brain.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10

Kazakh-Russian Medical University Independent work Theme: The Brain Prepared by: Zhantenova Indira Group: 203 B Faculty: General medicine Checked by: Kosbatyrova Nauat Almaty 2013
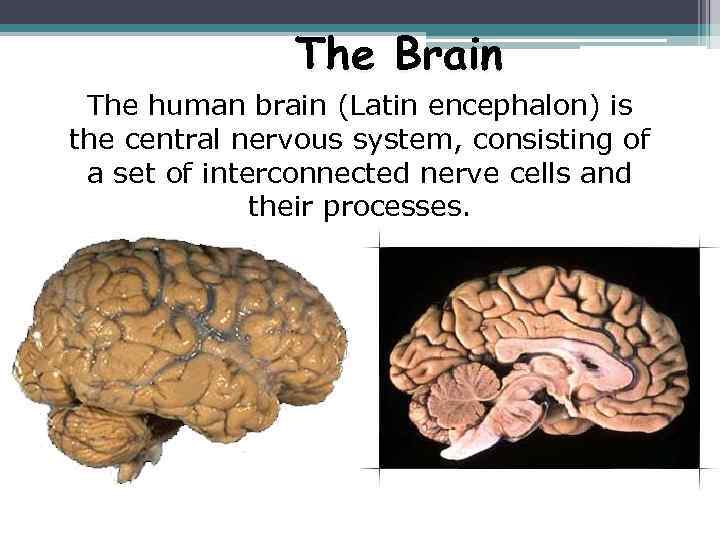
The Brain The human brain (Latin encephalon) is the central nervous system, consisting of a set of interconnected nerve cells and their processes.

The Brain • weighs 1300 - 1400 g • made up of about 100 billion neurons • “the most complex living structure on the universe” Society for Neuroscience • makes us who we are

The Brain • Absolute brain mass is not to judge the intelligence of man. Interesting figures led MA Gremyatsky: Turgenev's brain mass is equal to 2012, Cromwell 2000, Byron - 2238, Cuvier 1830, Schiller - 1871, Thackeray - 1294, poet Walt Whitman - 1282, physician Dellinger 1207, Anatole France -1017 was despite the fact that the weight of the brain of Anatole France was almost two times less than the mass of the brain Turgenev, they were both brilliant writers and thinkers.
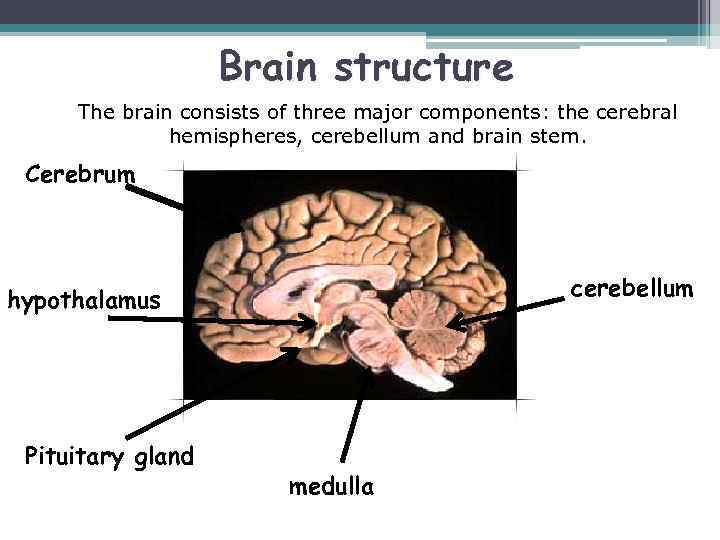
Brain structure The brain consists of three major components: the cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum and brain stem. Cerebrum cerebellum hypothalamus Pituitary gland medulla
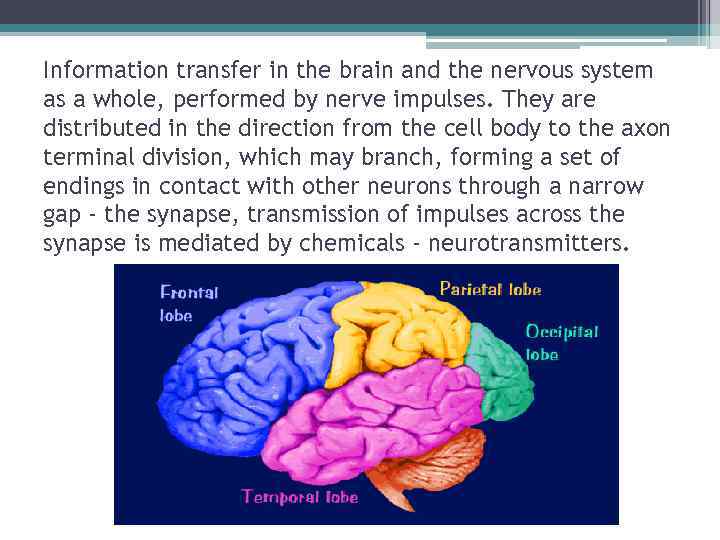
Information transfer in the brain and the nervous system as a whole, performed by nerve impulses. They are distributed in the direction from the cell body to the axon terminal division, which may branch, forming a set of endings in contact with other neurons through a narrow gap - the synapse, transmission of impulses across the synapse is mediated by chemicals - neurotransmitters.

• Many axons are covered with myelin sheath, which is formed by repeatedly swirling glial cell membrane. Myelin is composed primarily of lipids, which gives the characteristic form of the white matter of the brain and spinal cord. Due to the speed of the myelin sheath of the action potential along the axon is growing as the ions can move through the axon membrane only in areas not covered by myelin - the so-called nodes of Ranvier.
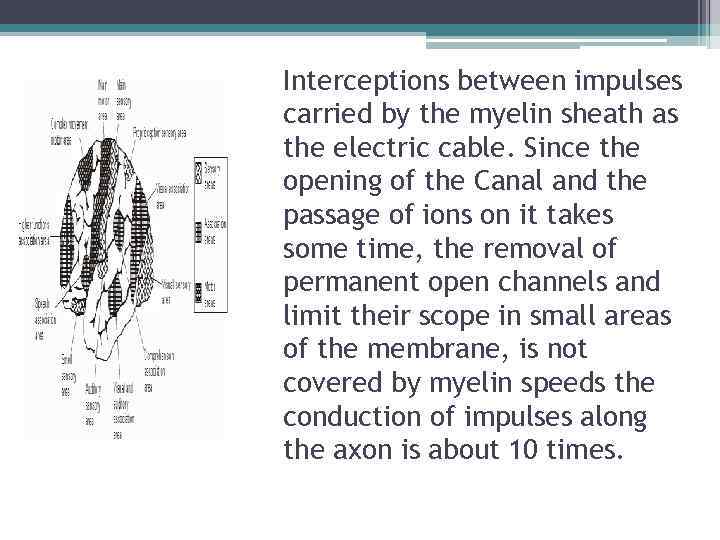
Interceptions between impulses carried by the myelin sheath as the electric cable. Since the opening of the Canal and the passage of ions on it takes some time, the removal of permanent open channels and limit their scope in small areas of the membrane, is not covered by myelin speeds the conduction of impulses along the axon is about 10 times.
The blood supply of the brain provide first carotid artery at the base of the brain are divided into large branches, going to its various departments. Although the weight of the brain is only 2. 5% of body weight, to him all the time, day and night, 20% received the circulating blood in the body and therefore oxygen. Energy reserves of the brain is extremely small, so that it is highly dependent on the oxygen supply.

• There are safeguards that will support cerebral blood flow in case of bleeding or injury. Feature of the cerebral circulation is the presence of socalled blood-brain barrier. It consists of several membranes that limit the permeability of the vascular walls and entry of many compounds from the blood into brain tissue, so that the barrier is protective. Not penetrate through it, for example, many drugs.
brain.ppt