 K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y E-voting VS. E-auction Sakurai Lab. Kyushu University Dr-course HER, Yong-Sork 2005 -02 -22 1
K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y E-voting VS. E-auction Sakurai Lab. Kyushu University Dr-course HER, Yong-Sork 2005 -02 -22 1
 What is a Electronic-Voting ? K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y • To prevent the losses by the conventional voting system • Using Network and cryptography techniques • Automatic and fast voting procedure • Untill it is realized the home–voting, Convenient place-voting…. 2005 -02 -22 2
What is a Electronic-Voting ? K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y • To prevent the losses by the conventional voting system • Using Network and cryptography techniques • Automatic and fast voting procedure • Untill it is realized the home–voting, Convenient place-voting…. 2005 -02 -22 2
 Requirements for E-voting system K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y Completeness : All valid votes are counted correctly, if all participants are honest Robustness : Dishonest voters, other participants or outsiders can not disturb of disrupt an election Privacy : The votes are cast anonymously Unreuability : Every voter can vote only once. Eligibility : Only legitmate voters can vote Fairness : A voter casts his vote independently and is not influenced Universal Verifiability : anyone can verify a correctness of election. Receipt-freeness: A voter can not prove to a coercer, how he has voted 2005 -02 -22 3
Requirements for E-voting system K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y Completeness : All valid votes are counted correctly, if all participants are honest Robustness : Dishonest voters, other participants or outsiders can not disturb of disrupt an election Privacy : The votes are cast anonymously Unreuability : Every voter can vote only once. Eligibility : Only legitmate voters can vote Fairness : A voter casts his vote independently and is not influenced Universal Verifiability : anyone can verify a correctness of election. Receipt-freeness: A voter can not prove to a coercer, how he has voted 2005 -02 -22 3
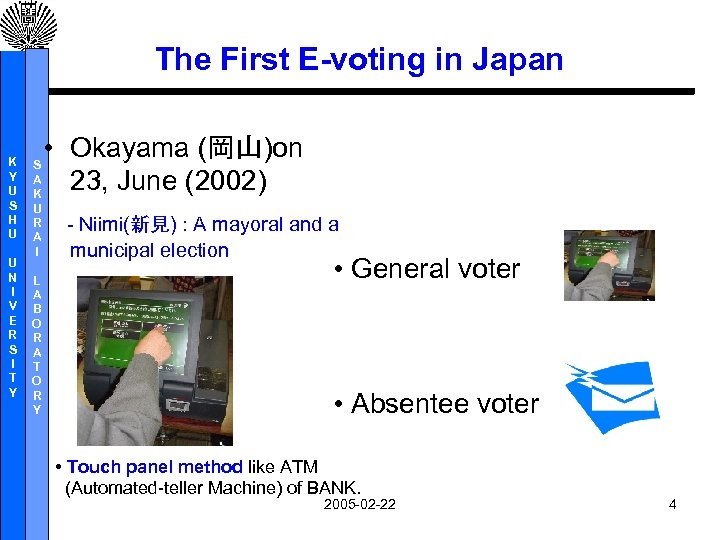 The First E-voting in Japan K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y • Okayama (岡山)on 23, June (2002) - Niimi(新見) : A mayoral and a municipal election • General voter • Absentee voter • Touch panel method like ATM (Automated-teller Machine) of BANK. 2005 -02 -22 4
The First E-voting in Japan K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y • Okayama (岡山)on 23, June (2002) - Niimi(新見) : A mayoral and a municipal election • General voter • Absentee voter • Touch panel method like ATM (Automated-teller Machine) of BANK. 2005 -02 -22 4
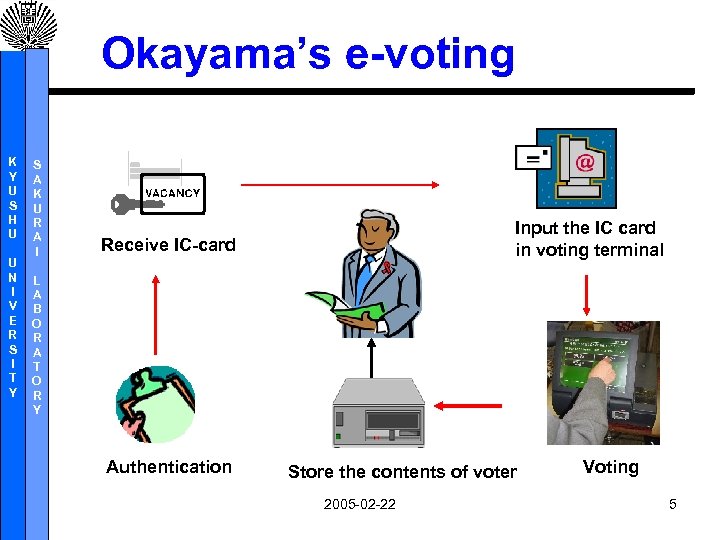 Okayama’s e-voting K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I Input the IC card in voting terminal Receive IC-card L A B O R A T O R Y Authentication Store the contents of voter 2005 -02 -22 Voting 5
Okayama’s e-voting K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I Input the IC card in voting terminal Receive IC-card L A B O R A T O R Y Authentication Store the contents of voter 2005 -02 -22 Voting 5
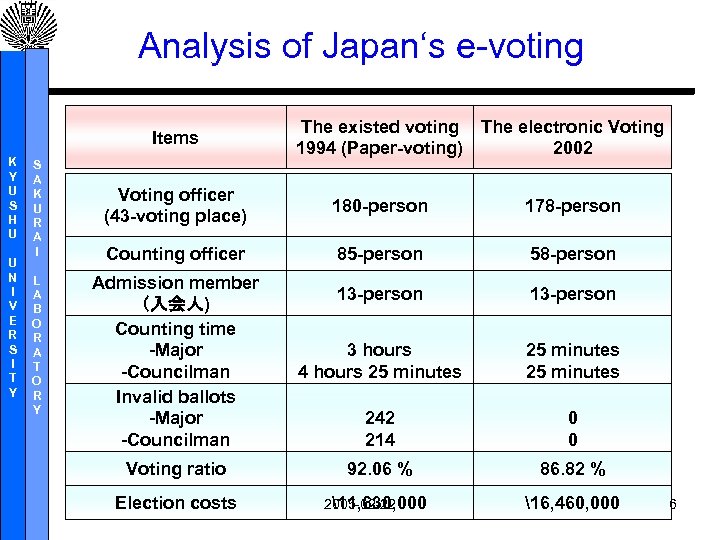 Analysis of Japan‘s e-voting Items K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y The existed voting The electronic Voting 1994 (Paper-voting) 2002 Voting officer (43 -voting place) 180 -person 178 -person Counting officer 85 -person 58 -person Admission member (入会人) Counting time -Major -Councilman Invalid ballots -Major -Councilman 13 -person 3 hours 4 hours 25 minutes 242 214 0 0 Voting ratio 92. 06 % 86. 82 % Election costs 2005 -02 -22 11, 630, 000 16, 460, 000 6
Analysis of Japan‘s e-voting Items K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y The existed voting The electronic Voting 1994 (Paper-voting) 2002 Voting officer (43 -voting place) 180 -person 178 -person Counting officer 85 -person 58 -person Admission member (入会人) Counting time -Major -Councilman Invalid ballots -Major -Councilman 13 -person 3 hours 4 hours 25 minutes 242 214 0 0 Voting ratio 92. 06 % 86. 82 % Election costs 2005 -02 -22 11, 630, 000 16, 460, 000 6
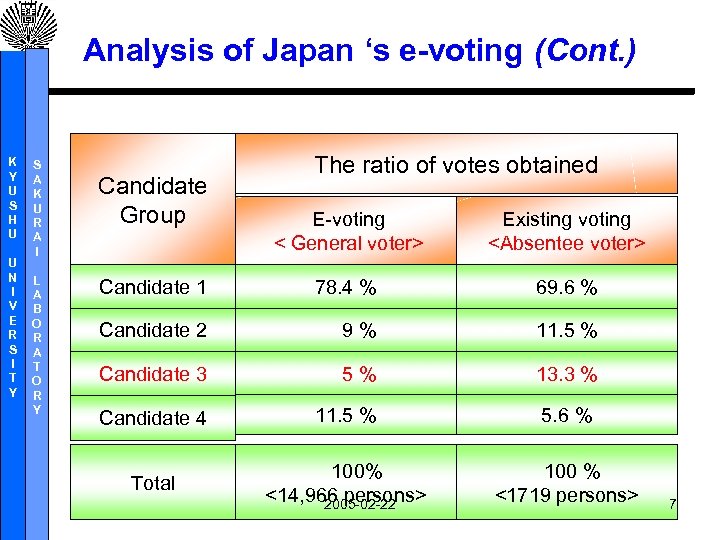 Analysis of Japan ‘s e-voting (Cont. ) K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y Candidate Group The ratio of votes obtained E-voting < General voter> Existing voting
Analysis of Japan ‘s e-voting (Cont. ) K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y Candidate Group The ratio of votes obtained E-voting < General voter> Existing voting
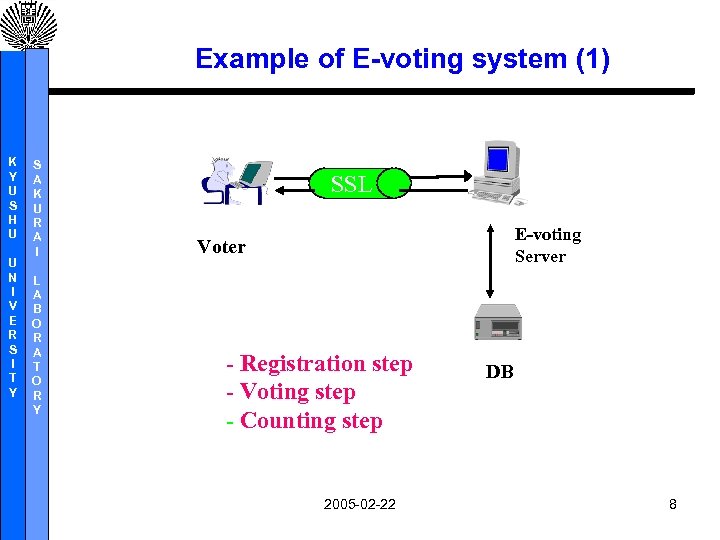 Example of E-voting system (1) K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y SSL E-voting Server Voter - Registration step - Voting step - Counting step 2005 -02 -22 DB 8
Example of E-voting system (1) K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y SSL E-voting Server Voter - Registration step - Voting step - Counting step 2005 -02 -22 DB 8
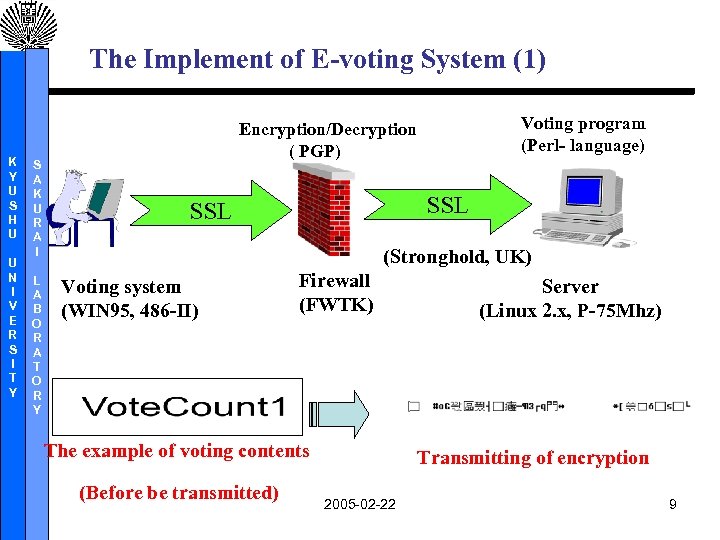 The Implement of E-voting System (1) K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y Voting program (Perl- language) Encryption/Decryption ( PGP) SSL (Stronghold, UK) Voting system (WIN 95, 486 -II) Firewall (FWTK) The example of voting contents (Before be transmitted) Server (Linux 2. x, P-75 Mhz) Transmitting of encryption 2005 -02 -22 9
The Implement of E-voting System (1) K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y Voting program (Perl- language) Encryption/Decryption ( PGP) SSL (Stronghold, UK) Voting system (WIN 95, 486 -II) Firewall (FWTK) The example of voting contents (Before be transmitted) Server (Linux 2. x, P-75 Mhz) Transmitting of encryption 2005 -02 -22 9
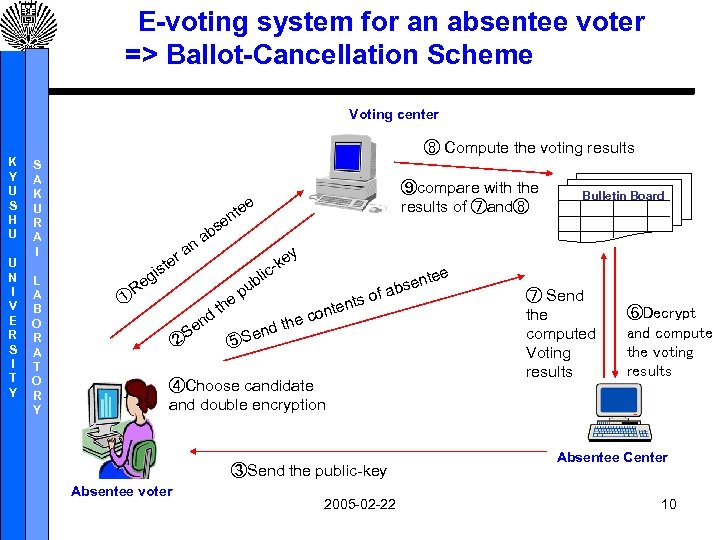 E-voting system for an absentee voter => Ballot-Cancellation Scheme Voting center K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y ⑧ Compute the voting results S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y ⑨compare with the results of ⑦and⑧ e te n ra ste n se ab i eg R ① d en S ② y e -k c e th bli pu e ⑤S he nd t e f nts o e cont te bsen a ④Choose candidate and double encryption ③Send the public-key Absentee voter Bulletin Board 2005 -02 -22 ⑦ Send the computed Voting results ⑥Decrypt and compute the voting results Absentee Center 10
E-voting system for an absentee voter => Ballot-Cancellation Scheme Voting center K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y ⑧ Compute the voting results S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y ⑨compare with the results of ⑦and⑧ e te n ra ste n se ab i eg R ① d en S ② y e -k c e th bli pu e ⑤S he nd t e f nts o e cont te bsen a ④Choose candidate and double encryption ③Send the public-key Absentee voter Bulletin Board 2005 -02 -22 ⑦ Send the computed Voting results ⑥Decrypt and compute the voting results Absentee Center 10
 What is a auction ? K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y n Not a fixed Price n A kind of trade for special goods n In real world, a various type auctions have been enforced for decision of price 2005 -02 -22 11
What is a auction ? K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y n Not a fixed Price n A kind of trade for special goods n In real world, a various type auctions have been enforced for decision of price 2005 -02 -22 11
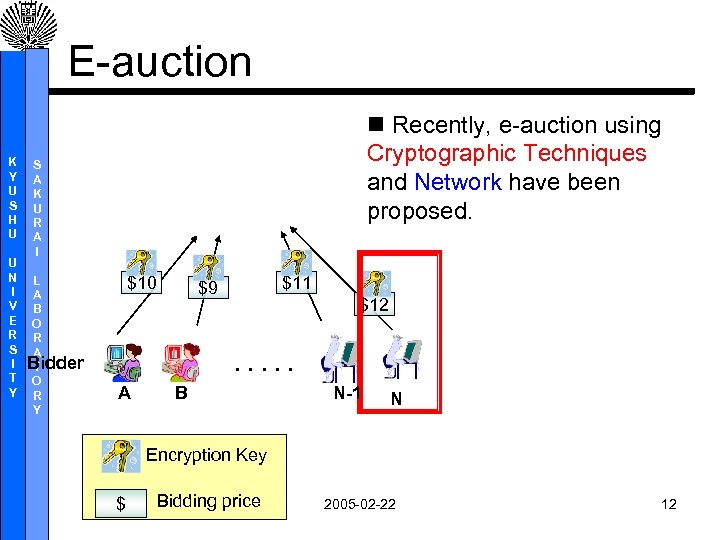 E-auction K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y n Recently, e-auction using Cryptographic Techniques and Network have been proposed. S A K U R A I L A B O R A Bidder T O R Y $10 $11 $9 $12 . . . A B N-1 N Encryption Key $ Bidding price 2005 -02 -22 12
E-auction K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y n Recently, e-auction using Cryptographic Techniques and Network have been proposed. S A K U R A I L A B O R A Bidder T O R Y $10 $11 $9 $12 . . . A B N-1 N Encryption Key $ Bidding price 2005 -02 -22 12
 Types of an E-auction n A first-price sealed-bid auction K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y The winner is the highest bidding price, he should pay his own bidding price. n A second-price sealed-bid auction The winner is the highest bidding price, he should pay the second-price. n M+1 st –price auction Multiple units of a single item are auctioned. The M highest bidders win and pay (M+1)st highest bid . . . 2005 -02 -22 13
Types of an E-auction n A first-price sealed-bid auction K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y The winner is the highest bidding price, he should pay his own bidding price. n A second-price sealed-bid auction The winner is the highest bidding price, he should pay the second-price. n M+1 st –price auction Multiple units of a single item are auctioned. The M highest bidders win and pay (M+1)st highest bid . . . 2005 -02 -22 13
 Requirements K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y n Privacy of bid : No bid is revealed to anyone except the winner and the winning bid n Proof of winner : Everyone can verify the winner and the winning price which are decided correctly n Non-repudiation : The winner cannot repudiate his/her own bidding at the winning price n Accountability of bidder : Any auctioneer can verify that bidders follow a protocol to cast their bids. n Bid Security Nobody can forge (falsify) and tap a bid。 n Robustness Even if a bidder sends an invalid bid, the auction process is unaffected. 2005 -02 -22 14
Requirements K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y n Privacy of bid : No bid is revealed to anyone except the winner and the winning bid n Proof of winner : Everyone can verify the winner and the winning price which are decided correctly n Non-repudiation : The winner cannot repudiate his/her own bidding at the winning price n Accountability of bidder : Any auctioneer can verify that bidders follow a protocol to cast their bids. n Bid Security Nobody can forge (falsify) and tap a bid。 n Robustness Even if a bidder sends an invalid bid, the auction process is unaffected. 2005 -02 -22 14
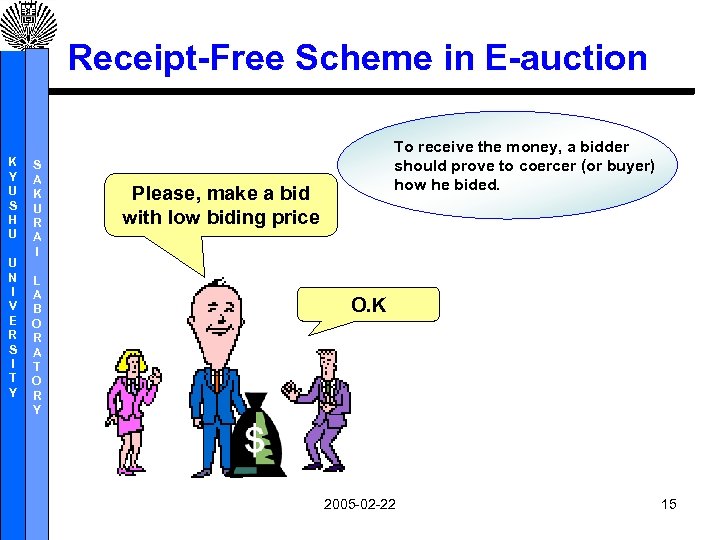 Receipt-Free Scheme in E-auction K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y To receive the money, a bidder should prove to coercer (or buyer) how he bided. Please, make a bid with low biding price O. K 2005 -02 -22 15
Receipt-Free Scheme in E-auction K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y To receive the money, a bidder should prove to coercer (or buyer) how he bided. Please, make a bid with low biding price O. K 2005 -02 -22 15
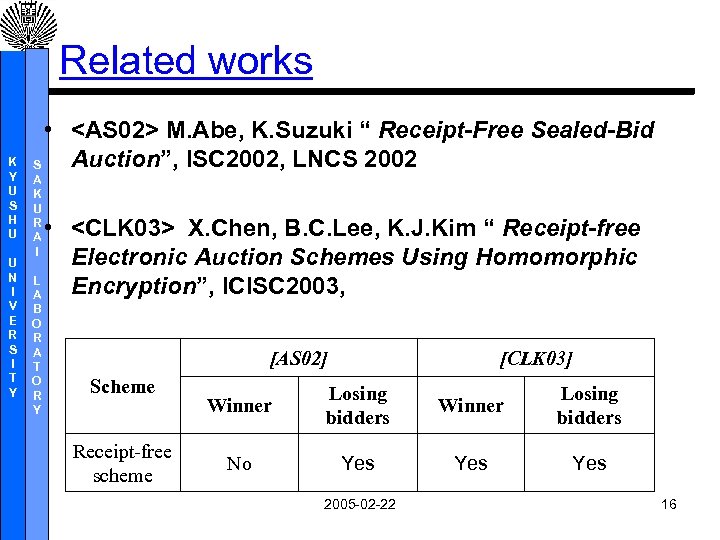 Related works K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y •
Related works K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y •
 Example of e-auction (1) K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I n Participants l Auctioneer : An auctioneer decides the winning price and publishes it. … l Multi-Auction issuer L Each auction issuer mixes the encrypted bidding price. We suppose that the auctioneer does not collude A B with last-auction issuer manages Pseudo ID of each bidder. The last auction issuer O R A l. Bidder : T A bidder offers a bid only one time by an auction rule O R Y l Bulletin Board Everyone can see the content of BB and can not erase/modify it. 2005 -02 -22 17
Example of e-auction (1) K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I n Participants l Auctioneer : An auctioneer decides the winning price and publishes it. … l Multi-Auction issuer L Each auction issuer mixes the encrypted bidding price. We suppose that the auctioneer does not collude A B with last-auction issuer manages Pseudo ID of each bidder. The last auction issuer O R A l. Bidder : T A bidder offers a bid only one time by an auction rule O R Y l Bulletin Board Everyone can see the content of BB and can not erase/modify it. 2005 -02 -22 17
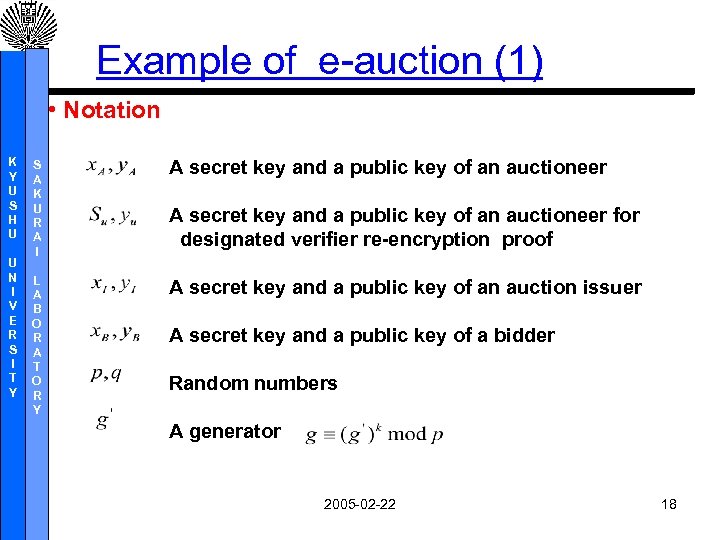 Example of e-auction (1) • Notation K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I A secret key and a public key of an auctioneer L A B O R A T O R Y A secret key and a public key of an auction issuer A secret key and a public key of an auctioneer for designated verifier re-encryption proof A secret key and a public key of a bidder Random numbers A generator 2005 -02 -22 18
Example of e-auction (1) • Notation K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I A secret key and a public key of an auctioneer L A B O R A T O R Y A secret key and a public key of an auction issuer A secret key and a public key of an auctioneer for designated verifier re-encryption proof A secret key and a public key of a bidder Random numbers A generator 2005 -02 -22 18
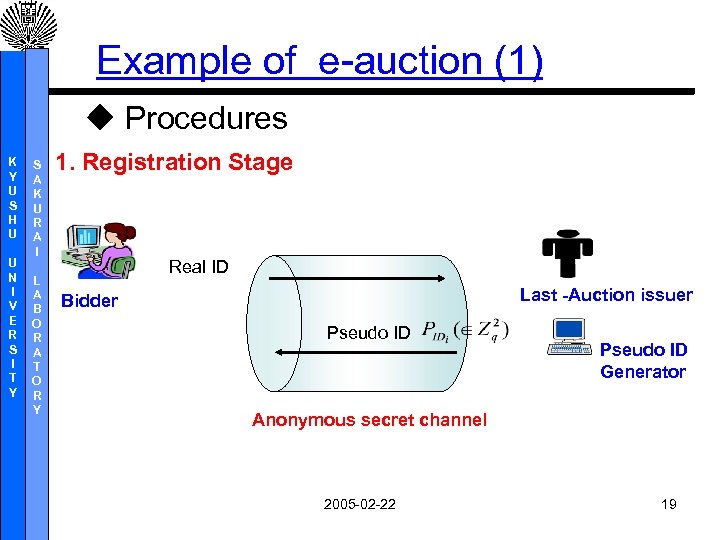 Example of e-auction (1) u Procedures K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y 1. Registration Stage Real ID Last -Auction issuer Bidder Pseudo ID Generator Anonymous secret channel 2005 -02 -22 19
Example of e-auction (1) u Procedures K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y 1. Registration Stage Real ID Last -Auction issuer Bidder Pseudo ID Generator Anonymous secret channel 2005 -02 -22 19
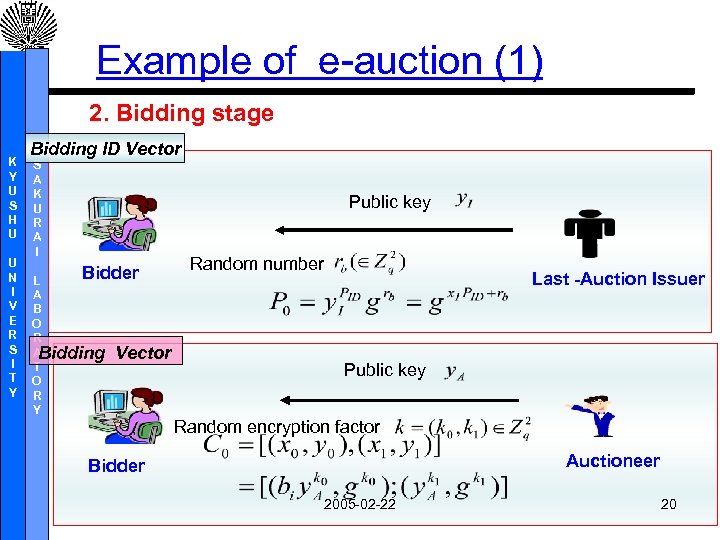 Example of e-auction (1) 2. Bidding stage K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y Bidding ID Vector S A K U R A I Public key Bidder L A B O R A Bidding T O R Y Vector Random number Last -Auction Issuer Public key Random encryption factor Auctioneer Bidder 2005 -02 -22 20
Example of e-auction (1) 2. Bidding stage K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y Bidding ID Vector S A K U R A I Public key Bidder L A B O R A Bidding T O R Y Vector Random number Last -Auction Issuer Public key Random encryption factor Auctioneer Bidder 2005 -02 -22 20
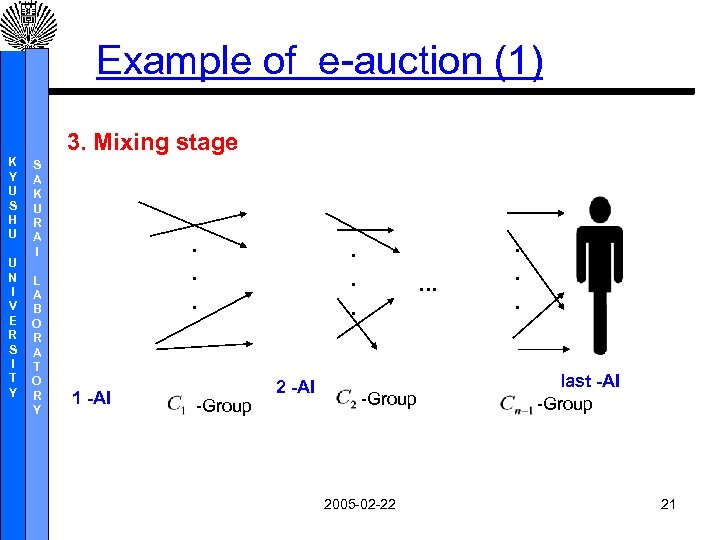 Example of e-auction (1) 3. Mixing stage K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y . . . 1 -AI -Group . . . 2 -AI . . . -Group 2005 -02 -22 . . . last -AI -Group 21
Example of e-auction (1) 3. Mixing stage K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y . . . 1 -AI -Group . . . 2 -AI . . . -Group 2005 -02 -22 . . . last -AI -Group 21
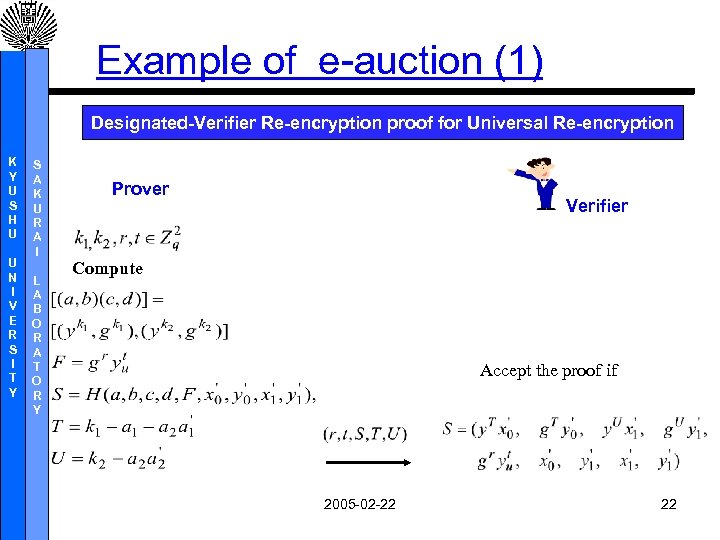 Example of e-auction (1) Designated-Verifier Re-encryption proof for Universal Re-encryption K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y Prover Verifier Compute Accept the proof if 2005 -02 -22 22
Example of e-auction (1) Designated-Verifier Re-encryption proof for Universal Re-encryption K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y Prover Verifier Compute Accept the proof if 2005 -02 -22 22
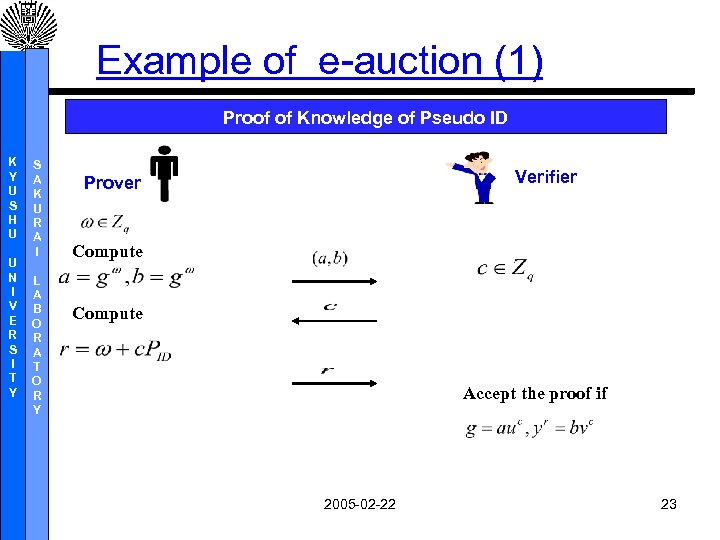 Example of e-auction (1) Proof of Knowledge of Pseudo ID K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y Verifier Prover Compute Accept the proof if 2005 -02 -22 23
Example of e-auction (1) Proof of Knowledge of Pseudo ID K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y Verifier Prover Compute Accept the proof if 2005 -02 -22 23
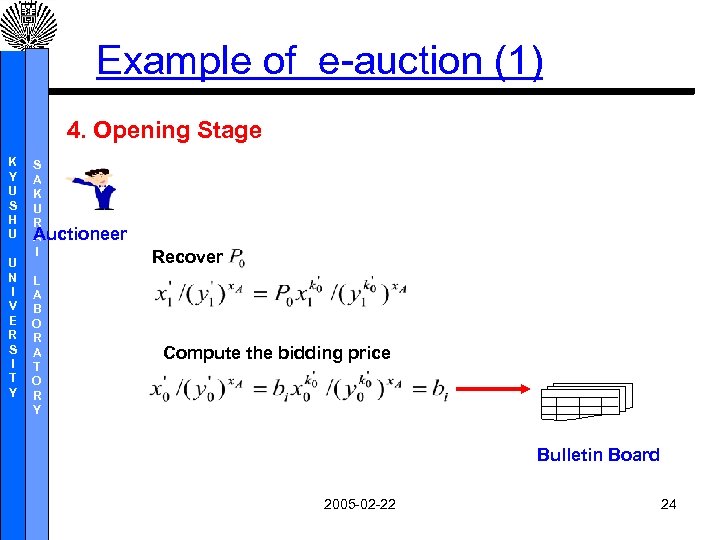 Example of e-auction (1) 4. Opening Stage K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R Auctioneer A I L A B O R A T O R Y Recover Compute the bidding price Bulletin Board 2005 -02 -22 24
Example of e-auction (1) 4. Opening Stage K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R Auctioneer A I L A B O R A T O R Y Recover Compute the bidding price Bulletin Board 2005 -02 -22 24
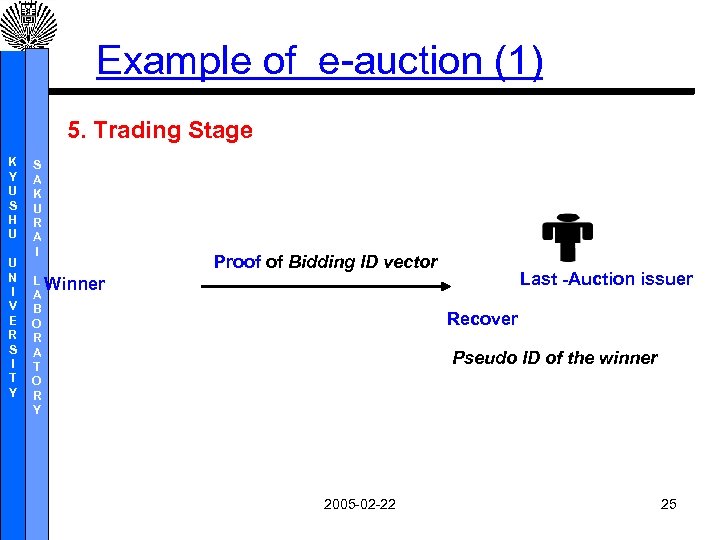 Example of e-auction (1) 5. Trading Stage K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I Proof of Bidding ID vector L Winner A B O R A T O R Y Last -Auction issuer Recover Pseudo ID of the winner 2005 -02 -22 25
Example of e-auction (1) 5. Trading Stage K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I Proof of Bidding ID vector L Winner A B O R A T O R Y Last -Auction issuer Recover Pseudo ID of the winner 2005 -02 -22 25
 Future works K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y • Compare E-voting system with E-auction system • Extended Receipt-free Scheme for Eauction system • Develop E-voting System for an absentee 2005 -02 -22 26
Future works K Y U S H U U N I V E R S I T Y S A K U R A I L A B O R A T O R Y • Compare E-voting system with E-auction system • Extended Receipt-free Scheme for Eauction system • Develop E-voting System for an absentee 2005 -02 -22 26


