cef804c9c6ebb2c921e5fc48a1028d03.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Judge Business School Creating World-Class Supply Chains Matthias Holweg Ph. D. Judge Business School University of Cambridge Email: m. holweg@jbs. cam. ac. uk World Bank - Knowledge Economy Forum VI Cambridge, April 17 2007

Outline Supply chain mangement § § § Why is it important? Features of high-performing supply chains The role of technology The automotive industry § § Global trends The case of Slovakia Conclusions § Policy recommendations

Outline Supply chain mangement § § § Why is it important? Features of high-performing supply chains The role of technology The automotive industry § § Global trends The case of Slovakia Conclusions § Policy recommendations

Why do we talk about it? Traditional thinking: competition is driven by the 4 P’s § Today: supply chain capabilities determine competitiveness! § Wal-Mart versus K-Mart § Compaq/HP versus Dell A final product is not the sole achievement of the OEM § Customer experience is determined by supply chain: quality, cost, delivery § Significant proportion of value sourced from suppliers! Supply chains are connected systems: § Competitiveness of one tier is a function of the supply and distribution functions, i. e. surrounding tiers. “Value Chains compete, not individual companies!” (Christopher 1992)
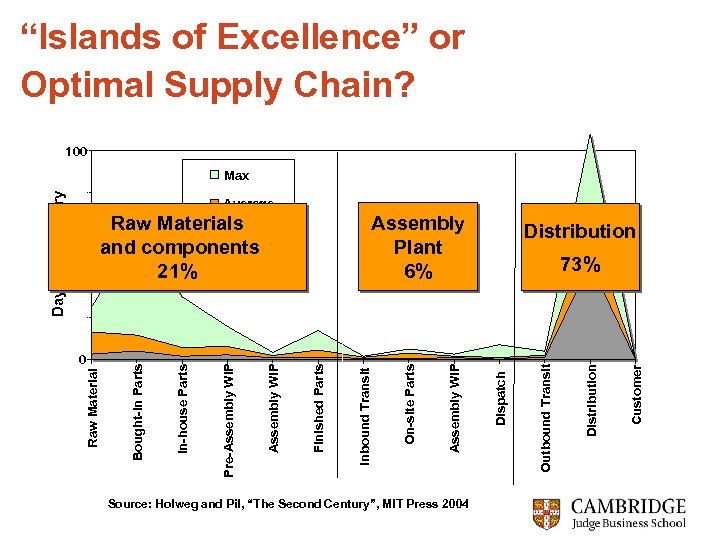
“Islands of Excellence” or Optimal Supply Chain? 100 Average Source: Holweg and Pil, “The Second Century”, MIT Press 2004 Distribution Customer Distribution Outbound Transit 73% Dispatch Assembly WIP On-site Parts Inbound Transit Finished Parts Assembly WIP Pre-Assembly WIP In-house Parts 0 Assembly Plant 6% Raw Materials Min and components 21% Bought-in Parts 50 Raw Material Days of Inventory Max

Features of High-performing Supply Chains Long-term collaborative relationships § Trust and commitment, respect of the right of mutual existence Single or dual sourcing § § Component volume is adjusted according to performance Constant positive pressure by dual sourcing Improvement § § Collaboration with suppliers on operational improvement; example: Toyota’s Supplier Support Center (TSSC) in Kentucky Annual cost reductions are realised in collaboration, not isolation Operations and logistics § § § Level production schedules to avoid spikes in the supply chain Milk-round delivery systems that can handle mixed-load, small-lot deliveries Disciplined system of JIT delivery windows at the plant; suppliers deliver only what is needed, even if this compromises load efficiency in transport
The Role of Technology The ‘Holy Grail’ in curing supply chain ills? Example: ‘Bullwhip problem’ § Demand visibility is key: RFID / Auto. ID, EDIFACT, EPOS, CPFR § …yet they only work if the planning systems use this information! Example: transaction costs in automotive § COVISINT (est. 2000) and the B 2 B/e-commerce revolution § Predicted savings of $1, 000 per vehicle in transaction costs! The Role of Technology § Technology alone is not a sufficient, it can assist problem solving § If the underlying processes are not capable, technology will fail § It is a means to an end, not an end in itself!

Outline Supply chain mangement § § § Why is it important? Features of high-performing supply chains The role of technology The automotive industry § § Global trends The case of Slovakia Conclusions § Policy recommendations
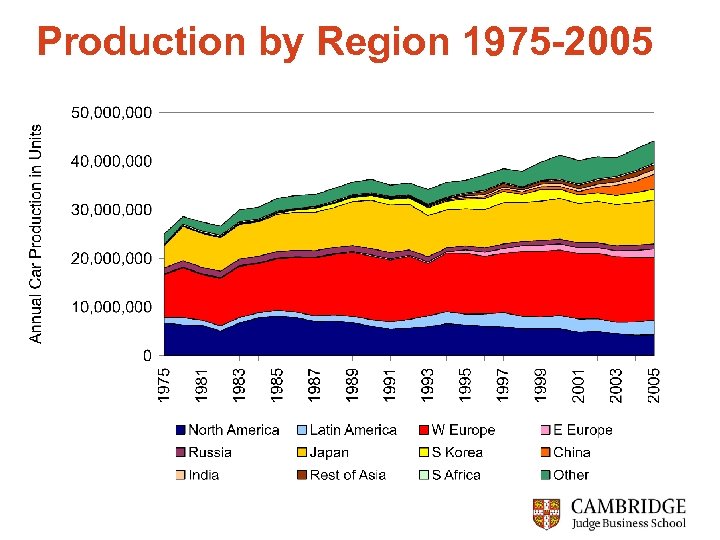
Production by Region 1975 -2005

Auto Industry: Major Trends Overall global growth by 1. 85% CAGR since 1975 Substitution of production with adjacent low-cost regions Major growth of production in China (2000 -05: x 5. 2), and India (2000 -05: x 1. 7), - 4% in Western Europe Auto industry is regionalising, not globalising! What does this mean for the dynamics of competition? Competing in a global, distributed industry: § § Future competition on cost is a futile battle. . Rely on quality? Brand? Design? Proximity to customer?
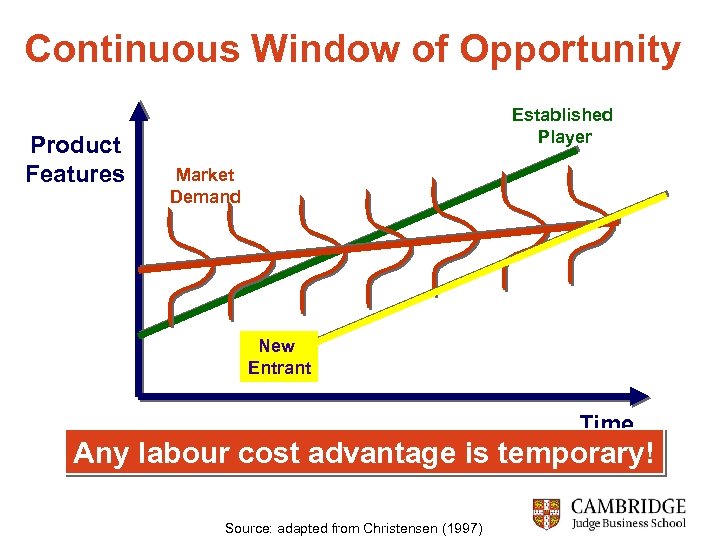
Continuous Window of Opportunity Product Features Established Player Market Demand New Entrant Time Any labour cost advantage is temporary! Source: adapted from Christensen (1997)

The Auto Industry in Emerging Countries Automotive industry very attractive § Job multiplier of 5 -7 for every assembly job § Technology transfer Many subsidies, but questions of long-term viability! The case of Slovakia’s auto industry § VW Bratislava, PSA Trnava, Kia Zilina, growing cluster CZ, PL, HU § 5 m inhabitants, c. 900 k production, domestic sales of <80 k units Challenges § Logistics: lead-time to customer, reliability of supply § Labour shortage, migration and rising compensation Migration further east is inevitable § Domestic demand in Russia, growing labour cost differential

Outline Supply chain mangement § § § Why is it important? Features of high-performing supply chains The role of technology The automotive industry § § Global trends The case of Slovakia Conclusions § Policy recommendations
Conclusion: Supply Chain ‘Enemies’ Common logic behind all SCM initiatives! Inventory & delays § Time worsens ‘swing’ of amplification § Decision delays require stock § Safety stock decisions send false signals Unreliability or uncertainty § Any kind of uncertainty needs to be covered with inventory § Unreliable processes cause unreliable delivery Hand-offs or decision points § Every hand-off or tier in the system bears danger of distortion! ‘Inventory is a substitute for information’

Policy Recommendations Infrastructure is a always a concern. . …but uncertainty is a sure killer of any location decision! § Customs clearance § Currency § Regulation (labour, traffic, taxation) § Crime & bribes Supply chains are connected systems: § Labour cost differential is only a short-term advantage § Strong need to attract suppliers, not just manufacturers! § Need to build local competencies, rather than “screw-driver factories” § Domestic demand is not essential if logistics systems work

Centre for Competitiveness and Innovation, Judge Business School, Univ. of Cambridge http: //www-innovation. jbs. cam. ac. uk Judge Business School International Motor Vehicle Program Massachusetts Institute of Technology http: //imvp. mit. edu Email: m. holweg@jbs. cam. ac. uk
cef804c9c6ebb2c921e5fc48a1028d03.ppt