2965443f892066bb74238f216a82de7a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 A Proposal to IEEE 802. 11 i: Optional MAC-Level Authentication and Encryption Key Management Carlos Rios Lin. Com Wireless Submission 1 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 A Proposal to IEEE 802. 11 i: Optional MAC-Level Authentication and Encryption Key Management Carlos Rios Lin. Com Wireless Submission 1 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 TGi Accomplishments to Date • Good solution (ESN) proposed for Enterprise WLANs: – – – – Mutual AP and STA Authentication Per Link, Per Session Keys Key Generation, Distribution, Expiration, Regeneration Replay Protection Message Authentication Strong Encryption (AES) Not Quite So Strong Encryption (WEP 2) for legacy support • Authentication and Key Management are provided by Upper Layer entities – 802. 1 x Port – Kerberos, Radius Authentication Servers Submission 2 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 TGi Accomplishments to Date • Good solution (ESN) proposed for Enterprise WLANs: – – – – Mutual AP and STA Authentication Per Link, Per Session Keys Key Generation, Distribution, Expiration, Regeneration Replay Protection Message Authentication Strong Encryption (AES) Not Quite So Strong Encryption (WEP 2) for legacy support • Authentication and Key Management are provided by Upper Layer entities – 802. 1 x Port – Kerberos, Radius Authentication Servers Submission 2 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 TGi Unfinished Business • Per Document 00/245 r 1, Security framework must scale to: – Simple Environments (Home, So. Ho, etc) – Public Environments (Hotels, Public Services) – Ad Hoc WLANs It’s unclear AT BEST that ESN can comply • There has been talk about embedding Authentication Servers into home and small business APs – Still don’t address peer to peer networks – Add significant costs to devices primarily marketed at consumers This is a “Let Them Eat Cake” Solution Submission 3 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 TGi Unfinished Business • Per Document 00/245 r 1, Security framework must scale to: – Simple Environments (Home, So. Ho, etc) – Public Environments (Hotels, Public Services) – Ad Hoc WLANs It’s unclear AT BEST that ESN can comply • There has been talk about embedding Authentication Servers into home and small business APs – Still don’t address peer to peer networks – Add significant costs to devices primarily marketed at consumers This is a “Let Them Eat Cake” Solution Submission 3 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 What does this mean? • The 802. 11 i solution on the table either calls for sophisticated infrastructure equipment to supplement APs and NICs… – Not too many homes will buy such equipment – Not too many Hotels and Starbucks will buy such equipment – “Ad Hoc Networkers” have no hope Their security solution would remain the discredited 802. 11 -99 WEP • Or, it requires that sophisticated upper layer mechanisms be incorporated into low cost products – This, in general, will NOT happen – More cost-effective (proprietary) security solutions will be developed instead – Such equipment will be non-standard and non-interoperable And we’ll get blamed for it Submission 4 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 What does this mean? • The 802. 11 i solution on the table either calls for sophisticated infrastructure equipment to supplement APs and NICs… – Not too many homes will buy such equipment – Not too many Hotels and Starbucks will buy such equipment – “Ad Hoc Networkers” have no hope Their security solution would remain the discredited 802. 11 -99 WEP • Or, it requires that sophisticated upper layer mechanisms be incorporated into low cost products – This, in general, will NOT happen – More cost-effective (proprietary) security solutions will be developed instead – Such equipment will be non-standard and non-interoperable And we’ll get blamed for it Submission 4 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 An Approach: DHAKM • “Diffie-Hellman Authentication and Key Management” – MAC-level Mutual STA and AP (or peer STA) Authentication – MAC-level Key generation, distribution, expiration and regeneration – Per Link, Per Session Encryption Keys • Combines with AES to get Strong Security – AES adds Strong Encryption, Replay Protection and Message Authentication – Readily supports Home, Public and Ad Hoc WLANs – Enterprise can (should) still be served with ESN • Combines with “WEP 2+” to get Not Quite So Strong Security – – – WEP 2+ is WEP 2 plus keyed IV (Replay Protection), MIC (Message Authentication) WEP 2 RC 4 provides Not Quite So Strong Encryption Legacy Equipment upgrades can be supported via firmware download Can be immediate, interim solution for Home, Public and Ad Hoc WLANs Enterprise can (should) still be served with ESN Submission 5 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 An Approach: DHAKM • “Diffie-Hellman Authentication and Key Management” – MAC-level Mutual STA and AP (or peer STA) Authentication – MAC-level Key generation, distribution, expiration and regeneration – Per Link, Per Session Encryption Keys • Combines with AES to get Strong Security – AES adds Strong Encryption, Replay Protection and Message Authentication – Readily supports Home, Public and Ad Hoc WLANs – Enterprise can (should) still be served with ESN • Combines with “WEP 2+” to get Not Quite So Strong Security – – – WEP 2+ is WEP 2 plus keyed IV (Replay Protection), MIC (Message Authentication) WEP 2 RC 4 provides Not Quite So Strong Encryption Legacy Equipment upgrades can be supported via firmware download Can be immediate, interim solution for Home, Public and Ad Hoc WLANs Enterprise can (should) still be served with ESN Submission 5 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 The General Idea • All STAs have unique, factory assigned “Secret Keys” (SKs) – “Partial Keys” (PKs) are derived from the SKs using one-way functions – PKs are publicly exchanged to create a “Common Key” (CK) secret to both STAs – Authentication Signatures and Per Link, Per Session Keys are derived from the CK • “Signed Diffie-Hellman” exchanges occur between STAs – One time “DHAKM Registration” of STA and AP/Peer STA • Provides a “chaperoned formal introduction” • The devices negotiate parameters to be used in future sessions – “DHAKM Key Generation” occurs upon initiation of every subsequent session • The devices use previously negotiated parameters to mutually authenticate • The devices use previously negotiated parameters to generate the session key – “DHAKM Key Regeneration” occurs at periodic intervals within a given session • The devices suspend data exchange • They again mutually authenticate and generate a new session key • The devices resume data exchange using the new encryption key Submission 6 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 The General Idea • All STAs have unique, factory assigned “Secret Keys” (SKs) – “Partial Keys” (PKs) are derived from the SKs using one-way functions – PKs are publicly exchanged to create a “Common Key” (CK) secret to both STAs – Authentication Signatures and Per Link, Per Session Keys are derived from the CK • “Signed Diffie-Hellman” exchanges occur between STAs – One time “DHAKM Registration” of STA and AP/Peer STA • Provides a “chaperoned formal introduction” • The devices negotiate parameters to be used in future sessions – “DHAKM Key Generation” occurs upon initiation of every subsequent session • The devices use previously negotiated parameters to mutually authenticate • The devices use previously negotiated parameters to generate the session key – “DHAKM Key Regeneration” occurs at periodic intervals within a given session • The devices suspend data exchange • They again mutually authenticate and generate a new session key • The devices resume data exchange using the new encryption key Submission 6 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Registration • Occurs upon first instantiation of STA and AP/PSTA communications – New STA gets added to an infrastructure network, has to register with all APs – Pull a new NIC for the home WLAN out of the box – First meeting between two or more Ad Hoc STAs • DHAKM Registration is a “monitored and protected” exchange – Opportunity for an attacker to make mischief by “impersonating” STA or AP – One or more “Operators” (i. e. , “the computer guy”, Ad-Hoc users) need be involved • Initiate the Registration process (enable the “formal introduction”) • Provide Authorization that the devices are to be networked (“chaperone the introduction”) • Detect and foil any impersonation attacks (“deter any hanky-panky”) – A “Registration Enabling Event” (REE) external to the WLAN is involved • Menu selection or Key Sequence depression on computer hosts • Simultaneous enclosure pushbutton sequence on non-GUI devices • “Docking Procedure” for non UI devices – Registration then proceeds and terminates automatically • • • Devices are placed in “DHAKM Registration mode”, provide feedback to Operator(s) Devices calculate PKs from their respective SKs (New) Authentication frames exchange PKs to create the CK Authentication frames include“Common Key Signatures” (CKSs) to deter MIM attacks Seeds for future CKSs are incremented at both STAs to deter “signature replay” attacks Devices automatically exit Registration, provide positive feedback to Operator(s) Submission 7 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Registration • Occurs upon first instantiation of STA and AP/PSTA communications – New STA gets added to an infrastructure network, has to register with all APs – Pull a new NIC for the home WLAN out of the box – First meeting between two or more Ad Hoc STAs • DHAKM Registration is a “monitored and protected” exchange – Opportunity for an attacker to make mischief by “impersonating” STA or AP – One or more “Operators” (i. e. , “the computer guy”, Ad-Hoc users) need be involved • Initiate the Registration process (enable the “formal introduction”) • Provide Authorization that the devices are to be networked (“chaperone the introduction”) • Detect and foil any impersonation attacks (“deter any hanky-panky”) – A “Registration Enabling Event” (REE) external to the WLAN is involved • Menu selection or Key Sequence depression on computer hosts • Simultaneous enclosure pushbutton sequence on non-GUI devices • “Docking Procedure” for non UI devices – Registration then proceeds and terminates automatically • • • Devices are placed in “DHAKM Registration mode”, provide feedback to Operator(s) Devices calculate PKs from their respective SKs (New) Authentication frames exchange PKs to create the CK Authentication frames include“Common Key Signatures” (CKSs) to deter MIM attacks Seeds for future CKSs are incremented at both STAs to deter “signature replay” attacks Devices automatically exit Registration, provide positive feedback to Operator(s) Submission 7 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
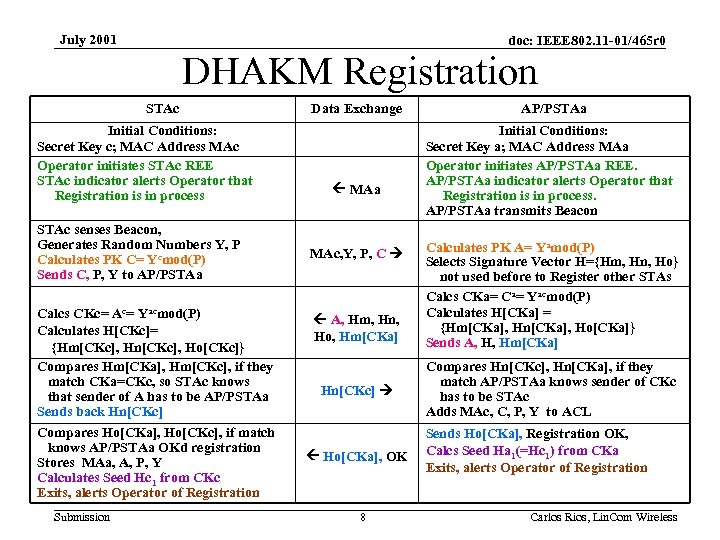 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Registration STAc Initial Conditions: Secret Key c; MAC Address MAc Operator initiates STAc REE STAc indicator alerts Operator that Registration is in process STAc senses Beacon, Generates Random Numbers Y, P Calculates PK C= Ycmod(P) Sends C, P, Y to AP/PSTAa Calcs CKc= Ac= Yacmod(P) Calculates H[CKc]= {Hm[CKc], Hn[CKc], Ho[CKc]} Compares Hm[CKa], Hm[CKc], if they match CKa=CKc, so STAc knows that sender of A has to be AP/PSTAa Sends back Hn[CKc] Compares Ho[CKa], Ho[CKc], if match knows AP/PSTAa OKd registration Stores MAa, A, P, Y Calculates Seed Hc 1 from CKc Exits, alerts Operator of Registration Submission Data Exchange MAa MAc, Y, P, C A, Hm, Hn, Ho, Hm[CKa] Hn[CKc] Ho[CKa], OK 8 AP/PSTAa Initial Conditions: Secret Key a; MAC Address MAa Operator initiates AP/PSTAa REE. AP/PSTAa indicator alerts Operator that Registration is in process. AP/PSTAa transmits Beacon Calculates PK A= Yamod(P) Selects Signature Vector H={Hm, Hn, Ho} not used before to Register other STAs Calcs CKa= Ca= Yacmod(P) Calculates H[CKa] = {Hm[CKa], Hn[CKa], Ho[CKa]} Sends A, H, Hm[CKa] Compares Hn[CKc], Hn[CKa], if they match AP/PSTAa knows sender of CKc has to be STAc Adds MAc, C, P, Y to ACL Sends Ho[CKa], Registration OK, Calcs Seed Ha 1(=Hc 1) from CKa Exits, alerts Operator of Registration Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Registration STAc Initial Conditions: Secret Key c; MAC Address MAc Operator initiates STAc REE STAc indicator alerts Operator that Registration is in process STAc senses Beacon, Generates Random Numbers Y, P Calculates PK C= Ycmod(P) Sends C, P, Y to AP/PSTAa Calcs CKc= Ac= Yacmod(P) Calculates H[CKc]= {Hm[CKc], Hn[CKc], Ho[CKc]} Compares Hm[CKa], Hm[CKc], if they match CKa=CKc, so STAc knows that sender of A has to be AP/PSTAa Sends back Hn[CKc] Compares Ho[CKa], Ho[CKc], if match knows AP/PSTAa OKd registration Stores MAa, A, P, Y Calculates Seed Hc 1 from CKc Exits, alerts Operator of Registration Submission Data Exchange MAa MAc, Y, P, C A, Hm, Hn, Ho, Hm[CKa] Hn[CKc] Ho[CKa], OK 8 AP/PSTAa Initial Conditions: Secret Key a; MAC Address MAa Operator initiates AP/PSTAa REE. AP/PSTAa indicator alerts Operator that Registration is in process. AP/PSTAa transmits Beacon Calculates PK A= Yamod(P) Selects Signature Vector H={Hm, Hn, Ho} not used before to Register other STAs Calcs CKa= Ca= Yacmod(P) Calculates H[CKa] = {Hm[CKa], Hn[CKa], Ho[CKa]} Sends A, H, Hm[CKa] Compares Hn[CKc], Hn[CKa], if they match AP/PSTAa knows sender of CKc has to be STAc Adds MAc, C, P, Y to ACL Sends Ho[CKa], Registration OK, Calcs Seed Ha 1(=Hc 1) from CKa Exits, alerts Operator of Registration Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Key Generation • Mutual Authentication, Key generation upon start of session – Infrastructure STA powers on or roams into range of a new AP – Ad Hoc STA powers on or emerges from Registration – Uses parameters negotiated at Registration, or updated during the previous session • Key material for Common Key is recalled, NOT exchanged • Key material to divine Signature Functions is recalled, NOT exchanged • Mutual Authentication, Session Key Generation requires knowledge of both • Public exchange of new Authentication Frames – Supplicant STA senses Beacon, issues Authentication Request to other STA – Both STAs independently recover parameters associated with other’s MAC Address – STAs Mutually Authenticate by exchanging, comparing Common Key Signatures – STAs generate new session key based on the CK, update seeds for next session Submission 9 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Key Generation • Mutual Authentication, Key generation upon start of session – Infrastructure STA powers on or roams into range of a new AP – Ad Hoc STA powers on or emerges from Registration – Uses parameters negotiated at Registration, or updated during the previous session • Key material for Common Key is recalled, NOT exchanged • Key material to divine Signature Functions is recalled, NOT exchanged • Mutual Authentication, Session Key Generation requires knowledge of both • Public exchange of new Authentication Frames – Supplicant STA senses Beacon, issues Authentication Request to other STA – Both STAs independently recover parameters associated with other’s MAC Address – STAs Mutually Authenticate by exchanging, comparing Common Key Signatures – STAs generate new session key based on the CK, update seeds for next session Submission 9 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
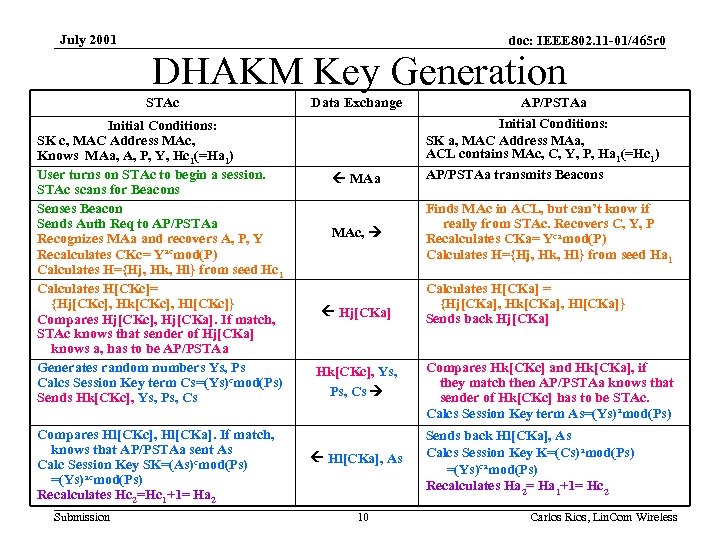 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Key Generation STAc Initial Conditions: SK c, MAC Address MAc, Knows MAa, A, P, Y, Hc 1(=Ha 1) User turns on STAc to begin a session. STAc scans for Beacons Senses Beacon Sends Auth Req to AP/PSTAa Recognizes MAa and recovers A, P, Y Recalculates CKc= Yacmod(P) Calculates H={Hj, Hk, Hl} from seed Hc 1 Calculates H[CKc]= {Hj[CKc], Hk[CKc], Hl[CKc]} Compares Hj[CKc], Hj[CKa]. If match, STAc knows that sender of Hj[CKa] knows a, has to be AP/PSTAa Generates random numbers Ys, Ps Calcs Session Key term Cs=(Ys)cmod(Ps) Sends Hk[CKc], Ys, Ps, Cs Compares Hl[CKc], Hl[CKa]. If match, knows that AP/PSTAa sent As Calc Session Key SK=(As)cmod(Ps) =(Ys)acmod(Ps) Recalculates Hc 2=Hc 1+1= Ha 2 Submission Data Exchange AP/PSTAa Initial Conditions: SK a, MAC Address MAa, ACL contains MAc, C, Y, P, Ha 1(=Hc 1) MAa AP/PSTAa transmits Beacons MAc, Finds MAc in ACL, but can’t know if really from STAc. Recovers C, Y, P Recalculates CKa= Ycamod(P) Calculates H={Hj, Hk, Hl} from seed Ha 1 Hj[CKa] Hk[CKc], Ys, Ps, Cs Hl[CKa], As 10 Calculates H[CKa] = {Hj[CKa], Hk[CKa], Hl[CKa]} Sends back Hj[CKa] Compares Hk[CKc] and Hk[CKa], if they match then AP/PSTAa knows that sender of Hk[CKc] has to be STAc. Calcs Session Key term As=(Ys)amod(Ps) Sends back Hl[CKa], As Calcs Session Key K=(Cs)amod(Ps) =(Ys)camod(Ps) Recalculates Ha 2= Ha 1+1= Hc 2 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Key Generation STAc Initial Conditions: SK c, MAC Address MAc, Knows MAa, A, P, Y, Hc 1(=Ha 1) User turns on STAc to begin a session. STAc scans for Beacons Senses Beacon Sends Auth Req to AP/PSTAa Recognizes MAa and recovers A, P, Y Recalculates CKc= Yacmod(P) Calculates H={Hj, Hk, Hl} from seed Hc 1 Calculates H[CKc]= {Hj[CKc], Hk[CKc], Hl[CKc]} Compares Hj[CKc], Hj[CKa]. If match, STAc knows that sender of Hj[CKa] knows a, has to be AP/PSTAa Generates random numbers Ys, Ps Calcs Session Key term Cs=(Ys)cmod(Ps) Sends Hk[CKc], Ys, Ps, Cs Compares Hl[CKc], Hl[CKa]. If match, knows that AP/PSTAa sent As Calc Session Key SK=(As)cmod(Ps) =(Ys)acmod(Ps) Recalculates Hc 2=Hc 1+1= Ha 2 Submission Data Exchange AP/PSTAa Initial Conditions: SK a, MAC Address MAa, ACL contains MAc, C, Y, P, Ha 1(=Hc 1) MAa AP/PSTAa transmits Beacons MAc, Finds MAc in ACL, but can’t know if really from STAc. Recovers C, Y, P Recalculates CKa= Ycamod(P) Calculates H={Hj, Hk, Hl} from seed Ha 1 Hj[CKa] Hk[CKc], Ys, Ps, Cs Hl[CKa], As 10 Calculates H[CKa] = {Hj[CKa], Hk[CKa], Hl[CKa]} Sends back Hj[CKa] Compares Hk[CKc] and Hk[CKa], if they match then AP/PSTAa knows that sender of Hk[CKc] has to be STAc. Calcs Session Key term As=(Ys)amod(Ps) Sends back Hl[CKa], As Calcs Session Key K=(Cs)amod(Ps) =(Ys)camod(Ps) Recalculates Ha 2= Ha 1+1= Hc 2 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Key Regeneration • Mutual Authentication and Key Regeneration upon current key expiration – Infrastructure STA determines current encryption key’s end of life has been reached – Ad Hoc STA determines current encryption key’s end of life has been reached – Data exchange is temporarily suspended • Nearly identical process as DHAKM Key Generation – Supplicant STAc senses Beacon, issues DHAKM Authenticate Request to AP/PSTAa – Both STAs independently recover parameters associated with other’s MAC Address – STAs Mutually Authenticate by exchanging, comparing Common Key Signatures – STAs generate new session key based on the CK, update seeds for next session key regeneration Submission 11 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Key Regeneration • Mutual Authentication and Key Regeneration upon current key expiration – Infrastructure STA determines current encryption key’s end of life has been reached – Ad Hoc STA determines current encryption key’s end of life has been reached – Data exchange is temporarily suspended • Nearly identical process as DHAKM Key Generation – Supplicant STAc senses Beacon, issues DHAKM Authenticate Request to AP/PSTAa – Both STAs independently recover parameters associated with other’s MAC Address – STAs Mutually Authenticate by exchanging, comparing Common Key Signatures – STAs generate new session key based on the CK, update seeds for next session key regeneration Submission 11 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
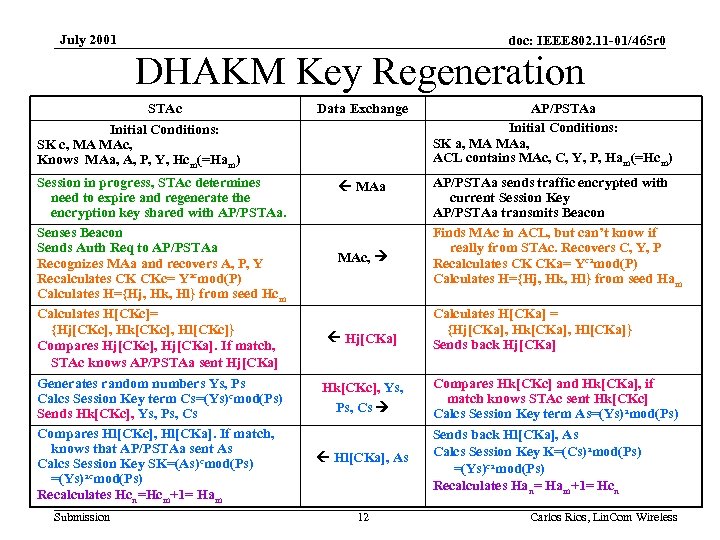 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Key Regeneration STAc Initial Conditions: SK c, MA MAc, Knows MAa, A, P, Y, Hcm(=Ham) Session in progress, STAc determines need to expire and regenerate the encryption key shared with AP/PSTAa. Senses Beacon Sends Auth Req to AP/PSTAa Recognizes MAa and recovers A, P, Y Recalculates CK CKc= Yacmod(P) Calculates H={Hj, Hk, Hl} from seed Hcm Calculates H[CKc]= {Hj[CKc], Hk[CKc], Hl[CKc]} Compares Hj[CKc], Hj[CKa]. If match, STAc knows AP/PSTAa sent Hj[CKa] Generates random numbers Ys, Ps Calcs Session Key term Cs=(Ys)cmod(Ps) Sends Hk[CKc], Ys, Ps, Cs Compares Hl[CKc], Hl[CKa]. If match, knows that AP/PSTAa sent As Calcs Session Key SK=(As)cmod(Ps) =(Ys)acmod(Ps) Recalculates Hcn=Hcm+1= Ham Submission Data Exchange MAa MAc, Hj[CKa] Hk[CKc], Ys, Ps, Cs Hl[CKa], As 12 AP/PSTAa Initial Conditions: SK a, MA MAa, ACL contains MAc, C, Y, P, Ham(=Hcm) AP/PSTAa sends traffic encrypted with current Session Key AP/PSTAa transmits Beacon Finds MAc in ACL, but can’t know if really from STAc. Recovers C, Y, P Recalculates CK CKa= Ycamod(P) Calculates H={Hj, Hk, Hl} from seed Ham Calculates H[CKa] = {Hj[CKa], Hk[CKa], Hl[CKa]} Sends back Hj[CKa] Compares Hk[CKc] and Hk[CKa], if match knows STAc sent Hk[CKc] Calcs Session Key term As=(Ys)amod(Ps) Sends back Hl[CKa], As Calcs Session Key K=(Cs)amod(Ps) =(Ys)camod(Ps) Recalculates Han= Ham+1= Hcn Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 DHAKM Key Regeneration STAc Initial Conditions: SK c, MA MAc, Knows MAa, A, P, Y, Hcm(=Ham) Session in progress, STAc determines need to expire and regenerate the encryption key shared with AP/PSTAa. Senses Beacon Sends Auth Req to AP/PSTAa Recognizes MAa and recovers A, P, Y Recalculates CK CKc= Yacmod(P) Calculates H={Hj, Hk, Hl} from seed Hcm Calculates H[CKc]= {Hj[CKc], Hk[CKc], Hl[CKc]} Compares Hj[CKc], Hj[CKa]. If match, STAc knows AP/PSTAa sent Hj[CKa] Generates random numbers Ys, Ps Calcs Session Key term Cs=(Ys)cmod(Ps) Sends Hk[CKc], Ys, Ps, Cs Compares Hl[CKc], Hl[CKa]. If match, knows that AP/PSTAa sent As Calcs Session Key SK=(As)cmod(Ps) =(Ys)acmod(Ps) Recalculates Hcn=Hcm+1= Ham Submission Data Exchange MAa MAc, Hj[CKa] Hk[CKc], Ys, Ps, Cs Hl[CKa], As 12 AP/PSTAa Initial Conditions: SK a, MA MAa, ACL contains MAc, C, Y, P, Ham(=Hcm) AP/PSTAa sends traffic encrypted with current Session Key AP/PSTAa transmits Beacon Finds MAc in ACL, but can’t know if really from STAc. Recovers C, Y, P Recalculates CK CKa= Ycamod(P) Calculates H={Hj, Hk, Hl} from seed Ham Calculates H[CKa] = {Hj[CKa], Hk[CKa], Hl[CKa]} Sends back Hj[CKa] Compares Hk[CKc] and Hk[CKa], if match knows STAc sent Hk[CKc] Calcs Session Key term As=(Ys)amod(Ps) Sends back Hl[CKa], As Calcs Session Key K=(Cs)amod(Ps) =(Ys)camod(Ps) Recalculates Han= Ham+1= Hcn Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
 July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 Summary • DHAKM is a MAC-level Authentication and Key Management scheme – Requires no Upper Layer entities to provide any functionality • DHAKM provides – Mutual Authentication – Per Link, per Session Encryption Key generation, expiration and regeneration • DHAKM can be combined with AES encryption to provide a comprehensive Strong Security solution for non-enterprise WLANs • DHAKM can be combined with an improved WEP 2 to provide comprehensive Not Quite So Strong Security for legacy WLANs • DHAKM could be the basis for an IEEE 802. 11 i Enhanced Security solution for Home, Public Access and Ad Hoc WLANs Submission 13 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless
July 2001 doc: IEEE 802. 11 -01/465 r 0 Summary • DHAKM is a MAC-level Authentication and Key Management scheme – Requires no Upper Layer entities to provide any functionality • DHAKM provides – Mutual Authentication – Per Link, per Session Encryption Key generation, expiration and regeneration • DHAKM can be combined with AES encryption to provide a comprehensive Strong Security solution for non-enterprise WLANs • DHAKM can be combined with an improved WEP 2 to provide comprehensive Not Quite So Strong Security for legacy WLANs • DHAKM could be the basis for an IEEE 802. 11 i Enhanced Security solution for Home, Public Access and Ad Hoc WLANs Submission 13 Carlos Rios, Lin. Com Wireless


