Kazakh Ablai khan university of international relations and




























yl_reading.ppt
- Размер: 1.5 Мб
- Автор: Mereke Kaskyrbekkyzy
- Количество слайдов: 28
Описание презентации Kazakh Ablai khan university of international relations and по слайдам
 Kazakh Ablai khan university of international relations and world languages Teaching Reading and Writing to Young Learners Anastassiya Nam, M
Kazakh Ablai khan university of international relations and world languages Teaching Reading and Writing to Young Learners Anastassiya Nam, M
 Why do we read? • To obtain information for some purpose • To obtain instructions on how to perform some task for our work or daily life • To act in a play , play a game , or do a puzzle
Why do we read? • To obtain information for some purpose • To obtain instructions on how to perform some task for our work or daily life • To act in a play , play a game , or do a puzzle
 Why do we read? • To keep in touch by correspondence • To know when or where smth will take place or what is available. • To know what has happened ( news) • For enjoyment or excitement
Why do we read? • To keep in touch by correspondence • To know when or where smth will take place or what is available. • To know what has happened ( news) • For enjoyment or excitement
 Questions to ask before teaching reading to YL • What is the developmental stage of the child? • Can the child already read in his/her first language? • Does the child’s first language share a similar script with English?
Questions to ask before teaching reading to YL • What is the developmental stage of the child? • Can the child already read in his/her first language? • Does the child’s first language share a similar script with English?
 Questions to ask before teaching reading to YL • What is the child’s level of oral proficiency in English? • Does the child have a physical impairment or visual problem that may affect his/her ability to learn to read
Questions to ask before teaching reading to YL • What is the child’s level of oral proficiency in English? • Does the child have a physical impairment or visual problem that may affect his/her ability to learn to read
 Task 1 • Compare and contrast English and Kazakh /Russian scripts and predict what difficulties may occur while teaching reading to YL. • How can we solve these problems?
Task 1 • Compare and contrast English and Kazakh /Russian scripts and predict what difficulties may occur while teaching reading to YL. • How can we solve these problems?
 Reading is easier when • Print size is larger
Reading is easier when • Print size is larger
 Reading is easier when there are illustrations
Reading is easier when there are illustrations
 Reading is easier when students read something they are familiar with
Reading is easier when students read something they are familiar with
 Reading is easier when grammar is simple • That’s a bird. It’s green • That’s a butterfly. It’s red. • That’s a fish. It’s blue. • That’s a crab. It’s yellow. • That’s a cat. It’s white
Reading is easier when grammar is simple • That’s a bird. It’s green • That’s a butterfly. It’s red. • That’s a fish. It’s blue. • That’s a crab. It’s yellow. • That’s a cat. It’s white
 Belinda’s story • I am an elephant and I’m grey. • That’s an elephant. It’s super. • I’m an elephant. I’m super.
Belinda’s story • I am an elephant and I’m grey. • That’s an elephant. It’s super. • I’m an elephant. I’m super.
 What can we read with YL? • Fairy tales that children can read. A teacher can re-write a story he knows, simplifying it. • Short stories • Poems
What can we read with YL? • Fairy tales that children can read. A teacher can re-write a story he knows, simplifying it. • Short stories • Poems
 Fairy tales
Fairy tales
 Fairy tales
Fairy tales
 Fairy tale
Fairy tale
 Fairy tales
Fairy tales
 Comicbook speech bubble
Comicbook speech bubble
 Poems • Rain, Rain • Rain, rain , go away • Come again another day • Little Johnny wants to play
Poems • Rain, Rain • Rain, rain , go away • Come again another day • Little Johnny wants to play
 Choral reading • The teacher reads a phrase or sentence and the class repeats it. • It improves students’ intonation, pronunciation and listening skills
Choral reading • The teacher reads a phrase or sentence and the class repeats it. • It improves students’ intonation, pronunciation and listening skills
 Checking comprehension • Comprehension questions • Making a story timeline. (Listing the events of the story in the correct order. What happened 1 st , 2 nd , 3 rd and etc)
Checking comprehension • Comprehension questions • Making a story timeline. (Listing the events of the story in the correct order. What happened 1 st , 2 nd , 3 rd and etc)
 Create story cards • Take short stories and put them on cards. Have students, working in pairs, read the stories and then tell them to their partner
Create story cards • Take short stories and put them on cards. Have students, working in pairs, read the stories and then tell them to their partner
 Do jigsaw reading • Separate a story into 4 equal parts. Number each part and post it in a different corner of a room. Divide the students into groups of 4 and have students in each group number off from one to four. Ask students to go to the corner that matches their number andsilently read the part of the story. They then return to their seats and write down from memory what they recall from the story. After they finish writing , in numerical order each student tells the others in the group his or her part of the story.
Do jigsaw reading • Separate a story into 4 equal parts. Number each part and post it in a different corner of a room. Divide the students into groups of 4 and have students in each group number off from one to four. Ask students to go to the corner that matches their number andsilently read the part of the story. They then return to their seats and write down from memory what they recall from the story. After they finish writing , in numerical order each student tells the others in the group his or her part of the story.
 Use story theater • Divide a story into several parts • Form groups of 4 -5 students • Give each group a section of a story • Allow students to practice their section for 15 -20 minutes • Ask students to line up according to the story’s sequence and to read or perform it
Use story theater • Divide a story into several parts • Form groups of 4 -5 students • Give each group a section of a story • Allow students to practice their section for 15 -20 minutes • Ask students to line up according to the story’s sequence and to read or perform it
 What can YL write? • Address labels • Book titles • Cards( Birthday’s, Mother’s Day, Get well) • Cartoon speech balloons • Invitations
What can YL write? • Address labels • Book titles • Cards( Birthday’s, Mother’s Day, Get well) • Cartoon speech balloons • Invitations
 Writing a postcard • Address • Dear Michael, • Miami is fantastic_______ • ______________ • Yesterday __________ • ______________
Writing a postcard • Address • Dear Michael, • Miami is fantastic_______ • ______________ • Yesterday __________ • ______________
 Writing a postcard • Tomorrow______________ • Love, Kate • We went to the movies, it’s got nice beaches, there a lot of cafes , we went to a restaurant, we are going to a famous park, the water is warm, we saw a very good film.
Writing a postcard • Tomorrow______________ • Love, Kate • We went to the movies, it’s got nice beaches, there a lot of cafes , we went to a restaurant, we are going to a famous park, the water is warm, we saw a very good film.
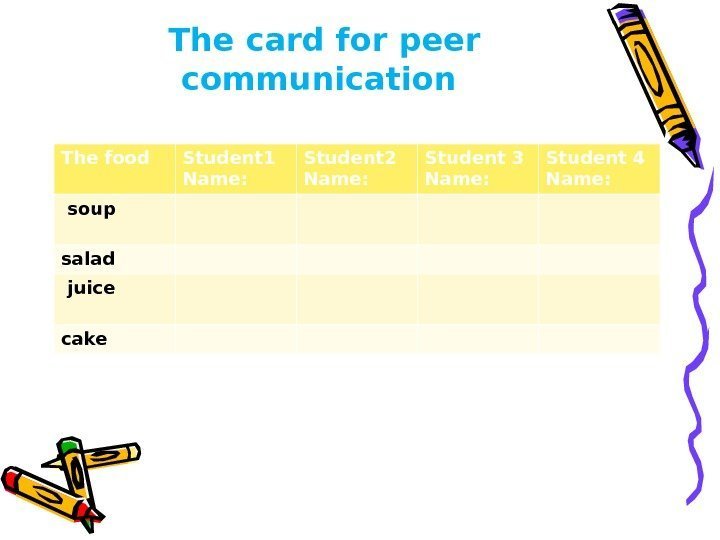
 The card for peer communication The food Student 1 Name: Student 2 Name: Student 3 Name: Student 4 Name: soup salad juice cake
The card for peer communication The food Student 1 Name: Student 2 Name: Student 3 Name: Student 4 Name: soup salad juice cake
 Writing a menu for a birthday party • Using the completed like/dislike card a learner should write a menu for the birthday party. ( The students he/she questioned will be guests!). • The learner may write the following. • Anna and Marat like orange juice. I will have orange juice for my party. Misha and Marat like the chicken soup, Anna doesn’t like. I will have chicken soup. • And so on. • This task is good not only because it will make them use their active vocabulary and grammar structures. It will be also very good because it will develop their analytical thinking and decision making skills
Writing a menu for a birthday party • Using the completed like/dislike card a learner should write a menu for the birthday party. ( The students he/she questioned will be guests!). • The learner may write the following. • Anna and Marat like orange juice. I will have orange juice for my party. Misha and Marat like the chicken soup, Anna doesn’t like. I will have chicken soup. • And so on. • This task is good not only because it will make them use their active vocabulary and grammar structures. It will be also very good because it will develop their analytical thinking and decision making skills

