3ca3a672fa2b09ccb40a1d3df0b0215a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Katherine L. Mc. Eldoon, Caroline Cochrane-Braswell & Bethany Rittle-Johnson

Outline Current Study Three different problem formats Their effect on problem solving strategy use What is Functional Thinking What makes it challenging What facilitates student understanding 2
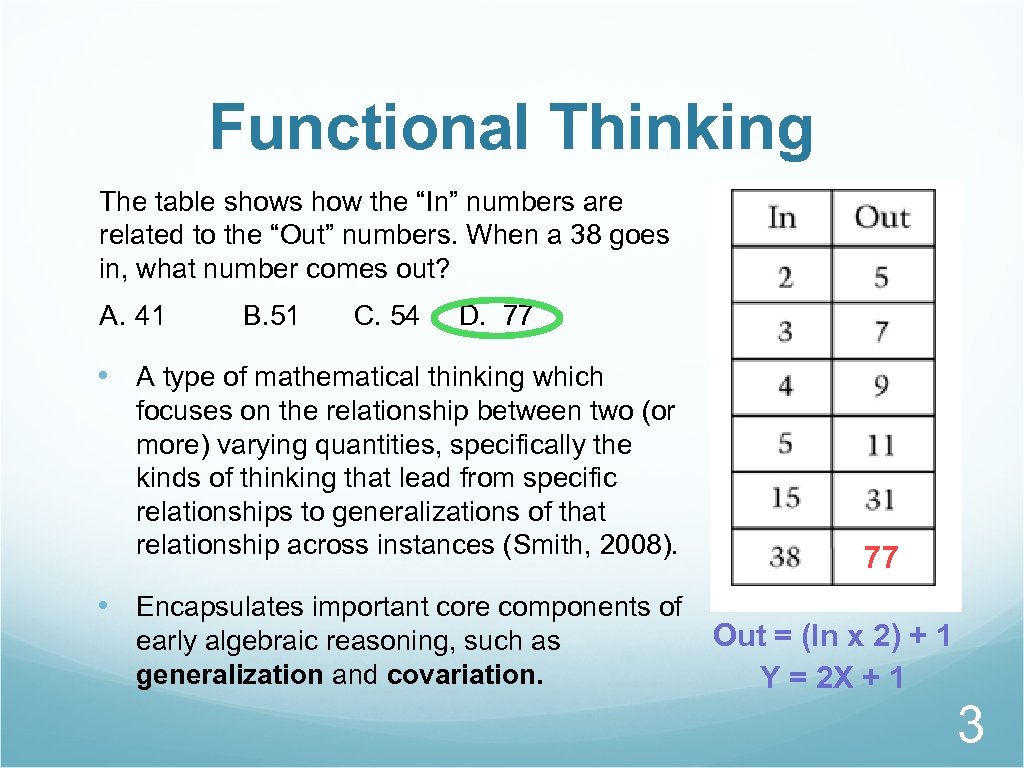
Functional Thinking The table shows how the “In” numbers are related to the “Out” numbers. When a 38 goes in, what number comes out? A. 41 B. 51 C. 54 D. 77 • A type of mathematical thinking which focuses on the relationship between two (or more) varying quantities, specifically the kinds of thinking that lead from specific relationships to generalizations of that relationship across instances (Smith, 2008). • Encapsulates important core components of early algebraic reasoning, such as generalization and covariation. 77 Out = (In x 2) + 1 Y = 2 X + 1 3
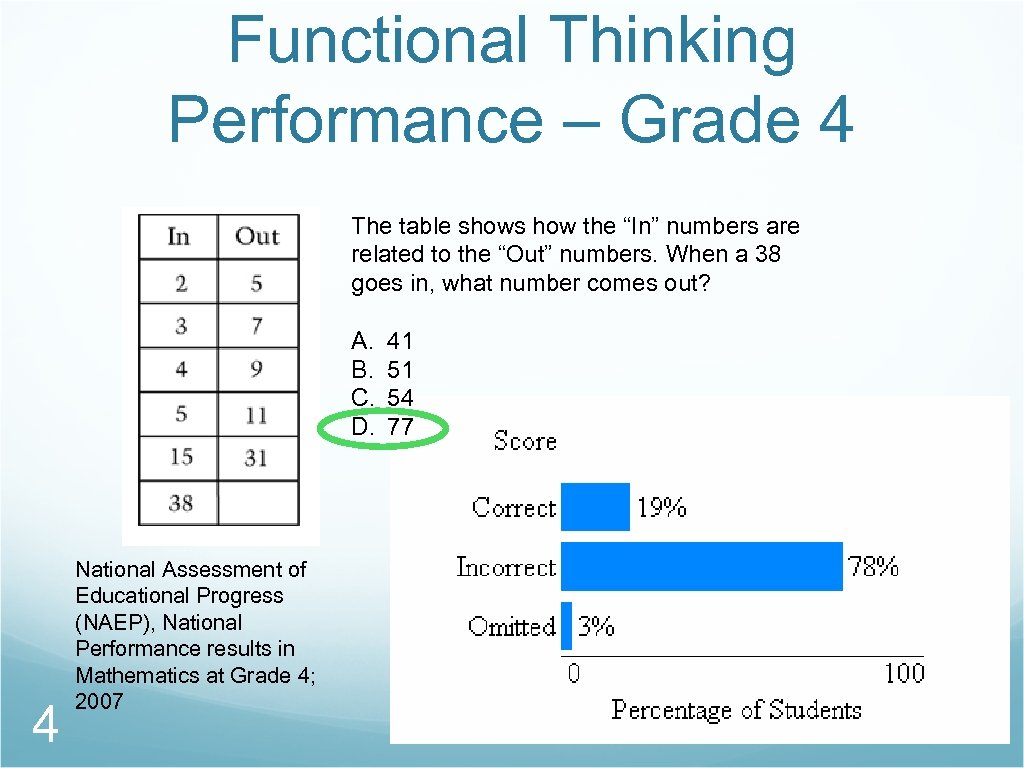
Functional Thinking Performance – Grade 4 The table shows how the “In” numbers are related to the “Out” numbers. When a 38 goes in, what number comes out? A. B. C. D. 4 National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP), National Performance results in Mathematics at Grade 4; 2007 41 51 54 77
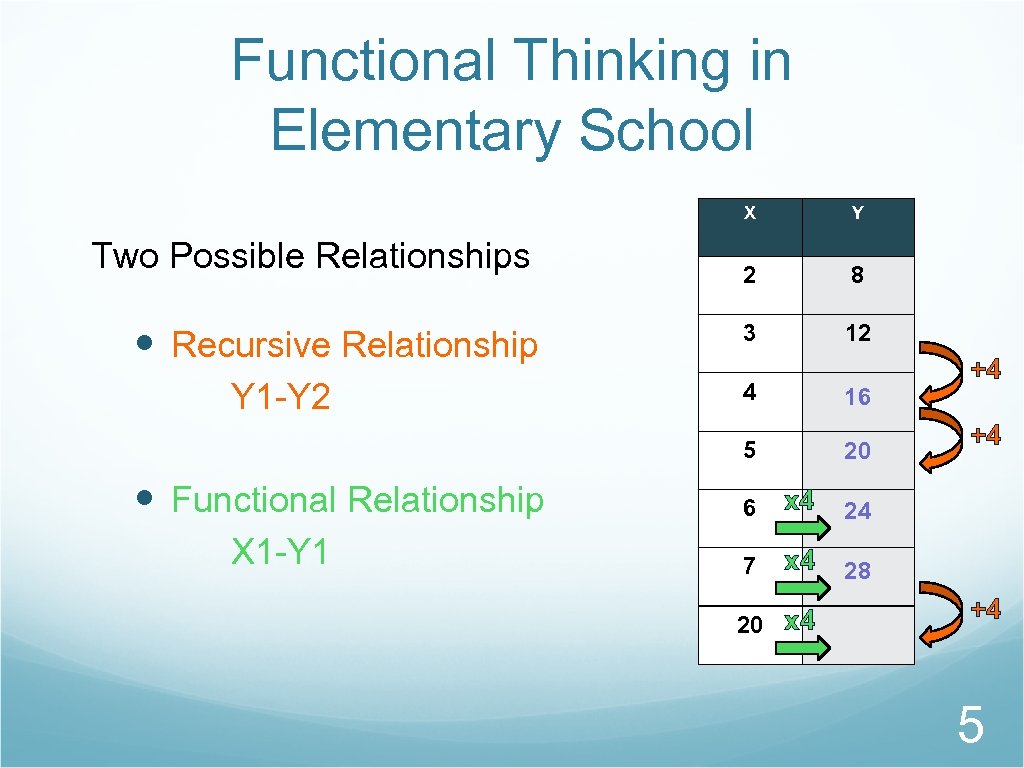
Functional Thinking in Elementary School X Two Possible Relationships Recursive Relationship Y 1 -Y 2 8 3 12 X 1 -Y 1 16 5 Functional Relationship 4 20 6 x 4 +4 24 7 +4 28 20 x 4 +4 5

Fostering Functional Thinking In novices, surface features compete with deep Y 3 8 5 Alternate Surface Feature Format X 16 features attentionally (Sloutsky & Yarlas, 2000) • Story Problem Format • • 6 Depends on linguistic proficency (Kintsch & Greeno, 1985; Koedinger, Alibali & Nathan, 2008) When readers can handle it, they help support informal solution methods (Carraher et al. , 2003) Julia is selling boxes of cookies as a fundraiser for her school. Three boxes cost $9 and five boxes cost $15. Her aunt wants to buy 6 boxes, and her neighbor wants to buy 8. How much do they have to pay? Julia sells 25 boxes in all. How much did she earn? 9 25 6

Current Study Investigate the effect of problem context on problem solving strategy within function table problems Contexts (between subjects) Baseline Alternate Surface Story 7
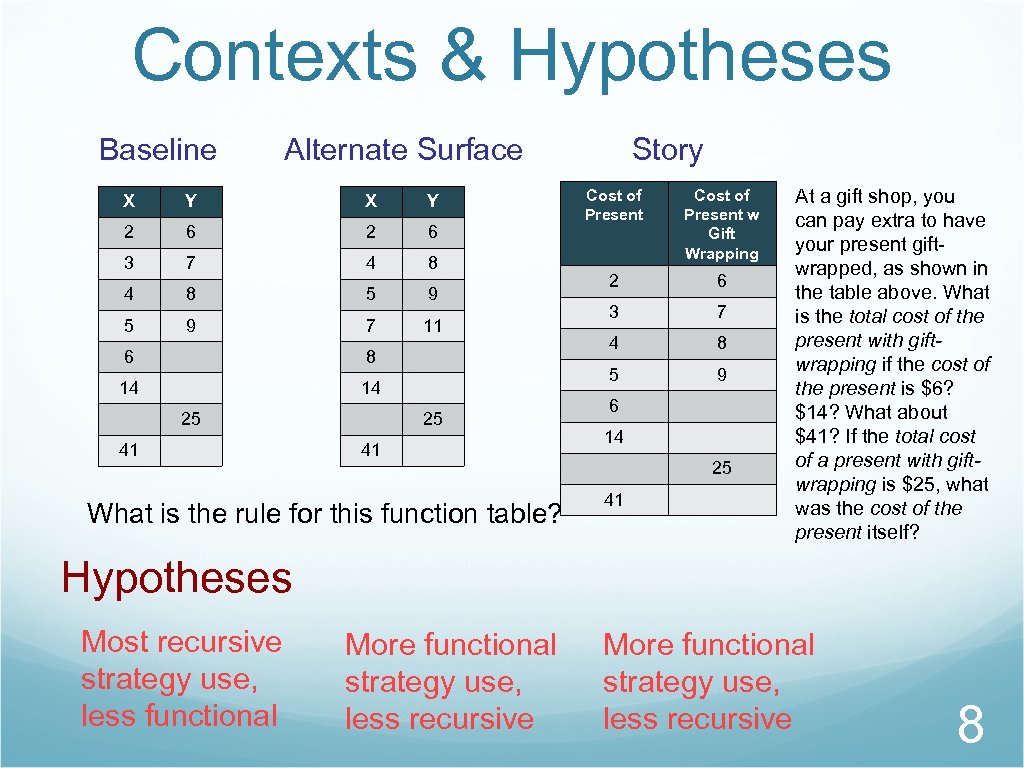
Contexts & Hypotheses Baseline Alternate Surface Y X Y 2 6 3 7 4 8 5 9 7 11 8 14 14 25 41 What is the rule for this function table? Cost of Present w Gift Wrapping 2 6 3 7 4 8 5 X 6 Story 9 6 14 25 41 At a gift shop, you can pay extra to have your present giftwrapped, as shown in the table above. What is the total cost of the present with giftwrapping if the cost of the present is $6? $14? What about $41? If the total cost of a present with giftwrapping is $25, what was the cost of the present itself? Hypotheses Most recursive strategy use, less functional More functional strategy use, less recursive 8

Method Participants 232 students in grades two through six in a middle class community Procedure Three different forms of the assessment (baseline, alternate surface, and story) were randomly distributed to students during their normal math class as a whole class activity. 9

Assessment Three isomorphic versions of the assessment Baseline (or) Alternate Surface (or) Story Three function table problems Additive Y = X + 4 (and) Multiplicative Y = 3 X (and) Combo Y = 3 X + 2 10
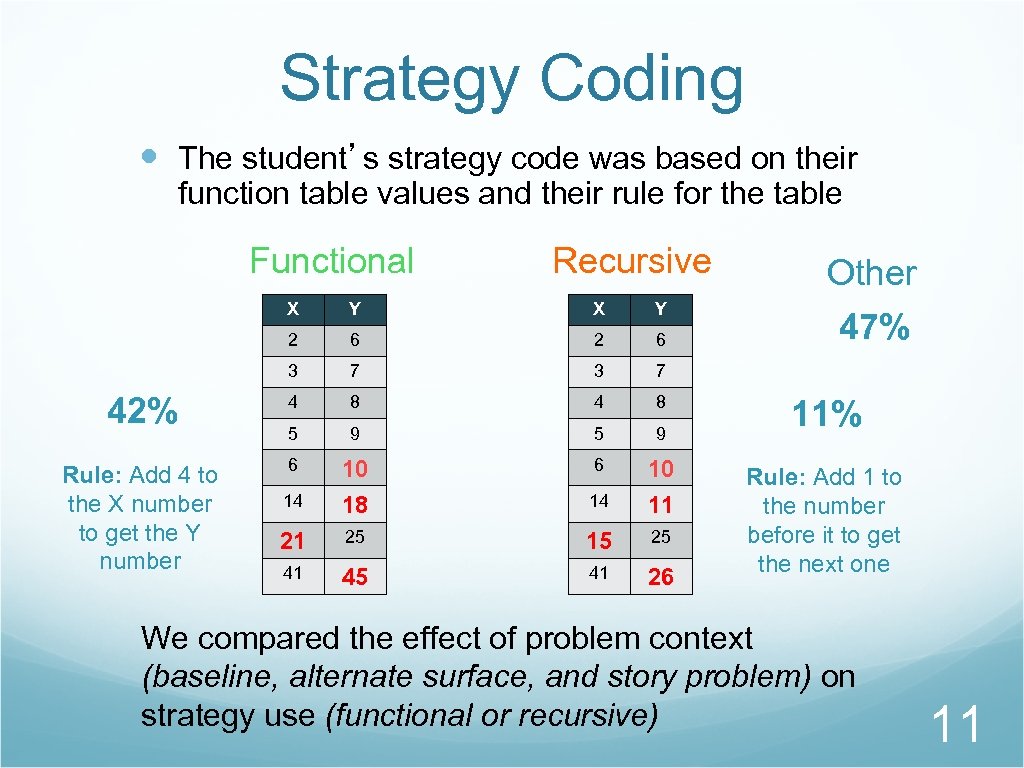
Strategy Coding The student’s strategy code was based on their function table values and their rule for the table Functional Recursive X Y 2 6 3 7 42% 4 8 5 9 Rule: Add 4 to the X number to get the Y number 6 10 14 18 14 11 21 25 15 25 41 45 41 26 Other 47% 11% Rule: Add 1 to the number before it to get the next one We compared the effect of problem context (baseline, alternate surface, and story problem) on strategy use (functional or recursive) 11
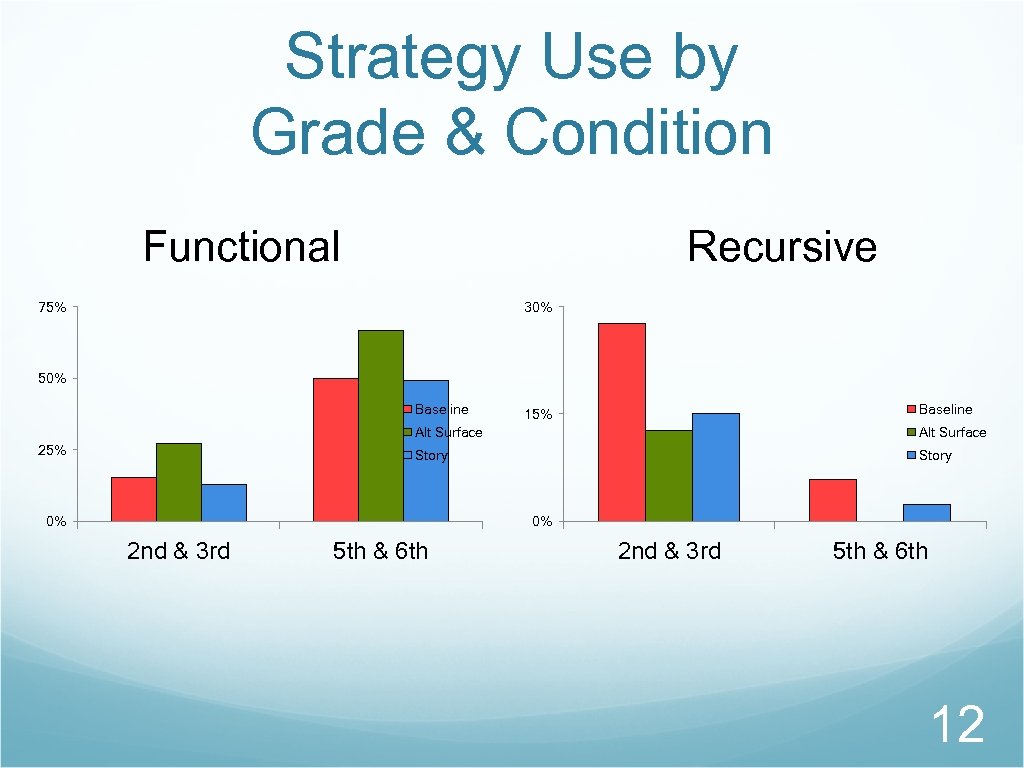
Strategy Use by Grade & Condition Functional Recursive 75% 30% 50% Baseline 15% Alt Surface Story 25% Alt Surface Story 0% 0% 2 nd & 3 rd 5 th & 6 th 12

Results- Functional Strategy Alt Surface Overall, the alternate surface context was the most conducive to the functional strategy significantly more than the story contex marginally more than the baseline There was no difference in strategy use in the baseline and story contexts. 13
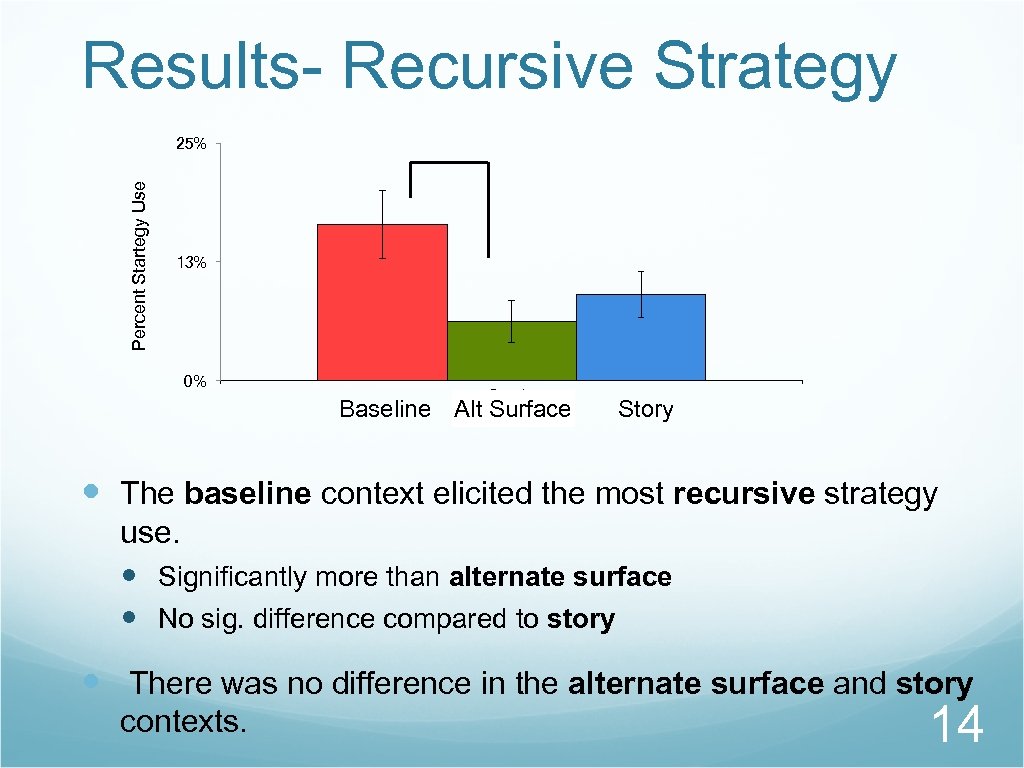
Results- Recursive Strategy Percent Startegy Use 25% 13% 0% Recursive Baseline Alt Surface Story The baseline context elicited the most recursive strategy use. Significantly more than alternate surface No sig. difference compared to story There was no difference in the alternate surface and story contexts. 14

Conclusions Strategy Use by Context 60% 40% Baseline Alternate Numeric 20% Story 0% Recursive Functional The baseline context resulted in the most use of the naïve recursive strategy The alternate surface context elicited the most functional strategy use Story context did not increase recursive strategy use, but it also did not encourage functional strategy use 15

Thank you
3ca3a672fa2b09ccb40a1d3df0b0215a.ppt