissues Considered: Substantial manipulation
Tissue dissociation by enzymatic digestion Aim: Dissociate cells-cell contacts, i. e. epithelium Involve several steps including: Collagenase treatment to digest extracellular matrix and Protease (e. g. trypsin) to disperse tightly associated cells. Result: Disruption of stable cell-cell interactions (i. e. gap junctions, tight junctions, adherens junctions) which play a crucial role for the biological activity or structural characteristics of the cells and tissues Considered: Substantial manipulation
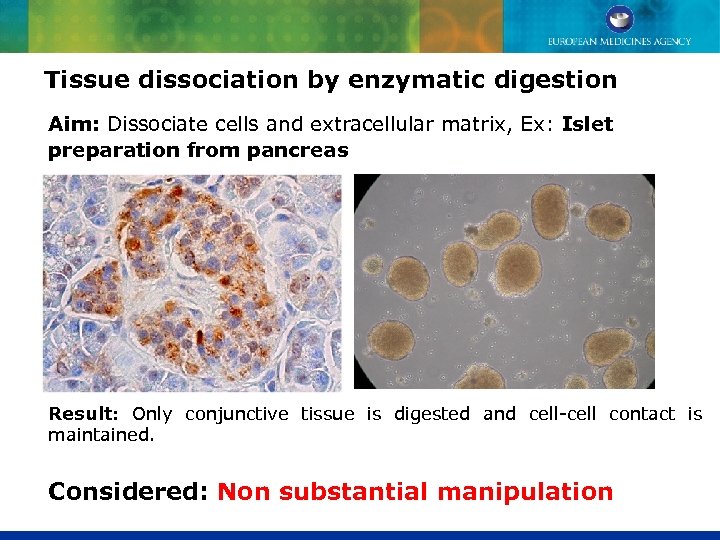 Tissue dissociation by enzymatic digestion Aim: Dissociate cells and extracellular matrix, Ex: Islet preparation from pancreas Result: Only conjunctive tissue is digested and cell-cell contact is maintained. Considered: Non substantial manipulation
Tissue dissociation by enzymatic digestion Aim: Dissociate cells and extracellular matrix, Ex: Islet preparation from pancreas Result: Only conjunctive tissue is digested and cell-cell contact is maintained. Considered: Non substantial manipulation
 Same essential function in the recipient and the donor Legislation: Cells or tissues that are not intended to be used for the same essential function(s) in the recipient and the donor The CAT classification is based on two different criteria: Location Function For stem cells (HSC and MSC), the function is not dependent on the histological location
Same essential function in the recipient and the donor Legislation: Cells or tissues that are not intended to be used for the same essential function(s) in the recipient and the donor The CAT classification is based on two different criteria: Location Function For stem cells (HSC and MSC), the function is not dependent on the histological location
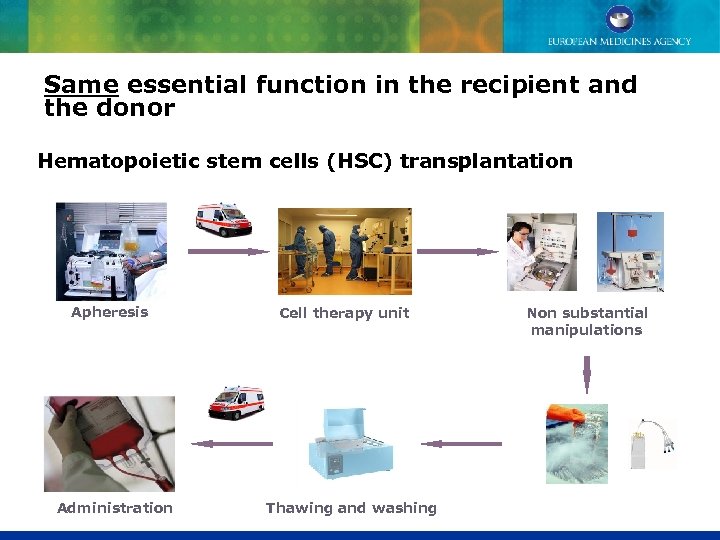 Same essential function in the recipient and the donor Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) transplantation Apheresis Administration Cell therapy unit Thawing and washing Non substantial manipulations
Same essential function in the recipient and the donor Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) transplantation Apheresis Administration Cell therapy unit Thawing and washing Non substantial manipulations
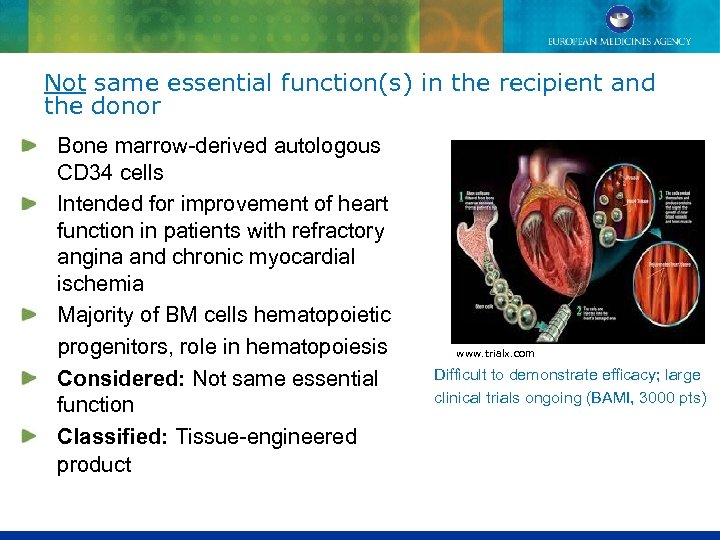 Not same essential function(s) in the recipient and the donor Bone marrow-derived autologous CD 34 cells Intended for improvement of heart function in patients with refractory angina and chronic myocardial ischemia Majority of BM cells hematopoietic progenitors, role in hematopoiesis Considered: Not same essential function Classified: Tissue-engineered product www. trialx. com Difficult to demonstrate efficacy; large clinical trials ongoing (BAMI, 3000 pts)
Not same essential function(s) in the recipient and the donor Bone marrow-derived autologous CD 34 cells Intended for improvement of heart function in patients with refractory angina and chronic myocardial ischemia Majority of BM cells hematopoietic progenitors, role in hematopoiesis Considered: Not same essential function Classified: Tissue-engineered product www. trialx. com Difficult to demonstrate efficacy; large clinical trials ongoing (BAMI, 3000 pts)
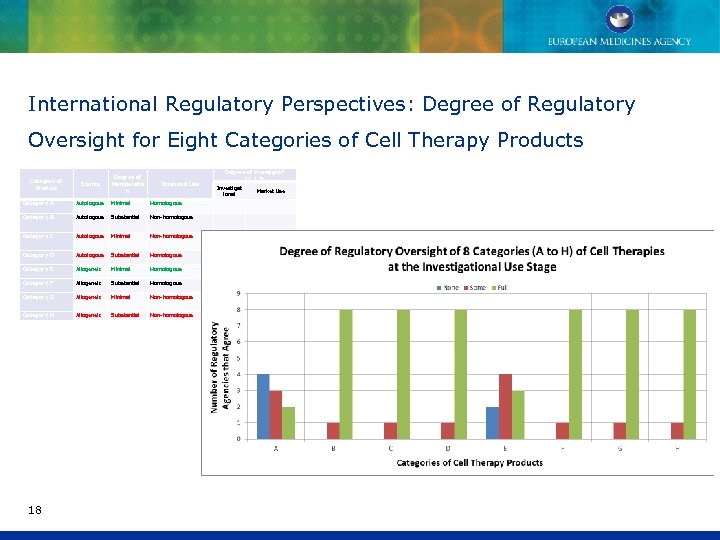 International Regulatory Perspectives: Degree of Regulatory Oversight for Eight Categories of Cell Therapy Products Category of Product Source Degree of Manipulatio n Intended Use Degree of Oversight* (1, 2, 3) Investigat ional Market Use Category A Autologous Minimal Homologous Category B Autologous Substantial Non-homologous Category C Autologous Minimal Non-homologous Category D Autologous Substantial Homologous Category E Allogeneic Minimal Homologous Category F Allogeneic Substantial Homologous Category G Allogeneic Minimal Non-homologous Category H Allogeneic Substantial Non-homologous 18
International Regulatory Perspectives: Degree of Regulatory Oversight for Eight Categories of Cell Therapy Products Category of Product Source Degree of Manipulatio n Intended Use Degree of Oversight* (1, 2, 3) Investigat ional Market Use Category A Autologous Minimal Homologous Category B Autologous Substantial Non-homologous Category C Autologous Minimal Non-homologous Category D Autologous Substantial Homologous Category E Allogeneic Minimal Homologous Category F Allogeneic Substantial Homologous Category G Allogeneic Minimal Non-homologous Category H Allogeneic Substantial Non-homologous 18
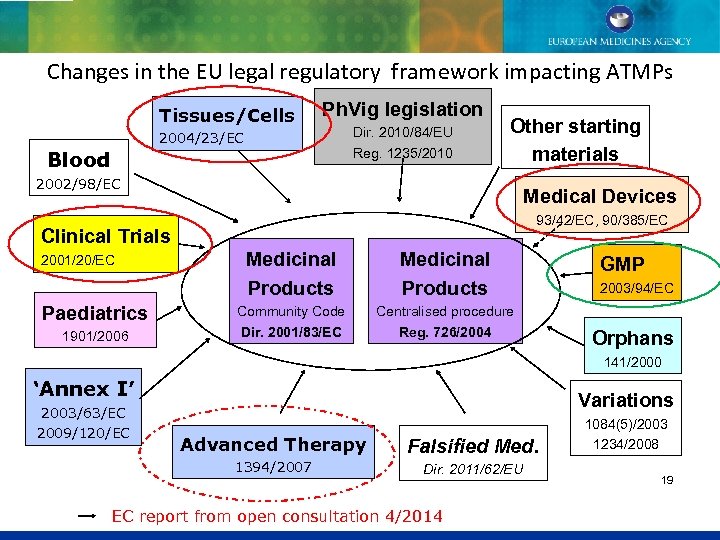 Changes in the EU legal regulatory framework impacting ATMPs Tissues/Cells Ph. Vig legislation 2004/23/EC Blood Dir. 2010/84/EU Reg. 1235/2010 Other starting materials 2002/98/EC Medical Devices 93/42/EC, 90/385/EC Clinical Trials 2001/20/EC Paediatrics 1901/2006 Medicinal Products Community Code Dir. 2001/83/EC Centralised procedure Reg. 726/2004 GMP 2003/94/EC Orphans 141/2000 ‘Annex I’ 2003/63/EC 2009/120/EC Variations Advanced Therapy Falsified Med. 1394/2007 Dir. 2011/62/EU EC report from open consultation 4/2014 1084(5)/2003 1234/2008 19
Changes in the EU legal regulatory framework impacting ATMPs Tissues/Cells Ph. Vig legislation 2004/23/EC Blood Dir. 2010/84/EU Reg. 1235/2010 Other starting materials 2002/98/EC Medical Devices 93/42/EC, 90/385/EC Clinical Trials 2001/20/EC Paediatrics 1901/2006 Medicinal Products Community Code Dir. 2001/83/EC Centralised procedure Reg. 726/2004 GMP 2003/94/EC Orphans 141/2000 ‘Annex I’ 2003/63/EC 2009/120/EC Variations Advanced Therapy Falsified Med. 1394/2007 Dir. 2011/62/EU EC report from open consultation 4/2014 1084(5)/2003 1234/2008 19
 Changes in the regulatory framework impacting ATMPs - Clinical trial regulation 536/2014 need guidance for ATIMPs Specific GMP requirements for ATIPMs - Revision of the Device legislation Combined ATMPs and borderline MP/ device cases? - New T&C legislation on importation CAT identified several problems for small ATMP developers and especially concerning cell-based products (short shelf-lives), e. g. concerning the request to import also ATMP starting materials through licensed tissue banks - Revision of the ATMP Regulation 1394/2007 and correction all problematic points have been much awaited by the developers, but perhaps not amongst the ones to be opened soon…? Commission has started to work on those points, that can be changed/improved without the need to change the legislation; CAT input required 20
Changes in the regulatory framework impacting ATMPs - Clinical trial regulation 536/2014 need guidance for ATIMPs Specific GMP requirements for ATIPMs - Revision of the Device legislation Combined ATMPs and borderline MP/ device cases? - New T&C legislation on importation CAT identified several problems for small ATMP developers and especially concerning cell-based products (short shelf-lives), e. g. concerning the request to import also ATMP starting materials through licensed tissue banks - Revision of the ATMP Regulation 1394/2007 and correction all problematic points have been much awaited by the developers, but perhaps not amongst the ones to be opened soon…? Commission has started to work on those points, that can be changed/improved without the need to change the legislation; CAT input required 20
 GMP requirements - GMP mandatory for all products entering clinical trials - GMP or equivalent quality system for Hospital Exemption (Jacie standard for transplantation) - Many trials from academic / hospital investigators - Other quality systems in use in tissue banks - Current requirements heavily critized during consultation § Revision of the GMP framework for CT § Special GMP guidance for all ATMPs (both CT and MA) under public consultation Q 3/2015
GMP requirements - GMP mandatory for all products entering clinical trials - GMP or equivalent quality system for Hospital Exemption (Jacie standard for transplantation) - Many trials from academic / hospital investigators - Other quality systems in use in tissue banks - Current requirements heavily critized during consultation § Revision of the GMP framework for CT § Special GMP guidance for all ATMPs (both CT and MA) under public consultation Q 3/2015
 Guideline(s) on investigational ATMPs - EC has given the CAT the mandate to draft guideline(s) for investigational ATMPs (01/2015) - No available IMP guideline for cell-based ATMPs, old GL on gene therapy IMPs two separate documents will be drafted, maybe fused later on, if feasible main focus on first in man studies, but will provide guidance also for later phases - IP meeting Q 4/2015 – Q 1/2016 on the IMP GLs 22
Guideline(s) on investigational ATMPs - EC has given the CAT the mandate to draft guideline(s) for investigational ATMPs (01/2015) - No available IMP guideline for cell-based ATMPs, old GL on gene therapy IMPs two separate documents will be drafted, maybe fused later on, if feasible main focus on first in man studies, but will provide guidance also for later phases - IP meeting Q 4/2015 – Q 1/2016 on the IMP GLs 22
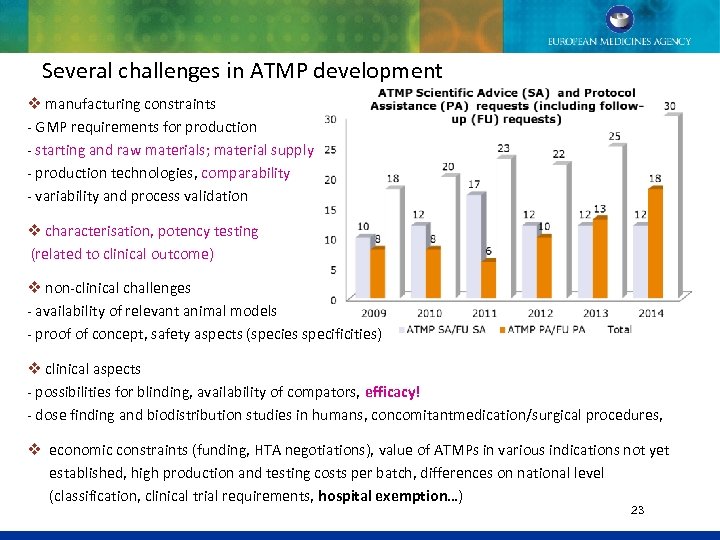 Several challenges in ATMP development v manufacturing constraints - GMP requirements for production - starting and raw materials; material supply - production technologies, comparability - variability and process validation v characterisation, potency testing (related to clinical outcome) v non-clinical challenges - availability of relevant animal models - proof of concept, safety aspects (species specificities) v clinical aspects - possibilities for blinding, availability of compators, efficacy! - dose finding and biodistribution studies in humans, concomitantmedication/surgical procedures, v economic constraints (funding, HTA negotiations), value of ATMPs in various indications not yet established, high production and testing costs per batch, differences on national level (classification, clinical trial requirements, hospital exemption…) 23
Several challenges in ATMP development v manufacturing constraints - GMP requirements for production - starting and raw materials; material supply - production technologies, comparability - variability and process validation v characterisation, potency testing (related to clinical outcome) v non-clinical challenges - availability of relevant animal models - proof of concept, safety aspects (species specificities) v clinical aspects - possibilities for blinding, availability of compators, efficacy! - dose finding and biodistribution studies in humans, concomitantmedication/surgical procedures, v economic constraints (funding, HTA negotiations), value of ATMPs in various indications not yet established, high production and testing costs per batch, differences on national level (classification, clinical trial requirements, hospital exemption…) 23
 Risk-based approach - Propectively planned strategy to justify the need for data in the MAA, not a traditional risk analysis - Does not provide a rigid classification system of different risks of a product as whole (e. g. high-risk product vs. low-risk product) - Is intended to provide flexibility to regulation of ATMPs - Additional help or burden for developers? - How to do the risk/risk factor profiling? GL on risk-based approach (EMA/CAT/CPWP/686637/2011) Q/A document on RBA under preparation scientific advice 24
Risk-based approach - Propectively planned strategy to justify the need for data in the MAA, not a traditional risk analysis - Does not provide a rigid classification system of different risks of a product as whole (e. g. high-risk product vs. low-risk product) - Is intended to provide flexibility to regulation of ATMPs - Additional help or burden for developers? - How to do the risk/risk factor profiling? GL on risk-based approach (EMA/CAT/CPWP/686637/2011) Q/A document on RBA under preparation scientific advice 24
 Adaptive pathways - Prospectively planned approach for MA with conditions - Based on existing procedures (conditional MA, MA with exceptional circumstances, joint EMA/HTA SA…) - Pilot phase with 3 ATMPs ongoing - Important to understand the impact of conditional MA post-marketing obligations impact on reimbursement negotiations 25
Adaptive pathways - Prospectively planned approach for MA with conditions - Based on existing procedures (conditional MA, MA with exceptional circumstances, joint EMA/HTA SA…) - Pilot phase with 3 ATMPs ongoing - Important to understand the impact of conditional MA post-marketing obligations impact on reimbursement negotiations 25
 CAT participates to joint cross-committee objectives - adaptive pathways (3 ATMPs in the pilot) - benefit/risk project - patient registries, …. 26 CAT specific objectives - finalise the RP on classification and GL on GTMPs - draft a guideline for investigational ATMPs (EC task); - CAT/IP meeting Q 3/4, in relation to the GL on investigational ATMPs - support EC in developing GMP guideline for ATMPs - provide training for assessor´s (2015, webinars) and developers (CAT workshop with learned societies - 2015 with ISCT in Sevilla) - new survey of clinical trials and developers (2010 -2014)
CAT participates to joint cross-committee objectives - adaptive pathways (3 ATMPs in the pilot) - benefit/risk project - patient registries, …. 26 CAT specific objectives - finalise the RP on classification and GL on GTMPs - draft a guideline for investigational ATMPs (EC task); - CAT/IP meeting Q 3/4, in relation to the GL on investigational ATMPs - support EC in developing GMP guideline for ATMPs - provide training for assessor´s (2015, webinars) and developers (CAT workshop with learned societies - 2015 with ISCT in Sevilla) - new survey of clinical trials and developers (2010 -2014)
 Where to find information Further information from the CAT and it’s monthly reports http: //www. ema. europa. eu Committees CAT Summaries of scientific recommendations on classification of ATMP Go to: Advanced therapies ATMP classification Summaries For general queries: Advanced. Therapies@ema. europa. eu, Paula. Salmikangas@fimea. fi
Where to find information Further information from the CAT and it’s monthly reports http: //www. ema. europa. eu Committees CAT Summaries of scientific recommendations on classification of ATMP Go to: Advanced therapies ATMP classification Summaries For general queries: Advanced. Therapies@ema. europa. eu, Paula. Salmikangas@fimea. fi
 Colton And Abbygail Ainslie, Siblings With SCID, Among First Cured Of 'Bubble Boy Disease' (Photo: Facebook/Jessica Ainslie) B. Mellor, Nature 2008 Thank you for your attention! Special thanks to Margarida Menezes Ferreira (CAT) Patrick Celis (CAT) Rocio Salvador Roldan (EC) Marit Hystad (CAT) Nicolas Ferry (CAT) Egbert Flory (CAT) 28
Colton And Abbygail Ainslie, Siblings With SCID, Among First Cured Of 'Bubble Boy Disease' (Photo: Facebook/Jessica Ainslie) B. Mellor, Nature 2008 Thank you for your attention! Special thanks to Margarida Menezes Ferreira (CAT) Patrick Celis (CAT) Rocio Salvador Roldan (EC) Marit Hystad (CAT) Nicolas Ferry (CAT) Egbert Flory (CAT) 28


