f81a8e08626fcab2eb864af320121064.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Jump Start! 1) Discuss the Monroe Doctrine. What did it say? Why did the US believe it was necessary? 2) Discuss the Missouri Compromise. What was the issue involved? Why was it important - what effect did it have on the United States?
Jump Start! 1) Discuss the Monroe Doctrine. What did it say? Why did the US believe it was necessary? 2) Discuss the Missouri Compromise. What was the issue involved? Why was it important - what effect did it have on the United States?
 Age of Jackson Indian Removal Nullification Bank of the United States
Age of Jackson Indian Removal Nullification Bank of the United States
 Two Faced Policy • Since Jefferson, US Presidents had two Indian policies: Assimilation – Change and fit in Removal – Move to preserve culture • Inconsistently applied from 1801 – 1831, after which the US made full efforts to resettle the tribes.
Two Faced Policy • Since Jefferson, US Presidents had two Indian policies: Assimilation – Change and fit in Removal – Move to preserve culture • Inconsistently applied from 1801 – 1831, after which the US made full efforts to resettle the tribes.
 Large Native Population • 60, 000 Native Americans occupied Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi • Five Tribes – Cherokee, Choctaw, Chickasaw, Creek and Seminoles in SE United States • Occupied millions of acres • 94 treaties existed allowing them to live there, Jackson helped negotiate 9.
Large Native Population • 60, 000 Native Americans occupied Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi • Five Tribes – Cherokee, Choctaw, Chickasaw, Creek and Seminoles in SE United States • Occupied millions of acres • 94 treaties existed allowing them to live there, Jackson helped negotiate 9.
 Cherokee Adapt - Assimilate • 1820 s – Sequoyah Leads Cherokee • Develops Alphabet • Single family farming (Jefferson) • Opened schools, churches, roads • Constitution
Cherokee Adapt - Assimilate • 1820 s – Sequoyah Leads Cherokee • Develops Alphabet • Single family farming (Jefferson) • Opened schools, churches, roads • Constitution
 Government Policy Changes • Pres. Monroe began the real push to evict in 1825 resettlement plan sent to Congress. • Discovery of gold in GA may have changed everything • State abolishes Cherokee tribal rule won’t recognize their sovereignty.
Government Policy Changes • Pres. Monroe began the real push to evict in 1825 resettlement plan sent to Congress. • Discovery of gold in GA may have changed everything • State abolishes Cherokee tribal rule won’t recognize their sovereignty.
 Cherokee Challenge • Two law suits Cherokee Nation v. Georgia - 1831 Worcester v. Georgia – 1832 • Result – Supreme Court rules for Cherokee States cannot invalidate treaties w/Federal Government. Georgia must help keep white settlers off Indian land.
Cherokee Challenge • Two law suits Cherokee Nation v. Georgia - 1831 Worcester v. Georgia – 1832 • Result – Supreme Court rules for Cherokee States cannot invalidate treaties w/Federal Government. Georgia must help keep white settlers off Indian land.
 Jackson Favors Removal • Moves from balanced approach to complete removal. • “Marshall made his decision, now let him enforce it. ” • Allows state militia to force Indians off land
Jackson Favors Removal • Moves from balanced approach to complete removal. • “Marshall made his decision, now let him enforce it. ” • Allows state militia to force Indians off land
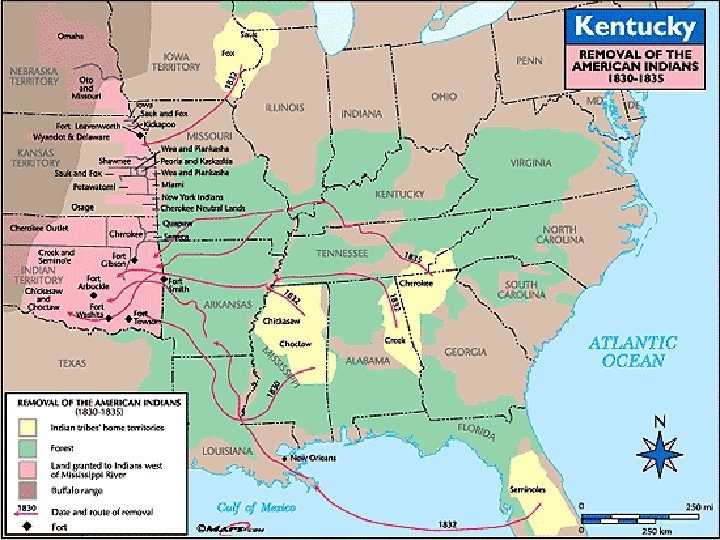
 “Trail of Tears”
“Trail of Tears”
 7 Years of Migration • 1831 – Choctaw were first • 1836 – Creek were removed • 1838 – Last of the Cherokee leave
7 Years of Migration • 1831 – Choctaw were first • 1836 – Creek were removed • 1838 – Last of the Cherokee leave
 States’ Rights & Nullification • All about tariffs (again!) • As America rebuilds manufacturing capacity Britain flood US w/cheap goods – hurts American manufacturing. • Government raises tariffs twice to protect business. • South says – ENOUGH! – tariffs hurt British sales so they buy less cotton, hurting southern exports. • John C. Calhoun – Tariff of Abominations -1828 Says tariffs make So dependent on No – making it rich
States’ Rights & Nullification • All about tariffs (again!) • As America rebuilds manufacturing capacity Britain flood US w/cheap goods – hurts American manufacturing. • Government raises tariffs twice to protect business. • South says – ENOUGH! – tariffs hurt British sales so they buy less cotton, hurting southern exports. • John C. Calhoun – Tariff of Abominations -1828 Says tariffs make So dependent on No – making it rich
 Nullification Theory • Calhoun bases theory on VA & KY Resolutions – that unconstitutional laws can be nullified by states. • States had the right to “nullify” – cancel laws damaging to ‘sovereign states’ and SC refuses to collect tariffs, threaten secession. • Webster/Hayne debate…Government of people or of states. • President Jackson & Calhoun make conflicting toasts in public – sets up the two as enemies over the issue. • Jackson cites SC treasonous – Passes FORCE BILL threatens to hang Calhoun – SC backs down and pays tariffs.
Nullification Theory • Calhoun bases theory on VA & KY Resolutions – that unconstitutional laws can be nullified by states. • States had the right to “nullify” – cancel laws damaging to ‘sovereign states’ and SC refuses to collect tariffs, threaten secession. • Webster/Hayne debate…Government of people or of states. • President Jackson & Calhoun make conflicting toasts in public – sets up the two as enemies over the issue. • Jackson cites SC treasonous – Passes FORCE BILL threatens to hang Calhoun – SC backs down and pays tariffs.
 Bank of the United States • Jackson’s distrust of banks leads him to kill its charter, when Webster & Clay try to renew early • IF it became a campaign issue – gain public support – harder for Jackson to kill it. • Jackson says BUS exists for wealthy and targets Nicholas Biddle (better rates to Congressmen) as the culprit. • Re-directs country’s accounts to regional “Pet Banks” & kills the BUS – New York becomes financial capital.
Bank of the United States • Jackson’s distrust of banks leads him to kill its charter, when Webster & Clay try to renew early • IF it became a campaign issue – gain public support – harder for Jackson to kill it. • Jackson says BUS exists for wealthy and targets Nicholas Biddle (better rates to Congressmen) as the culprit. • Re-directs country’s accounts to regional “Pet Banks” & kills the BUS – New York becomes financial capital.
 Effects of Age of Jackson • Presidency strengthened under Jackson • Democrats split off to form Whig Party (believers in the American System) • Jackson’s successors – Van Buren deal with financial problems due to no centrally controlled bank. Panic of 1837 – banks fail – printed more money than they had gold and silver to back up. • Whig presidencies – William H. Harrison and John Tyler
Effects of Age of Jackson • Presidency strengthened under Jackson • Democrats split off to form Whig Party (believers in the American System) • Jackson’s successors – Van Buren deal with financial problems due to no centrally controlled bank. Panic of 1837 – banks fail – printed more money than they had gold and silver to back up. • Whig presidencies – William H. Harrison and John Tyler


