e506ac079fe6032468e2f32306201bfa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

KAISER PERMANENTE Introduction to Kaiser Permanente Robert M. Crane Director, Kaiser Permanente Institute for Health Policy 1

KAISER PERMANENTE • • • Overview Mission Structure & Key Features History Comparison To NHS & US Plans Areas Of Focus – Care Management – Information Technology 2
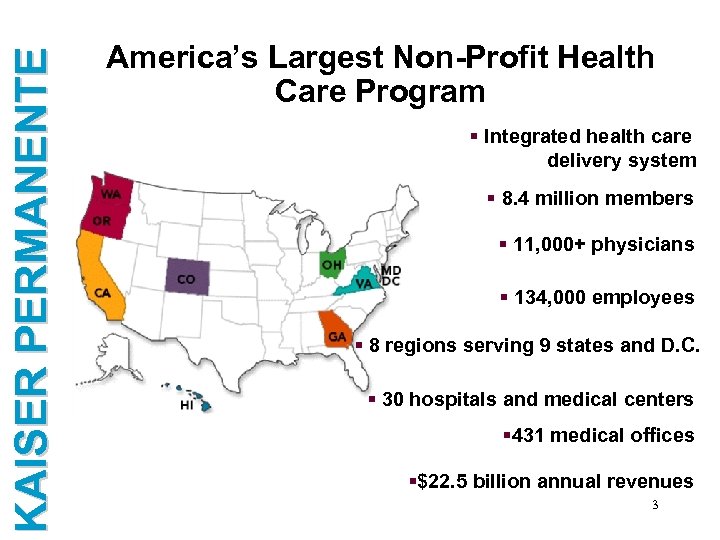
KAISER PERMANENTE America’s Largest Non-Profit Health Care Program § Integrated health care delivery system § 8. 4 million members § 11, 000+ physicians § 134, 000 employees § 8 regions serving 9 states and D. C. § 30 hospitals and medical centers § 431 medical offices §$22. 5 billion annual revenues 3

KAISER PERMANENTE Our Mission To provide high quality, affordable health care services and to improve the health of our members and the communities we serve. 4
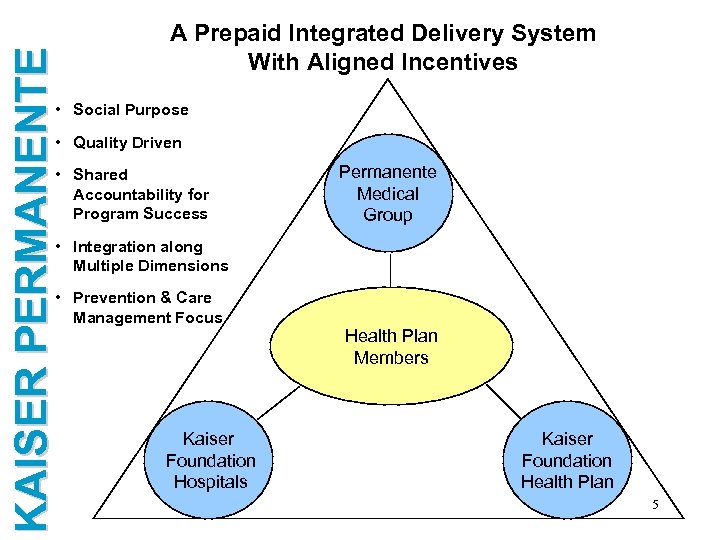
KAISER PERMANENTE A Prepaid Integrated Delivery System With Aligned Incentives • Social Purpose • Quality Driven • Shared Accountability for Program Success Permanente Medical Group • Integration along Multiple Dimensions • Prevention & Care Management Focus Kaiser Foundation Hospitals Health Plan Members Kaiser Foundation Health Plan 5
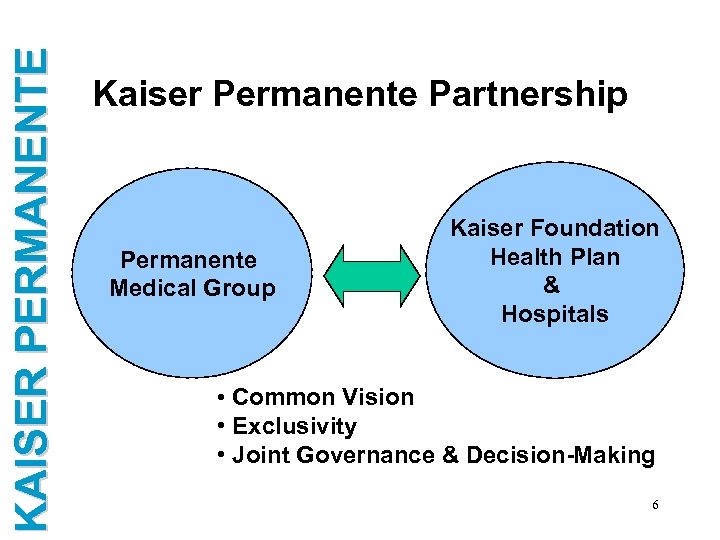
KAISER PERMANENTE Kaiser Permanente Partnership Permanente Medical Group Kaiser Foundation Health Plan & Hospitals • Common Vision • Exclusivity • Joint Governance & Decision-Making 6

KAISER PERMANENTE A Brief History 1933: Dr. Garfield’s prepaid health plan in the California desert 1938: 6, 500 workers at the Grand Coulee Dam, Washington 1942: Kaiser shipyards in Richmond, CA; Vancouver, WA; and steel mill in Fontana, CA 1945: Membership opened to the public 1948: The Permanente Medical Group founded 1955: The Tahoe agreement, roles of PMGs and KFHP set 7

KAISER PERMANENTE A Brief History 1958: Hawaii added as 4 th region 1997: The Labor Management Partnership (LMP) was forged and ratified by 26 AFL-CIO unions. It is the largest and most complex health care partnership in the United States - both operationally and in scope. 1969: Colorado and Ohio regions added 1980: Mid-Atlantic region added through acquisition 1985: Georgia region started 1998 Care Management Institute started 1999: Commitment to implement common automated medical record Health. Connect 8

KAISER PERMANENTE Comparing KP and NHS • In many ways KP is like the NHS, providing a similar range of services for a population equivalent to that of a small country. • KP is roughly the same age as the NHS. • Unlike the NHS, Permanente physicians cannot work outside the system. Feachem, et. al. , BMJ January 19, 2002 • Unlike the NHS, KP does not serve the entire population of a geographic area but rather operates in a competitive environment. 9
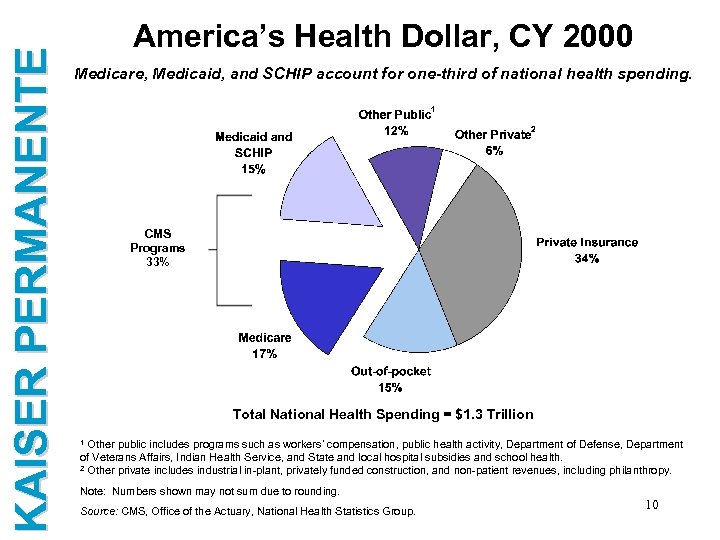
KAISER PERMANENTE America’s Health Dollar, CY 2000 Medicare, Medicaid, and SCHIP account for one-third of national health spending. CMS Programs 33% Total National Health Spending = $1. 3 Trillion Other public includes programs such as workers’ compensation, public health activity, Department of Defense, Department of Veterans Affairs, Indian Health Service, and State and local hospital subsidies and school health. 2 Other private includes industrial in-plant, privately funded construction, and non-patient revenues, including philanthropy. 1 Note: Numbers shown may not sum due to rounding. Source: CMS, Office of the Actuary, National Health Statistics Group. 10
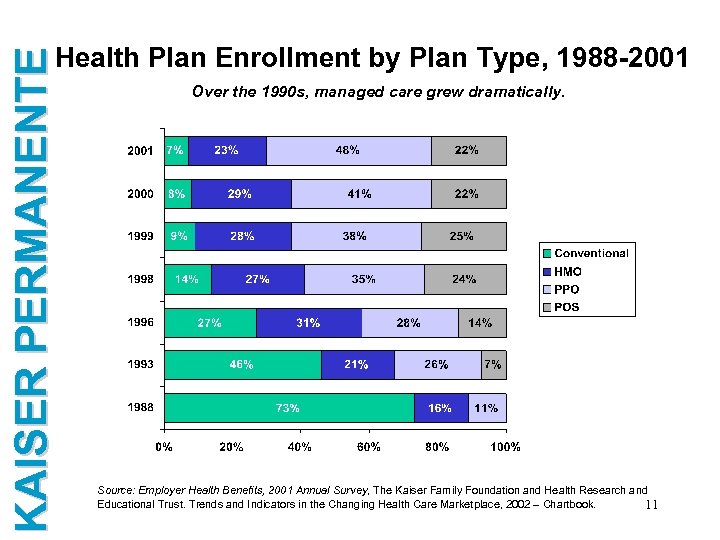
KAISER PERMANENTE Health Plan Enrollment by Plan Type, 1988 -2001 Over the 1990 s, managed care grew dramatically. Source: Employer Health Benefits, 2001 Annual Survey, The Kaiser Family Foundation and Health Research and Educational Trust. Trends and Indicators in the Changing Health Care Marketplace, 2002 – Chartbook. 11
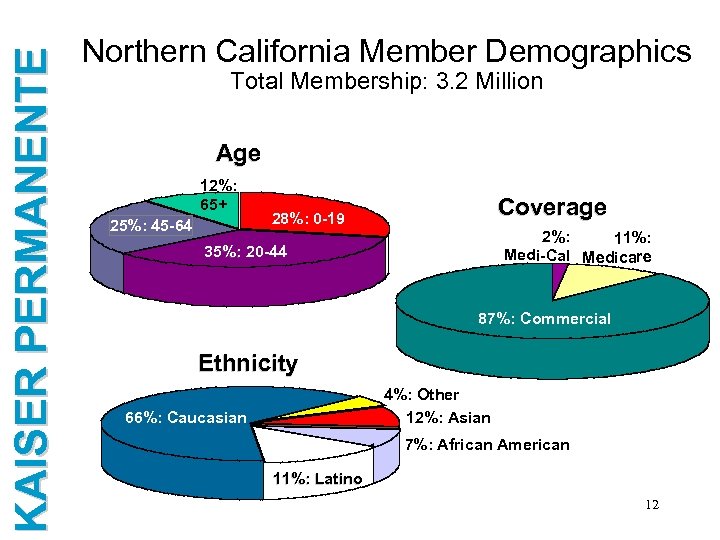
KAISER PERMANENTE Northern California Member Demographics Total Membership: 3. 2 Million Age 12%: 65+ 25%: 45 -64 Coverage 28%: 0 -19 2%: 11%: Medi-Cal Medicare 35%: 20 -44 87%: Commercial Ethnicity 4%: Other 12%: Asian 66%: Caucasian 7%: African American 11%: Latino 12

KAISER PERMANENTE Areas of Focus • Care Management • Information Technology 13
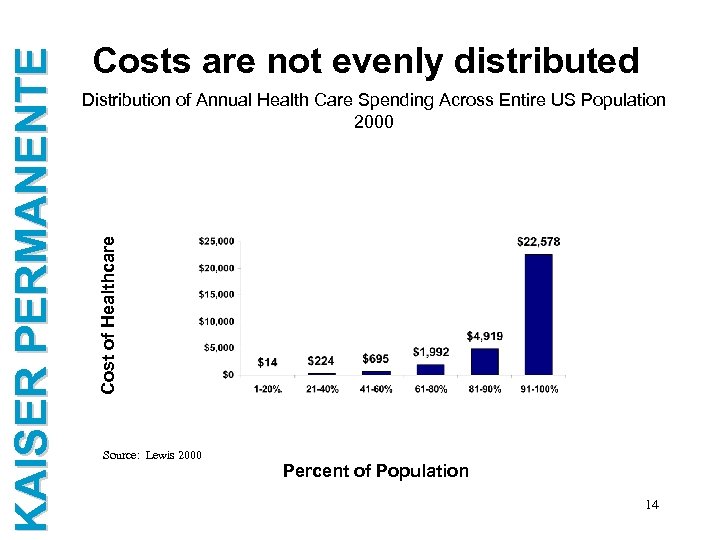
Distribution of Annual Health Care Spending Across Entire US Population 2000 Cost of Healthcare KAISER PERMANENTE Costs are not evenly distributed Source: Lewis 2000 Percent of Population 14
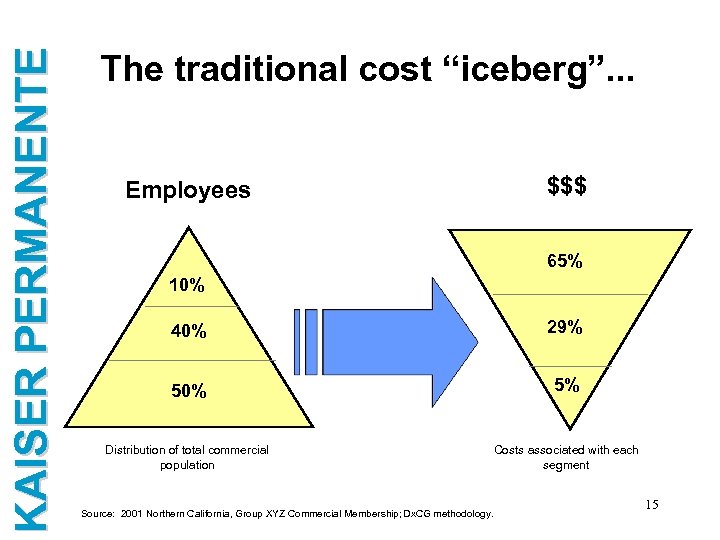
KAISER PERMANENTE The traditional cost “iceberg”. . . Employees $$$ 65% 10% 40% 29% 50% 5% Distribution of total commercial population Source: 2001 Northern California, Group XYZ Commercial Membership; Dx. CG methodology. Costs associated with each segment 15
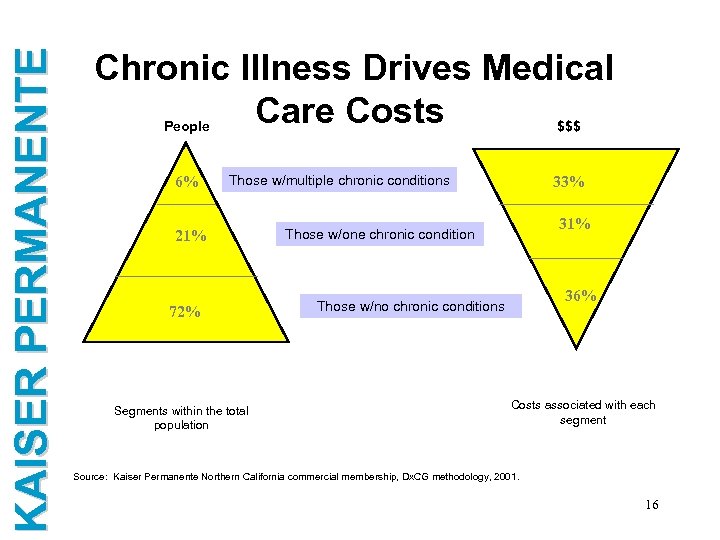
KAISER PERMANENTE Chronic Illness Drives Medical Care Costs People 6% $$$ Those w/multiple chronic conditions 21% 72% Segments within the total population 33% 31% Those w/one chronic condition 36% Those w/no chronic conditions Costs associated with each segment Source: Kaiser Permanente Northern California commercial membership, Dx. CG methodology, 2001. 16

KAISER PERMANENTE 10 Clinical Priority Areas KP Members Area with this Condition Asthma 141, 000 Coronary Artery Disease Clinical 256, 000 Depression Diabetes Heart Failure Cancer Chronic Pain Elder Care Obesity Self Care 411, 000 577, 000 94, 000 25, 000 new cases/yr ~1, 000 917, 000 ~25% of adults 8. 4 MM 17
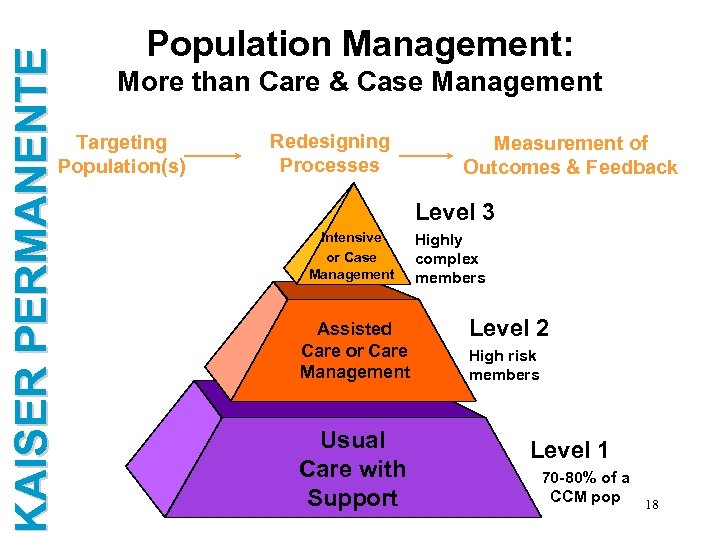
KAISER PERMANENTE Population Management: More than Care & Case Management Targeting Population(s) Redesigning Processes Measurement of Outcomes & Feedback Level 3 Intensive or Case Management Assisted Care or Care Management Usual Care with Support Highly complex members Level 2 High risk members Level 1 70 -80% of a CCM pop 18

KAISER PERMANENTE Strategy: Make it easier to do the right thing. . . • Identify the right thing – Define evidence-based medicine – Identify successful practices – Leverage measurement to guide performance improvement • Make the right thing easier – – Embed guidelines within systems to support practice Implement effective and innovative models of care Support teams of professionals to care for members Leverage technology to support population-based care 19

KAISER PERMANENTE Information Technology • Diverse current capacities • • Disease registries Notes and prompts Order entry Results reporting • New system of computerized support tools • Opportunity to re-engineer care 20

KAISER PERMANENTE Kaiser Permanente Health. Connect • More than just an electronic medical record • A sophisticated information management and delivery system • A program-wide system that will integrate the clinical record with appointments, registration and billing • A complete healthcare business system that will enhance the quality of patient care and support the KP Promise 21
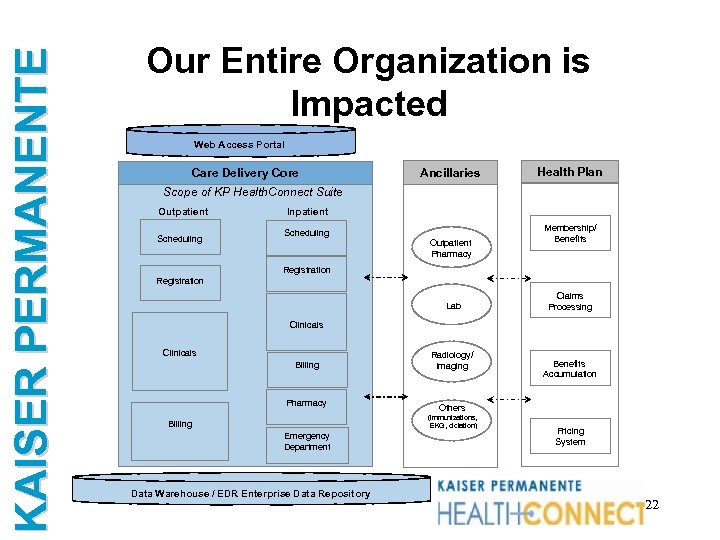
KAISER PERMANENTE Our Entire Organization is Impacted Web Access Portal Care Delivery Core Ancillaries Health Plan Scope of KP Health. Connect Suite Outpatient Scheduling Inpatient Scheduling Outpatient Pharmacy Membership/ Benefits Registration Lab Claims Processing Clinicals Billing Pharmacy Radiology/ Imaging Others (immunizations, EKG, dictation) Billing Emergency Department Data Warehouse / EDR Enterprise Data Repository Benefits Accumulation Pricing System 22

KAISER PERMANENTE KP Health. Connect Delivers • Approaches to advanced care planning (simple registries, reminder systems, protocols) • Coordination across sites of care (patient is identified throughout system, locations) • Shared decision-making tools • Multiple points of contact (email, web, phone) • Chronic disease management models • Supports for patient self-care • Open access scheduling systems • Enhanced research capability 23

KAISER PERMANENTE Kaiser Permanente • People • Understanding • Health 24
e506ac079fe6032468e2f32306201bfa.ppt