 Kazakh – Russian Medical University THE CARDIAC RHYTHM DONE BY: AIBEK BAZILOV, 206 A CHECKED BY: DINARA AZRETALIEVNA ALMATY 2016
Kazakh – Russian Medical University THE CARDIAC RHYTHM DONE BY: AIBEK BAZILOV, 206 A CHECKED BY: DINARA AZRETALIEVNA ALMATY 2016
 Plan 1. Cardiac cycle 2. Systole 3. Diastole 4. Questions
Plan 1. Cardiac cycle 2. Systole 3. Diastole 4. Questions
 Cardiac cycle - a concept that reflects the sequence of the processes taking place in a single contraction of the heart and its subsequent relaxation. Each cycle includes three major stages: atrial systole, ventricular systole and diastole. The term systole means contraction of the muscle. There are electric systole - the electrical activity that stimulates the myocardium and causes mechanical systole - contraction of the heart muscle and a decrease in the volume of cardiac chambers
Cardiac cycle - a concept that reflects the sequence of the processes taking place in a single contraction of the heart and its subsequent relaxation. Each cycle includes three major stages: atrial systole, ventricular systole and diastole. The term systole means contraction of the muscle. There are electric systole - the electrical activity that stimulates the myocardium and causes mechanical systole - contraction of the heart muscle and a decrease in the volume of cardiac chambers
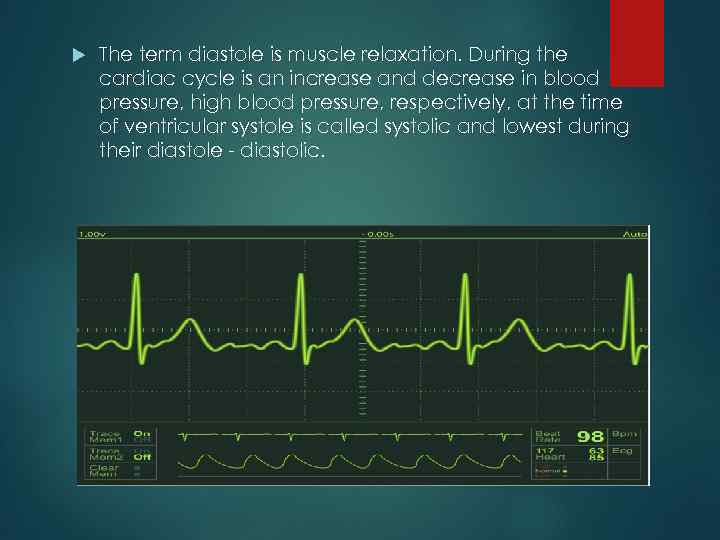 The term diastole is muscle relaxation. During the cardiac cycle is an increase and decrease in blood pressure, high blood pressure, respectively, at the time of ventricular systole is called systolic and lowest during their diastole - diastolic.
The term diastole is muscle relaxation. During the cardiac cycle is an increase and decrease in blood pressure, high blood pressure, respectively, at the time of ventricular systole is called systolic and lowest during their diastole - diastolic.
 Systole - one of the states of the heart muscle during a heartbeat, namely contraction of the left and right ventricles and ejection of blood into the aorta from the left ventricle into the pulmonary trunk and from the right ventricle. At the same time remain open Pulmonary and aortic valves, and closed mitral and tricuspid valves. Blood pressure is recorded at the time of systole to the first diastolic, for example, systolic pressure is 130/70 entry 130. Place of hearing: 5 edge.
Systole - one of the states of the heart muscle during a heartbeat, namely contraction of the left and right ventricles and ejection of blood into the aorta from the left ventricle into the pulmonary trunk and from the right ventricle. At the same time remain open Pulmonary and aortic valves, and closed mitral and tricuspid valves. Blood pressure is recorded at the time of systole to the first diastolic, for example, systolic pressure is 130/70 entry 130. Place of hearing: 5 edge.
 . Diastole - one of the states of the heart muscle during a heartbeat, and it is relaxed in the interval between beats (systole). Blood pressure is recorded at the time of diastole after the second systolic, for example, "120/80" recording pressure 80 is the diastolic pressure.
. Diastole - one of the states of the heart muscle during a heartbeat, and it is relaxed in the interval between beats (systole). Blood pressure is recorded at the time of diastole after the second systolic, for example, "120/80" recording pressure 80 is the diastolic pressure.
 Diastole (. From the Greek diastole extension) - enlargement of the heart cavities (due to the relaxation of the muscles of the atria and ventricles), during which it is filled with blood; with systole (contraction) of cardiac cycle. At the same time open the mitral and tricuspid valves, and pulmonary and aortic valves are closed. Upon the occurrence of death the heart is in diastole.
Diastole (. From the Greek diastole extension) - enlargement of the heart cavities (due to the relaxation of the muscles of the atria and ventricles), during which it is filled with blood; with systole (contraction) of cardiac cycle. At the same time open the mitral and tricuspid valves, and pulmonary and aortic valves are closed. Upon the occurrence of death the heart is in diastole.
 Question 1. What happens during systole? 2. Which valves remain open during systole? 3. Place listening to the cardiac cycle? ? 4. At which cycle the heart fills with blood? 5. Which valves remain open during diastole?
Question 1. What happens during systole? 2. Which valves remain open during systole? 3. Place listening to the cardiac cycle? ? 4. At which cycle the heart fills with blood? 5. Which valves remain open during diastole?