Эндокардит.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 11

Kazakh – Russian Medical University ENDOCARDITIS DONE BY: AIBEK BAZILOV, 206 A CHECKED BY: ABDYKADYROVA. G. I ALMATY 2017

Plan 1. Endocarditis 2. Etiological and clinical-morphological features 3. Symptoms 4. Diagnosis of endocarditis 5. Questions

Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner shell of the heart, often with damage to the valve apparatus and a layer of cells lining the surface of adjacent vessels.

According to etiological and clinical-morphological features, there are: Infectious (bacterial, septic) acute; Subacute or chronic (protracted); Non-infectious thromboendocarditis; Rheumatic; Parietal fibroplastic eosinophilic (endocarditis of Leffler).
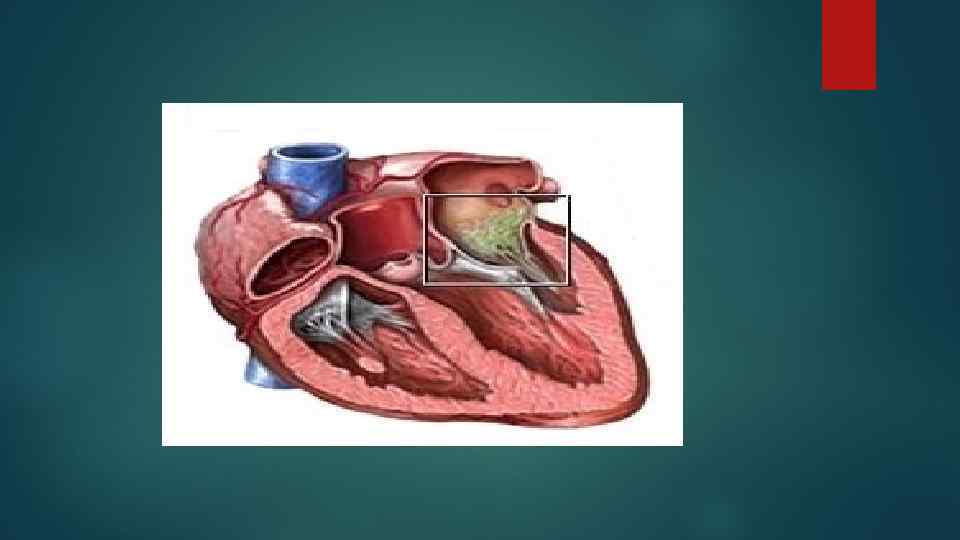

When the clinical picture is expanded, the following symptoms are noted: Severe intoxication: weakness, anorexia, headache, arthralgia; Changes in the skin: pale yellowish skin color, small-dot hemorrhages on the skin and mucous membranes, spots on the palms, feet, trunk; Changes in terminal phalanges and nails; Arthritis of large joints of upper and lower extremities; Damage to the aortic or mitral valve; Thromboembolism of large arteries with the development of infarctions of the corresponding organs; Signs of dry or exudative pericarditis; Enlarged lymph nodes; Kidney damage (focal nephritis, kidney infarction); Defeat of the central nervous system: meningoencephalitis, thromboembolism of the brain vessels, psychosis; Progressive heart failure.
Diagnosis of endocarditis To establish the correct diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account the whole complex of manifestations of the pathological process. In typical cases, the diagnosis of endocarditis is based on the following symptoms: the presence of fever with chills, valvular defects with the appearance of myocardial murmur, thromboembolic complications and positive results of bacteriological examination.
Diagnosis of endocarditis On an electrocardiogram (ECG) Echocardiography (echocardiography) Blood tests: general, biochemical and immunological

Treatment of endocarditis Depending on the causative agent of the disease use: benzylpenicillin, gentamicin or amikatsin intramuscularly (infection with green streptococcus); Semisynthetic penicillins in combination with cephalosporins or aminoglycosides (with staphylococcal endocarditis) Antibiotic therapy Immunocorrection Passive immunization is used to neutralize microbial toxins circulating in the bloodstream with ready-made antitoxic sera. The most effective is hyperimmune plasma and human immunoglobulin, which is administered intravenously daily for 3 -5 days.

Surgery The surgical method involves the mechanical removal of intracardiac foci of infection and affected valve structures, followed by the reconstruction and implantation of an artificial mechanical or biological prosthesis. It is realized in case of ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, developing heart failure, myocardial abscess, arterial thromboembolism, fungal endocarditis and other unfavorable outcomes of therapy.

Questions 1. What causes damage to the valves of the heart? 2. At what age does endocarditis occur? 3. What is the diagnosis of endocarditis? 4. What treatment is prescribed for a patient with endocarditis?
Эндокардит.pptx