Туберкулез.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 10

Kazakh – Russian Medical University Tuberculosis. Done by: Aibek Bazilov, 206 A Checked by: Abdykadyrova. G. I Almaty 2016

Plan 1. Symptoms of Tuberculosis 2. Types of tuberculosis 3. Causes of tuberculosis 4. Treatment of tuberculosis 5. Prevention of Tuberculosis
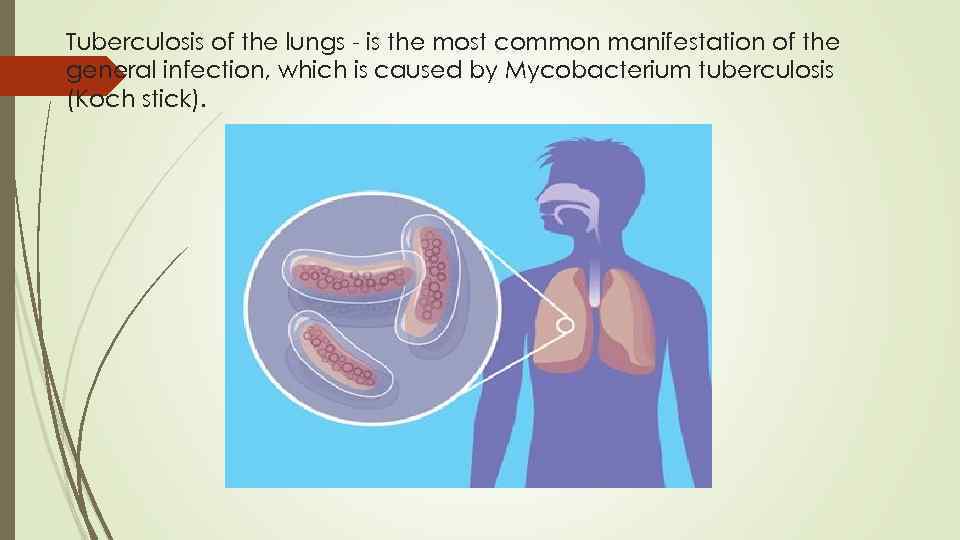
Tuberculosis of the lungs - is the most common manifestation of the general infection, which is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Koch stick).

1. Symptoms of Tuberculosis is manifested first general malaise, fever body, headaches. As a result, the process of tuberculous intoxication (poisoning of the organism of bacterial cells) the patient loses weight rapidly (5 -10 kg or more), there is a weakness, fatigue. His bother sweating, especially at night, decreased performance, lack of appetite. In the fever sick and can not pay attention, because in tuberculosis, it is not high, usually 37 -37, 5 ° C, and often increases only in the evening. Chest pain and cough does not always accompany the onset of the disease, but further development of the tubercular process, these symptoms may begin to disturb the patient. Later joined by hemoptysis, chest pain

2. Types of tuberculosis Tuberculosis other than the lungs can infect other organs and human tissue: the eyes, bones, skin, genitourinary system, intestines. There are open (when mycobacteria are found in the sputum or other discharge of the patient) and closed (mycobacteria in the discharge is not determined, the patient is not dangerous in terms of possible contamination) TB.

3. Causes of tuberculosis Source of infection is a sick man. The infection plays a major role airborne route of transmission, but transmission is also possible through contact with personal belongings of the patient (contacthousehold path). Therefore, you can catch anywhere and not necessarily in direct contact with the patient.

4. Treatment of tuberculosis In the absence of the drug sensitivity data treatment is prescribed standard set of first-line drugs. This combination successfully cures the majority of patients infected with TB. However, a smaller proportion of patients infected with drug-resistant tuberculosis bacteria, immune to the action of first-line drugs. Treatment of tuberculosis - a long process and takes six months in the case of normal (sensitive) TB up to two years in the case of drug resistance. Treatment should be continuous. Koch's bacillus should not be able to recover from the "bombing" of its powerful artillery, anti-TB drugs to complete its destruction. Treatment must necessarily be carried out simultaneously by several anti-TB drugs. Each of the medications that the patient takes a daily basis, has different mechanisms of action, ie, each of them affects the various aspects and manifestations of the life of the Koch bacillus, and only together they can achieve the goal - to destroy it. Under no circumstances should not be treated by an incomplete set of drugs, prematurely terminate or temporarily discontinue treatment started or to take pills regularly. If it is impossible to carry out a full course, it is better to delay treatment than to allow an inferior rate.

5. Prevention of Tuberculosis For prevention to avoid the influence of the major risk factors for pulmonary tuberculosis are: contact with the patient open tuberculosis (patients distinguishing causative agent of tuberculosis, sputum, sweat, saliva, feces, urine, breast milk into the environment) in overcrowded conditions (poor housing conditions , prisons, etc. ). ; reduced resistance of the organism; availability of professional pulmonary disease (eg silicosis); prolonged treatment with corticosteroid hormones; alcoholism; diabetes; HIV infection; malnutrition, hypothermia, stress (single people are elderly, the homeless, immigrants)

Tests 1. When there is profuse sweating with Tuberculosis disease? A) night b)morning c)afternoon 2. The source of infection is tuberculosis? A) man b)animal c)insect 3. Wherewith identify tuberculosis? A) sputum b) blood c) urine 4. Which comes from the bacterium tuberculosis? A) Koh bacillus b) Brucella bacteria c) pneumococcus bacteria 5. Many forms of tuberculosis exist? A)2 b)1 c)3
Туберкулез.pptx