 Justification of a State intervention into the right to privacy online
Justification of a State intervention into the right to privacy online
 Article 8 of the European Convention on Human Rights (1950), Articles 14 and 17 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (1966), Articles 16 and 40 in the Convention on the Rights of the Child (1989), Article 14 of the International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families (1990), Article 22 of the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (2008), Article 4 of the African Charter on Human and Peoples' Rights (1986).
Article 8 of the European Convention on Human Rights (1950), Articles 14 and 17 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (1966), Articles 16 and 40 in the Convention on the Rights of the Child (1989), Article 14 of the International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families (1990), Article 22 of the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (2008), Article 4 of the African Charter on Human and Peoples' Rights (1986).
 The definition of the right to privacy in the frames of the Article 8 of the European Convention on Human Rights 8(1). Everyone has the right to respect for his private and family life, his home and his correspondence. 8(2). There shall be no interference by a public authority with the exercise of this right except such as is in accordance with the law and is necessary in a democratic society in the interests of national security, public safety or the economic well being of the country, for the prevention of disorder or crime, for the protection of health or morals, or for the protection of the rights and freedoms of others.
The definition of the right to privacy in the frames of the Article 8 of the European Convention on Human Rights 8(1). Everyone has the right to respect for his private and family life, his home and his correspondence. 8(2). There shall be no interference by a public authority with the exercise of this right except such as is in accordance with the law and is necessary in a democratic society in the interests of national security, public safety or the economic well being of the country, for the prevention of disorder or crime, for the protection of health or morals, or for the protection of the rights and freedoms of others.
 4 core elements of the principle of the right to privacy 1) privacy of communications and correspondence; 2) privacy of information that has been gathered by a third party (data protection); 3) privacy related to the body (invasive medical procedures, searches of the person); 4) territorial privacy.
4 core elements of the principle of the right to privacy 1) privacy of communications and correspondence; 2) privacy of information that has been gathered by a third party (data protection); 3) privacy related to the body (invasive medical procedures, searches of the person); 4) territorial privacy.
 The notion of the right to privacy in the context of the Internet The right to privacy mainly concerns the interception of correspondence electronic communications: - email; - web browsing.
The notion of the right to privacy in the context of the Internet The right to privacy mainly concerns the interception of correspondence electronic communications: - email; - web browsing.
 The notion of the “interference” in the Internet space
The notion of the “interference” in the Internet space
 In what cases may states interfere into the right to privacy? the interference with the rights protected by Article 8 may be justified only in the case if such actions were done: - in accordance with law; - to pursue a legitimate aim; - as those, which necessary in a democratic society.
In what cases may states interfere into the right to privacy? the interference with the rights protected by Article 8 may be justified only in the case if such actions were done: - in accordance with law; - to pursue a legitimate aim; - as those, which necessary in a democratic society.
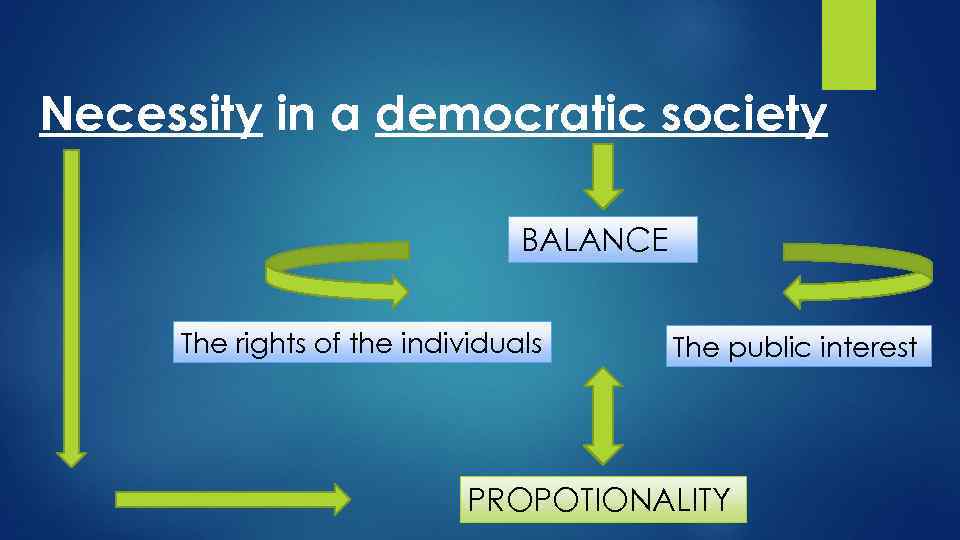 Necessity in a democratic society BALANCE The rights of the individuals The public interest PROPOTIONALITY
Necessity in a democratic society BALANCE The rights of the individuals The public interest PROPOTIONALITY
 Thank you for attention
Thank you for attention