WIFI technology.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 12

KAZATU Wi Fi TECHNOLOGY • Sapar Zhanbolat 212 group RET 1
OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION PURPOSE WI-FI TECHNOLOGY COMPONENTS HOW WI-FI NETWORKS ? ARCHITECTURE ADVANTAGES LIMITATIONS OR DISADVANTAGES 2

INTRODUCTION q Wi-Fi is a short form of Wireless Fidelity. q Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that uses radio frequency to transmit data through the air. q Wi-Fi is a generic term that refers to the IEEE 802. 11 communications standard for Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs). q Wireless Technology is an alternative to Wired Technology. q The main attractive feature of this technology is that it can provide wireless broadband connection within a specific geographic boundary. q Wi-Fi Network connect computers to each other, to the internet and to the wired network. q Wi-Fi works on physical and data link layer. 3

PURPOSE The purpose of Wi-Fi is to hide complexity by enabling wireless access to applications and data. The main aims of Wi-Fi are the following-: q Make access to information easier. q Ensure compatibility and co-existence of devices. q Eliminate cabling and wiring. q Eliminate switches, adapters, plugs, pins and connectors. 4

Wi-Fi TECHNOLOGY Wi-Fi Networks use Radio Technologies to transmit & receive data at high speed-: These technologies are-: q IEEE 802. 11 b q IEEE 802. 11 a q IEEE 802. 11 g q IEEE 802. 11 n 5
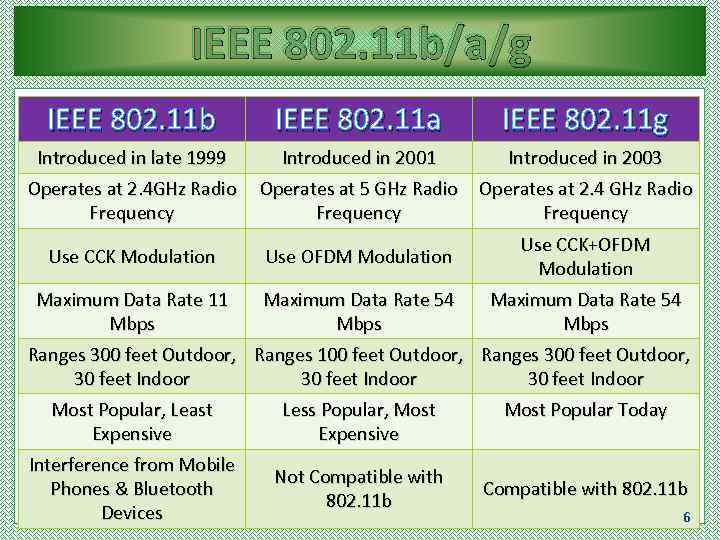
IEEE 802. 11 b/a/g IEEE 802. 11 b IEEE 802. 11 a IEEE 802. 11 g Introduced in late 1999 Introduced in 2001 Introduced in 2003 Operates at 2. 4 GHz Radio Frequency Operates at 5 GHz Radio Frequency Operates at 2. 4 GHz Radio Frequency Use CCK Modulation Use OFDM Modulation Use CCK+OFDM Modulation Maximum Data Rate 11 Mbps Maximum Data Rate 54 Mbps Ranges 300 feet Outdoor, Ranges 100 feet Outdoor, Ranges 300 feet Outdoor, 30 feet Indoor Most Popular, Least Expensive Less Popular, Most Expensive Interference from Mobile Phones & Bluetooth Devices Not Compatible with 802. 11 b Most Popular Today Compatible with 802. 11 b 6

COMPONENTS OF Wi-Fi NETWORK Access Point-: An AP operates within a specific frequency spectrum and uses an 802. 11 standard specified modulation technique that connect one or many wireless devices simultaneously to the Internet. Wi-Fi Card-: A PC or workstation uses a wireless Network Interface Card (NIC)/adaptor to connect to the wireless network. NIC card accept the wireless signal and relay information. They can be internal and external. (e. g. PCMCIA Card for Laptop and PCI Card for Desktop PC). Bridge-: Wireless bridge are used to connect multiple LANs. Station (STA)-: A STA is a wireless endpoint device. Typical examples of STAs are laptop computers, personal digital assistants (PDA), mobile phones, and other consumer electronic devices with IEEE 802. 11 capabilities. 7

HOW Wi-Fi NETWORKS q Basic concept is same as Walkie talkies. q A Wi-Fi hotspot is created by installing an access point to an internet connection. It acts as a base station. q When Wi-Fi enabled device encounters a hotspot the device can then connect to that network wirelessly. q A single access point can support up to 30 users and can function within a range of 100 to 300 feet. q Many access points can be connected to each other via Ethernet cables to create a single large network. 8
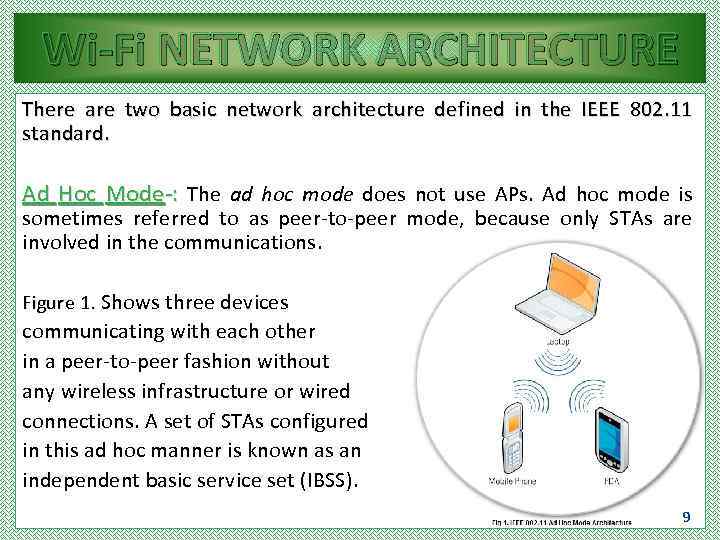
Wi-Fi NETWORK ARCHITECTURE There are two basic network architecture defined in the IEEE 802. 11 standard. Ad Hoc Mode-: The ad hoc mode does not use APs. Ad hoc mode is sometimes referred to as peer-to-peer mode, because only STAs are involved in the communications. Figure 1. Shows three devices communicating with each other in a peer-to-peer fashion without any wireless infrastructure or wired connections. A set of STAs configured in this ad hoc manner is known as an independent basic service set (IBSS). 9
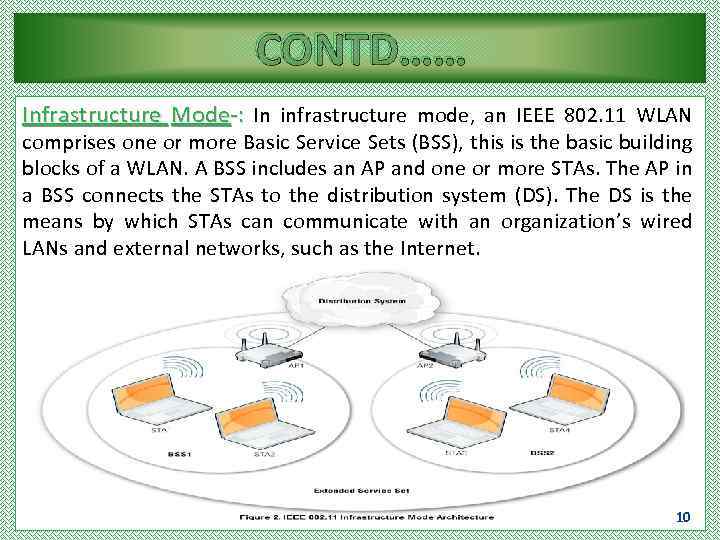
CONTD…… Infrastructure Mode-: In infrastructure mode, an IEEE 802. 11 WLAN comprises one or more Basic Service Sets (BSS), this is the basic building blocks of a WLAN. A BSS includes an AP and one or more STAs. The AP in a BSS connects the STAs to the distribution system (DS). The DS is the means by which STAs can communicate with an organization’s wired LANs and external networks, such as the Internet. 10

ADVANTAGES OF Wi-Fi q Wireless – Wire free connection with no conjunction while connecting to other PC or laptop. q Low cost – Installation of wireless network cost less when compared to cable network. q Mobility – Can access internet outside their normal work area. q Expandability – Can suddenly add increased number of clients with existing equipment. q Deployment – Set up for infrastructure-based wireless network requires more than a single access point. q Productivity – Users connected to wireless network can maintain a constant connection with the desired network. q Convenience – Can access network in near by from any convenient location within their primary environment. 11

DISADVANTAGES OF Wi-Fi q q q Interference Degradation in performance High power consumption Limited range Data Security Risks 12
WIFI technology.pptx