a080dfe79b280ba5158417384dab51c2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 KEELE Struct 3 D Automated Structural Restoration David Meredith, Graham Williams, Jay Leonard, Andrew Richards Keele University & Platte River Associates
KEELE Struct 3 D Automated Structural Restoration David Meredith, Graham Williams, Jay Leonard, Andrew Richards Keele University & Platte River Associates
 Struct 3 D Sponsors KEELE l PDVSA l REPSOL YPF l CHEVRON TEXACO l UNIVERSITY OF WALES, BANGOR l KEELE UNIVERSITY, UK
Struct 3 D Sponsors KEELE l PDVSA l REPSOL YPF l CHEVRON TEXACO l UNIVERSITY OF WALES, BANGOR l KEELE UNIVERSITY, UK
 Struct 3 D Aims KEELE l l Automated structural restoration of faulted earth models. Generation of structural geometries at multiple time steps for petroleum systems modelling (GEM Module). Account for compaction during each stage of restoration. Restoration inversion - solve for coupled temperature / pressure evolution used to refine porosity reduction due to chemical processes.
Struct 3 D Aims KEELE l l Automated structural restoration of faulted earth models. Generation of structural geometries at multiple time steps for petroleum systems modelling (GEM Module). Account for compaction during each stage of restoration. Restoration inversion - solve for coupled temperature / pressure evolution used to refine porosity reduction due to chemical processes.
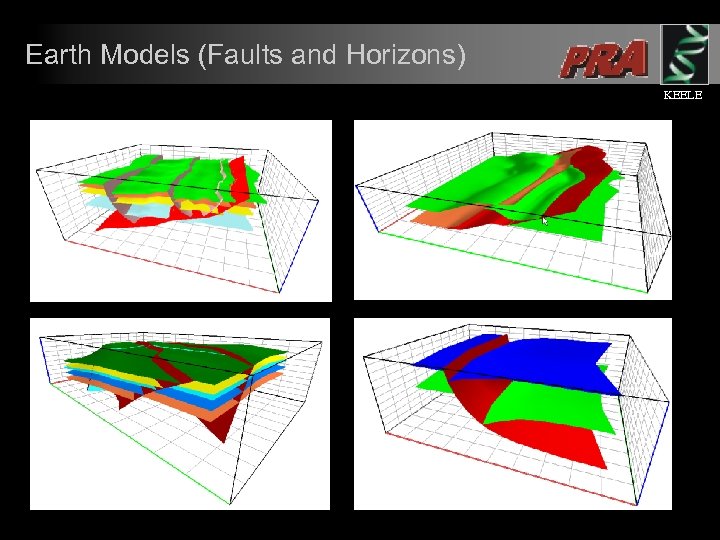 Earth Models (Faults and Horizons) KEELE
Earth Models (Faults and Horizons) KEELE
 Talk Outline KEELE l Model Building / Input l Interpretation Tools l Restoration Kinematics / Model Operation l Restoration Inversion (Iterative Pressure. Temperature Modelling)
Talk Outline KEELE l Model Building / Input l Interpretation Tools l Restoration Kinematics / Model Operation l Restoration Inversion (Iterative Pressure. Temperature Modelling)
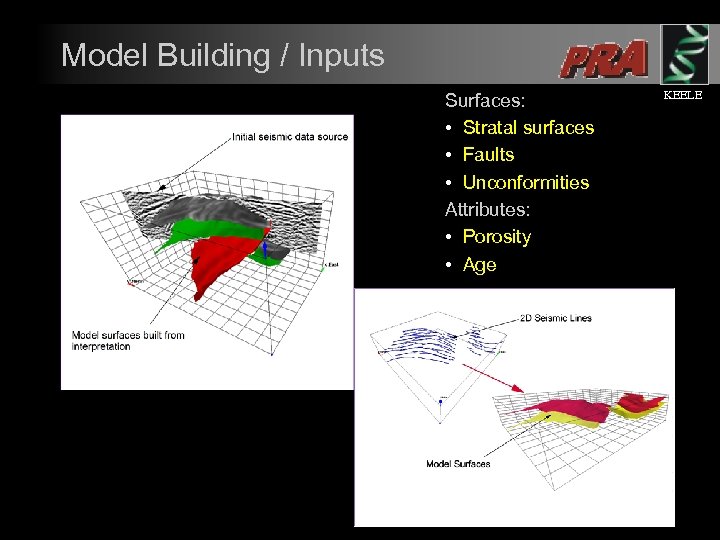 Model Building / Inputs Surfaces: • Stratal surfaces • Faults • Unconformities Attributes: • Porosity • Age KEELE
Model Building / Inputs Surfaces: • Stratal surfaces • Faults • Unconformities Attributes: • Porosity • Age KEELE
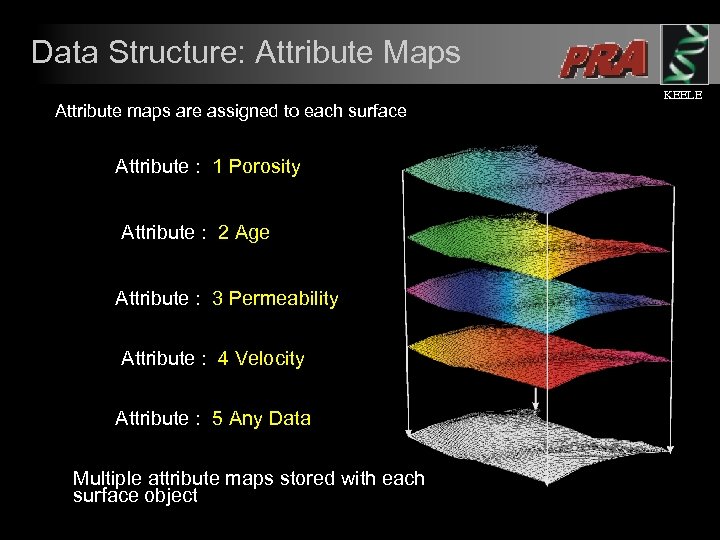 Data Structure: Attribute Maps Attribute maps are assigned to each surface Attribute : 1 Porosity Attribute : 2 Age Attribute : 3 Permeability Attribute : 4 Velocity Attribute : 5 Any Data Multiple attribute maps stored with each surface object KEELE
Data Structure: Attribute Maps Attribute maps are assigned to each surface Attribute : 1 Porosity Attribute : 2 Age Attribute : 3 Permeability Attribute : 4 Velocity Attribute : 5 Any Data Multiple attribute maps stored with each surface object KEELE
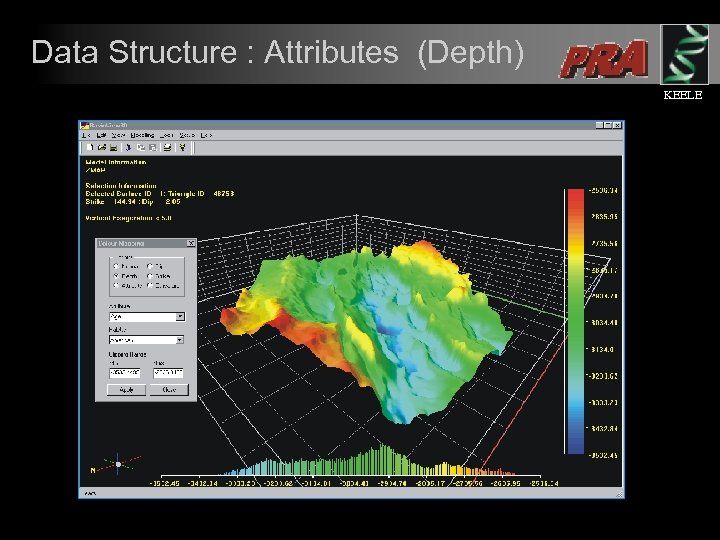 Data Structure : Attributes (Depth) KEELE
Data Structure : Attributes (Depth) KEELE
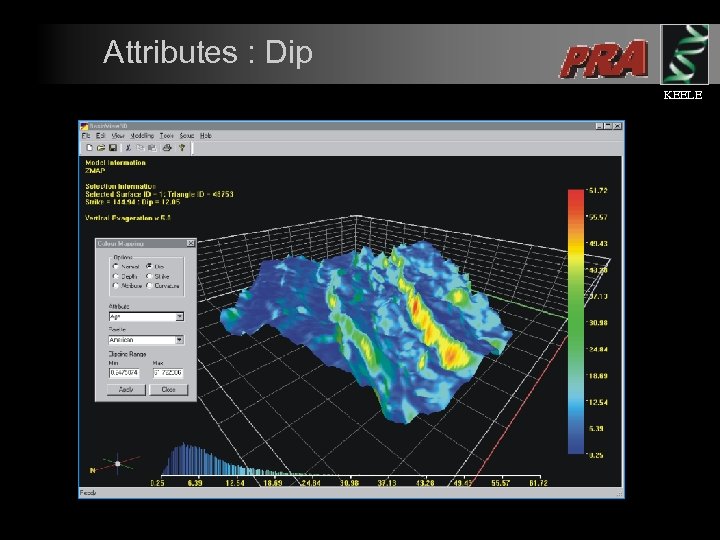 Attributes : Dip KEELE
Attributes : Dip KEELE
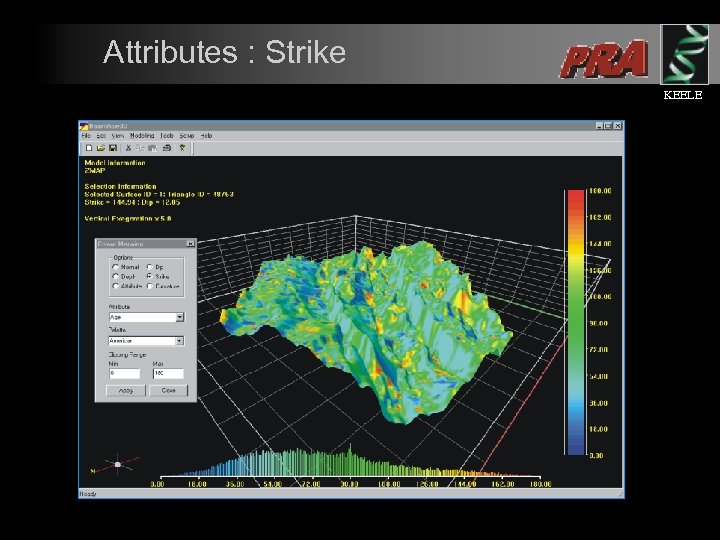 Attributes : Strike KEELE
Attributes : Strike KEELE
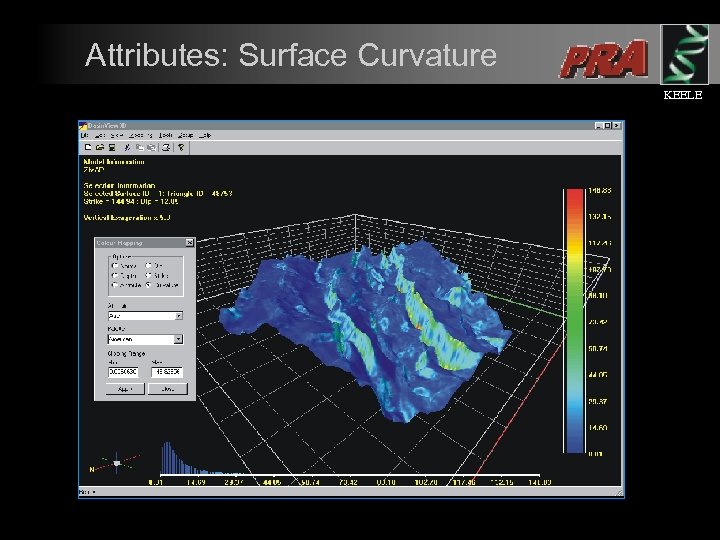 Attributes: Surface Curvature KEELE
Attributes: Surface Curvature KEELE
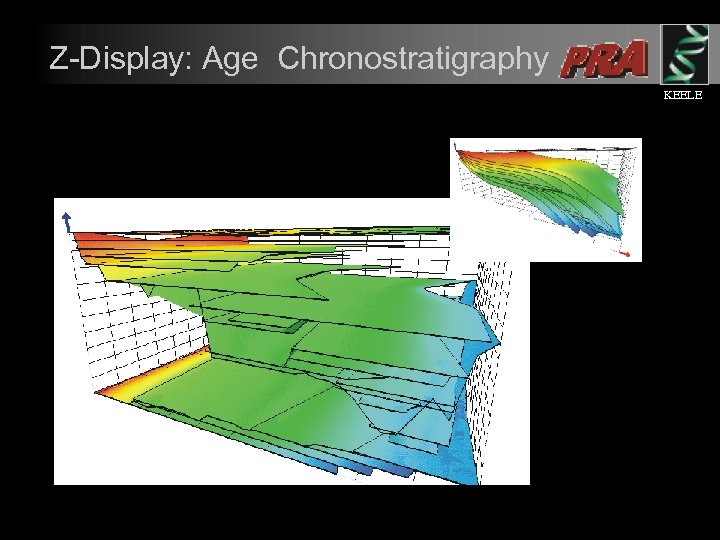 Z-Display: Age Chronostratigraphy KEELE
Z-Display: Age Chronostratigraphy KEELE
 Automated Structural Restoration KEELE l l l Earth model is structurally restored working from the present day interpretation backwards through geological time. Reconstructed structural geometries at each time step are used in a forward model run solving for temperature and pressure. Restoration Inversion used to refine porosity reduction due to chemical processes.
Automated Structural Restoration KEELE l l l Earth model is structurally restored working from the present day interpretation backwards through geological time. Reconstructed structural geometries at each time step are used in a forward model run solving for temperature and pressure. Restoration Inversion used to refine porosity reduction due to chemical processes.
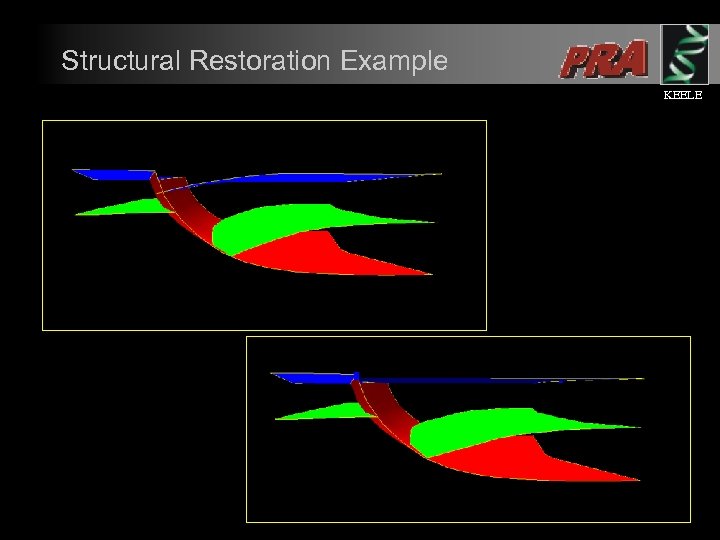 Structural Restoration Example KEELE
Structural Restoration Example KEELE
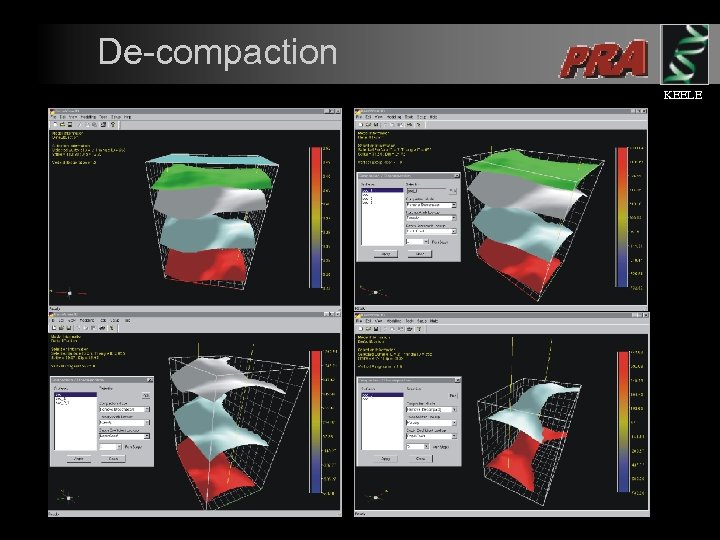
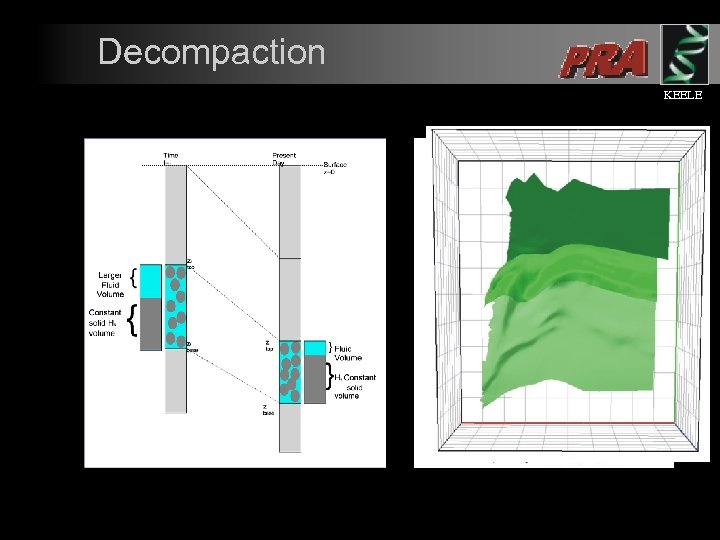
 Decompaction KEELE l l Coupled with structural restoration are calculations to compensate for the amount of decompaction of sediments. Corrections for decompaction are required in order to generate the correct structural geometries.
Decompaction KEELE l l Coupled with structural restoration are calculations to compensate for the amount of decompaction of sediments. Corrections for decompaction are required in order to generate the correct structural geometries.
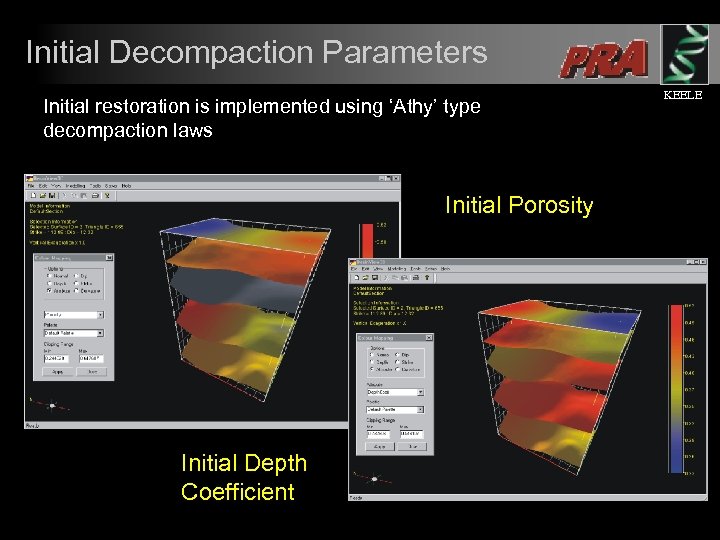 Initial Decompaction Parameters Initial restoration is implemented using ‘Athy’ type decompaction laws Initial Porosity Initial Depth Coefficient KEELE
Initial Decompaction Parameters Initial restoration is implemented using ‘Athy’ type decompaction laws Initial Porosity Initial Depth Coefficient KEELE
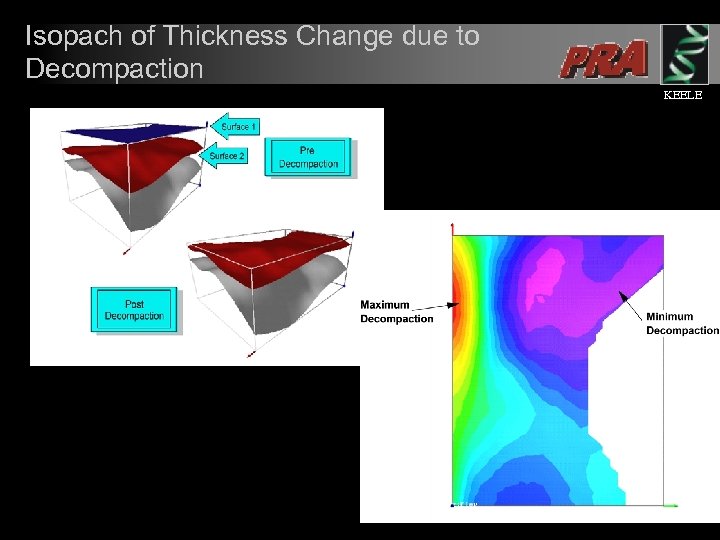 Isopach of Thickness Change due to Decompaction KEELE
Isopach of Thickness Change due to Decompaction KEELE
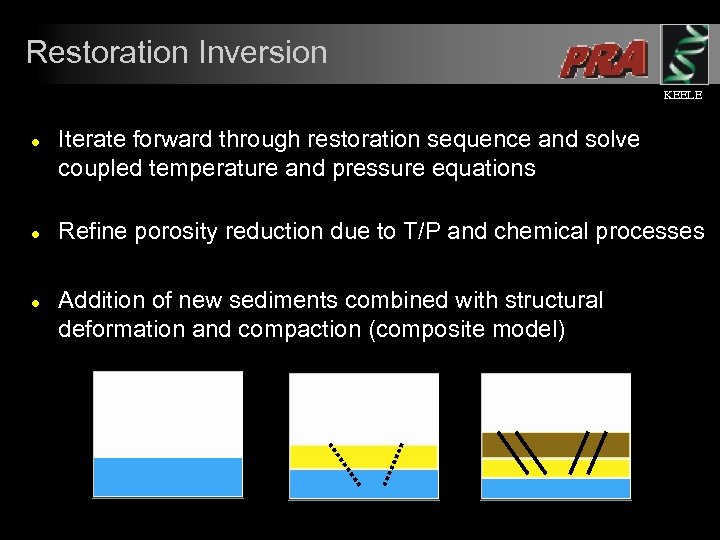 Restoration Inversion KEELE l l l Iterate forward through restoration sequence and solve coupled temperature and pressure equations Refine porosity reduction due to T/P and chemical processes Addition of new sediments combined with structural deformation and compaction (composite model)
Restoration Inversion KEELE l l l Iterate forward through restoration sequence and solve coupled temperature and pressure equations Refine porosity reduction due to T/P and chemical processes Addition of new sediments combined with structural deformation and compaction (composite model)
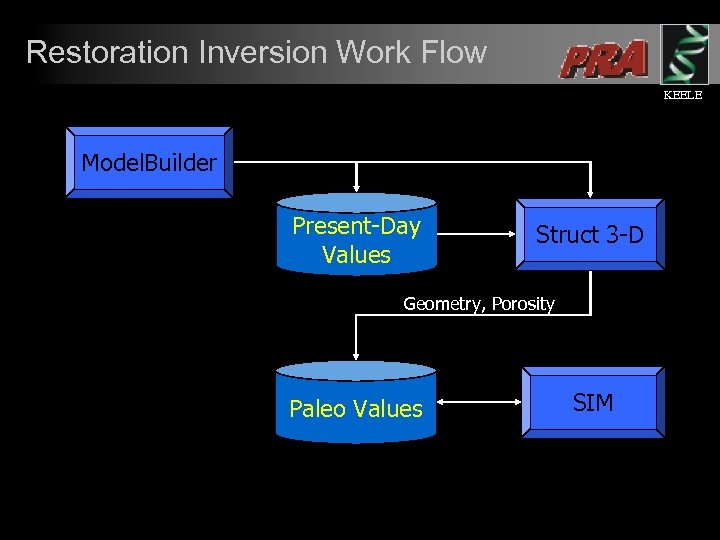 Restoration Inversion Work Flow KEELE Model. Builder Present-Day Values Struct 3 -D Geometry, Porosity SIM Paleo Values Pressure Temperature
Restoration Inversion Work Flow KEELE Model. Builder Present-Day Values Struct 3 -D Geometry, Porosity SIM Paleo Values Pressure Temperature
 Struct 3 D Model Operation KEELE l Assign surface groups prior to restoration – l (Fault dissected lithological horizons) Begin Restoration (Pick fault and restore) – Volume balanced restoration process is completely automated: • • • Footwall / hangingwall allocation for each restoration step Optimum heave azimuth calculation for best fit restoration Variable heave calculation for precise restoration
Struct 3 D Model Operation KEELE l Assign surface groups prior to restoration – l (Fault dissected lithological horizons) Begin Restoration (Pick fault and restore) – Volume balanced restoration process is completely automated: • • • Footwall / hangingwall allocation for each restoration step Optimum heave azimuth calculation for best fit restoration Variable heave calculation for precise restoration
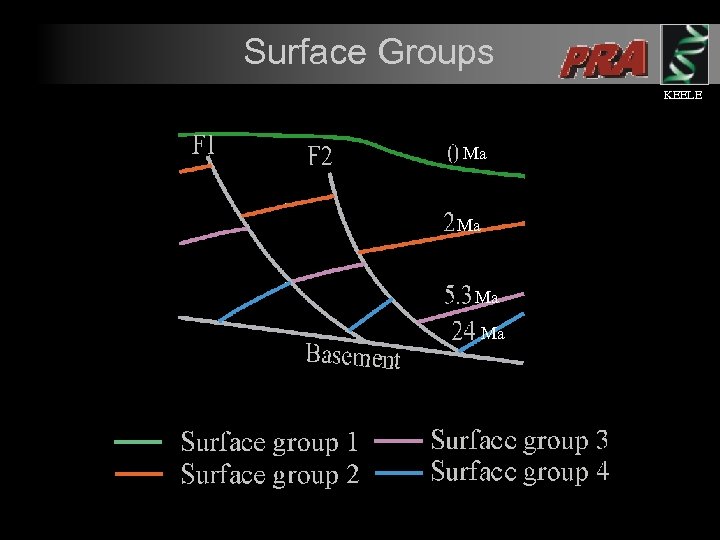 Surface Groups KEELE Ma Ma
Surface Groups KEELE Ma Ma
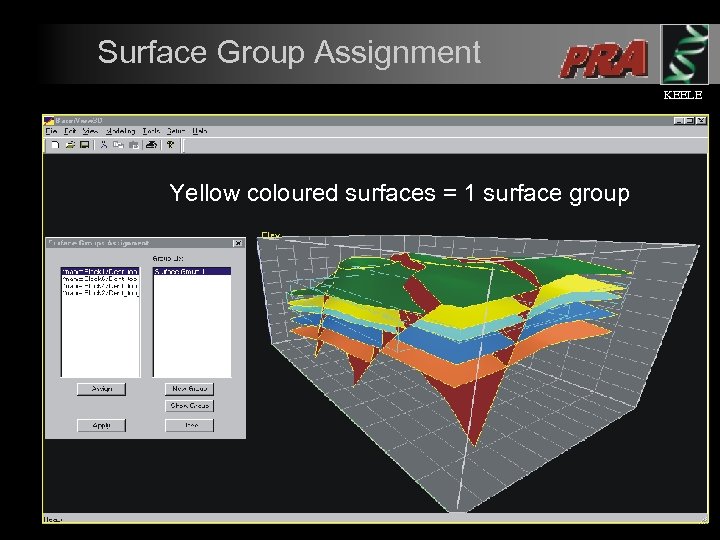 Surface Group Assignment KEELE Yellow coloured surfaces = 1 surface group
Surface Group Assignment KEELE Yellow coloured surfaces = 1 surface group
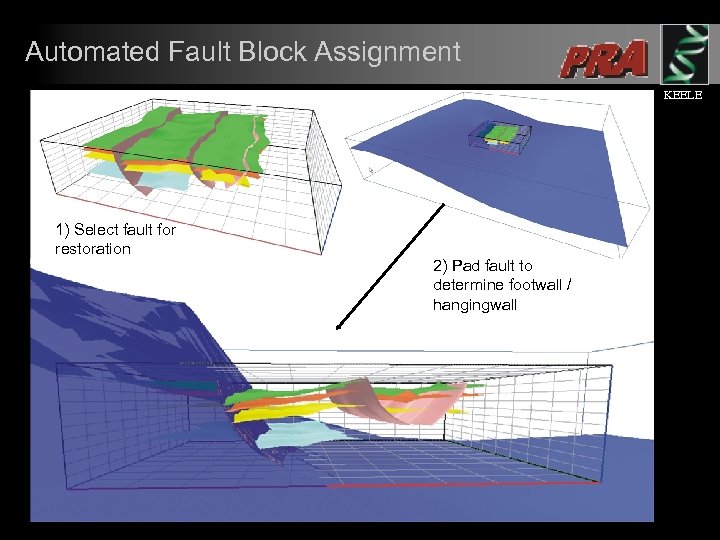 Automated Fault Block Assignment KEELE 1) Select fault for restoration 2) Pad fault to determine footwall / hangingwall
Automated Fault Block Assignment KEELE 1) Select fault for restoration 2) Pad fault to determine footwall / hangingwall
 Restoration Kinematics Piercing Points plus Variable Displacement Vector Fields l l l The basis for determining the displacement vector field utilises hangingwall / footwall ‘piercing points’. The match of HW / FW piercing points is used to calculate the optimum move azimuth for restoration. Variable displacement vector fields are automatically calculated (i. e. restoring variable fault displacement gradients). KEELE
Restoration Kinematics Piercing Points plus Variable Displacement Vector Fields l l l The basis for determining the displacement vector field utilises hangingwall / footwall ‘piercing points’. The match of HW / FW piercing points is used to calculate the optimum move azimuth for restoration. Variable displacement vector fields are automatically calculated (i. e. restoring variable fault displacement gradients). KEELE
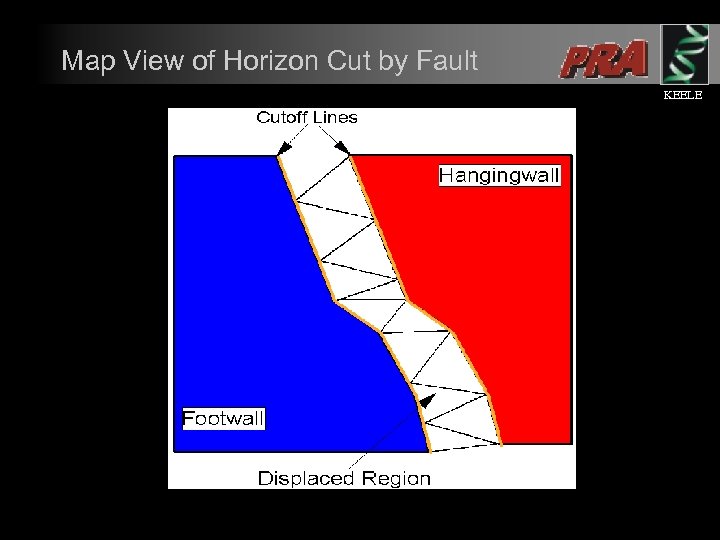 Map View of Horizon Cut by Fault KEELE
Map View of Horizon Cut by Fault KEELE
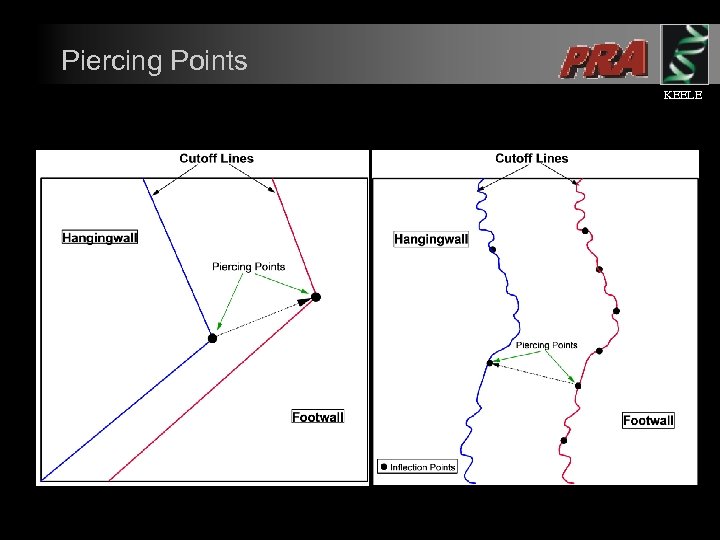 Piercing Points KEELE
Piercing Points KEELE
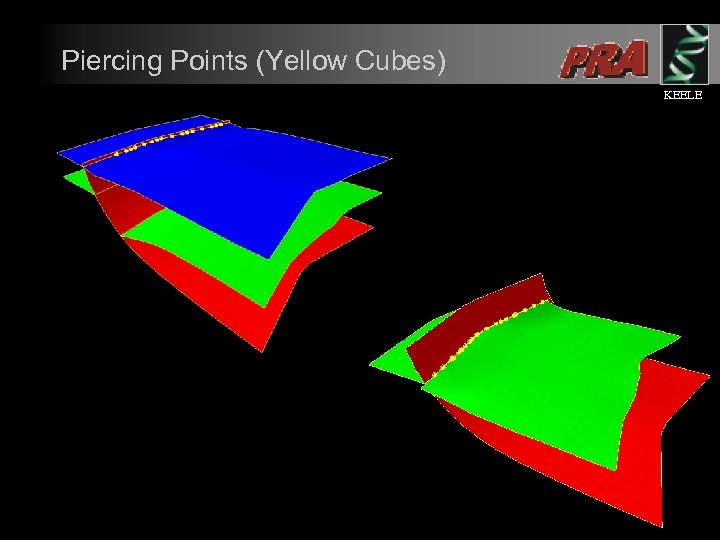 Piercing Points (Yellow Cubes) KEELE
Piercing Points (Yellow Cubes) KEELE
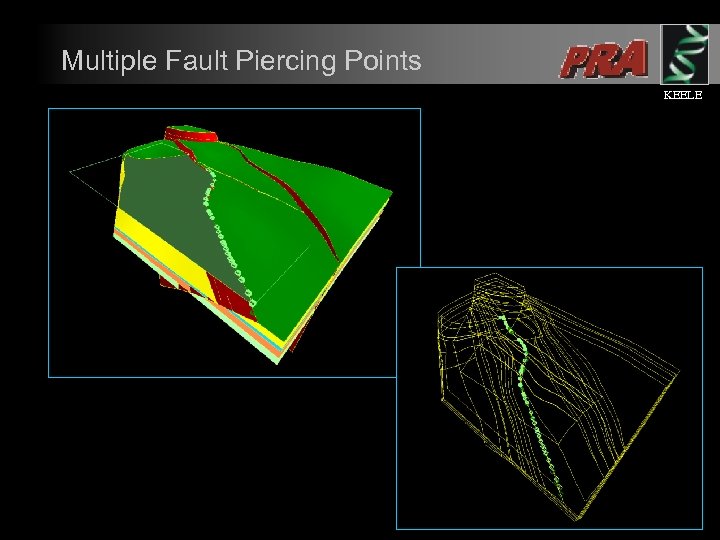 Multiple Fault Piercing Points KEELE
Multiple Fault Piercing Points KEELE
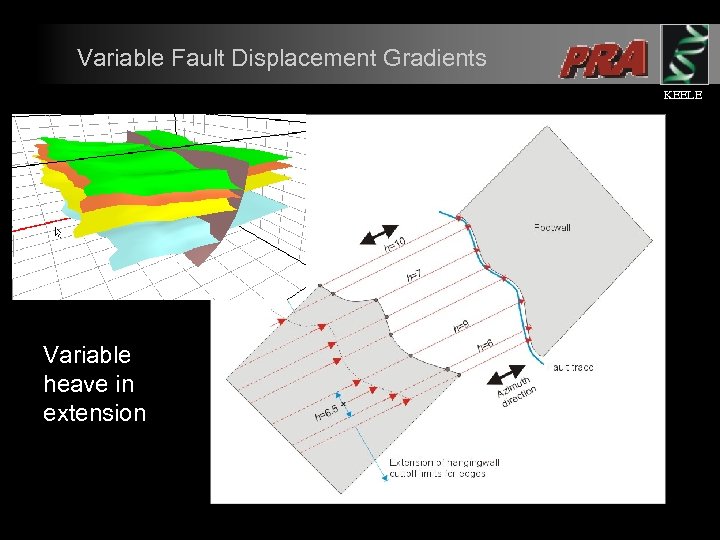 Variable Fault Displacement Gradients KEELE Variable heave in extension
Variable Fault Displacement Gradients KEELE Variable heave in extension
 Thrust Sheet Restoration Using Go-Cad Model KEELE
Thrust Sheet Restoration Using Go-Cad Model KEELE
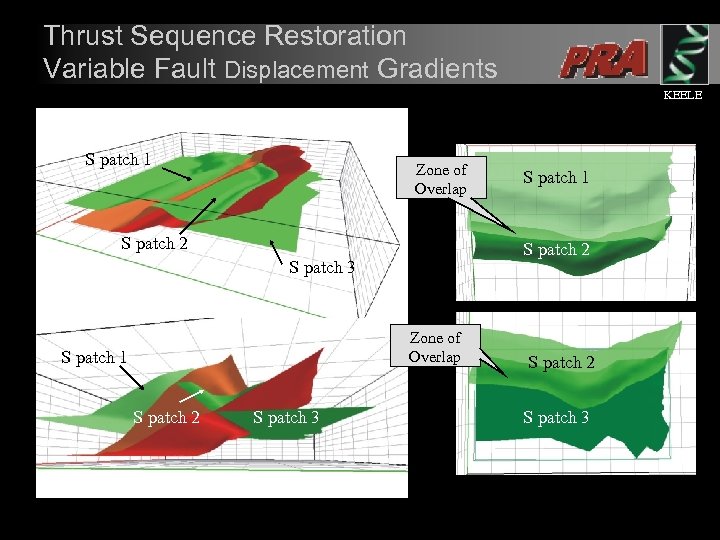 Thrust Sequence Restoration Variable Fault Displacement Gradients KEELE S patch 1 Zone of Overlap S patch 2 S patch 3 Zone of Overlap S patch 1 S patch 2 S patch 3
Thrust Sequence Restoration Variable Fault Displacement Gradients KEELE S patch 1 Zone of Overlap S patch 2 S patch 3 Zone of Overlap S patch 1 S patch 2 S patch 3
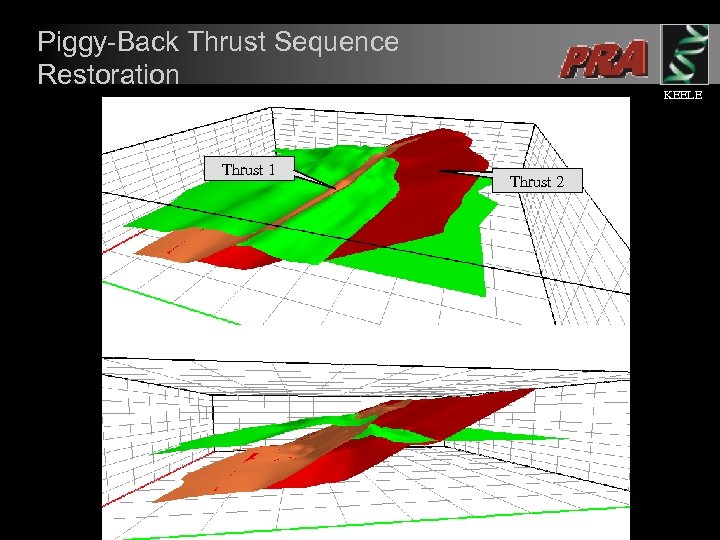 Piggy-Back Thrust Sequence Restoration Thrust 1 KEELE Thrust 2
Piggy-Back Thrust Sequence Restoration Thrust 1 KEELE Thrust 2
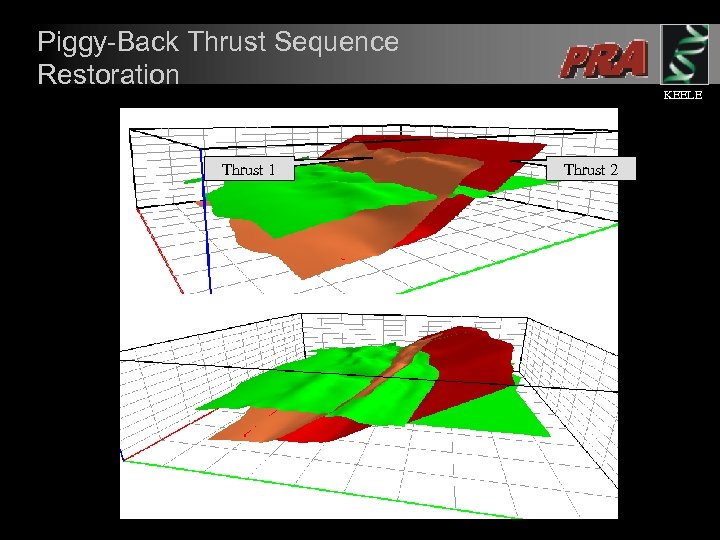 Piggy-Back Thrust Sequence Restoration Thrust 1 KEELE Thrust 2
Piggy-Back Thrust Sequence Restoration Thrust 1 KEELE Thrust 2
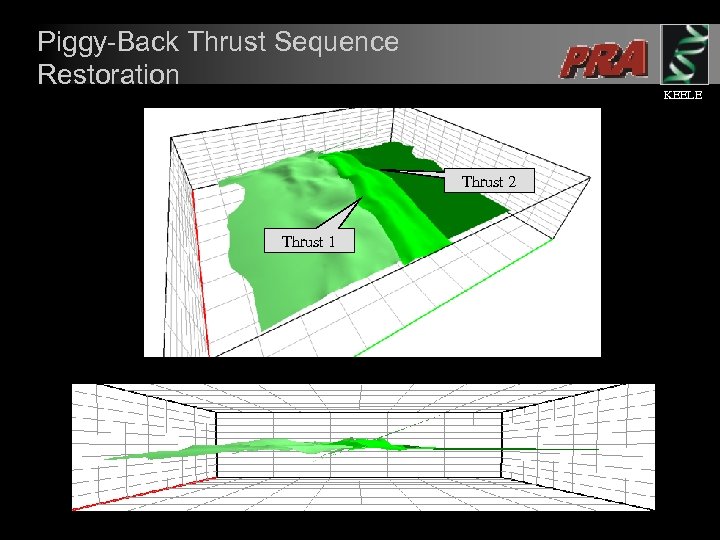 Piggy-Back Thrust Sequence Restoration KEELE Thrust 2 Thrust 1
Piggy-Back Thrust Sequence Restoration KEELE Thrust 2 Thrust 1
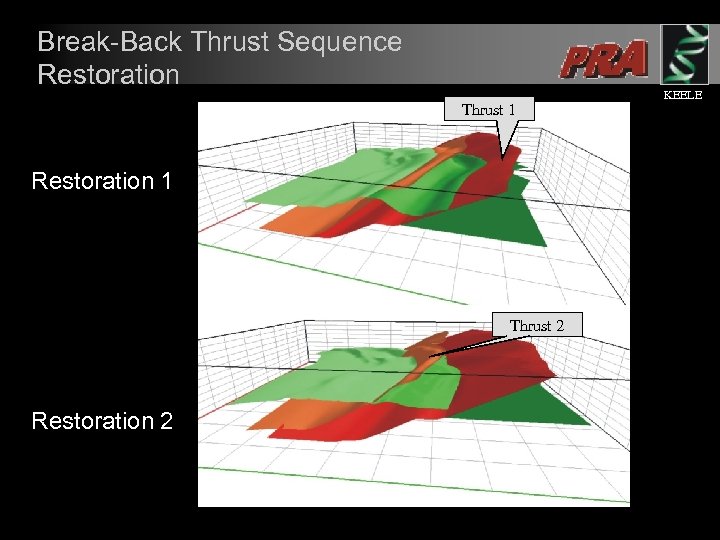 Break-Back Thrust Sequence Restoration Thrust 1 Restoration 1 Thrust 2 Restoration 2 KEELE
Break-Back Thrust Sequence Restoration Thrust 1 Restoration 1 Thrust 2 Restoration 2 KEELE
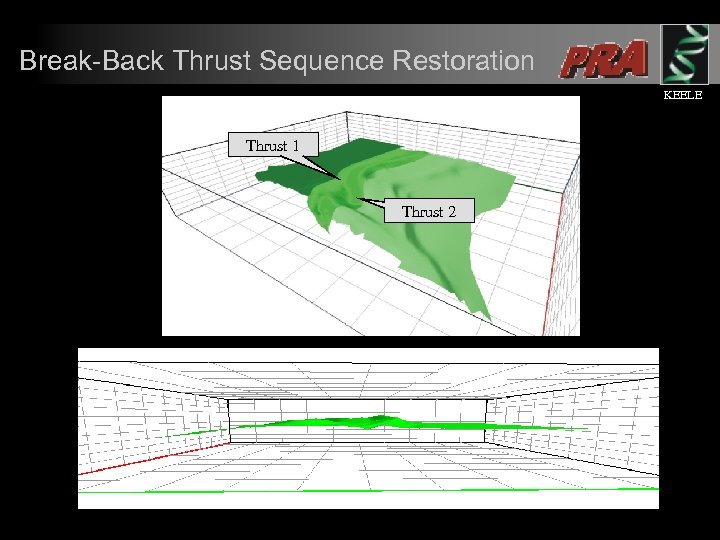 Break-Back Thrust Sequence Restoration KEELE Thrust 1 Thrust 2
Break-Back Thrust Sequence Restoration KEELE Thrust 1 Thrust 2
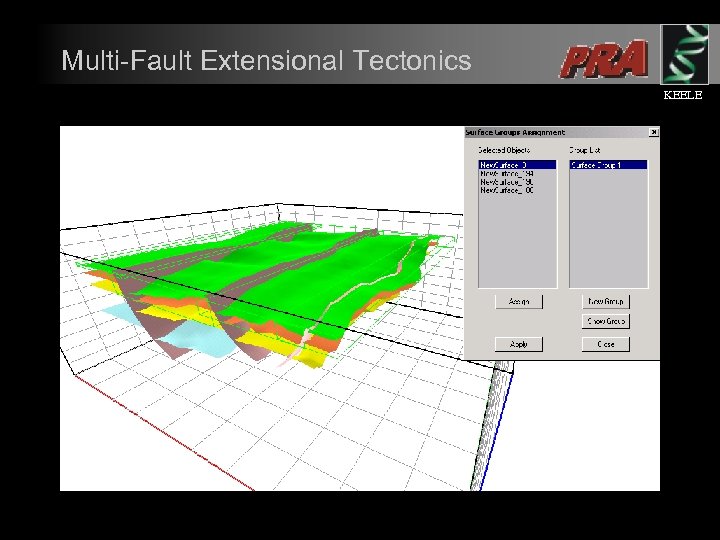 Multi-Fault Extensional Tectonics KEELE
Multi-Fault Extensional Tectonics KEELE
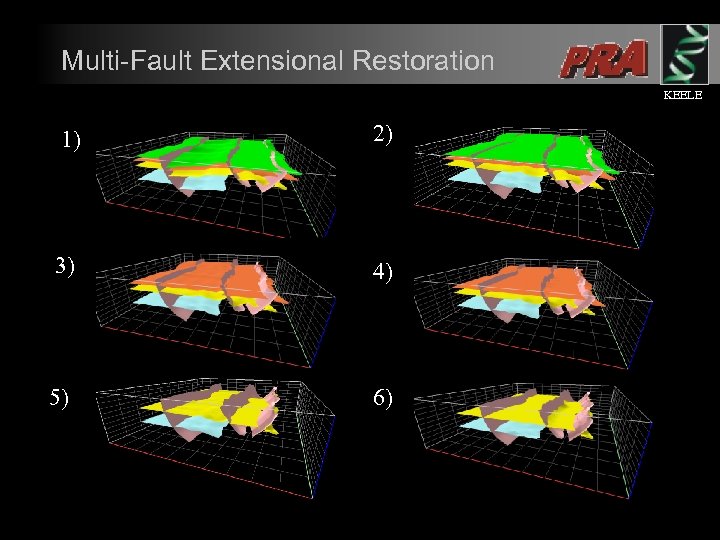 Multi-Fault Extensional Restoration KEELE 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6)
Multi-Fault Extensional Restoration KEELE 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6)
 Forward Modelling KEELE l l A final model involving retro-deformation, decompaction and coupled pressure / temperature analysis is generated through multiple time steps. Forward iteration of this composite model is used in petroleum systems analysis to determine hydrocarbon charge and accumulation.
Forward Modelling KEELE l l A final model involving retro-deformation, decompaction and coupled pressure / temperature analysis is generated through multiple time steps. Forward iteration of this composite model is used in petroleum systems analysis to determine hydrocarbon charge and accumulation.
 Summary, Struct 3 D • Provides automated structural restoration and generation of KEELE structural geometries at multiple time steps. • Restoration is driven by simply selecting the fault to be restored and ‘pressing go. ’ This enables the user to investigate multiple restoration scenarios. • Automated calculation of optimum heave azimuth. • Restores variable displacement gradients for precise restoration • Restoration inversion accounts for compaction during each stage of restoration. • Restoration can be run in reverse to forward model the petroleum system.
Summary, Struct 3 D • Provides automated structural restoration and generation of KEELE structural geometries at multiple time steps. • Restoration is driven by simply selecting the fault to be restored and ‘pressing go. ’ This enables the user to investigate multiple restoration scenarios. • Automated calculation of optimum heave azimuth. • Restores variable displacement gradients for precise restoration • Restoration inversion accounts for compaction during each stage of restoration. • Restoration can be run in reverse to forward model the petroleum system.
 Unconformities KEELE l l Unconformities need to be accounted for in order to generate a full restoration sequence. Missing section needs to be added to the model during the restoration sequence.
Unconformities KEELE l l Unconformities need to be accounted for in order to generate a full restoration sequence. Missing section needs to be added to the model during the restoration sequence.
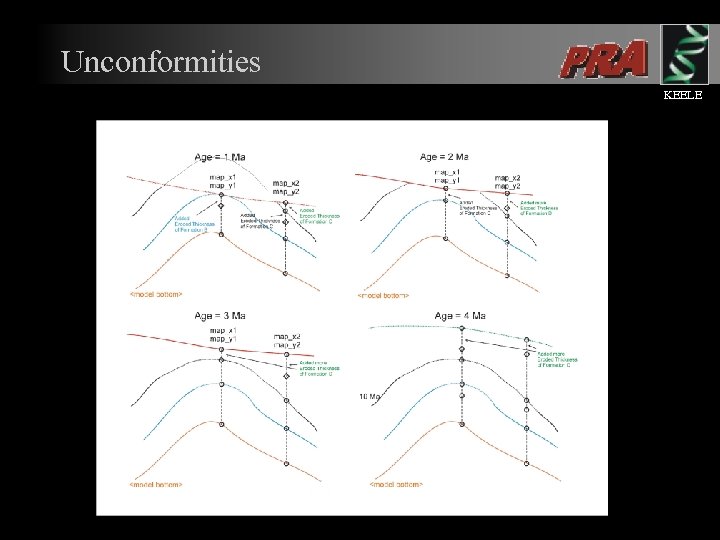 Unconformities KEELE
Unconformities KEELE
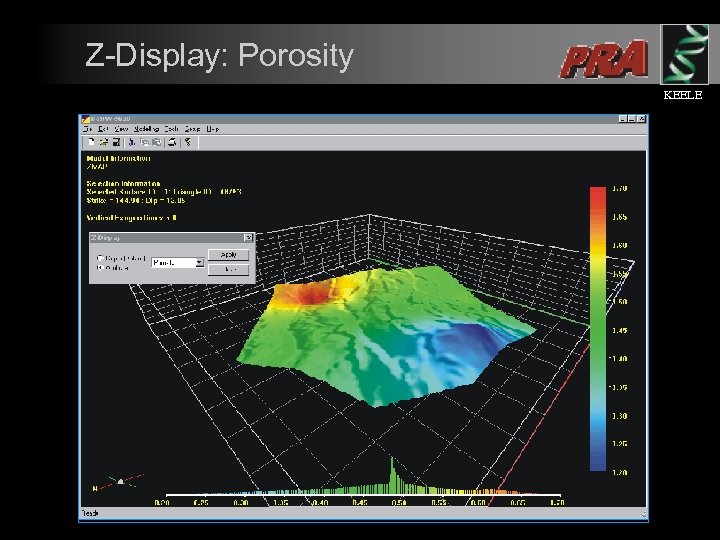 Z-Display: Porosity KEELE
Z-Display: Porosity KEELE
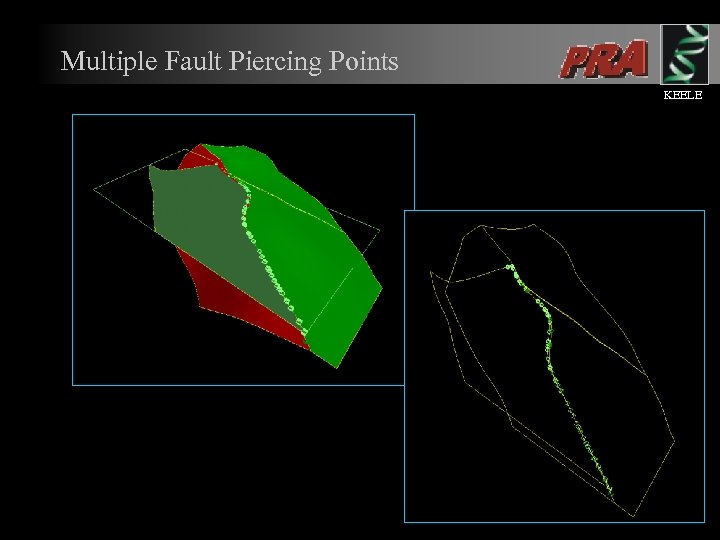 Multiple Fault Piercing Points KEELE
Multiple Fault Piercing Points KEELE
 De-compaction KEELE
De-compaction KEELE
 Decompaction KEELE
Decompaction KEELE


