8dc6e0932589a035d490a8ecc40cdec4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
 Kaiser Permanente San FAMILY MEDICINE RESIDENCY PROGRAM Diego
Kaiser Permanente San FAMILY MEDICINE RESIDENCY PROGRAM Diego
 Understanding and Overcoming Generation Gaps In Your Training Program’s Interdisciplinary Teams Katherine Balazy, MD Sherwin Gallardo, MD
Understanding and Overcoming Generation Gaps In Your Training Program’s Interdisciplinary Teams Katherine Balazy, MD Sherwin Gallardo, MD
 Objectives -List the characteristics of the 4 generations potentially present in today’s interdisciplinary Health Care Teams: Traditional/Silent, Baby Boomers, Generation X, Generation Y -Identify how differences in generational characteristics can potentially lead to differing views of professionalism -Discuss how staff, residents and medical students in Generation Y prefer to learn and communicate. -Identify and utilize potentially new/novel methods to teach staff, medical students and residents in Generation Y.
Objectives -List the characteristics of the 4 generations potentially present in today’s interdisciplinary Health Care Teams: Traditional/Silent, Baby Boomers, Generation X, Generation Y -Identify how differences in generational characteristics can potentially lead to differing views of professionalism -Discuss how staff, residents and medical students in Generation Y prefer to learn and communicate. -Identify and utilize potentially new/novel methods to teach staff, medical students and residents in Generation Y.
 Why is this important? • Culture has increased in importance – now there are new “cultures” of age/generations • Successful teaching/learning and healthcare outcomes depend on effective communication & understanding between these age cultures • Recruitment and retention issues • Management/motivation issues
Why is this important? • Culture has increased in importance – now there are new “cultures” of age/generations • Successful teaching/learning and healthcare outcomes depend on effective communication & understanding between these age cultures • Recruitment and retention issues • Management/motivation issues
 Background • This is the first time in history that there are four generations in the workforce • The business world has been incorporating these principles for 10 -15 years • The youngest of the 4 generations are the new physicians now joining the workforce • Changes in resident work hours • Our own experiences
Background • This is the first time in history that there are four generations in the workforce • The business world has been incorporating these principles for 10 -15 years • The youngest of the 4 generations are the new physicians now joining the workforce • Changes in resident work hours • Our own experiences
 The times they are a changin’… • Solo practices are being replaced by large medical corporations • Knowledge and skill domains have become much more complex • Hospitalized patients are much sicker • Information flow is nonstop, response time is reduced • Regulatory and paperwork burden has increased • Skills in financial management, collaboration, communication, organizational politics and negotiation are not optional but critical in
The times they are a changin’… • Solo practices are being replaced by large medical corporations • Knowledge and skill domains have become much more complex • Hospitalized patients are much sicker • Information flow is nonstop, response time is reduced • Regulatory and paperwork burden has increased • Skills in financial management, collaboration, communication, organizational politics and negotiation are not optional but critical in
 Background • Generations are bound together by shared life experiences and societal events and trends during their formative years • Independent of age
Background • Generations are bound together by shared life experiences and societal events and trends during their formative years • Independent of age
 Generational Differences These new doctors don’t recognize the value of a long day at work and are just plain lazy! OMG The older doctors are way behind in their computer knowledge! And they are workaholics
Generational Differences These new doctors don’t recognize the value of a long day at work and are just plain lazy! OMG The older doctors are way behind in their computer knowledge! And they are workaholics
 Generational Differences Retention bonus? When I was a new associate I was just thankful I had a job! If she’s looking for loyalty, she should get a dog! LOL
Generational Differences Retention bonus? When I was a new associate I was just thankful I had a job! If she’s looking for loyalty, she should get a dog! LOL
 Results of Recent Informal Kaiser San Diego PC Dept Survey:
Results of Recent Informal Kaiser San Diego PC Dept Survey:
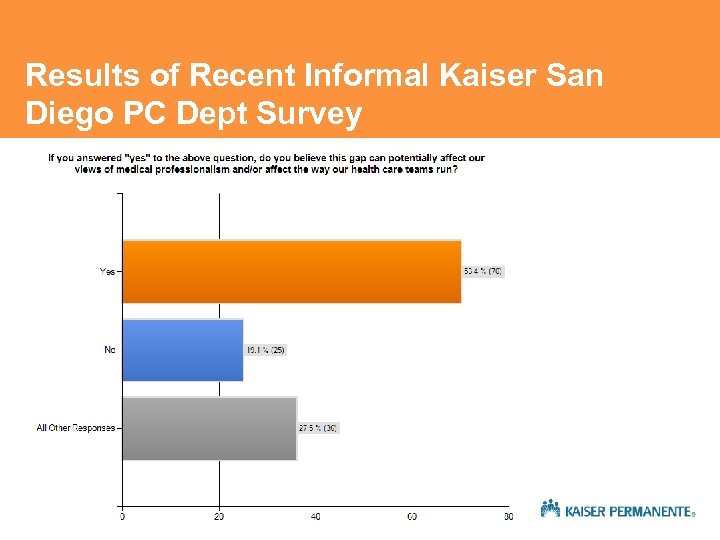 Results of Recent Informal Kaiser San Diego PC Dept Survey
Results of Recent Informal Kaiser San Diego PC Dept Survey
 Ground rules • Open minds… • Look for common ground and respect/value differing perspectives • These are general guidelines only • Many persons have many characteristics outside of their generation’s characteristics • An individual’s life experiences and unique external infuences may supercede their generation’s characteristics
Ground rules • Open minds… • Look for common ground and respect/value differing perspectives • These are general guidelines only • Many persons have many characteristics outside of their generation’s characteristics • An individual’s life experiences and unique external infuences may supercede their generation’s characteristics
 Ground rules • Individual influences may trump generational characteristics (birth order, class, ethnicity) • Nevertheless, understanding these basic differences in the culture of generations may help optimize § § Comptence and performance in health care teams Teaching, learning, and overall communication Provider satisfaction Patient outcomes
Ground rules • Individual influences may trump generational characteristics (birth order, class, ethnicity) • Nevertheless, understanding these basic differences in the culture of generations may help optimize § § Comptence and performance in health care teams Teaching, learning, and overall communication Provider satisfaction Patient outcomes
 Talkin’ About My Generation… • “Traditional” or “Silent” Generation § Born 1922 -1945 • “Baby Boomer” Generation § Born 1946 -1964 • “Generation X” § Born 1965 -1979 • “Generation Y” or “Millenials” § Born 1980 -2000
Talkin’ About My Generation… • “Traditional” or “Silent” Generation § Born 1922 -1945 • “Baby Boomer” Generation § Born 1946 -1964 • “Generation X” § Born 1965 -1979 • “Generation Y” or “Millenials” § Born 1980 -2000
 Objective #1 • List the characteristics of the 4 generations potentially present in today’s Interdisciplinary Health Care Teams: Traditional/Silent, Baby Boomers, Generation X, and Generation Y
Objective #1 • List the characteristics of the 4 generations potentially present in today’s Interdisciplinary Health Care Teams: Traditional/Silent, Baby Boomers, Generation X, and Generation Y
 The Traditional or Silent Generation • Born between 1922 and 1945 • 55 million • Financially conservative: hold 75% of nation’s wealth • Traditional “American values” § hard work, personal sacrifice, law and order, conformity, delayed gratification, traditional gender roles
The Traditional or Silent Generation • Born between 1922 and 1945 • 55 million • Financially conservative: hold 75% of nation’s wealth • Traditional “American values” § hard work, personal sacrifice, law and order, conformity, delayed gratification, traditional gender roles
 The Traditional or Silent Generation • High degree of respect for hierarchy • Like civic/fraternal/professional organizations • See medicine as a “vocational calling” • Lower degree of computer literacy
The Traditional or Silent Generation • High degree of respect for hierarchy • Like civic/fraternal/professional organizations • See medicine as a “vocational calling” • Lower degree of computer literacy
 The Traditional or Silent Generation • Teamwork is important • Success defined by achievements of the team • Recognition for work done above and beyond expectations • Usually easy to get along with • Leaving the work force
The Traditional or Silent Generation • Teamwork is important • Success defined by achievements of the team • Recognition for work done above and beyond expectations • Usually easy to get along with • Leaving the work force
 The Traditional or Silent Generation • Information technology: Traditional – Radio, Newspapers • Families gathered “around the table”
The Traditional or Silent Generation • Information technology: Traditional – Radio, Newspapers • Families gathered “around the table”
 Baby Boomer Generation • Born 1946 -1964 • Nearly 80 million strong • Came of age during political and social turmoil § § Vietnam war Civil rights riots JFK, MLK Woodstock and Watergate
Baby Boomer Generation • Born 1946 -1964 • Nearly 80 million strong • Came of age during political and social turmoil § § Vietnam war Civil rights riots JFK, MLK Woodstock and Watergate
 Baby Boomer Generation • Also a period of post-war optimism § Space Age, race to the moon • “Live to work” § “Workaholics” § Prosperity, material wealth, titles • Currently in most of the organizational leadership positions
Baby Boomer Generation • Also a period of post-war optimism § Space Age, race to the moon • “Live to work” § “Workaholics” § Prosperity, material wealth, titles • Currently in most of the organizational leadership positions
 Baby Boomer Generation • Respect authority and title, experience • Loyal towards their employers/company • “pay dues” • Confident, may shun constant feedback • Ambitious, driven, motivated
Baby Boomer Generation • Respect authority and title, experience • Loyal towards their employers/company • “pay dues” • Confident, may shun constant feedback • Ambitious, driven, motivated
 Baby Boomer Generation • Information technology: Television • For the first time, this generation could “put a face” to the news/information
Baby Boomer Generation • Information technology: Television • For the first time, this generation could “put a face” to the news/information
 Generation X § Born 1965 and 1979, children of early baby boomers § 47 million § “Latchkey kids” § Parents were victims of downsizing in exchange for their loyalty
Generation X § Born 1965 and 1979, children of early baby boomers § 47 million § “Latchkey kids” § Parents were victims of downsizing in exchange for their loyalty
 Generation X § Skeptical, self-reliant § Not intimidated by authority § Parental divorce § Changing gender roles § Work to live § Being a physician is only part of their identity
Generation X § Skeptical, self-reliant § Not intimidated by authority § Parental divorce § Changing gender roles § Work to live § Being a physician is only part of their identity
 Generation X § Value informality, look for a “family” at work § See feedback as a way to better themselves § Are direct with feedback § Technoliteracy important
Generation X § Value informality, look for a “family” at work § See feedback as a way to better themselves § Are direct with feedback § Technoliteracy important
 Generation X § Information technology: Computers, First cell phones, First VCRs § Now they could watch news “on their own time”
Generation X § Information technology: Computers, First cell phones, First VCRs § Now they could watch news “on their own time”
 Generation Y • Born generally about 1980 -2000 • Approximately 80 million + • “Millenials”, “Generation Next”, “Net Generation”, “Generation Why” • Came of age during dramatic technological change, rise of social media, post-cold war • First true “Digital Natives” • 9/11/2001
Generation Y • Born generally about 1980 -2000 • Approximately 80 million + • “Millenials”, “Generation Next”, “Net Generation”, “Generation Why” • Came of age during dramatic technological change, rise of social media, post-cold war • First true “Digital Natives” • 9/11/2001
 Generation Y
Generation Y
 Generation Y • “Baby on Board”, parents were younger Baby Boomers or older Gen X’ers • “Trophy Children of Helicopter Parents” § § “Hover and Rescue” “Blackhawk Parents” – hover, rescue and attack Often received awards for simply participating “Grade inflation” • Protected and coddled as a backlash from “hands-off” parenting of previous generation • Achievement oriented • Expect constant and immediate feedback (praise)
Generation Y • “Baby on Board”, parents were younger Baby Boomers or older Gen X’ers • “Trophy Children of Helicopter Parents” § § “Hover and Rescue” “Blackhawk Parents” – hover, rescue and attack Often received awards for simply participating “Grade inflation” • Protected and coddled as a backlash from “hands-off” parenting of previous generation • Achievement oriented • Expect constant and immediate feedback (praise)
 Generation Y • Expect diversity, the most tolerant of any generation • Multi-tasking “hands-on” learners • Don’t fear change, they fear boredom § “Blackberry Prayer” • They were always presented with choices • The bulk of current residents and medical students are in this
Generation Y • Expect diversity, the most tolerant of any generation • Multi-tasking “hands-on” learners • Don’t fear change, they fear boredom § “Blackberry Prayer” • They were always presented with choices • The bulk of current residents and medical students are in this
 Generation Y • Information technology: Internet, instant access • Speed, anonymity – boldness of expression
Generation Y • Information technology: Internet, instant access • Speed, anonymity – boldness of expression
 Generation Y • Potential to be the greatest generation in history § 9 -11 is their Pearl Harbor, the duty, resolve and values of the Silent Generation § They outnumber the Baby Boomers § Will be political and economic drivers for years to come § Creativity, diversity and work-life balance of Generation X § Social awareness is greater than any previous generation
Generation Y • Potential to be the greatest generation in history § 9 -11 is their Pearl Harbor, the duty, resolve and values of the Silent Generation § They outnumber the Baby Boomers § Will be political and economic drivers for years to come § Creativity, diversity and work-life balance of Generation X § Social awareness is greater than any previous generation
 Objective #2 • Identify how differences in generational characteristics can potentially lead to differing views of professionalism
Objective #2 • Identify how differences in generational characteristics can potentially lead to differing views of professionalism
 “Generations come into conflict when values differ” • Formality § Younger generations feel more comfortable calling everyone by first name rather than a title • Role in planning § Generation Y has grown up being asked for input about family decisions and have a greater expectation that they will be asked for their opinion in all situations and expect their opinion to be considered • Recognition § Older generations expect the team as a whole to be recognized while younger generations like individual recognition
“Generations come into conflict when values differ” • Formality § Younger generations feel more comfortable calling everyone by first name rather than a title • Role in planning § Generation Y has grown up being asked for input about family decisions and have a greater expectation that they will be asked for their opinion in all situations and expect their opinion to be considered • Recognition § Older generations expect the team as a whole to be recognized while younger generations like individual recognition
 “Generations come into conflict when values differ” • Merit § Younger generations expect recognition (compensation) even for doing what is required. The older generations do not • Communication § Silent generation and baby boomers want written memos. Generation X favors e-mail. Generation Y favors text and social media • Management § Generation X prefer being assigned a task and being left alone. Generation Y require frequent (positive) feedback • Work-life balance
“Generations come into conflict when values differ” • Merit § Younger generations expect recognition (compensation) even for doing what is required. The older generations do not • Communication § Silent generation and baby boomers want written memos. Generation X favors e-mail. Generation Y favors text and social media • Management § Generation X prefer being assigned a task and being left alone. Generation Y require frequent (positive) feedback • Work-life balance
 Work-life balance § JAMA 2003 § Most important factor in choosing a job was predictable work schedule § Total hours, salary were very low on the list § Independent of gender
Work-life balance § JAMA 2003 § Most important factor in choosing a job was predictable work schedule § Total hours, salary were very low on the list § Independent of gender
 Older on younger generations § Don’t want to do extra things § Too much reliance on technology, not enough thinking § Always hear “Why do I have to do that? ” § Professionalism issues: Dress, music players, cell phones, time off when they want § Not motivated § Find OMG/LOL disrespectful § 75% of program directors could not identify with residents
Older on younger generations § Don’t want to do extra things § Too much reliance on technology, not enough thinking § Always hear “Why do I have to do that? ” § Professionalism issues: Dress, music players, cell phones, time off when they want § Not motivated § Find OMG/LOL disrespectful § 75% of program directors could not identify with residents
 Younger on older generations § Teams and committees led by the older generations are not able to make decisions § Residents are made to feel guilty for obeying duty hour rules § Older faculty are behind on using technology § Feel lack of respect for their contributions § Not enough autonomy § Their decisions are micromanaged
Younger on older generations § Teams and committees led by the older generations are not able to make decisions § Residents are made to feel guilty for obeying duty hour rules § Older faculty are behind on using technology § Feel lack of respect for their contributions § Not enough autonomy § Their decisions are micromanaged
 Professionalism Generations see this issue differently and their perception causes potential conflict.
Professionalism Generations see this issue differently and their perception causes potential conflict.
 Professionalism Consider this… § Dr Z (age 61) says he is offended that the quality of his practice is measured by numbers rather than time spent in the office and his relationships with patients § Dr A (age 38) says he takes excellent care of his patients through telemedicine even though he leaves daily at 5 pm
Professionalism Consider this… § Dr Z (age 61) says he is offended that the quality of his practice is measured by numbers rather than time spent in the office and his relationships with patients § Dr A (age 38) says he takes excellent care of his patients through telemedicine even though he leaves daily at 5 pm
 Professionalism Consider this… § Dr. XY (age 31) is seeing a patient and the patient asks him some questions, Dr. XY looks up the answers on his Droid smartphone on the Dyna. Med app § Patient Z (age 74) files a service complaint with KP stating “my doctor was either texting or playing video games on his phone while I was talking to him”
Professionalism Consider this… § Dr. XY (age 31) is seeing a patient and the patient asks him some questions, Dr. XY looks up the answers on his Droid smartphone on the Dyna. Med app § Patient Z (age 74) files a service complaint with KP stating “my doctor was either texting or playing video games on his phone while I was talking to him”
 Professionalism Consider this… • Mentor Dr. XY (age 60) asks Dr. XX (age 30) at an informal 1: 1 meeting “What are some of the clinical issues or questions you have that I can help you with? ” • Dr. XX answers “finding competent child care, ” to which Dr. XY does not really have a good response, expecting instead something related to academics or patient care.
Professionalism Consider this… • Mentor Dr. XY (age 60) asks Dr. XX (age 30) at an informal 1: 1 meeting “What are some of the clinical issues or questions you have that I can help you with? ” • Dr. XX answers “finding competent child care, ” to which Dr. XY does not really have a good response, expecting instead something related to academics or patient care.
 Today’s medical education environment • Teaching faculty are mostly Boomers and X’ers • Residents and students are mostly Millenials (Gen Y) • Staff, nursing in health care teams could be from any generation
Today’s medical education environment • Teaching faculty are mostly Boomers and X’ers • Residents and students are mostly Millenials (Gen Y) • Staff, nursing in health care teams could be from any generation
 Professionalism Considerable recent research on this topic General consensus is that professionalism is decreasing in medicine Education in residency programs • Inclusion/creation of generational diversity training
Professionalism Considerable recent research on this topic General consensus is that professionalism is decreasing in medicine Education in residency programs • Inclusion/creation of generational diversity training
 Professionalism “…dynamic framework derived from interaction of many forces such as the tradition of healing, social change, rising medical challenges, and scientific advances, as well as the interest of members and subgroups within and outside the profession” –Sharon Johnston
Professionalism “…dynamic framework derived from interaction of many forces such as the tradition of healing, social change, rising medical challenges, and scientific advances, as well as the interest of members and subgroups within and outside the profession” –Sharon Johnston
 Professionalism § Core values are the same § Newer generations skeptical of the “total commitment” especially to primary care due to “burnout” experienced by older generations § Resident duty hours? § Work life balance § Self interest vs patient interest
Professionalism § Core values are the same § Newer generations skeptical of the “total commitment” especially to primary care due to “burnout” experienced by older generations § Resident duty hours? § Work life balance § Self interest vs patient interest
 Professionalism § Adapt teaching styles for young physicians according to the ways they learn best § Patient focused environment with flexible practice design § Value physician well being § Reward excellence, rather than endurance § Patient directed team care approach § Expect excellence in our profession § Foster joy of being a doctor
Professionalism § Adapt teaching styles for young physicians according to the ways they learn best § Patient focused environment with flexible practice design § Value physician well being § Reward excellence, rather than endurance § Patient directed team care approach § Expect excellence in our profession § Foster joy of being a doctor
 Professionalism § Appropriate guidance at each level of training § Role modeling § Use real time examples § Adapt discussions to their learning styles § Focus on importance of professionalism in bettering themselves as an individual § Empower new physicians in building an environment which fosters professionalism
Professionalism § Appropriate guidance at each level of training § Role modeling § Use real time examples § Adapt discussions to their learning styles § Focus on importance of professionalism in bettering themselves as an individual § Empower new physicians in building an environment which fosters professionalism
 Objective #3 • Discuss how staff, residents and medical students in Generation Y prefer to learn and communicate.
Objective #3 • Discuss how staff, residents and medical students in Generation Y prefer to learn and communicate.
 Generation Y • • • Visual learners “Hands-on” learners Multimedia Multitaskers Teamwork is important
Generation Y • • • Visual learners “Hands-on” learners Multimedia Multitaskers Teamwork is important
 Generation Y • Autonomy • Less “formal” didactics/learning sessions • Flexibility and balance • Career/vocation no longer defines them
Generation Y • Autonomy • Less “formal” didactics/learning sessions • Flexibility and balance • Career/vocation no longer defines them
 Generation Y • Information technology and processing § Instant/continuous bedside access to info § Reliance on technology vs. critical thinking • Focus on: § Self § Relationships § Patients • Embrace diversity, social awareness
Generation Y • Information technology and processing § Instant/continuous bedside access to info § Reliance on technology vs. critical thinking • Focus on: § Self § Relationships § Patients • Embrace diversity, social awareness
 Generation Y • Quality and efficiency § Streamlining processes § EMR “shortcuts” § Self-study online vs. sitting in lecture • Expect instant and continuous feedback • Expect to have a say in how things are run • Expect to be surrounded by bright, intelligent colleagues
Generation Y • Quality and efficiency § Streamlining processes § EMR “shortcuts” § Self-study online vs. sitting in lecture • Expect instant and continuous feedback • Expect to have a say in how things are run • Expect to be surrounded by bright, intelligent colleagues
 Objective #4 • Identify and utilize potentially new/novel methods to teach staff, medical students and residents in Generation Y.
Objective #4 • Identify and utilize potentially new/novel methods to teach staff, medical students and residents in Generation Y.
 Teaching Generation Y • The incorporation of technology § § § § § Avoiding “Powerpoint Karaoke” Increase media in presentations Real time online learning (Web. Ex) Virtual patients/simulations Policies and expectations for smartphone or laptop use Regulations for the use of social media Competition/games Make it fun! Audience Response Systems (ARS)
Teaching Generation Y • The incorporation of technology § § § § § Avoiding “Powerpoint Karaoke” Increase media in presentations Real time online learning (Web. Ex) Virtual patients/simulations Policies and expectations for smartphone or laptop use Regulations for the use of social media Competition/games Make it fun! Audience Response Systems (ARS)
 Teaching Generation Y • Learning how to give feedback § Constant coaching – timely and regular § The importance of transparency – let them know exactly what is expected up front § Use the “feedback sandwich” § Personalize your comments
Teaching Generation Y • Learning how to give feedback § Constant coaching – timely and regular § The importance of transparency – let them know exactly what is expected up front § Use the “feedback sandwich” § Personalize your comments
 Teaching Generation Y • Mentoring • Professional development, emotional support, career planning • Using self-awareness techniques • Using support groups • Create a sense of “psychological safety”
Teaching Generation Y • Mentoring • Professional development, emotional support, career planning • Using self-awareness techniques • Using support groups • Create a sense of “psychological safety”
 Teaching Generation Y • Communication issues § Formality and titles – How to deal with this? § Determine how they prefer to be contacted, and how you prefer them to contact you: § Phone call § E-mail § Text messaging § They embrace small group/teamwork § It’s still about forming relationships
Teaching Generation Y • Communication issues § Formality and titles – How to deal with this? § Determine how they prefer to be contacted, and how you prefer them to contact you: § Phone call § E-mail § Text messaging § They embrace small group/teamwork § It’s still about forming relationships
 Teaching Generation Y • Dealing with flexibility and balance § New ACGME duty hour restrictions § They will request changes and excused absences § The importance of setting expectations of attendance in advance, and examples of possible exceptions; consequences § Activities outside the work environment
Teaching Generation Y • Dealing with flexibility and balance § New ACGME duty hour restrictions § They will request changes and excused absences § The importance of setting expectations of attendance in advance, and examples of possible exceptions; consequences § Activities outside the work environment
 Teaching Generation Y • Other issues of professionalism • Dress code? § White coat or not? Ties? Scrubs? • Do we need a policy for “helicopter parents” ? ? • Schedule flexibility
Teaching Generation Y • Other issues of professionalism • Dress code? § White coat or not? Ties? Scrubs? • Do we need a policy for “helicopter parents” ? ? • Schedule flexibility
 Teaching Generation Y • Jeopardy Journal Club • Family Feud, Trivial Pursuit, Who Wants to be a Millionaire, Are You Smarter Than a Third Year? • Gift certificate competitions for board review • Form process improvement groups with members from different generations • Plan activities outside of work with their families
Teaching Generation Y • Jeopardy Journal Club • Family Feud, Trivial Pursuit, Who Wants to be a Millionaire, Are You Smarter Than a Third Year? • Gift certificate competitions for board review • Form process improvement groups with members from different generations • Plan activities outside of work with their families
 Teaching Generation Y • Texting questions to attending while on call • Texting/tweeting during lecture for real time interaction • Be serious about duty hours • Work in small groups • Give feedback in a timely manner • Make sure rules are clear
Teaching Generation Y • Texting questions to attending while on call • Texting/tweeting during lecture for real time interaction • Be serious about duty hours • Work in small groups • Give feedback in a timely manner • Make sure rules are clear
 Teaching Generation Y – Your Thoughts
Teaching Generation Y – Your Thoughts
 Final thoughts… “…providing quality, compassionate care will never change. However, unless it’s a matter of safety, doctors should be open to the idea that things can be done differently. ”
Final thoughts… “…providing quality, compassionate care will never change. However, unless it’s a matter of safety, doctors should be open to the idea that things can be done differently. ”
 Final thoughts… "Imagine life as a game in which you were juggling 5 balls in the air. You name them: Work, family, health, friends, and spirit, and you’re keeping all of those in the air. You will soon understand that work is a rubber ball. If you drop it it will bounce back. But the other four balls: Family, health, friends, and spirit are made of glass. If you drop one of these, they will be irrevocably scuffed, marked, nicked, damaged, or even shattered. They will never be the same. You must understand that and strive for balance in your life. " -Brian Dyson, CEO of Coca Cola Enterprises
Final thoughts… "Imagine life as a game in which you were juggling 5 balls in the air. You name them: Work, family, health, friends, and spirit, and you’re keeping all of those in the air. You will soon understand that work is a rubber ball. If you drop it it will bounce back. But the other four balls: Family, health, friends, and spirit are made of glass. If you drop one of these, they will be irrevocably scuffed, marked, nicked, damaged, or even shattered. They will never be the same. You must understand that and strive for balance in your life. " -Brian Dyson, CEO of Coca Cola Enterprises
 What to take home: 1. Differences in generations do exist 2. These differences potentially cause conflict and differing views on professionalism 3. The new generation of staff and physicians, (Generation Y) is now entering the work force and to be successful they require new and innovative ways of learning
What to take home: 1. Differences in generations do exist 2. These differences potentially cause conflict and differing views on professionalism 3. The new generation of staff and physicians, (Generation Y) is now entering the work force and to be successful they require new and innovative ways of learning
 References 1. "Generation Gaps: Managing a Multigenerational Staff"; Stagg Ellott, Victoria; amednews. com; first posted 6/14/2010. 2. "Medical Professionalism and the Generation Gap"; Smith, Lawrence G. , American Journal of Medicine, 118: 4, 439 -442. 3. "Generational Synchronicity: Improving the Medical Work Environment"; Gilhooly, Joseph and Gilhooly, Jennifer; Neo. Reviews 2009, 10: 6; e 265 -e 269 4. "See One, Do One, Teach One: Developing Professionalism Across the Generations"; Johnston, Sharon; Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 2006; 186 -192. 5. "Is the Generation Gap a Growth Opportunity? "; Berthold, Jessica; ACP Internist, 4/2008. 6. "Generational Diversity: Implications for Healthcare Leaders"; Olson, Valerie D. ; Journal of Business & Economics Research 2008, 6: 11; 27 -31. 7. "Working Together. Turning Generational Differences Into Strengths"; Bickel, Janet. San Francisco Medical Society
References 1. "Generation Gaps: Managing a Multigenerational Staff"; Stagg Ellott, Victoria; amednews. com; first posted 6/14/2010. 2. "Medical Professionalism and the Generation Gap"; Smith, Lawrence G. , American Journal of Medicine, 118: 4, 439 -442. 3. "Generational Synchronicity: Improving the Medical Work Environment"; Gilhooly, Joseph and Gilhooly, Jennifer; Neo. Reviews 2009, 10: 6; e 265 -e 269 4. "See One, Do One, Teach One: Developing Professionalism Across the Generations"; Johnston, Sharon; Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 2006; 186 -192. 5. "Is the Generation Gap a Growth Opportunity? "; Berthold, Jessica; ACP Internist, 4/2008. 6. "Generational Diversity: Implications for Healthcare Leaders"; Olson, Valerie D. ; Journal of Business & Economics Research 2008, 6: 11; 27 -31. 7. "Working Together. Turning Generational Differences Into Strengths"; Bickel, Janet. San Francisco Medical Society
 Questions? ? ?
Questions? ? ?


