8aeca68c9bb9361a04d17f26e49d655d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Just-in Time Management Supplier Partnerships B 7801 April 17, 1998 u Supplier management issues u Supplier Development Outreach Program: Video: The case for Toyota u JIT 1

Supplier Partnerships: Organizational Culture and Strategy Issues u Feeling of trust u Management u Strategic u Top attitude/outlook for the future fit management compatibility u Compatibility across levels and functions of buyer and supplier firms u Supplier's organizational structure &personnel 2

Supplier Partnerships: Technology Issues u Assessment of current manufacturing facilities/capabilities u Assessment of future manufacturing capabilities u Supplier's design capabilities u Supplier's speed in development 3
Supplier Partnerships: Other Factors u Safety record of the supplier u Business references u Supplier's customer base 4

Supplier Development Outreach Program: The case for Toyota 5

Supply management statistics u Purchased inputs as percentage of total manufacturing costs (‘ 87) Japan U. S. u External sourcing percentages at the big three (Dyer 1993) GM Ford Chrysler u 69% 58% 30% 50% 70% Percentage of major corporations pursuing outsourcing initiatives (A. T. Kearney survey) 1992 1996 58% 86% 6

Practical mechanisms for achieving cooperation u u u Reputation for “honest dealing” (e. g. past behavior of the buyer/supplier) Proximity/personnel relationships Preferred supplier programs – numerical performance ratings (“score cards”) » delivery performance » quality » cost – signals how suppliers will be viewed in upcoming negotiations u u “Soft” penalties for poor performance (e. g. less business in subsequent rounds) Equity ownership 7

Changing role of purchasing u Competitive bidding – solicit large number of bids – “winner takes all” contracts u Cooperative supplier management – – – learn suppliers costs monitor supplier performance signal prospect of future business disseminate best practices among supplier pool develop new supplier capabilities as needed 8

Just-In-Time Production Systems JIT Underlying philosophy is elimination of waste and variability through synchronized “pull” type production systems 9

JIT Purchasing--Requirements u Reduced lot sizes u Frequent and reliable delivery schedules u Reduced and highly reliable lead times u Consistently high quality levels for purchased materials 10

JIT Purchasing--Suppliers u Fewer, nearby suppliers u Repeat business u Support suppliers’ competitiveness u Clusters of remote suppliers u Limit competitive bidding to new parts u Resist vertical integration u Encourage suppliers to implement JIT purchasing 11
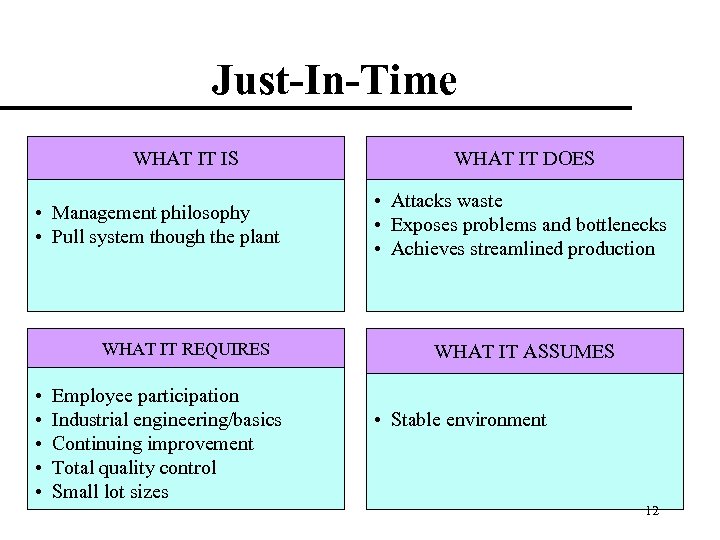
Just-In-Time WHAT IT IS • Management philosophy • Pull system though the plant WHAT IT REQUIRES • • • Employee participation Industrial engineering/basics Continuing improvement Total quality control Small lot sizes WHAT IT DOES • Attacks waste • Exposes problems and bottlenecks • Achieves streamlined production WHAT IT ASSUMES • Stable environment 12

JIT: Part Philosophy - Part Technique u “Big JIT” (Lean Production) – Focus on elimination of all sources of waste and variability through synchronized “pull” type operation systems. u “Little JIT” – Focuses more narrowly on scheduling goods inventories and providing service resources where and when needed 13
Waste Reduction (“Big JIT”) 14
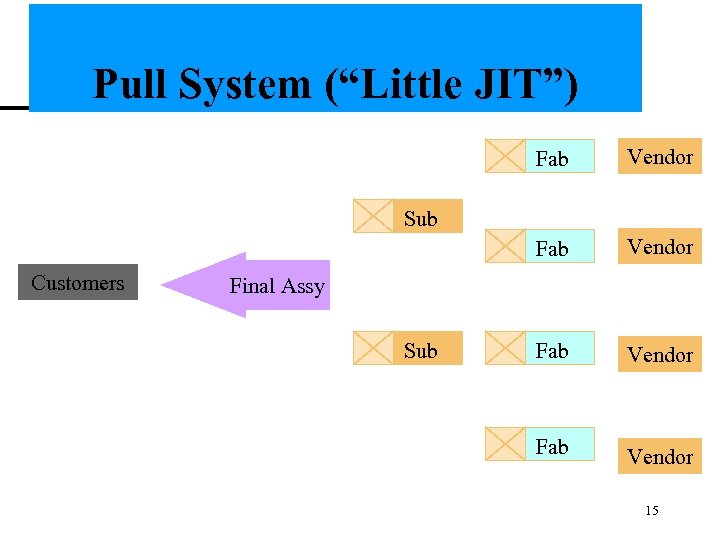
Pull System (“Little JIT”) Fab Vendor Sub Customers Final Assy Sub 15

Waste--Operations (1) Waste from overproduction (2) Waste of waiting time (3) Transportation waste (4) Inventory waste (5) Processing waste (6) Waste of motion - setup reduction (7) Waste from product defects 16
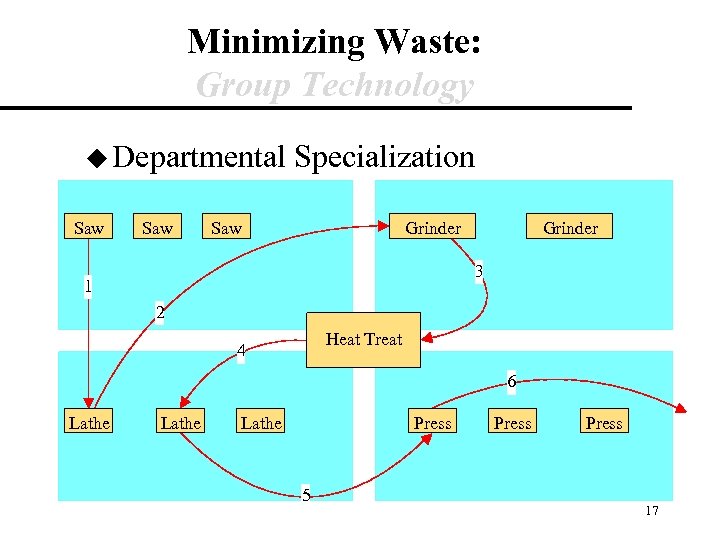
Minimizing Waste: Group Technology u Departmental Saw Specialization Saw Grinder 3 1 2 Heat Treat 4 6 Lathe Press 5 Press 17
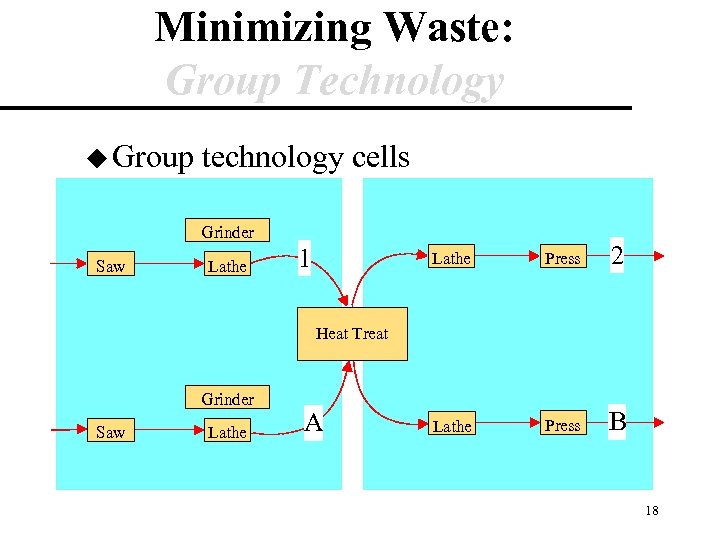
Minimizing Waste: Group Technology u Group technology cells Grinder Saw Lathe 1 Press 2 Lathe Press B Heat Treat Grinder Saw Lathe A 18

Minimizing Waste: Quality at the Source u Self-inspection u Automated inspection u Line-stopping empowerment 19
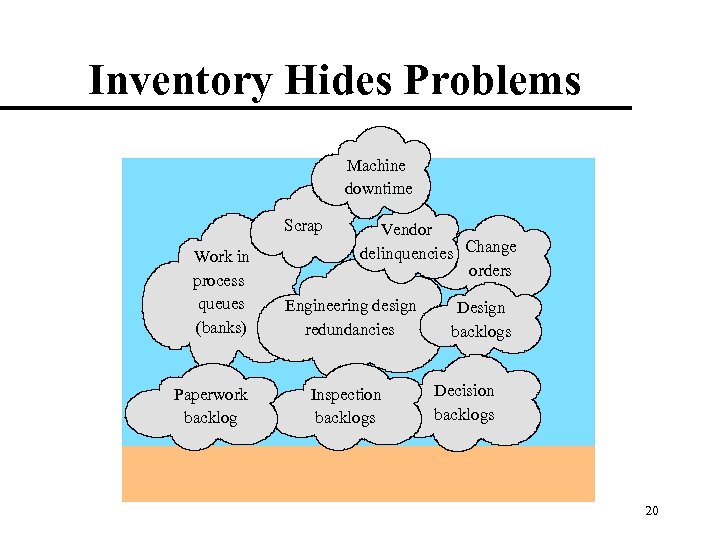
Inventory Hides Problems Machine downtime Scrap Work in process queues (banks) Paperwork backlog Vendor delinquencies Change orders Engineering design redundancies Inspection backlogs Design backlogs Decision backlogs 20

Minimizing Waste: JIT Production Produce what is needed when it’s needed NOTHING MORE! 21

Minimizing Waste: Uniform Plant Loading This does not mean building a single product. We need to maintain a stable mix of products, and firm monthly schedules 22
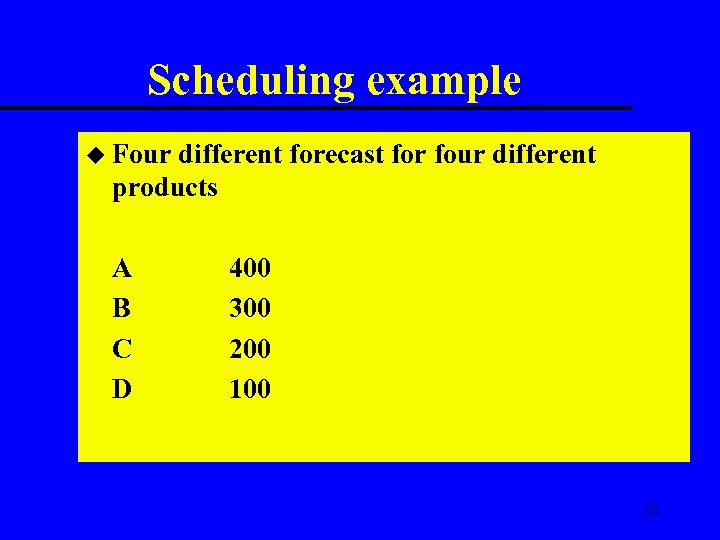
Scheduling example u Four different forecast for four different products A B C D 400 300 200 100 23
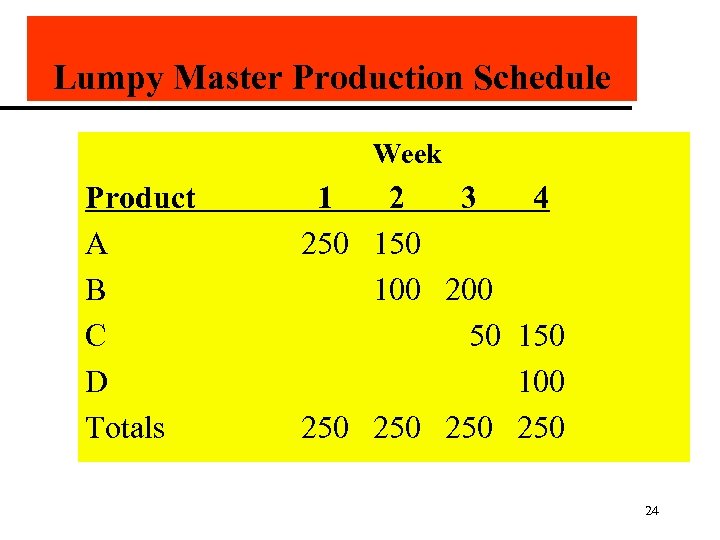
Lumpy Master Production Schedule Week Product A B C D Totals 1 2 3 4 250 100 200 50 100 250 250 24
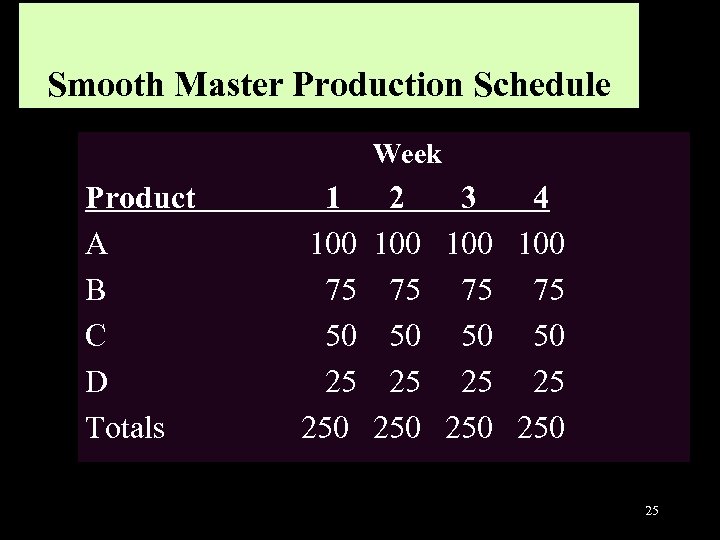
Smooth Master Production Schedule Week Product A B C D Totals 1 2 3 4 100 100 75 75 50 50 25 25 250 250 25

Setup Time Reduction u Shift internal elements to external u Learning and training u Better tools u Product standardization, product line simplification u Equipment automation u Common sense solutions 26

Setup reduction: an industrial example 27
HOW-TO: Design Flow Process u Link operations u Balance workstation capacities u Relayout for flow u Emphasize preventive maintenance u Reduce lot sizes u Reduce setup/changeover time 28

HOW-TO: Total Quality Control u Worker responsibility u Measure u Enforce Statistical Quality Control compliance u Fail-safe methods u Automatic inspection 29
HOW-TO: Stabilize Schedule u Level schedule u Underutilize u Establish capacity freeze windows 30

HOW-TO: Work with Vendors u Vital Few u Evaluation & certification u Proximity u Reduce lead times u Frequent deliveries u JIT Technology transfer u Inter-firm teams 31

HOW-TO: Improve Product Design u Standard product configuration u Standardize u Process and reduce number of parts design with product design 32

Applying JIT Concepts u Organize Problem-Solving Groups u Upgrade Housekeeping u Upgrade Quality u Clarify u Revise Process Flows Equipment and Process Technologies 33
Applying JIT Concepts u Level the Facility Load u Eliminate Unnecessary Activities u Reorganize u Introduce u Develop Physical Configuration Demand-Pull Scheduling Supplier Networks 34

Benefits of JIT u Reduced inventories u Reduced lead times u Simplified production control u Better quality u Increased labor efficiency & effectiveness u Increased space utilization u Lower overall costs u Better working conditions u Improved flexibility u Increased responsiveness 35

Common obstacles to JIT implementation u Management complacency u Short-term vision u Inability to recognize waste u Focus on surface rather than source u Inventory perceived as convenient u Unions u Suppliers u “Theory X” management 36
8aeca68c9bb9361a04d17f26e49d655d.ppt